Detection of blood after defecation is an abnormal phenomenon for a healthy body. Therefore, if such a picture is observed, you need to be wary of it. Some people put off visiting a doctor, explaining this for many reasons: they don’t have enough time, work doesn’t allow it, and simple embarrassment plays a role. However, the disease will not go away, it will progress, and after regular visits to the toilet, the person again and again notices traces of blood after bowel movement. In this case, he may not experience any discomfort or pain at all.
Blood drops
When faced with bleeding after stool, people wonder which doctor should they contact? In this case, if the patient is sure that blood was discharged from the anus, then he needs to go to a proctologist to examine the condition of the rectum. It is also worth visiting a gastroenterologist to determine the exact cause of bleeding and take stool tests. All this will help you find out the diagnosis and stage of the disease.
Causes of bleeding from the anus
If you notice blood on toilet paper after bowel movements, even if the process of bowel movement occurs without pain, you should definitely consult a proctologist for advice in order to establish the cause of the bleeding, start treatment in a timely manner and avoid possible complications.
Why does blood appear from the anus after stool in both men and women:
- A fairly common factor is hemorrhoids (enlargement of the veins of the rectum). Scarlet blood appears from the anus during defecation.
- Anal fissure is the second most common cause of rectal bleeding. The disease is characterized by a burning sensation during bowel movements, sometimes accompanied by acute pain (patients describe it as cutting and then squeezing). Bloody discharge appears in both small and copious portions.
- Inflammatory diseases of the colon.
- The presence of benign formations (polyps). A characteristic symptom is the discharge of blood from the rectum after defecation. The blood is darker, often with mucus.
- The presence of a malignant tumor of the rectum. Blood of different colors may be released. Quite often, the blood released does not differ in any way from the blood that is released, for example, from hemorrhoidal tissue. And if the presence of hemorrhoidal disease only worsens the quality of life (hemorrhoidal tissue never degenerates into a malignant tumor), then the presence of a benign formation or a malignant tumor can be harmful to health and life-threatening, which is why you should not try to independently determine the source.
Only a coloproctologist can determine the true cause of bleeding from the anus and select the appropriate treatment. Timely diagnosis allows for effective conservative and minimally invasive treatment.
Causes of bleeding
Rectal bleeding cannot be considered a frivolous phenomenon, since they are sometimes caused by extremely dangerous pathological conditions. If such a problem arises, you must immediately contact a proctologist. The most common pathological conditions that explain the appearance of blood from the anus are:
- hemorrhoids
- they are characterized by bright scarlet blood, not mixed with feces, which appears after defecation; - anal fissures
are also accompanied by bloody discharge, and with cracks it bleeds a little at a time, there is a characteristic burning sensation, usually appears after stool; - proctitis
, characterized by inflammatory lesions of the rectal mucous membranes, is accompanied by bloody rectal discharge mixed with mucus; - constipation
can also provoke the appearance of blood, since in the rectal area there is too extensive a vascular network, which is injured when passing hard feces, which brings pain to patients; - colitis, gastritis, polyps and ulcerative lesions, diverticula in the gastrointestinal tract
- all these diseases can manifest as anal bleeding; - varicose veins of the esophagus
, various kinds of systemic pathologies can also be characterized by the release of blood from the anus; - intestinal cancer
, in which bleeding is profuse or mild, depending on the stage of the lesion and the degree of malignancy.
Sometimes scarlet blood appears under the influence of components of medications such as potassium-containing medications or antibiotics.
Haemorrhoids
With the development of inflammatory lesions of hemorrhoids, traces of blood may appear during or after the bowel movement. Scarlet stains will clearly appear on paper or linen. Blood clots may also appear in stool.
A characteristic sign of the hemorrhoidal process is the scarlet tint of the blood and the presence of red nodular bumps that are prone to prolapse. Usually, increased physical stress leads to severe bleeding from hemorrhoids.
Cracks
Another common cause of anal bleeding is fissures in the anus. This problem is more typical for people suffering from chronic or frequent constipation. Excessively hard feces during constipation injure the anus, causing the formation of cracks. In such a case, traces of blood appear only after defecation, and characteristic itching is often present.
Blood from the anus in men who lead a sedentary lifestyle most often appears precisely because of fissures or hemorrhoids. With each subsequent trip to the toilet, the pain only intensifies, which creates a fear in patients of bowel movements, provoking the occurrence of psychological constipation. If a fissure in the anus bleeds, it must be treated, otherwise complications may arise. The main signs of anal fissures are severe pain during bowel movements and red bloody drops in the stool.
Diverticulosis
When the intestinal mucosa protrudes through the outer wall, diverticulosis is diagnosed. The beginning of the pathology is manifested by symptoms:
- the stomach begins to ache, the pain syndrome is localized mainly on the left side in the lower part of the peritoneum;
- blood is released from the anus;
- Sometimes patients are concerned about hyperthermia.
Diverticulosis is complicated by bleeding, intestinal invasion or the development of peritonitis. To prevent the occurrence of new diverticula, defecation processes should be established.
Polyps in the intestines
Sometimes benign growths called polyps form in the intestines. They can be located on a stem or on a wide base. For a long time, polypous formations may not reveal themselves.
Over time, diarrhea or constipation begins to appear due to impaired intestinal motility. A feature of this disease is the danger of degeneration of polypous formations into malignant tumors. The surface of these growths may bleed due to injury, and the larger the polyp, the higher the risk of injury.
Crohn's disease
This disease is characterized by damage to the intestinal walls by ulcerative formations, which occurs against the background of autoimmune intraorganic processes. Due to ulcerative defects, bleeding develops, severe pain in the abdominal area occurs, hyperthermic reactions may occur, and appetite is disturbed.
Stool in nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's pathology may have the character of melena, when the stool becomes black due to the presence of coagulated and partially digested blood in it. The stool may contain heavy bloody impurities, indicating severe bleeding.
Intestinal infections and parasitic infestations
With acute infectious lesions of the intestines, patients may experience pronounced anal bleeding, which occurs with hyperthermic reactions, nausea and vomiting, and severe diarrhea. Patients complain of abdominal pain, and during bowel movements they are bothered by a strong burning sensation in the anus, which occurs due to irritation caused by diarrhea. Most often, such bleeding is typical for a child, because it is pediatric patients who are usually worried about such infections.
Rectal bleeding occurs due to infections caused by:
- enterovirus or rotavirus;
- salmonellosis or typhoid fever;
- dysentery or hemorrhagic fever.
Parasitic infestations are also the cause of rectal bleeding. Such lesions do not cause heavy bleeding, but still, when parasites damage the mucous membranes, blood penetrates into the stool, but it can only be detected in the laboratory. In very rare cases, with advanced parasitic infestations, blood clots may appear.
Tumors in the gastrointestinal tract
The most dangerous factor in which blood is released from the anus is intestinal cancer. Colon or small bowel malignancies are considered extremely common in medical practice. Rectal bleeding is considered a characteristic manifestation of malignant formations of such localization.
The appearance of blood in the stool during colon cancer is usually due to damage to the walls by the breakdown of tumor tissue. In this case, the bloody masses are mixed with feces and may contain pus and mucous impurities, indicating the presence of concomitant colitis. If oncology has formed in the rectum, then blood in the stool will be present in almost all patients and can be considered as the first sign of pathology.
In intestinal cancer, blood is released even before defecation or during intestinal bowel movement, which distinguishes cancer from hemorrhoidal processes. If the patient already has diagnosed hemorrhoids or a chronic anorectal fissure, then it is worth paying closer attention to the nature of the bleeding so as not to miss the moment of their change and the onset of the tumor process.
Risk factors for anal bleeding
In addition to the reasons described above, experts also highlight a list of risk factors that cause rectal bleeding. These factors include:
- digestive disorders and functional disorders, dyspeptic intestinal processes, diarrhea and constipation, in which the load on the intestinal vessels increases;
- inactivity, sedentary activity, which provokes congestive pelvic phenomena;
- increased physical stress, which increases venous pressure in the pelvic area;
- inflammatory lesions of the abdominal and pelvic organs such as hepatitis, prostatitis or endometritis, etc.;
- genetic and hereditary predisposition;
- alcohol abuse;
- unhealthy approach to nutrition, obesity or simply being overweight;
- period of pregnancy or childbirth, multiple births or large fetus size.
All these factors sometimes involuntarily provoke the appearance of bloody discharge from the anus.
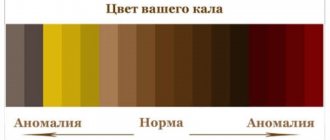
Discharge color and disease
- bright red, scarlet blood from the anus on toilet paper or underwear, drops at the end of a bowel movement (stool) - hemorrhoids or anal fissure;
- red color of blood during anal bleeding - cancerous tumor, intestinal polyp;
- dark blood clots - tumors of the distal colon, diverticulosis;
- cherry-colored blood from the anus - pathology of the colon;
- black, tarry stools - diseases of the stomach, duodenum and small intestine.
IMPORTANT!
Bleeding is a serious symptom, after the appearance of which you cannot postpone a visit to the doctor. Unfortunately, blood from the anus can cause diseases such as a tumor of the rectum or colon. And in the worst case, this tumor may turn out to be malignant. Blood can also occur as a result of injury to a polyp - a benign tumor. Long-term polyposis can be a sign of colon cancer.
Anal bleeding in pregnant women
The appearance of blood from the anus in women often occurs during pregnancy. Usually, bleeding is observed during defecation, although in some patients the anus bleeds constantly.
Due to the circumstances, it is extremely important to make sure that the bleeding is of anorectal origin and not vaginal. Usually, the causes of rectal bleeding in pregnant women are the same as in other patients, the only difference is that pregnancy itself is considered a provoking factor for anorectal bleeding.
Against this background, many patients, from about the middle of pregnancy to the very birth, experience problems with hemorrhoids and bowel movements, since during this period the uterus begins to enlarge, compresses the intestines, causing constipation, varicose anal veins and other troubles. The difficulty is that it is difficult for pregnant women to treat such pathologies, because the therapy must not only be effective, but also safe for the child.
Bleeding pattern and disease
- Regular heavy bleeding not associated with bowel movements - diverticulosis, polyposis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rectal or colon cancer;
- Blood mixed with feces - cancer of the rectum and colon;
- Bleeding with diarrhea - dysbiosis, irritable bowel syndrome;
- Discharge of blood with mucus or pus - internal hemorrhoids, rectal prolapse or polyp;
- Severe bleeding with mucus - proctitis, colitis, rectal cancer.
Make an appointment
What does the color of the secreted blood indicate?
A certain pattern can be observed - the brighter the color of the blood from the anus, the closer to the anus the source of the disease is located. Bacteria can turn stool dark. Thus, during diseases of the digestive tract, microbes have time to have their effect and the output will be a dark burgundy color of the blood. With intestinal diseases, bright scarlet blood is usually observed, since the source of the disease is nearby, and the shade does not have time to change.
Shades of blood
Characteristic types of discharge:
- Thick, dark blood or blood clots may indicate a worsening stomach ulcer. Blood sometimes appears after drinking large amounts of alcohol or with advanced alcoholism. Bloody clots indicate serious bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, and a dark color indicates that the focus of the pathology is located above the rectum. In conditions of such symptoms, it is important to conduct an examination to clarify and eliminate the factors that caused the bleeding,
- Small red stripes after wiping with a napkin and itching in the anus indicate a high probability of worms in the intestines in men and women. To make a diagnosis, you need to be tested for helminths. After fighting the parasites, the patient is prescribed a diet that prevents the development of hemorrhoids in areas of inflammation,
- Small drops of fresh blood on a napkin are a characteristic symptom of postpartum hemorrhoids. Such hemorrhoids are acute in nature, but they are quickly treated,
- If women notice blood when wiping, this may be a sign of gynecological problems, especially if the spot is shapeless and dimly colored. Such “daub” may indicate polyps.
Important! If a pregnant woman discovers bleeding from her anus, she should immediately begin to stop the bleeding and seek medical help. This condition is fraught with serious complications. Pregnancy is not the time when you need to do home self-treatment or experiment with traditional methods. If the blood flow becomes profuse, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Diagnosis and treatment
When faced with an intimate problem, especially such as bleeding from the anus during bowel movements, you can get confused, especially if you don’t know about the methods of diagnosing and treating such ailments or don’t understand which doctor to contact.
A proctologist or coloproctologist is a doctor who diagnoses and treats diseases of the colon, rectum and anus, as well as problems of the sacrum, coccyx and perineum. You should not postpone a visit to this specialist if there is blood from the anus after stool.
A proctologist will listen to complaints and the history of their occurrence, and to determine the cause of the appearance of blood from the rectum, he may perform the following procedures:
Digital examination of the rectum: a primary research method that makes it possible to assess the condition of the anus and identify possible pathologies in the form of neoplasms, anal fissures, uncharacteristic discharge, and bleeding.
After a digital examination, the coloproctologist, if necessary, prescribes further diagnostic methods using special equipment:
- Anoscopy. This is an examination of the last 3-7 cm of the rectum; it is in this area that almost half of the sources of visible bleeding are located. There are several types of anoscopes (straight, conical, with and without a cutout, transparent and not transparent), each of them is used strictly according to indications, but any of these types allows you to perform a full examination of the anal canal and lower ampullary rectum. Anoscopy is used when performing minimally invasive methods of treating hemorrhoids (ligation, sclerotherapy), as well as performing a number of surgical interventions (bipolar coagulation). As a rule, no preparation is required to perform diagnostic anoscopy; preparation is required for anoscopy for therapeutic purposes.
- Sigmoidoscopy or rectoscopy (RRS or RRS) is a diagnostic procedure using a special device with a camera. It makes it possible at the initial appointment to quickly and painlessly visually assess the condition of the rectal mucosa, identify the presence of mucosal formations and compression of the intestine. During rectoscopy, up to 20 cm of the intestine is examined (the entire rectum and the place of its transition to the sigmoid). Preparation is required for rectoscopy.
- Colonoscopy is the most informative method of examining the large intestine compared to others. It is carried out using a flexible fiber colonoscope equipped with a high-resolution camera that will show even the smallest sources of bleeding. The procedure is also prescribed for the purpose of endoscopic removal of colon formations. A colonoscopy is performed by an endoscopist.
The appropriate method of treating the disease is determined and prescribed by the doctor. You should not engage in self-treatment and neglect contacting a coloproctologist.
When is it time to sound the alarm?
Imprints and drops of blood on paper after bowel movement can be an independent symptom of the disease. Sometimes before their appearance, people suffer from bowel problems, such as diarrhea or prolonged constipation with hard stool.
In many cases, bleeding from the intestines is a sign of hemorrhoids. Patients with this disease find red-brown marks on their underwear after severe physical exertion or bowel movements. Bleeding is often observed in women during pregnancy. This is due to the heavy load on the pelvic internal vessels, since the child in the womb puts pressure on them. But this phenomenon is not considered normal, so a woman should definitely tell her doctor about the blood.
Before visiting a proctologist for research, you need to carefully look at the color of the discharge, track the time of its appearance, as well as the events preceding it. In some cases, girls confuse traces of blood from the anus with vaginal discharge, which may be caused by endometriosis. In any case, both the first and second phenomena become a reason for examination.
Intestinal problems
How to prepare for the examination?
The own research of specialists from the proctology department of the Altermed clinic made it possible to make a visit to a proctologist as easy and comfortable as possible. There is no longer any need to fast the day before and plan the procedure for the morning. In the proctology departments of Altermed, a way has been found to successfully cope with all these difficulties. This is Microlax bowel preparation.
The use of Microlax microenemas makes fasting unnecessary, does not require special equipment or premises, and saves a lot of time. The laxative effect occurs 5-15 minutes after administration of the drug. The quality of bowel cleansing is such that treatment can begin immediately after rectoscopy and anoscopy. If it is necessary to use during pregnancy and lactation, Microlax does not require special precautions.
The Proctology Clinic provides diagnostics using the most modern equipment. The best doctors in St. Petersburg - both men and women - and a delicate approach are at your service.
Other articles by the author
- Blood from the anus
- Prolapse of the rectum (rectal prolapse)
- Pain in the anus
- Anal fringes
- Treatment of anal fissure
Forecasts
With timely identification of the cause of bleeding and prompt treatment, selected taking into account the root cause of the pathology, the prognosis for recovery is the most favorable. As a rule, it is possible to achieve remission if the pathology is chronic in nature, or get rid of the disease completely if it is acute.
A unified therapeutic method for rectal bleeding has not been developed, since such a condition occurs for various reasons; the cause should be eliminated first, and then the symptom itself should be treated. Although blood from the anus is not always a serious symptom, such a phenomenon requires consultation with a proctologist.
Diagnostic features
Before prescribing therapy, the proctologist conducts a complete examination of the patient. Many diagnostic methods in proctology are unpleasant, but they are mandatory. The following procedures are usually performed:
- Irigoscopy,
- Colonoscopy,
- Laparoscopy,
- Gastroduodenoscopy,
- Rectoscopy,
- Stool tests.
Diagnostics