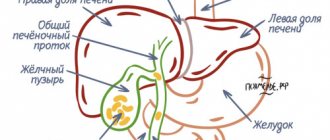
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen is a protrusion of preperitoneal tissue and the hernial sac through the slit-like spaces of the aponeurosis along the midline of the abdomen. With a hernia of the linea alba, a painful tumor-like protrusion appears on the anterior abdominal wall, abdominal pain, and sometimes dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, constipation, flatulence). Diagnosis of a hernia includes consultation with a surgeon, X-ray of the stomach, gastroscopy, herniography, ultrasound, CT scan of the abdominal organs. For hernias of the white line of the abdomen, hernioplasty using local tissues or synthetic materials is indicated.
What it is?
A hernia of the white line is a protrusion of subcutaneous fatty tissue and internal organs through large gaps between the plexus of tendons of the white line of the abdomen.
As practice shows, pathology is 3-10% more common in men under the age of 30. With this form of the disease, parts of internal organs and fat begin to appear through the openings between the muscles. A typical location is the epigastric region.
Depending on the location relative to the umbilical cavity, the following types of hernias are distinguished:
- Supraumbilical (located above the navel);
- Peri-umbilical (located near the umbilical cavity);
- Subumbilical (localized below the umbilical cavity).
The location of a hernia of the white line near and below the navel is uncommon.
Modern treatment methods make it easy to get rid of the disease, but to identify it at the initial stage, you need to become familiar with the causes of the development of the pathology and the symptoms that accompany it. A hernia, like any other disease, is easier to treat at the initial stage of development.
At first glance, education does not cause significant discomfort, but the disease is still fraught with danger. The main threat is pinching of organs trapped inside the hernial sac. In some cases, compression of the nerves occurs.
Causes
The linea alba is a narrow tendon plate between the rectus abdominis muscles between the pubis and the xiphoid process of the sternum. The rectus abdominis muscle, which forms this area, has 3-6 tendon bridges. The cause of hernia formation in this area is congenital or acquired weakness of the connective tissue of the white line of the abdomen. Sometimes this leads to its thinning and expansion, the appearance of holes in the white line and the formation of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles (divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles). The width of the white line is normally 1-3 cm, and if it changes more, it can reach 10 cm, depending on the degree of diastasis.
Hernia of the white line most often occurs in men 20-30 years of age. A typical location is the epigastric part of the linea alba.
Predisposing factors that weaken the connective tissue of the white line of the abdomen include:
- hereditary weakness of connective tissue;
- obesity;
- postoperative scars.
Risk factors associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure:
- physical stress;
- constipation;
- pregnancy;
- ascites;
- prolonged cough.
Causes
Factors that provoke the development of the disease are divided into 2 categories: causes arising from weakness of the white line, and factors caused by increased pressure inside the peritoneum.
The reasons belonging to the first group act as prerequisites for the occurrence of a hernia. This:
- Genetic predisposition If you have relatives with this diagnosis, the risk of the disease increases.
- Excess weight Due to a thick layer of subcutaneous fat, the anterior abdominal wall becomes weak and the linea alba begins to stretch.
- Scars formed as a result of surgical interventions Each of them is a vulnerable place where a hernia can bulge.
- Injuries Any injury to the abdomen makes the anterior abdominal wall weaker.
- Pregnancy During this period, the abdominal muscles weaken and the abdominal wall stretches.
Factors included in the second group are direct provocateurs of the disease. These include:
- strong and prolonged crying in children;
- difficult birth, large baby;
- diseases occurring against the background of problems with urination;
- great physical activity;
- constipation;
- diseases of the abdominal cavity occurring against the background of a severe cough.
Symptoms of hernia of the white line of the abdomen, photo
The symptoms of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen (see photo) are the same in men and women, the pathology does not depend on gender characteristics. In some cases, a hernia may even manifest itself only as a protrusion, which is typical for the initial stage of the pathology.
Over time, the hernia begins to manifest itself as pain, which intensifies significantly during intense movements and when straining. Pain in each specific case may be of a different nature. They can be sharp, dull, pulling, prolonged or paroxysmal, sharp and even “dagger-like”.
Also, the disease in men and women is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nausea followed by vomiting;
- pain of a different nature - when bending, turning and other movements;
- stretching of the midline abdominal muscles;
- pain after meals;
- belching, heartburn, hiccups.
As the disease progresses, the signs of pathology intensify:
- pain intensifies and becomes unbearable for the patient;
- vomiting constantly torments the patient;
- blood may be found in the stool;
- it becomes impossible to repair the hernia.
In the event of a pinched hernia, assistance to the patient should be urgent. If any of the manifestations occur, you should immediately contact the clinic.
Stages of formation of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
In its development, a hernia of the white line of the abdomen goes through the stage of preperitoneal lipoma, the initial stage and the stage of final formation.
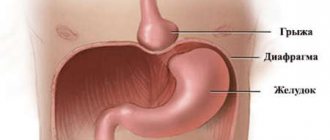
At the first stage, preperitoneal tissue emerges through a slit-like defect in the tendon fibers to form a preperitoneal lipoma. At the initial stage, a hernial sac is formed, the contents of which are part of the omentum or a section of the small intestine. At the stage of a formed hernia, all components of the disease are present - the hernial orifice, the hernial sac with hernial contents, which may include the omentum, loops of the small intestine, the umbilical-hepatic ligament, the transverse colon, and the stomach wall. At the stage of final formation, a hernia of the white line of the abdomen is well identified visually and by palpation.
A hernia of the white line of the abdomen rarely reaches large sizes; sometimes the process stops at the stage of preperitoneal lipoma: the protrusion does not protrude beyond the white line, is hidden and does not progress further.
According to the level of location relative to the navel, the following types of hernia of the white line of the abdomen are found:
- supra-umbilical (epigastric, epigastric) – formed above the navel, most common (80%)
- peri-umbilical (paraumbilical) – located near the umbilical ring (1%)
- subumbilical (hypogastric) – located below the navel (9%)
More often, hernias of the white line of the abdomen are single, less often - multiple, located one above the other.
Stages
Normally, the white line from the sternum to the navel is 10–25 mm wide, and below it it narrows to several millimeters. In the place where a hernia of the linea alba develops, the tendon fibers can diverge by 100 and even 120 mm, forming hernial orifices of various shapes (oval, diamond-shaped, round).
Wide hernial orifices do not appear immediately - the hernial protrusion goes through several stages of development:
- The first stage is preperitoneal lipoma. It occurs when one or more provoking factors appear, which we discussed earlier. In this case, through the still small holes in the diverging tendon, fatty tissue protrudes under the skin.
- Initial stage. The peritoneum enters the hernial orifice, which begins to form a membrane for the internal organs that extend under the skin. The peritoneum is a thin membrane that covers the inner walls of the abdominal cavity and the surface of the internal organs.
A hernia of the white line of the abdomen at the stage of final formation includes all the required elements:
- hernial orifice - an opening in the linea alba from which organs emerge;
- hernial sac - peritoneum;
- contents of the bag: omentum, intestines, stomach walls, some ligaments.
Depending on when the disease was discovered, the complexity of the operation depends.
Diagnosis of hernia of the white line of the abdomen
A thorough physical examination can identify a hernia of the linea alba without significant difficulty. Upon palpation, a dense, painful protrusion of an oval or round shape, with a diameter of 1 to 12 cm, located along the white line of the abdomen is determined. The hernial protrusion is more clearly contoured through the anterior abdominal wall when the body is tilted back, as this is associated with tension in the linea alba. With a reducible hernia of the white line of the abdomen, the slit-like hernial orifice can be palpated. With the help of auscultation, rumbling is heard above the hernial sac.
To clarify the anatomical structures involved in the hernial process, barium X-ray of the stomach, gastroscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy), ultrasound of the hernial protrusion, and MSCT of the abdominal organs are performed. In some cases, herniography is performed - an x-ray contrast study of the hernia.
Differential diagnosis of hernia of the white line of the abdomen is carried out with peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, pancreatitis, cholecystitis.
Strangulated hernia
Infringement of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen is compression of the organs and tissues located in the hernial sac. Depending on the mechanism of development, elastic, fecal and retrograde strangulated hernias are distinguished.
Elastic strangulation of a hernia occurs when there is a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure (for example, during defecation, coughing, sneezing, etc.), when the hernial orifice expands sharply, and most of the abdominal organ protrudes into it. Then the hernial orifice returns to its original state, since the tissues are elastic, and the prolapsed organs do not have time to return back to the abdominal cavity.
With fecal strangulation, the loop of intestine trapped in the hernial sac is gradually filled with feces and gases. As a result, the intestinal loop stretches and increases in size, as a result of which it is pinched.
With retrograde strangulation, a part of the intestinal loop or other organ that is not in the hernial sac, but in the abdominal cavity, is compressed. With this type of strangulation, peritonitis and intestinal necrosis develop very quickly, and the severity of clinical symptoms increases rapidly.
Course of the disease
Depending on the location relative to the navel, the following hernias of the white line of the abdomen are distinguished:
- supra-umbilical - located above the navel;
- peri-umbilical - located next to the umbilical ring;
- subumbilical - located below the navel.
In some cases, hernias of the white line of the abdomen do not manifest themselves in any way and are discovered by chance.
There are three stages of hernia: preperitoneal lipoma, initial and formed hernia.
At the lipoma stage, preperitoneal fat protrudes through slit-like defects in the linea alba. Then a hernial sac forms - this is the initial stage. When muscle divergence (diastasis) appears and the process progresses, part of the omentum or a section of the wall of the small intestine enters the hernial sac. A hernia has formed: a dense painful formation appears in the area of the white line of the abdomen, the hernial gate (through which the abdominal organs emerge) is usually oval or round in shape, their diameter ranges from 1 to 12 cm. Multiple hernias of the white line of the abdomen often occur, located one above the other .
Pain syndrome is expressed even in the early stages of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen, which is associated with pinching of the nerves of the preperitoneal tissue.
Diagnostics
The primary diagnosis can be made based on an external examination of the patient; additional examinations are required to accurately determine the condition.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. The condition of the internal organs is checked.
- X-ray examination of the hernial sac. Before the examination, the patient is given a barium preparation to increase the contrast of the image.
- Multislice tomography. Used in the most difficult cases, it allows you to completely eliminate errors during diagnosis and assessment of the current condition.
Treatment
Often, when treating a disease, mistakes are made that negatively affect the pathology:
- Treatment with painkillers or anti-spasm drugs will only eliminate the pain.
- Constantly wearing a bandage. The device must not be used for an extended period. The belt does not replace full muscle work. With frequent use of the device, muscle fibers may lose tone, which will lead to their atrophy.
- Folk remedies (infusions of drupe leaves, immortelle, wormwood), taken orally, can reduce gas formation and improve intestinal function. This will reduce the degree of intestinal protrusion, but the defect in the tendons will not heal due to the properties of this tissue.
- Using medications to enhance gastric motility. Over time, this type of treatment does provide relief, but does not solve the problem. It is recommended to treat the pathology with surgery.
- Exercise is good for preventing hernia formation, but not for treating it.
Refusal of self-medication, timely diagnosis of pathology and its correct therapy is the only way to avoid complications and return to a normal lifestyle.
Preparing for surgery
Self-preparation of the patient includes the following points:
- abstinence from alcohol no later than three days before the scheduled surgery;
- eliminating drugs that impair blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding (you must tell your doctor about all medications you are taking, and he will give you a list of prohibited ones);
- 14 days before the operation, provide yourself with a balanced diet, which includes all the necessary microelements and vitamins (this will help you endure the procedure and anesthesia more easily, and also improve rehabilitation);
- complete refusal to eat after 20.00 on the day before surgery.
The hospital must take the necessary laboratory tests to check sugar levels, exclude HIV, hepatitis and other sexually transmitted diseases, and accurately determine the blood type and Rh factor. An ECG is also performed to check the heart's function to make sure the patient will tolerate the anesthesia.
Surgery to remove a hernia of the linea alba
Surgical intervention is carried out as planned. The doctor examines the patient, establishes a diagnosis, prescribes an examination and a date for hospitalization.
Types of operations for hernia of the white line of the abdomen:
- Open surgery with tension-free plastic surgery. To strengthen the linea alba, the surgeon uses special mesh prostheses. This method is used most often today, since after it a relapse is least likely.
- Open surgery with tension plasty. After removing the hernia, the surgeon tightens the linea alba with sutures, thereby strengthening it - hence the word “tension” in the name. This type of operation is simple, but has disadvantages: you have to make a fairly long incision (a large scar remains), and the risk of relapse is high.
- Paraperitoneal surgery. Three punctures are also made, but, unlike laparoscopic surgery, the instruments are not inserted into the abdomen or pierced the peritoneum. A special balloon is placed between it and the surrounding tissues and inflated - a space is formed from which you can access the hernial sac and perform surgery. The advantages of this operation are the same as those of laparoscopic surgery. However, its implementation is technically more complex; it is impossible to reliably fasten the mesh prosthesis.
- Laparoscopic surgery. With the advent of high-tech equipment in modern clinics, this type of operation for hernia of the white line of the abdomen has become increasingly popular. Instead of an incision, the surgeon makes three holes through which he removes the hernia and installs a mesh prosthesis. Laparoscopic surgery provides a low risk of relapse and allows the rehabilitation period to be reduced to 10 days - after which the patient can return to normal activities. But this operation cannot be performed for diseases of the lungs and heart. It is also impossible if the clinic does not have the appropriate equipment and specialists.
In case of a strangulated hernia of the white line of the abdomen, surgical intervention should be carried out as an emergency. The surgeon opens the hernial sac and examines the part of the intestine located in it. If it is dead, it must be removed. Sometimes it turns out that a large area of the intestine has become necrotic; the incision has to be enlarged and all the dead tissue has to be removed.
Treatment of hernia of the white line of the abdomen
You can only get rid of a hernia surgically in a hospital setting. Types of operations (hernioplasty):
1) Plastic surgery with local tissues - suturing the defect of the white line of the abdomen with the elimination of possible diastasis of the rectus muscles. However, due to the weakness of the connective tissue and significant load on the sutures after surgery, relapses (re-formation of a hernia) occur in 20-40% of cases.
2) Plastic surgery with the use of synthetic prostheses - installation of a mesh to close the aponeurosis defect after eliminating diastasis of the rectus muscles due to a hernia of the white line of the abdomen. The chance of relapse is very low. The operation is performed under anesthesia.
A feature of the surgical treatment of hernias of the white line of the abdomen is that eliminating just one hernia is not enough. It is necessary to eliminate diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles.
Rehabilitation period
After a planned operation, that is, when the hernia was not strangulated, recovery occurs quite quickly. The patient is kept in the hospital for no more than three days. During this period, the nurse regularly makes dressings, and the doctor monitors the condition of the stitches and the patient’s well-being to exclude the possibility of infection. For the same purpose, a prophylactic course of antibiotics is prescribed.
The rehabilitation period requires compliance with certain rules:
- It is forbidden to lift weights over 5 kg (the restriction is valid for at least 3 months from the date of surgery);
- Leaning forward, sudden movements and too intense training are prohibited;
- moderate physical activity is indicated, especially walking;
- it is necessary to take laxatives prescribed by the doctor (constipation can cause sutures to come apart);
- It’s worth reviewing your diet and switching to a balanced diet.
People whose profession involves heavy physical labor are transferred to light work for a period of up to 6 months.
Diet
Sometimes situations arise when immediate surgical treatment cannot be performed for various reasons, and it has to be postponed for a certain time. Following a diet can alleviate the course of the disease and minimize the risk of strangulation.
- It is recommended to introduce more rice cereals, fish, eggs and dairy products into the diet. Be sure to drink the physiological norm of fluid. All foods should be digested quickly with a minimum amount of gases.
- It is not recommended to eat foods that cause bloating: legumes, fried and smoked foods, chocolate, nuts, butter, pickled vegetables.
If there are initial problems with digestion, then they should be eliminated by any means, from medications to traditional methods. The condition for choosing the right diet is the final diagnosis made in a medical institution.
Prevention
Prevention of white line hernia includes the following measures:
- identifying the causes of extra pounds and normalizing body weight;
- timely cure of diseases accompanied by cough;
- avoiding heavy lifting;
- adherence to the principles of a balanced healthy diet that would promote regular bowel movements;
- avoiding injuries to the anterior abdominal wall;
- regular physical exercise to strengthen the abdominal muscles (morning exercises, gym classes);
- dosing physical activity that involves the abdominal muscles, proportionate to one’s own physical training;
- compliance with all doctor’s recommendations (including wearing an abdominal bandage) during pregnancy and in the postoperative period.
Remember that a bandage does not cure a hernia. When worn for a long time, on the contrary, it can contribute to its occurrence, since it begins to perform the function of the abdominal muscles, which, as a result of inactivity, weaken and diverge even more, which contributes to the occurrence of a hernia.
Forecast and prevention of hernia of the white line of the abdomen
With timely and rational treatment of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen, the prognosis is favorable. The likelihood of relapse is determined by the method of hernioplasty and the lifestyle followed by the patient after surgery.
To prevent the formation of a hernia of the linea alba, it is recommended to train the abdominal muscles, eat right, avoid constipation, maintain a stable optimal weight, wear a special bandage during pregnancy, and do not lift excessive weights.
Source: https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/white-line-hernia