Computed tomography is a first-class diagnostic equipment that allows you to see a highly accurate three-dimensional image and identify initial pathological changes in small organs that cannot be detected using other studies.
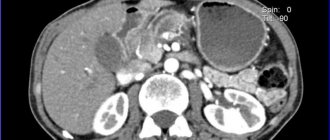
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is one of the main diagnostic methods, during which a specialist is able to visualize the condition, structure and localization of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity, as well as the retroperitoneal space. In addition, along with abdominal organs, CT allows you to see blood vessels and lymph nodes.
At the Yusupov Hospital, CT scans of the abdominal cavity are performed using innovative equipment - a multislice tomograph. Qualified hospital specialists have been studying the features of this technique for many years and use only the best contrast agent in their work, which does not cause unpleasant side effects.
Indications for use of the method and advantages of the study
Our hospital has a modern multislice computed tomography scanner for scanning the whole body. The device significantly reduces radiation exposure and allows the examination to be carried out as quickly as possible without discomfort. The result of the research is finished images and files recorded on electronic media. Tomography done in our clinic is recognized by all medical institutions in Russia and abroad.
The advantages of multislice tomography performed in our clinic over standard CT:
- a more contrasting picture due to a reduction in the amount of noise using a new generation of iterative reconstruction;
- reduction in radiation exposure by 30-80%;
- possibility of using less contrast agent;
- increasing the area of the study area;
- reducing the thickness of the section, giving a chance to track down even the smallest pathological focus;
- the ability to create 3D models of organs and foci of disease, as well as their multiplanar reconstructions.
Contrast perfusion allows you to cover more parameters, as well as detect bleeding, neoplasms and hemorrhages, so it is recommended for most studies. In 80-87% of cases, the examination is carried out using contrast.
In what cases is a CT scan of the abdominal organs prescribed:
- the presence of pain in the abdomen, bleeding, both due to injury and for unexplained reasons;
- suspicion of tumors;
- the presence of metastases in internal organs, lymph nodes, bones;
- the presence of stones in the kidneys, biliary and urinary tracts;
- upcoming surgery requiring precise examination of the intervention area;
- the need to assess the dynamics of the process and treatment results;
- peritonitis, abscesses;
- liver diseases;
- kidney inflammation;
- the presence of a hernia (area of the anterior abdominal wall, diaphragm);
- developmental anomalies.
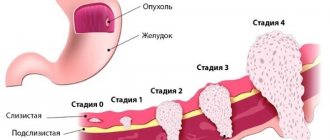
First of all, CT scan of the abdominal cavity is aimed at detecting volumetric processes in internal organs, which include polyps, cysts, abscesses, tumors, and stones. CT scan reveals benign and malignant tumors, metastases, stones, cysts, kidneys and liver, echinococosis, atherosclerosis, various changes in the structure of organs (cirrhosis, hepatosis).
Advantages
Abdominal CT with contrast in Moscow is the leading method for diagnosing many pathological processes. A computed tomograph qualitatively visualizes traumatic, inflammatory, cystic, and many other changes in the body, in particular neoplasms (both benign and malignant with metastasis). Using such images, it is possible to determine the true size, localization, boundaries of pathologies, the presence of metastases, the degree of invasion into organs and other important parameters that determine the stage of the disease and further tactics of patient management.
For example, computed tomography of the pancreas shows in detail the presence of neoplasms of various structures, and also perfectly differentiates them due to the difference in the density of the examined tissues. During a study with a contrast agent, the drug that passes through the splenic artery shows signs of tumor growth into the vessel.
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography also has a number of other advantages:
- Low radiation exposure;
- High scanning speed;
- Obtaining slices of minimal thickness;
- High image quality;
- Identification of minimal changes in internal organs that are not available for visualization in other studies;
- After the completion of the CT scan, the patient returns to his usual lifestyle;
- Construction of highly informative three-dimensional images;
- The results obtained are presented on film and CD, which the patient can provide to the attending physician for further therapy, diagnosis and development of further diagnostic tactics.
Preparing for a CT scan
Preparation for the study begins several days before and includes a special diet, tests and additional procedures. Before the session, you must provide the doctor with tests indicating the level of urea and creatinine (no later than 2 weeks). You can take a rapid test directly in our clinic. Below all the preparatory stages are presented in chronological order:
Desirable:
- A few days before the session, start following a diet that excludes foods that cause constipation and increased gas formation;
- 2 days before the session - start drinking adsorbents (usually activated carbon);
- On the eve of the procedure, perform a cleansing enema, repeat if necessary before starting the study.
Necessarily:
- 4 hours before the procedure - refuse to eat or take medications, only light drinks are allowed.
- If ultrasound, gastroscopy, colonoscopy, CT, or X-ray examinations have been previously performed, provide the results to the doctor for the most correct interpretation of the study.
- Before starting the study, a conversation is held during which the course, safety, painlessness of the method, and rules of behavior during the session are discussed.
Before starting the procedure, you must remove all metal objects - jewelry, piercings, belts, etc. You must be prepared to lie still and calm, breathing evenly, and strictly follow the radiologist's commands. Before the start of the study, a written receipt for the examination is taken. During the session, an unpleasant taste in the mouth and a feeling of heat in the body may appear during the administration of the contrast agent.
How is an abdominal CT scan performed: preliminary preparation before contrast injection
Testing with the introduction of an additional amplifier is required only if it is necessary to test hollow parts of the body. Contrast drugs contain iodine or barium. They are usually presented as solutions or pharmacological substances. After getting inside, the product clearly highlights the desired area and allows you to study in as much detail as possible the deformations that have occurred in the structure. The medication is administered to the patient prior to the start of a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast in three ways:
- Intravenous - done exclusively on an empty stomach.
- Oral - take the drug 24 hours before the start of the scan.
- Rectal - the patient first undergoes bowel cleansing using an enema or the use of laxatives.
Contraindications to CT
CT scan of the abdominal organs at the Yauza Clinical Hospital is a safe examination with virtually no contraindications. The only category of people for whom alternative types of studies may be recommended are pregnant women (for any CT studies) and lactating women (for studies with intravenous contrast).
The following are considered relative limitations for contrast-enhanced CT:
- renal failure;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- contrast intolerance.
What contrasts are used for CT
As a rule, various iodine-containing preparations are used to increase the contrast of the resulting image. All of them are divided into two groups - fat-soluble and water-soluble. Medicines of the first group are very viscous, so their use is limited. They are administered only locally, for example, into the peritoneal cavity to identify fistulas, etc. If we are talking about computed tomography with bolus contrast (the drug is administered into a vein with a special injector) or about the drug being administered orally, water-soluble contrast is used. The toxicity of such drugs is several times lower, and they also quickly enter the blood vessels.
Alternative methods for diagnosing abdominal organs
For patients who, for some reason, are not indicated for abdominal CT, several types of alternative studies are available:
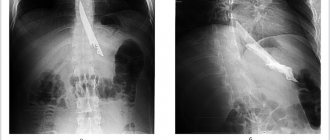
- Survey radiography of the abdominal organs - allows you to detect x-ray positive gallstones and stones in the urinary tract, free gas in the abdominal cavity (with perforation of a hollow organ), signs of intestinal obstruction;
- Ultrasound is a good screening method for most patients, for most of the most common pathologies;
- MRI is a highly sensitive method for diagnosing diseases of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, which is a full-fledged alternative to CT when performed at a high level. However, a significant limitation of MRI is the inability to detect small stones in the kidneys and gall bladder.
What can and cannot be eaten before an abdominal CT scan with contrast?
| Can | Not recommended |
|
|
How to sign up for a study
Leading expert doctors will perform a CT scan of the abdominal organs according to international protocols, provide a professional opinion and give recommendations on choosing a treating physician. Our specialized specialist will prescribe the optimal treatment for you and develop effective therapeutic programs. To sign up for a study, call us or fill out an application using the form on the website. Before the study, you can sign up for a consultation with a radiologist or the head of the radiology department (regular and extended).
What can be detected with an abdominal CT scan?
Firstly, this method helps to most accurately identify the source of the disease, determine the volume and boundaries of the pathology, and examine the state of the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Excellent visualization of tissue structure and uniformity. CT helps to see:
- Ulcerative bleeding;
- Polyps;
- Fibroids;
- Adenomas;
- Abscesses, foci of inflammation;
- Tumors of malignant and benign nature;
- Secondary foci of cancer;
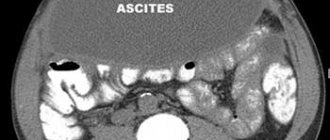
- Dropsy;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Lymphadenopathy;
- Lymphadenitis;
- Cholecystitis;
- Tissue necrosis;
- Cysts;
- Congenital structural anomalies;
- Hepatosis;
- Cirrhosis;
- Cholangitis;
- Pancreatitis;
- Gallbladder diseases;
- Aneurysms;
- Parasitic lesions;
- Chronic and acute hepatitis;
- Acute appendicitis.
Advantages of our clinic
- ultra-modern diagnostic equipment - unique Philips digital tomographs, which allow identifying many pathologies, including neoplasms and metastases, with high accuracy without high radiation exposure;
- highly qualified diagnostic doctors - specialists in the field of radiology are trained and trained in leading clinics in Russia, Europe, the USA, Israel on a regular basis;
- automated research quality control system - implemented on the basis of a modern IT platform, the system allows for triple control of results, the research results are sent to a single service center and become available to doctors caring for the patient;
- high-quality equipment of the department - creating a comfortable environment for the patient, the ability to conduct a wide range of studies.
CT (computed tomography) contraindications
Computed tomography is an X-ray examination of organs or parts of the body. Scanning occurs layer by layer. This is an informative diagnostic method. Thanks to it, you can correctly identify the disease, as well as predict its course.
After the examination, the doctor, after processing the information with a computer, receives a layer-by-layer image of the organ or its three-dimensional picture, or they take a targeted photo and study the pathological area separately.
Unlike an X-ray machine, the radiation dose in a tomograph is minimal, so there is practically no harm to health. A similar examination is scheduled again.
Important: before performing a CT scan, you need to find out about contraindications.
Principle of operation
Around the object being examined, an X-ray tube enclosed in a special ring rotates and emits X-rays that pass through the patient’s body. There are sensors at the opposite end. They pick up the X-ray attenuation coefficient (because they pass through tissue differently due to thickness and density). The sensors, having received the information, send it to the central processor of the tomograph, where it is analyzed and converted into a picture or a convenient form for interpretation by a specialist.
Contraindications for CT scanning
This research method is prescribed as planned. However, in some urgent cases, such as head injuries or suspected stroke, it may be performed unscheduled. Therefore, the benefits of the study must outweigh the risks.
Absolute
CT contraindications for which it is not permissible to perform:
- Pregnancy at any stage. Even minimal doses of radiation have a bad effect on a developing organism. Therefore, the study is either postponed to a later date or replaced by others.
- The patient is overweight. This is due to the fact that the tomograph is designed only for a certain mass, and X-rays do not pass through fatty tissue.
- Relative
- Children's age up to 12 years. A young and fragile body is most susceptible to the negative effects of radiation. Also, small children will not be able to lie still in the device.
- People with mental disorders or inappropriate behavior. In this case, it is recommended to do the examination under anesthesia.
- Lactation. After a CT scan, women are advised to express milk for 48 hours.
- Plaster and metal objects in the examination area. They distort the results.
- People with diabetes. Before the examination, they will need to stop taking medications, after which treatment can be resumed.
Contraindications to CT with contrast
- Individual intolerance to components. Therefore, it is first necessary to make a test for the manifestation of an inadequate reaction.
- Liver and kidney failure. The kidneys and liver are involved in removing the substance from the body. If the organ does not work well, then poisoning is possible.
- Thyroid dysfunction. The presence of iodine in the contrast agent can cause complications.
- The patient's serious condition.
- Possible complications
Before conducting the examination, you need to know the indications and contraindications. Weigh all the pros and cons. However, the X-ray radiation from the tomograph is low and does not accumulate in the body. The harm is minimal and boils down to the following:
- Changes in blood composition. - Premature aging. — Violation of the synthesis of new cells in the body. — There is a possibility of the formation of malignant tumors, but this probability is very small. - The appearance of cataracts.
To reduce the harmful effects of X-ray radiation, it is necessary to observe time intervals between examinations and the rules for using the device.
Radiation exposure
The X-ray radiation in the tomograph is minimal and does not exceed a level that would cause harm to the body. However, the dose received varies and depends on the following factors:
The larger the area being examined, the higher the dose. The denser the tissue that is examined, the more radiation there is. The number of rows of detectors in the apparatus. The fewer there are, the lower the dose received.
Types of tomography
MSCT (Multispiral tomography). Has high resolution. During the study, up to 300 images are obtained per revolution. During this examination, a person receives a higher dose of X-ray radiation than with a regular CT scan and is therefore done only in emergency cases. SCT (Spiral CT). In this case, the doctor can obtain several images in 1 rotation. The X-ray beam moves in a spiral. How often can a CT scan be done?
You can undergo a CT scan for preventive purposes no more than once a year. It is allowed to undergo up to 3 times; it is carried out to monitor the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. However, the break between procedures should be 2-3 months.
CT scanning is possible if prescribed by the attending physician. If pathology is present, an ultrasound diagnosis is first performed, and if there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, a computed tomography scan is prescribed.
Methods for removing radiation after a CT scan
Pharmacy products:
Activated carbon. Preparations with selenium and calcium. Nutritional supplements with iodine. Dimethyl sulfide.
Products:
Milk. Foods containing iodine. Clean water in large quantities. Products with potassium Vegetables and fruits. Decoctions of herbs, for example, St. John's wort or chamomile.
Which causes less harm - CT or MRI
It is impossible to say unequivocally which is better: MRI or CT. These studies complement each other and are more or less informative in different cases. For example, CT is more used to study bone tissue, and MRI is used more for soft tissue. However, when examined in a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, the body does not receive a dose of radiation.
Summarize
Computed tomography is a modern method of diagnosing diseases that gives good results. The principle of operation is that X-rays pass through the body. There are absolute and relative contraindications to CT. The harm of the research is minimal. If you follow the rules of the procedure, then it will not happen. Pregnant women should not have a CT scan. Nursing mothers need to express milk after the test for 2 days. Radiation is removed using special medications or products containing substances with an antioxidant effect. MRI and CT are different research methods and are used simultaneously. It is recommended to carry out computed tomography no more than once a year, if necessary up to 3 times.
Computed tomography will help make the correct diagnosis. The study will not harm the body, because the X-ray radiation in it is minimal and, if you listen to the doctor’s recommendations, the risks will be reduced to zero.
Price
When studying with contrasting, the cost of contrast is added if contrasting is not immediately included in the cost of services (then this is reflected in its name).
You can see prices for services
Preparation for CT scan of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum
| Bowel preparation | not required | |
| Diet on the day of the study |
| |
| Drugs | not required | |
| Take with you |
| |
| Keep in mind | the study is almost always performed with intravenous contrast | |
| see also | interview and preparation for intravenous contrast in CT | |
Contraindications to the procedure with contrast
To avoid complications, abdominal CT is not performed in patients with:
- allergy to iodine;
- severe renal failure with elevated creatinine levels in the blood (creatinine testing is included in the services of our diagnostic center);
- hyperthyroidism and other thyroid diseases.
Children over 12 years of age have their internal organs checked with contrast only according to indications with a doctor’s referral.
For women breastfeeding, the procedure is not prohibited. Radiation exposure does not affect milk, but the dye partially penetrates into it. Therefore, you will have to give up at least two consecutive feedings. Before the study, the woman must express and store the milk. After CT or MSCT with contrast, you must wait until the drug leaves the body and after two pumpings, feed the baby as usual.
Any questions you may have and the price for contrast examinations can be clarified with the administrator.
What to take with you to an abdominal CT scan
Diagnostic clinics licensed to perform computed tomography are asked to bring with them:
- Identity document: passport or birth certificate for minors;
- Medical history, results of laboratory tests and previous examinations;
- Referral from a specialist.
We must remember that timely diagnosis can not only preserve health and improve the quality of life, but also avoid death. After all, the effectiveness of therapy depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Computed tomography technique
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is carried out in a special room, where equipment is installed that makes the examination as effective and informative as possible. In preparation for diagnosis, the patient is injected with a contrast agent. Most often, the drug is given through an IV inserted into the cubital vein. After administration of the contrast agent, the person is placed in a horizontal position on a special table equipped with soft straps and comfortable pillows for the patient’s comfort. During the examination, this table moves along the tunnel. When a CT scan of the abdominal cavity is performed, a person may receive small recommendations from the operator, who closely monitors the progress of the diagnosis. For example, the operator may ask you to hold your breath for a few seconds. These tips will help you better see certain organs in order to detect even the smallest deviations in their structure.
Typically, the procedure lasts about 15-20 minutes. After performing a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity, the person goes home or awaits the results of the examination. Processing of volumetric images occurs in a computer station. Preparing the results does not take much time. Typically, the resulting images are sent to the treating physician. Having carefully studied them, he can quickly and correctly establish a diagnosis and draw up an optimal treatment plan.