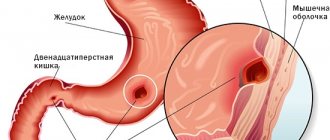
The cardia, or cardiac part of the stomach, is a cylindrical segment covering the esophagogastric junction and the space 2 cm above and below it. Cancer of the gastric cardia (cardioesophageal cancer, CER) differs in anatomical and clinical features, and requires a special approach to treatment. Many experts even identify it as a separate nosology, and there are several reasons for this:
- Tumors of this location tend to spread to the esophagus much more often than cancer of the underlying parts of the stomach.
- Such tumors metastasize to the abdominal and mediastinal lymph nodes.
- In addition, they have a poorer prognosis than gastric or esophageal cancer.
Cardioesophageal cancer is characterized by aggressive growth and a tendency to metastasize to the mediastinal lymph nodes.
- Causes
- Symptoms of gastric cardia cancer
- Classification
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of gastric cardia cancer
- Complications and relapses
- Prognosis and prevention
What is cardia?
The digestive tract contains circular muscles that act like valves. They help food move through the esophagus, stomach and intestines. Such muscles are called sphincters, they are able to contract when necessary and close the passage.
The cardia of the stomach is one of these muscles. It is located between the stomach and esophagus and regulates the flow of food. The sphincter is closed when a person is not eating and opens when eating so that food can enter the stomach. This happens during normal muscle functioning. The cardia prevents food and gastric juice from flowing back into the esophagus.
But sometimes the sphincter malfunctions, and then gastroenterologists diagnose “cardia insufficiency.” What it is? The pathology is that the muscle stops contracting or does not close completely, and food, along with gastric juice, is thrown into the esophagus. In medicine this is called reflux. This phenomenon can also occur in completely healthy people. But during normal functioning of the body, the esophagus is protected, the mucous membrane is quickly restored, and inflammation does not occur.
But if the protection of the esophagus is reduced, then the reflux of acid and food leads to burns and inflammation of the mucous membrane. This disease is called reflux esophagitis, and it requires immediate treatment. In advanced cases, ulcerations appear on the lower part of the esophagus.
Externally, the cardia resembles a round rosette. In a healthy body it closes in a circle. With its pathology, gastroenterologists talk about insufficiency of the cardia rosette.
Causes of pathology
Cardia failure with reflux esophagitis occurs due to not one, but several reasons. Factors that provoke sphincter weakness are divided into organic and functional. Organic causes are not related to the activity of the cardia rosette, but are caused by the fact that the sphincter has to work in unfavorable conditions. Such reasons include:
- excessive eating;
- excess body weight;
- systematic overeating in the evening;
- low mobility;
- chronic stomach diseases (ulcers, gastritis);
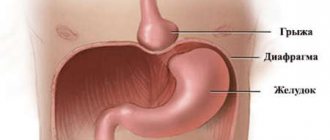
- lower esophageal hernia.
Functional reasons are associated with disruption of the sphincter muscle ring itself. These factors include:
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites);
- pregnancy;
- age over 35 years;
- physical stress during work or sports;
- intra-abdominal hypertension;
- unsuccessful operations on the gastrointestinal tract;
- pyloric spasm.
Stages of the disease
There are several degrees of gastric cardia insufficiency. What it is? Depending on how much the sphincter loses its ability to close, there are 3 stages of the disease:
- Stage 1. Incomplete closure of the cardia rosette occurs. Patients complain of frequent belching. During endoscopic examination, a small gap (about 1/3 of the diameter) can be seen in the cardia when the patient breathes deeply.
- Stage 2. With deep breathing, the gap increases to 1/2 the diameter. The patient complains of nausea and a feeling of heaviness in the digestive organs.
- Stage 3. The sphincter completely stops closing. If the patient suffers from liver pathologies, this aggravates the development of cardia failure. Symptoms of esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus) become pronounced.
In the photo you can see endoscopic changes in the cardia with insufficiency: gaping gaps and inflamed areas.
Drug therapy
In cases where the cardia rosette does not close completely, treatment is prescribed by a doctor according to the course of the diagnosed disease. Very often, the cause of cardia insufficiency is gastritis. In such cases, specialists prescribe medications that reduce the aggressiveness of the stomach contents:
- Medicines that slow gastric secretion.
- Drugs that neutralize high acidity.
- Film-forming drugs.
- Agents that stimulate mucus production.
At the initial stage of development of cardia failure, the course of treatment can be aimed at relieving and mitigating the symptoms of the disease.
Currently, medications that can stimulate gastrointestinal motility are gaining popularity. They are called prokinetics.
In cases of infection, antibiotics are also included in the course of treatment for this disease.
Identifying concomitant diseases and studying a detailed history allows specialists to select an individual course of treatment for each patient. There are cases (lack of effective treatment results, hiatal hernia) when surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Symptoms of cardia failure
It is difficult for a patient to determine on his own that he suffers from cardiac insufficiency. The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of many other stomach ailments. The following manifestations should be the reason for contacting a gastroenterologist:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- admixture of bile in vomit;
- belching with a sour taste;
- pain in the stomach and esophagus;
- dizziness, weakness, loss of appetite;
- frequent heartburn;
- burning sensation behind the sternum;
- nausea;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- a feeling of spasms in the area where the esophagus enters the stomach.
With cardia insufficiency, superficial gastritis is a common occurrence. These two diseases often accompany each other. Inflammation of the stomach can cause sphincter weakness. In this case, there is pain behind the sternum, constant rumbling in the abdomen, general weakness, the tongue is coated with a white coating. Superficial gastritis can be provoked not only by poor nutrition, but also by wearing tight clothing that squeezes the waist.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a common complication of cardia failure. What it is? The disease develops due to chronic reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. Severe pain occurs in the chest, which patients sometimes mistake for myocardial infarction. Symptoms from the stomach are accompanied by signs of damage to the upper respiratory tract: sore throat, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing.
The most dangerous complication of cardia insufficiency can be malignant degeneration of the cells of the esophageal mucosa. The aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid negatively affect the condition of the epithelium and over time can provoke the growth of tumors.
Symptoms of gastric cardia cancer
Cardia cancer is most characterized by weight loss, food aversion, pain and dysphagia. The pain is usually localized in the epigastric region, is constant, pressing in nature and does not depend on food intake. Sometimes it radiates to the lumbar region or behind the sternum. In the latter case, the disease can simulate heart pathology, such as angina.
The severity of dysphagia depends on the size of the tumor and obstruction of the digestive tract. It is mainly manifested by malnutrition, which leads to hypovolemia and changes in electrolyte balance.
Diagnosis of cardia failure
The disease is diagnosed based on the results of an X-ray of the stomach. Esophagoscopy will help determine the stage of the disease. The methylene blue test determines the presence of reflux esophagitis in cardiac insufficiency. What it is? During an endoscopic examination, a dye is injected into the patient's stomach. The substance colors only healthy areas; inflamed areas do not change color.
In addition, additional studies are prescribed:
- stomach acid test;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Based on all the studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis of “cardia insufficiency.” How to treat this pathology depends on the cause and stage of the disease.
Prognosis and prevention
The 5-year survival rate for any type of CER averages 23.6%. Type III tumors have the most unfavorable course, since they are predominantly represented by poorly or undifferentiated neoplasms. The 5-year survival rate for this location is about 14%. The prognosis is significantly worsened by the presence of metastases in the mediastinal lymph nodes.
The European clinic employs doctors with extensive experience in treating stomach cancer. We are guided by current European standards. For this, the clinic has everything necessary - from the latest medications to modern equipment, thanks to which we are ready to provide assistance in the most severe cases.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Drug treatment
Cardia failure is a chronic disease. It is difficult to cure it completely. But it is possible to reduce the relapse rate.
First of all, you need to eliminate the cause of sphincter weakness. If you are overweight, then diet and exercise are necessary to reduce body weight. Lifestyle changes are required: proper nutrition, refusal to wear tight clothes. It is recommended to sleep with your head elevated. Excessive physical exertion and sudden bending of the body should be avoided.
Drug treatment is aimed at strengthening the sphincter and relieving pain attacks. The following drugs are prescribed:
- means for increasing motility and tone of the digestive organs: “Metamol”, “Motilium”, “Propulsid”, “Raglan”, “Perinorm”, “Metoclopramide”;
- painkillers: “Ibuprofen”, “Tempalgin”;
- medications that coat the gastrointestinal mucosa: “Almagel”;
- Heartburn relievers: Ranitidine, Smecta.
Diet for cardia deficiency
If the sphincter is weak, split meals are useful. You need to eat often, but in small portions. If you eat too much food at one time, the rosette of the cardia will stop closing. The following nutritional principles must be observed:
- After eating, you cannot lie down for 2 hours, you can only walk or stand.
- You should eat food in semi-liquid form: porridge, low-fat broths.
- You can't overeat in the evening.
- You need to exclude chocolate, spicy, fried and fatty foods. Excessive amounts of salt and coffee can also aggravate symptoms of the disease.
- The consumption of alcohol and carbonated drinks is strictly prohibited.
- During each meal, you do not need to fully load your stomach.
- Food should not be too hot or too cold.
Treatment of gastric cardia cancer
Treatment of cardia cancer requires a combined approach and includes chemotherapy and surgery. For unresectable tumors, the main treatment method is chemotherapy, and operations are performed for life-threatening indications.
Surgical treatment
The choice of the extent of the operation and surgical approach is determined based on the type of cancer and its local prevalence. For type I CER, proximal gastrectomy is performed
| KER type I Proximal gastrectomy, subtotal esophageal resection. | KER type II Gastrectomy (the entire stomach is removed), resection of the lower thoracic esophagus | KER type III Gastrectomy, resection of the lower thoracic esophagus. |
The minimum volume of lymph node dissection involves the removal of 1st and 2nd order lymph nodes (extended lymph node dissection is performed in the volume of D2). In CER I, bilateral mediastinal lymph node dissection is performed.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is carried out using one of the following options:
- Perioperative chemotherapy. Performed in CF or ECF mode for 8-9 weeks before and after surgery.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy. It begins 4-6 weeks after surgery, if there are no severe complications, and is carried out for 6 months. XELOX or CAPOX schemes are used.
- Adjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Currently, it is rarely used and only in case of non-radical surgery.
Treatment of unresectable and disseminated tumors is carried out using chemotherapy according to the CF, CX, XELOX regimens in 6-8 three-week courses, or 9-12 two-week courses. After this, treatment is stopped and observation is carried out until the disease progresses. For HER2-positive gastric cancer, treatment with trastuzumab is possible.
After disease progression, chemotherapy is resumed, and the treatment regimen is selected taking into account the existing medical history.
Metastasis
With CER types I and II, metastasis mainly occurs in the lymphatic collectors of the paracardial zone, celiac trunk and lesser curvature of the stomach. In type I CER, the mediastinal nodes may also be involved in the process. Such features of metastasis are taken into account when planning surgery and lymph node dissection.
Surgical treatment of cardia failure
Surgical treatment is used in advanced cases. Sometimes surgical methods help get rid of the cause of cardia insufficiency, for example, a hernia.
To eliminate sphincter weakness, the following operations are performed:
- The wall of the esophagus is sutured to the stomach.
- Additional folds are surgically made in the esophagus.
- The muscles are sutured and the cardia ring is narrowed.
The surgeon decides which method to eliminate cardia insufficiency in each specific case.
Classification
The classification of cardia cancer is based on the location of the center of the tumor. The anatomical reference point is the Z-line - the line of the esophagogastric junction.
- Type I cancer - the center of the tumor is located at a distance of 1-5 cm above the Z-line towards the esophagus.
- Type II cancer - the center of the tumor is located within 1 cm orally and 2 cm below the Z-line.
- Type III cancer - the center of the tumor is located at a distance of 2-5 cm below the Z-line.
Traditional methods of treatment
Therapy with home remedies can only be carried out as an addition to the main treatment. Before using traditional medicine, you should consult your doctor. When treating insufficiency of the esophageal cardia, the following traditional medicine recipes are used:
- Juice is squeezed out of plantain leaves and taken 1 teaspoon before meals during an exacerbation of the disease.
- A mixture of St. John's wort, motherwort and valerian herbs is brewed in equal proportions, filtered and taken with honey.
- Dandelion flowers are ground with sugar to form a syrup. Dissolve 1 teaspoon of the composition in a glass of water and drink before meals.
- Cumin (1 teaspoon) is brewed in a glass of boiling water and drunk before meals. This drink perfectly relieves spasms in the gastrointestinal tract.
We can conclude that cardia failure is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. Such manifestations also occur in other gastrointestinal diseases. Therefore, you should not try to diagnose yourself. You need to contact a gastroenterologist as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment.