Irritable bowel syndrome
It is characterized by the appearance of abdominal pain, which is caused by increased intestinal motility, as well as spasms of the intestinal wall. This disorder most often manifests itself in young people who are emotionally labile.
With this disease, stools become more frequent and there is an admixture of mucus in the stool. A distinctive feature is the complete cessation of pain during sleep, when the person calms down.
Volvulus of the small intestine (jejunum)
It is a twisting of the intestinal wall in such a way that there is an obstacle to the movement of intestinal contents. The intestine seems to be tied into a “knot”. This is possible precisely in the small parts of the intestine, where the length of the mesentery allows the intestine to twist around its axis.
The person begins to feel a strong, sudden pain in the center of the abdomen near the navel. It is important to know that with intestinal volvulus, necrosis occurs quite quickly. Treatment consists of removing a section of damaged intestine and restoring integrity by creating an anastomosis (connection).
Doctor's advice
The periumbilical area is often used as a surgical approach for many operations, for example, umbilical hernia and linea alba. After surgery, many experience pain around the navel of varying intensity and duration. Some go away in 1-3 months - this is when the nerves cut during the operation grow together. Others last for years - they arise due to improper fusion of nerve endings, which are “shorted” like 2 exposed wires. Such pains eventually go away, but can manifest themselves as a reaction to changes in weather or occur during physical activity. There is no specific therapy. If there is a tendency to excessive growth of connective tissue (this is manifested by wide scars after incisions and injuries), Lidaza can be used.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Possible complications
Some pathologies do not pose a mortal threat, but reduce the quality of life, while others are fraught with death. These include appendicitis. If surgical amputation of the inflamed vermiform branch of the cecum is not performed in time, it will spontaneously open.
Peritonitis often leads to death. Pain caused by a hernia and localized above the navel from above requires rapid tissue reduction. Otherwise, there is a high risk of developing necrosis. Intestinal obstruction also poses a mortal threat. If it is not eliminated, gastric damage and systemic intoxication of the body are possible.
Umbilical ring hernia
One of the most common pathologies in infants. This is due to the relative incompetence of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall in the area of the umbilical ring, as a result of which intestinal loops can get into the hernial ring and even be pinched in it.
This pathology can also occur in adults. As a rule, a hernia appears after lifting heavy objects or increasing intra-abdominal pressure. A distinctive feature is the presence of protrusion.
An umbilical ring hernia is characterized by a positive cough symptom, in which the pain around the navel intensifies when the patient tries to imitate a cough.
If the intestinal wall is pinched, surgical intervention is necessary as early as possible to prevent necrosis.
Causes of pain around the navel
One of the common causes of pain in the navel is gastroenteritis.
If you place your palm on the navel area, under it there will be skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue, deeper - muscles and connective tissue (aponeurosis), even deeper - the small intestine and blood vessels. Any of these structures can hurt. In addition, due to the peculiarities of the location of the nerves, pain from another place in the abdomen sometimes radiates to the navel.
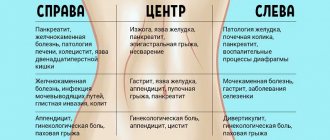
The causes of pain in the navel area can be the following diseases:
- Gastroenteritis (usually of an infectious nature, popularly known as poisoning). According to an American study, from 7 to 18% of patients with abdominal pain suffer from gastroenteritis. You can get sick at any age. Viruses or bacteria enter the stomach and intestines with food or water from objects or dirty hands, affecting the mucous membrane of these organs. The patient develops nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Body temperature may rise. Symptoms develop suddenly and in uncomplicated forms of the disease usually disappear within 2-3 days.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. According to the same study, 2.6 to 13% of all abdominal pain is caused by irritable bowel syndrome. This chronic disease is associated with an inadequate response of the intestine to the stretching of its wall by gases and dysregulation of motility (motor activity). Manifested by bloating, bowel dysfunction (constipation, diarrhea, or their alternation). The pain usually decreases after passing gas or going to the toilet.
- Appendicitis. One of the most common reasons for abdominal surgery between the ages of 4 and 40 years. The appendix is a small hollow appendix. During infectious inflammation, its wall swells, the lumen closes, and microbes from the lumen penetrate into the thickness of the organ wall. If the wall dies, the appendix “bursts.” With appendicitis, pain, as a rule, migrates from the epigastrium to the umbilical region, and from there to the right and down, to the right iliac region, and is usually accompanied by increased body temperature and poor appetite.
- Strangulation of the umbilical hernia. A hernia is a protrusion on the wall of the abdomen, into which the intestine or other organ enters from the abdominal cavity. The hernia comes to the surface through the hilum, a weak spot in the abdominal wall. The navel is one such place. If the protrusion is infringed at the point of exit from the abdominal cavity, the intestine and the vessels that are responsible for delivering blood to it are compressed, which sharply aggravates the patient’s condition, since it is accompanied by intense pain and intoxication syndromes. The intestine may die, so this disease requires urgent surgical intervention.
- Intestinal obstruction. It develops when a mechanical obstacle appears to the movement of intestinal contents. Often this occurs due to adhesions (adhesions) with another part of the intestine or a neighboring organ resulting from abdominal surgery. In addition, a section of the intestine may become twisted or maladjusted, and its lumen may become clogged with a tumor, a ball of helminths, or dense feces. Pain, depending on the level of obstruction, can be combined with bloating, repeated vomiting, intestinal colic (contractions, spasms with increasing and decreasing pain) and constipation.
- Ischemia (infarction, decreased blood flow) of the small intestine. Occurs when the blood vessels that supply blood to the intestines are blocked. A section of the intestinal wall does not receive oxygen and may die. The reason is fatty plaques or blood clots (thrombi) that formed in the heart (for example, due to arrhythmia) or other vessels and moved here with the blood flow. The disease is more common after sixty years of age. The risk is higher with atherosclerosis of blood vessels, weakness of the heart muscle and interruptions in heart function.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (particularly Crohn's disease) . This is a serious chronic disease that debuts mainly at a young age - up to 30 years. The tendency towards it is inherited. For unknown reasons, the mucous membrane of the small and large intestines is affected. In addition to abdominal pain, it is accompanied by prolonged diarrhea, blood in the stool, fever, nausea, and weight loss due to poor absorption of nutrients in the intestines.
- Ruptured aortic aneurysm . The aorta is the largest artery that carries blood from the heart to other organs, passing behind the intestines almost in the middle of the abdomen from top to bottom. An aneurysm is a protrusion of a section of the wall of a vessel. The aneurysm wall is thinner than normal and can burst if blood pressure rises. This is an acute life-threatening condition accompanied by severe intense pain and loss of consciousness. It most often develops in men over 65 years of age with vascular atherosclerosis and high blood pressure.
- Metabolic disease. In diabetes, when the body does not have enough insulin and glucose from the blood is not absorbed by its cells, it uses fats for energy. Fat breakdown products accumulate in the blood and cause a serious metabolic disorder - ketoacidosis. In addition to abdominal cramps, it may be accompanied by frequent vomiting, shortness of breath, severe general weakness and drowsiness. In children, this condition often develops with acetonemic syndrome.
- Neoplasms. Tumors of the intestines or other organs in the abdomen can also cause pain. Fortunately, this is still an unlikely cause of abdominal pain before the age of fifty.
- The accumulation of excess gas in the intestines (flatulence) causes pain due to stretching of the intestinal wall. The pain in this case is of a cramping nature, sometimes intensifying, sometimes disappearing, and migrates through the abdomen according to the movement of gases through the intestines.
- A sprain or injury to the abdominal muscles occurs after too intense physical activity or sudden movements.
Acute appendicitis
There is a common misconception that inflammation of the appendix manifests itself exclusively in the right iliac region. However, an early sign of appendicitis is pain in the center of the abdomen.
After a few hours, pain migrates to the right iliac region. Such a change in localization is called Kocher's symptom. If you suspect appendicitis, you should urgently consult a surgeon to rule out pathology.
Diagnostics
To determine the cause of pain in the umbilical area, a comprehensive examination is carried out. It combines hardware diagnostics with laboratory tests.
To make a diagnosis, the following is prescribed:
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- blood chemistry;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography;
- laparoscopic procedure - minimally invasive surgical intervention for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes;
- X-ray diagnostics;
In some cases, a tissue biopsy may be required for histological examination in the laboratory. It is often performed during laparoscopy. If the nature of the pain in the peri-umbilical region is unclear, an examination using topographic anatomy methods is prescribed.
It allows you to study tissues and organs in a layer-by-layer projection. For gastroenterological causes and urological disorders, the first diagnostic methods are laboratory analysis of fecal matter and urine.
The most effective examination method is magnetic resonance imaging. The price of functional MRI in metropolitan clinics is about 11,000 rubles. You can undergo a comprehensive examination at a public clinic or hospital with a doctor’s referral. Commercial diagnostic centers do not require such a document.
Atypical form of myocardial infarction
In a small percentage of cases, myocardial infarction is manifested by pain not in the chest area, but in the abdomen in the navel area.
Associated signs help to recognize the true cause of pain: the appearance of weakness, a drop in pressure, shortness of breath, the appearance of acrocyanosis (blueness of the fingertips, nose, nasolabial triangle).
You should be careful about pain in the navel area, as it can signal serious diseases in the body. If severe, intense pain occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor, as in some situations immediate medical attention is required.
Be healthy!
Useful articles on the topic:
Polyp in the intestine The first signs of hemorrhoids in women and treatment in the early stages What can you take for stomach pain: a review of medications
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Rate how helpful this article was
5 2 people voted, average rating 5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Prevention
In men, pain below the navel, on the left, on the right, in the upper abdomen is better to prevent than to treat later. First of all, it is recommended to monitor your diet. Of course, you should not go on a diet, but it is advisable to reconsider a diet that contains a lot of fried and fatty foods. Every day a man should eat enough vegetables and fruits. You also need to take care of your daily routine: spend more time in the fresh air, take walks, ride a bike. Do not neglect the rules of hygiene. Wash your hands thoroughly, handle food, and keep dishes clean. And most importantly, completely avoid street food.