Ascites - what is it?
Ascites is a variety of complications caused by a number of diseases.
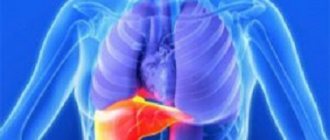
This pathology reveals itself as the accumulation of a large amount of liquid mass inside the peritoneal cavity. Hence the second name “edema of the abdomen”. The accumulated liquid mass increases the volume of the abdomen, causing unpleasant symptoms and secondary dysfunctions of the organs of the peritoneal cavity.
In such a condition, medical intervention is simply necessary, especially if the liquid mass accumulates rapidly.
Manifestations
A small amount of liquid mass accumulated in the abdominal cavity does not reveal itself in any way. How to determine the onset of the disease, since there are no symptoms? Ultrasound comes to the rescue here.
As the disease progresses, a feeling of heaviness appears in the abdomen, and the lower part is subject to dull aching pain. Next comes difficulty breathing, after which there is indigestion in its various varieties, and urination is impaired.
A severe form of pathology can dramatically worsen your health. The state of health leaves much to be desired:
- Unpleasant sensations in the stomach become the norm;
- Shortness of breath appears;
- An umbilical hernia develops;
- Legs swell;
- Internal organs are compressed.
Medical practice is faced with the fact that some patients accumulate up to twenty liters of fluid. As a result, they have:
- Increased pressure inside the peritoneum;
- The diaphragm becomes pressed into the chest cavity;
- Significant difficulty breathing;
- Heart failure develops.
If the order of things is not restored, the following are possible:
- Impaired drainage of the lymphatic system;
- The occurrence of impaired lymphatic drainage in the legs;
- Swelling of the extremities;
- Outflow of lymph to internal organs.
The result of such changes can be disastrous. Atypical cells penetrate from the affected lymph nodes to other organs.
Pathology in a small form can be determined during a medical examination: the abdomen is enlarged, it is saggy when a person is standing, or flattened when a person is lying down. In thin patients, the navel often protrudes.
Determining the pathology at the very beginning of its development is important, since its moderate form is diagnosed in almost half of patients in the early stages of oncology.
Complications
The accumulation of large amounts of fluid can trigger the development of many ailments. Clinicians identify the following exacerbations:
- bacterial peritonitis;
- hydrothorax and respiratory failure;
- intestinal disorders;
- umbilical hernia;
- hepatorenal syndrome.
The above consequences of abdominal dropsy can cause the death of the patient. But final conclusions can be drawn only after the degree of development of the initial pathology has been established.
Causes
The basis for the development of the disease is pathology: during the normal functioning of the peritoneal cavity, no significant amount of liquid mass is discharged. It is only insignificant, just to avoid adhesions from sliding intestinal loops. The liquid released for this purpose constantly flows back.
When the usual operation of this mechanism is disrupted, the function of secretion of the liquid mass is destabilized, as well as the function of its outflow. The consequence of such destabilization is the accumulation of excess liquid mass inside the abdomen.
Causes of pathology in adults
In many cases, pathology develops as a symptom of a number of diseases, including:
- Portal hypertension;
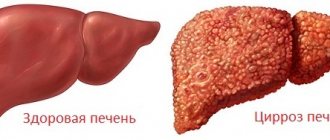
- Cirrhosis;
- Hepatitis;
- Thrombosis of the liver veins.
It is possible that the cause of the pathology is blood oncology, as well as pathologies whose nature has nothing in common with the tumor.
Heart failure can also cause pathology. Problems associated with lymph circulation and the activity of organs such as the thyroid gland and kidneys can also cause pathology.
Protein deficiency
How long do people live with ascites in liver cirrhosis?
Patients with cirrhotic changes in a vital organ often ask whether cirrhosis of the liver can be cured. The diseases are caused by irreversible changes in the liver tissue. Liver cirrhosis and ascites cannot be completely eliminated. The prognosis is determined by the literacy and timeliness of treatment.
According to statistics, the two-year survival rate of people with ascites is 45-50%. Life expectancy is reduced with complicated pathology - peritonitis, internal bleeding, encephalopathy. The prognosis is greatly worsened for elderly patients with kidney pathologies, arterial hypotension, and diabetes mellitus. But by following a diet and taking medications, it is possible to prevent more than 60% of complications and increase life expectancy by 30%.
Diagnostic methods
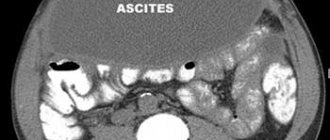
A certain amount of accumulated liquid mass (more than half a liter) can be determined during a medical examination. To confirm a preliminary diagnosis, an ultrasound is necessary.
The main problem is not to detect the liquid, but to identify the cause of its accumulation. Only then will the treatment be effective. To do this, it is necessary to conduct laboratory tests, namely:
- Blood clotting test;
- Biochemistry analysis;
- Analysis of ascitic fluid obtained during laparocentesis
Life expectancy at different stages of ascites
In order to choose the right treatment method, the doctor needs not only to know the etiology of the disease, but also to identify the stage of ascites. Clinicians distinguish 3 main degrees:
- a small amount of fluid that cannot be immediately diagnosed;
- moderate stage of ascites;
- tense ascites.
With a positive life prognosis at the initial stage of the disease, a person can live another 10 years. But this is only possible if the disease was diagnosed in a timely manner and the course of treatment was prescribed correctly. For adequate therapy, it is also important to follow a strict diet and perform laparocentesis.
At the second stage of the disease, the chances of a positive prognosis become less. The patient’s body is filled with a large amount of fluid, which significantly aggravates the healing process.
At the last stage of the development of the disease, only supportive therapy is carried out to maximize the patient’s life. With this development of the disease, death can occur a year after diagnosis. The patient’s life can be extended by selecting the correct treatment regimen that affects the source of ascites development.
Symptoms
Symptomatic manifestations of the disease depend on three main factors - the cause, the volume of accumulated liquid mass, and the rate of accumulation.
Symptoms can appear at any time: sometimes it’s weeks and months, sometimes hours.
As we have already noted, one of the visual symptoms is an enlarged abdomen. Let's add weight gain here.
The patient may develop a feeling of bursting pain, flatulence, belching, heartburn, and nausea.
An increase in the volume of the abdomen entails the appearance of severe shortness of breath, swelling of the extremities, difficulty moving and bending.
Another number of symptoms that a patient may encounter are hemorrhoids, hernias, intestinal prolapse, and the development of varicocele.
Common symptoms of the disease include:
- Feverish state;
- Toxic state;
- Losing weight and at the same time growing belly;
- The saphenous veins of the abdomen are dilated;
- Blueness on the limbs.
Types of disease
In the main classification, to differentiate pathology, the level of protein in the accumulated fluid is taken into account. According to this indicator, the disease is divided into:
- Exudative (25 g/l or more);
- Transudative (<25 g/l).
Such a division makes it possible to understand, albeit indirectly, what is the cause of the development of the disease.
Today, another indicator is used in medical practice - SAAG.
If this gradient is > 1.1, then most likely the cause of the disease is cirrhosis, heart failure, etc. All of them increase the pressure in the venous trunk.
If the gradient index is <1.1, then the cause of the disease can be considered pancreatitis or an oncological process.
Taking into account the clinical course of the disease, it is necessary to highlight the following varieties, which will be discussed below.
- Severity of the current:
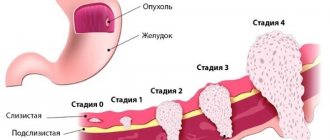
- First degree. There are no symptoms, diagnosed by examination and ultrasound.
- Second degree. The abdomen is slightly enlarged.
- Third degree. The abdomen is significantly enlarged.
- An uncomplicated option. There are no signs of infection of the accumulated fluid mass and abnormalities in kidney function.
- Refractory ascites:
- Unaffected by diuretics;
- Not controlled by diuretics.
Peritoneovenous shunt (Levine shunt)
Sometimes used to treat refractory ascites, i.e. one that does not respond to drug therapy and quickly returns after puncture. The operation consists of increasing the volume of circulating blood through the constant flow of fluid from the abdominal cavity into the general bloodstream system.
A Levine shunt is a long plastic tube that is inserted into the abdominal cavity, reaching the pelvic floor. Next, the shunt is connected to a valve and a silicone tube, which passes subcutaneously to the neck area for subsequent connection to the internal jugular and superior vena cava. The valve opens with the help of the resulting displacement force of the diaphragm and an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. Thus, there is an unimpeded flow of fluid into the superior vena cava.
Pathology and cancer
Medical statistics and practice show that the most common diseases leading to the accumulation of liquid mass in the peritoneal cavity are oncological forms:
- Ovaries;
- Mammary glands;
- Uterus;
- Stomach;
- Colon.
A liquid mass accumulates with a tumor due to damage to the peritoneal lining. Atypical cells, having settled on it, cause disruption of lymphatic drainage, which, in turn, impairs fluid absorption. This is very common, for example, in gastrointestinal oncology.
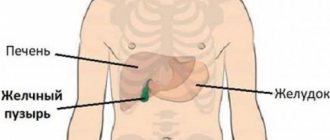
If we take an organ such as the liver, the picture will be different. A tumor or metastasis localized in an organ causes compression of the venous system of the organ and disruption of normal venous outflow from the intestine. In this case, the pathology develops rapidly and is more severe. About fifteen percent of ascites in cancer processes is diagnosed in this form.
Diet
Provides for reducing fluid intake, as well as salt, due to the fact that it retains fluid in the body. Doctors recommend the Avicenna diet. Such a diet for ascites involves almost complete abstinence from fatty foods, eating nuts in large quantities, and abandoning fresh fruits in favor of dry ones.
Also, liquid food (borscht, soup) should be replaced with broth with additives in the form of celery, parsley, fennel. The diet for ascites does not regulate how much meat the patient should eat, but all meat should be lean (chicken, turkey, rabbit).
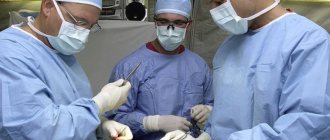
Specifics of treatment for cancer
Conservative methods are effective in treating pathologies of only minor and moderate severity. The diuretics used here allow you to remove up to a liter of liquid mass per day.
However, the surgical option is preferable. It is used when:
- The disease cannot be treated by other means;
- A significant form of the disease, in which it is necessary to evacuate up to ten liters of liquid mass at a time;
- A form of the disease that requires combined manipulation, including evacuation of a volume of liquid mass of up to seven liters on the first day and evacuation of the remaining mass at a rate of no more than one liter per day for a week.
The operation is performed on an empty stomach and with an empty bladder. The patient is positioned in a sitting position (lying down is possible).
Before the puncture, local anesthesia is performed, then the puncture is performed under ultrasound control.
As a rule, no more than five liters of liquid mass are evacuated at a time. To maintain blood pressure, it is pumped slowly.
It is important for the patient to lie on the side free from the puncture for several hours. If during this time all the planned liquid mass is not evacuated and continues to accumulate, a special reservoir is applied.
When removing large amounts of fluid, it is important that the patient does not experience protein deficiency. To do this, the patient is injected with albumin.
In modern practice, special catheters are used to evacuate accumulated fluid, and some patients undergo the procedure of omentohepatophrenopexy. This is an important part of palliative treatment.