Symptoms of the development of an umbilical hernia
A hernia in the abdominal area is difficult to miss. But in each patient the disease progresses differently: in some the hernial protrusion is large and interferes with normal life, in others the symptoms are mild.
But so that you can recognize a hernia in the first stages, we suggest familiarizing yourself with a set of characteristic symptoms:
- When standing, a round or oval protrusion appears in the abdominal area, which can increase with physical activity, coughing and after eating.
- The skin in the area of the protrusion stretches and becomes thinner. In later stages, a person can feel the intestine through the protrusion.
- It is worth paying attention to constipation, a feeling of nausea and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. This may indicate the beginning of the adhesive process and the worsening of the disease.
- Another symptom is pain in the abdominal area after tension and sports activities.
- If the pain is constant, this indicates the beginning of an adhesive process or a strangulated hernia. This symptom requires immediate medical attention!
Causes of hernia
Among the reasons, there are 6 most common ones:
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure after injury, lung disease and other pathologies.
- Increased pressure on the abdominal wall during pregnancy. Occurs with a large fetus, multiple pregnancies, or due to a large amount of amniotic fluid.
- Lack of physical activity, weak abdominal muscles.
- Stretching of the umbilical ring due to sudden weight gain or weight loss.
- Unsuccessfully performed operations or incorrectly carried out stage of rehabilitation after operations on the intestines, gall bladder or stomach.
- Regular constipation.
In rare cases, congenital weakness of connective tissue or a disorder of collagen metabolism occurs. But this must be taken into account in the event of an umbilical hernia and undergo a timely examination.
The disease and the intestinal surgery itself, which ended with an ostomy, are associated with the body losing a large amount of energy, vitamins, protein and minerals. All this can be manifested by a decrease in body weight, fatigue, weakness, a feeling of depression or irritability. Nutrition is a complex process of intake, digestion, absorption and assimilation in the body of food necessary for the construction and renewal of cells and tissues of the body, covering energy costs, and regulating body functions. Proper nutrition in the presence of a stoma, although it does not solve all problems, is a necessary condition for leading a full life. Rational nutrition is physiologically adequate nutrition for a person, taking into account his gender, age, nature of work, and climatic conditions.
The three main principles of rational nutrition are:
• balance between the energy supplied by food and the energy consumed by a person in the process of life; • satisfying the body's needs for a certain quantity, qualitative composition and ratio of nutrients; • adherence to diet. A balanced diet helps maintain health, resistance to harmful environmental factors, high mental and physical performance, and active longevity. To restore impaired intestinal function, you need to eat, observing four basic principles - regularity, caution, gradualness, moderation. Regularity is a very important principle, since it allows the body to establish the production and release of digestive juices at the same time, and therefore improve the process of digestion and absorption of nutrients and the release of the body from undigested foods. The more regularly you eat, the more regularly your intestines work. Disorderly eating will lead to the same disorderly operation of the stoma. Develop a diet for yourself and strictly follow it. Even if you don't have an appetite, try to eat something during the allotted hours. People who have a colostomy and eat regularly can achieve a bowel movement once a day, at the same time. Caution is a principle regarding the foods you eat after surgery. During the formation of postoperative scars (30–40 days), it is necessary to completely exclude the following products that cause gas formation: black bread, cabbage of any kind, eggs in any form, garlic and onions, spices and seasonings, grapes, mineral water with gases. You should be very careful with pickled, fatty and heavy foods. Gradualization is the principle of gradually introducing new foods into the diet so as not to cause an unpleasant reaction from the stomach and intestines. It is best to first keep a food log, which will allow you to accurately determine within a few weeks which foods and in what quantities are more acceptable, and which need to be eliminated. In the diary you need to record what foods you eat, their quantity and time of intake, time of bowel movement, consistency of discharge, smell and amount of gases (according to subjective sensations) through the stoma. Be sure to note the appearance of pain and the amount of urine. Moderation is good in everything, including food. Food should be consumed more often, but in small portions, up to 5–8 times a day. Food should be attractive and tasty. There are no products in nature that contain all the components necessary for humans. Only eating a wide variety of foods best provides the body with all nutrients. For normal functioning, the body requires a certain ratio of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and minerals. You can eat and drink the same things you ate and drank before surgery. There is no need to follow a special diet. It is enough to eat balanced food at regular intervals and chew it slowly and thoroughly.
It is useful to know the following:
• eggs, cabbage, onions, legumes, chocolate, beer and carbonated drinks, root vegetables, mushrooms increase gas formation; • eggs, fish, onions, peppers, garlic, spices, and some types of cheese enhance the smell of feces; • spinach, green salad, parsley, lingonberries, yogurt reduce the smell of feces. Diarrhea and constipation can happen to anyone, but you should be especially careful as these conditions can cause serious problems and pain. The causes of diarrhea or constipation are varied: from mild dietary errors to severe infectious diseases. In mild cases of diarrhea (diarrhea), it is recommended to take activated carbon and bismuth preparations; often a positive effect is achieved by crushing eggshells into powder. If diarrhea occurs due to errors in the diet, after taking an excessive amount of fresh vegetables, fruits or overeating, then boiled rice or rice water, white crackers, jelly, hard cheese, mashed potatoes, and bananas will help to fix the stool. If you have an ileostomy, diarrhea caused by poor functioning of the ileostomy or intestinal infection is dangerous, as there is a risk of loss of water and electrolytes. In this case, you need to consult a doctor. With diarrhea, it is necessary to constantly restore the level of fluid and salts in the body. To do this, add 1 teaspoon of salt and 8 teaspoons of sugar to 1 liter of boiled water. The mixture should be taken 0.5 cups every 15 minutes for 2 hours. This solution not only quenches thirst well, but also very quickly restores the required level of salts, thereby maintaining the normal functioning of the body. It is recommended to start eating food 24 hours after diarrhea stops, in small portions, up to 5-7 times a day. In case of persistent diarrhea, you should consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Constipation is also a serious obstacle to the normal functioning of the stoma. You should be careful when taking laxatives, as there are different reasons for constipation, including intestinal diseases. Before taking measures to eliminate this phenomenon, it is advisable to consult a doctor. If you suffer from constipation, then you can increase the amount of liquid consumed, meat broth, vegetables, salad, fresh and dry fruits, fruit juices, wholemeal bread, coffee. Spicy foods are acceptable, as well as the introduction of food additives into the diet. Plant fiber acts like a brush on our intestines; it can not only cleanse the body of toxins, but also neutralize toxic substances. One of the causes of constipation is intestinal spasm, which can occur when eating too hot food, smoking, stress, nervous fatigue, irregular eating, especially when you take a long break between meals or are fasting. Constipation is also caused by a sedentary lifestyle, a limited amount of fluid (less than 1.5 liters per day), as well as certain medications (painkillers, antidepressants, etc.).
A few simple rules will help you balance your diet:
• among cereals and legumes, preference should be given to those that contain more proteins, and with a higher proportion of essential amino acids in them. These are millet, oatmeal and pearl barley, beans, peas, lentils; • For vegetables, it is better to use white cabbage, beets and carrots, apples, hazelnuts, currants, and mushrooms. As you can see, these products have always been eaten in Russia, which once again confirms the wisdom of folk nutrition. The patient with an ostomy knows that the nature of the diet has a decisive influence on the frequency of stool. Fasting or restricting the amount of food you eat leads to excessive gas, diarrhea, or constipation. In principle, there are no special diets for patients with ileostomy or colostomy. The diet must be selected individually. For patients with a colostomy, the ideal is to return after surgery to their usual diet and diet with established regular bowel movements. Preventing constipation is important for colostomy patients. You should give preference to wheat and rye bread, bread made from wholemeal flour, soups with rich meat broth with plenty of coarsely chopped vegetables (beets, cabbage, legumes), dishes made from lean meat, fish, poultry, mushrooms, fresh vegetables and fruits in natural form or weakly boiled, milk (if tolerated) and a variety of dairy products, weak tea or coffee with milk, chilled juices and mineral water. Salt is added to taste. The volume of fluid consumed is at least 1.5 liters per day. It is recommended to eat food at least 3-5 times a day, at the same time. To regulate bowel movements, as prescribed by your doctor, you can use some medications that affect intestinal function. For constipation, laxatives may be used.
— V.G. Sukhanov, President of the Regional Public Organization of Disabled Ostomy Patients “ASTOM”, based on materials from the magazine “Together Against Cancer”
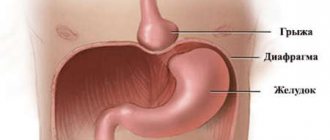
Treatment: remove or not remove
The first thing a patient with a hernia should know is that any decision about treatment or removal is discussed with a doctor. Making such decisions on your own without a full diagnosis is risky.
Conservative treatment of a hernia is possible only in childhood, when the process of formation and growth of the abdominal muscles occurs. In adults, the only possible treatment is surgical removal of the umbilical hernia. The earlier the operation is performed, the lower the risk of complications and the higher the likelihood of quick rehabilitation without consequences for the patient.
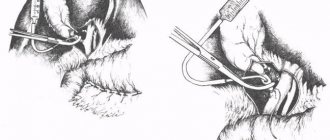
The operation to remove an umbilical hernia is called hernioplasty. The procedure is most often performed under anesthesia using laparoscopes. In the process, the surgeon uses one of the most suitable methods - suturing the umbilical ring or installing a mesh implant, which will hold the organs in the navel area and prevent the possibility of recurrence of a hernia.
Postoperative period
The main rehabilitation period lasts about 2 weeks. You will be able to move immediately after the operation, but carefully, increasing the load during the entire recovery time. A special bandage will reduce pressure on the stitches and speed up healing.
After 2 weeks, you will be able to begin general strengthening training without overexertion and heavy lifting. Patients are further advised to maintain high abdominal muscle tone and maintain sufficient physical activity.
Don't expect complications! Get examined as soon as possible and solve the problem of umbilical hernia in a medical clinic with qualified surgeons.
Cocktail for health
Cocktail for health
Recovery from any illness is a long process.
Nutrition after surgery, injury, or during stress should be complete and balanced, since the body at this time especially needs high-quality protein, essential food components: vitamins, microelements, omega fatty acids and much more. How can you enrich your diet so that your body receives the right amount of vitamins and microelements? How to balance nutrition even after intestinal surgery, with gastrointestinal diseases and digestive problems? The solution can be very simple - Specialized nutrition that is not only tasty, but also healthy.
The Nutricia group of companies produces a ready-to-use product called Nutridrink Compact (drink). Nutridrink Compact is available in various flavors: coffee, strawberry, vanilla. Each package contains:
- High-quality, easily digestible and well-absorbed milk protein, which is the main building material for all cells and tissues (12 g per 200 ml).
- It has a ratio of polyunsaturated fatty acids ω6:ω3 = 4:1, which provides the greatest anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating effect.
- Carbohydrates provide a feeling of satiety with food and provide energy for all processes that occur in the body.
- All vitamins necessary for the body (including: A, group B, D3, E, C) and minerals (potassium, sodium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, etc.).
- A complex of carotenoids that have a powerful antioxidant effect and are natural immune stimulants.
Restoring and maintaining physical activity, stimulating the immune system and reducing the risk of infections are the results of using Nutridrink Compact. The combination of tasty, ready-to-use, balanced medicinal products will allow you to diversify your diet, improve treatment results, and also improve the quality of life.
Nutridrink Compact is intended for adults and children over 3 years of age.
Nutridrink Compact – a taste of active life!
Before use, consult a specialist. Contraindicated for galactosemia, allergy to cow's milk proteins, individual intolerance to the components of the mixture
Nutridrink Compact - tasty and healthy nutrition for children and adults to maintain and restore the body during and after illness
| The nutritional value | Unit | Per 100 ml | For 125 ml |
| Energy value | kJ | 1010 | 1262,5 |
| kcal | 240 | 300 | |
| Protein (16% energy) | G | 14,4 | 18 |
| Fats | G | 9,4 | 11,75 |
| Saturated | G | 0,9 | 1,125 |
| Monounsaturated | G | 5,7 | 7,125 |
| Polyunsaturated | G | 2,8 | 3,5 |
| Carbohydrates | G | 24,4 | 30,5 |
| Sahara | G | 13,3 | 16,625 |
| Polysaccharides | G | 11,0 | 13,75 |
| Alimentary fiber | none | none | |
| Osmolarity | mOsm/l | 570 | 570 |
MINERALS
| The nutritional value | Unit measured | Per 100 ml | For 125 ml |
| Sodium (Na) | mg | 40 | 50 |
| Potassium (K) | mg | 105 | 131,25 |
| Chlorides (Cl) | mg | 60 | 75 |
| Calcium (Ca) | mg | 350 | 437,5 |
| Phosphorus (P) | mg | 300 | 375 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | mg | 55 | 68,75 |
| Iron (Fe) | mg | 2,1 | 2,625 |
| Zinc (Zn) | mg | 2,4 | 3 |
| Copper (Cu) | mcg | 350 | 437,5 |
| Manganese (Mn) | mg | 0,63 | 0,7875 |
| Fluorine (F) | mg | 0,19 | 0,2375 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | mcg | 20 | 25 |
| Selenium (Se) | mcg | 14 | 17,5 |
| Chromium (Cr) | mcg | 13 | 16,25 |
| Iodine (I) | mcg | 46 | 57,5 |
VITAMINS
| The nutritional value | Unit measured | Per 100 ml | For 125 ml |
| Carotenoids | none | none | |
| Vitamin A | μg-RE | 260 | 325 |
| Vitamin D3 | mcg | 2,1 | 2,625 |
| Vitamin E | mg-a TE | 3,7 | 4,625 |
| Vitamin K | mcg | 16 | 20 |
| Thiamine (B1) | mg | 0,45 | 0,5625 |
| Riboflavin (B2) | mg | 0,50 | 0,625 |
| Niacin | mg | 3,6 | 4,5 |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) | mg | 1,6 | 2 |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | mg | 0,53 | 0,6625 |
| Folic acid | mcg | 80 | 100 |
| Cyanocobalamin (B12) | mcg | 1,1 | 1,375 |
| Biotin | mcg | 12 | 15 |
| Vitamin C | mg | 30 | 37,5 |
| Kholin | mg | 110 | 137,5 |