The gallbladder, despite its small size, is an important organ of the gastrointestinal tract. It collects bile from the liver and regulates its release into the duodenum, and also activates digestive enzymes and fat emulsification, thereby facilitating digestion. Also, cholecystokinin is produced in the gallbladder, and resorption processes occur (protein, important salts and amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream). If one of these processes is disrupted, one or another disease of this organ may appear.
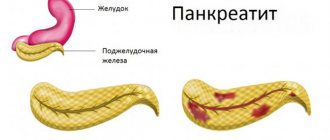
Cholecystitis in chronic or acute form
The disease is provoked by inflammation of the mucous membrane. The nature of pain with cholecystitis intensifies, increases, and becomes chronic. The disease can be caused by excessive consumption of fried foods and alcoholic drinks, and frequent stress.
Symptoms of cholecystitis:
- episodic pain in the right side of the abdomen, radiating to the back;
- weakened physical condition;
- vomit mixed with bile;
- increased gas formation;
- rancid taste in the mouth.
Manifestations
A symptom such as biliary colic, as a rule, does not cause difficulties in making a diagnosis.
Note! In women, the symptom occurs more often than in men, which is due to their physiological characteristics.
Biliary colic is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- An attack of pain occurs suddenly, a sharp pain is felt. As a rule, biliary colic occurs after eating fatty foods, drinking alcoholic beverages, and also due to excessive physical activity.
- During the first hour after the onset of the attack, the pain increases.
- Biliary colic is felt within 2-6 hours.
- The pain is felt in the abdominal cavity above the navel, radiating to the back, right arm and right hypochondrium.
- Movement and attempts to take a deep breath intensify the symptom.
- The skin acquires a jaundiced tint.
- Body temperature rises.
- Nausea occurs and vomiting with bile is possible.
The pain syndrome is acute or paroxysmal in nature and is localized in the upper part of the abdominal cavity (epigastrium). In some cases, biliary colic can be felt in the sternum and is similar to an attack of angina.
Cholelithiasis
Accompanied by dull but constant pain. Unbearable pain occurs when a stone moves through the bile duct. In this situation, the patient’s condition is considered critical and urgent medical attention is required.
Gallstone disease can lead to irreversible consequences if all stones are not removed in a timely manner. The safety of the organ also remains in question.
The signs of the disease are as follows:
- pain in the right side;
- copious amounts of vomit;
- after a meal there is heaviness in the stomach;
- gradual weakening of the body;
- yellowness of the skin due to a sharp jump in bilirubin in the blood;
- impaired peristalsis.
In remission, the disease does not bother a person, but when it becomes chronic or acute, it is accompanied by severe pain.
How does your gallbladder hurt?
If a person knows how the gallbladder hurts and what diseases cause discomfort, you can consult a doctor in time, start following a diet and taking certain medications. And then it will be possible to stop the development of the disease. So, let's figure out why and where the gallbladder hurts, and what to do if such complaints appear.
Gallbladder diseases occur more often in women.
This is facilitated by the peculiarities of the hormonal system, childbirth, taking contraceptives, antibiotics, weight fluctuations and adherence to strict diets with a sharp restriction of fats. But despite the high prevalence of symptoms of gallbladder diseases, many women do not know how gall bladder hurts or simply stubbornly ignore the first signs of disorders.
Pain syndrome may be associated with nutrition. The gallbladder contracts and releases bile when certain foods, mainly those containing fat, are consumed. And you can’t refuse them at all. This often leads to thickening of bile and the formation of stones, inflammation of the mucous walls of the organ.
Women are very emotional and sensitive.
You've probably noticed how your gall bladder starts to hurt, especially if you have cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, if you get nervous. Palpable spasms immediately appear. When under stress, stones can even move, creating the risk of blocking the ducts.
Biliary dyskinesia
Dyskinesia is a functional disorder of the biliary system. A person’s motor skills deteriorate, and bile excretion occurs with severe problems. Symptoms include stabbing pain in the right side, vomiting and abnormal bowel movements.
The disease often takes a chronic form. Taking antispasmodics alleviates the condition, but does not eliminate the problem. If you suspect dyskinesia, you need to go to the hospital and undergo an ultrasound of the gallbladder.
What to do if you have pain
At the first signs of pathology, the patient should visit a medical facility as soon as possible to get advice from a gastroenterologist, and, if necessary, an oncologist and a surgeon. The patient must observe exactly when the pain appeared, what provoked it, what increased the sensation, and what decreased it. The nature of the pain and accompanying symptoms are also important.
Based on this information, the doctor will select the optimal diagnostic option.
If the pain is severe (hepatic colic has developed), you must call an ambulance. To relieve discomfort, the patient can lie on his right side and place a warm heating pad under him. If the pain is excessively intense, it is allowed to take antispasmodic drugs (No-Shpa, Buscopan, Spazmalgon, Baralgin). You must inform your doctor about the time of administration and the amount of medications taken.
At the hospital, the patient gives blood and urine samples for analysis. This will help to quickly identify the inflammatory process and assess its intensity. To obtain maximum information about the condition of the gallbladder, an MRI or CT scan is prescribed. In some cases, it is enough to do an ultrasound of the gallbladder. Treatment of gallbladder diseases requires an integrated approach. Based on the diagnostic results, treatment is selected. The important part is etiotropic therapy - eliminating the cause of the development of the pathological process. The first stage is the elimination of acute pain, carried out using injections of antispasmodics and painkillers.
Symptoms in women
Females are more likely to suffer from gallbladder lesions compared to males. A similar trend can be traced due to hormonal disruptions provoked by childbirth, contraceptives, antibiotics, weight changes and various diets. All these factors together form an environment favorable for the onset of pain in the gallbladder.
Pain may be the result of poor nutrition. The gallbladder contracts when consuming fatty or fried foods. It is not recommended to completely abandon such dishes, otherwise the bile will thicken and this will lead to the formation of stones.
The main symptoms of pain in the gallbladder in women are as follows:
- gagging that occurs before or after eating fatty foods;
- pain in the right side, occasional flatulence;
- dull and bursting pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the back;
- loss of appetite;
- increased bilirubin in the blood;
- problems with stool.
If the above symptoms are noticed, you should immediately consult a specialist and undergo an ultrasound of the bladder.
What is the cause of the disease?
In fact, the gallbladder is an unpaired organ that is directly involved in the digestion process. Pathologically, a negative process can affect any system within the body and cause serious problems in the future.
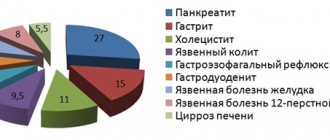
The most common causes of this disease include the following:
| Cause | Description |
| GSD - cholelithiasis | This cause is diagnosed when multiple or one stones are identified inside an organ. |
| Cholesterosis | A pathology associated with the development of an imbalance in the functioning of fat metabolism and deposits of cholesterol plaques on the mucous membranes, which leads to stagnation of the contents in the organ. |
| Complications from colic | As a rule, this reason occurs when stones come out in the colds. |
| Cholecystitis (acute and chronic) | The process of inflammation caused by bacterial flora within the body. It is a dangerous disease for health. The pathology arises and develops against the background of colic, and then surgical intervention may be required. |
| Dyskinesia | As a rule, a cause of this nature occurs when the sphincter muscles, which ensure the excretion of bile into the duodenum, are disrupted. |
| Organ injury | Isolated injuries are extremely rare, since the gallbladder is protected by the ribs, but injuries that are combined with deformation of the entire body and nearby organs are often encountered. |
| Parasites | The most common phenomenon among children, however, it is often diagnosed in adult women. As a rule, we are talking about giardiasis, opisthorchiasis and fascilosis. |
| Tumors | It is worth mentioning here that neoplasms can be benign and malignant. The gallbladder can be affected if there is an organ near it where a tumor has formed. |
All of the above reasons can lead to damage and inflammation of the gallbladder. It is important to carefully monitor your own body to avoid such a problem. It should be noted that if such a problem arises, you should not self-medicate, and without delay, go to a specialist and undergo a diagnostic procedure to make an accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms in men
Symptoms of pain in the gallbladder in men are completely similar to those that occur in women. But the provoking factors are different.
Excessive alcohol abuse negatively affects the condition of the gallbladder. Smoking can also make the situation worse. A sharp transition from fatty and fried foods to a lighter menu will certainly cause stress in the body, which will worsen the condition of the biliary organ.
If these signs are present, you should consult a doctor to prevent undesirable consequences.
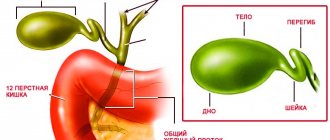
Features of the location of the gallbladder and the structure of the organ
Only an experienced specialist can accurately say how the gallbladder hurts in various pathologies and what stage of the disease is observed in a particular patient.
Most patients, at the first signs of the disease and when pain occurs, begin to take antispasmodic and painkillers, however, such actions are fundamentally wrong. The problem is related, first of all, to the fact that not all medications may be suitable for such pathology. Some drugs are approved only for different types of pain in the gallbladder area.
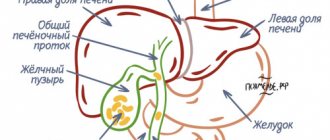
The organ itself is located directly above the liver and is connected to it by special bile ducts. The bubble is pear-shaped and small in size. The main task of the organ is to accumulate and promptly remove bile produced by the liver. Liquid is necessary to ensure the normal functioning of the general digestive system. In particular, we are talking about the absorption of fats. The fact is that bile is used by the body as a special composition for the flow of a food bolus through the intestines. The normal human liver is capable of producing one to two liters of bile in two days.
Treatment
The course of treatment is prescribed by a doctor. When biliary colic is diagnosed, the patient must be hospitalized in the surgical department. Primary measures are aimed at eliminating pain with the help of antispasmodics and painkillers.
If colic is caused by cholelithiasis, surgical removal of stones from the gallbladder is performed.
Drug therapy includes the use of the following drugs:
- drotaverine;
- Odeston;
- papaverine;
- spazgan;
- tramadol.
The patient must adhere to a diet that excludes sour, spicy, salty and fatty foods. It is allowed to eat light and sufficiently high-calorie foods. In this case, the consistency of the dishes can be liquid or puree, and drinking plenty of fluids is allowed. You should eat food regularly - every 2-3 hours - and in small portions. The temperature of the food should not be cold or hot.