Live broadcasts on Instagram every Sunday at 12:00
Subscribe so you don't miss out! Subscribe
- home
- general surgery
- Cholelithiasis
- Laparoscopic surgery to remove the gallbladder
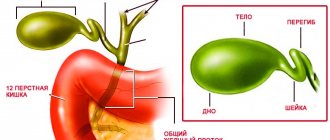
One of the most frequently performed operations in abdominal surgery is cholecystectomy—removal of the gallbladder. To date, such an intervention is the only way to safely treat gallstone disease. GSD is a disease of the biliary tract, in which stones (calculi) form in the gallbladder and ducts. Recently, the number of people suffering from cholelithiasis has been steadily growing; among older people, almost every third person has gallstones.
Different in shape and size, stones can be single, and their number can reach several dozen. But even the presence of one stone is accompanied by a health risk, including complications: block of the cystic duct and the development of acute cholecystitis, the development of obstructive jaundice or pancreatitis with obstruction of the outlet bile duct, rupture of the bladder, peritonitis, etc.
In what cases is the gallbladder removed?
Your doctor may refer you for gallbladder removal surgery if you:
- Choledocholithiasis is a form of gallstone disease in which stones form in the lumen of the common bile duct
- Bile duct blockage
- Acute cholecystitis - if the disease occurs against the background of an existing gallstone disease, the doctor may decide on urgent surgery
- Gallstone disease (GSD) with attacks of biliary colic or with the manifestation of “minor” symptoms of the disease: bitterness in the mouth, aching painful sensations in the hypochondrium on the right and a feeling of heaviness after eating in the same area
- Asymptomatic gallstone disease
- Gallbladder calcification
- Gallbladder polyps with cholelithiasis or at risk of developing a tumor
- Perforation of the gallbladder - this disease can be caused by malignant tumors, severe abdominal trauma and a number of systemic diseases
- Cholesterosis – deposition of cholesterol on the walls of the bladder due to cholelithiasis
- Development of secondary pancreatitis
These are the main problems for which the gallbladder is removed. The extent to which removal is necessary in your case will be determined by your attending physician based on the results of a thorough preliminary diagnosis and your general condition. It is important to know: if you do not perform the operation on time, sooner or later serious complications will arise that can cost you your life. Therefore, do not delay your visit to the doctor. Make an appointment and undergo preliminary diagnostics.
Is it necessary to remove the gallbladder?
Why is the gallbladder necessarily removed? Can't you just remove the stones or polyps?
These questions worry most patients. Alas, you cannot leave the gallbladder because:
- . Bile will interfere with the normal healing of the gallbladder wall after surgery.
- . Bile can enter the abdominal cavity and cause peritonitis.
- . Simply removing stones does not mean getting rid of cholelithiasis, since they form again.
- . Even with successful healing of the gallbladder wall, a scar will remain in which bile particles will crystallize and stones will form.
- . After surgery, adhesions often form that interfere with the normal release of bile, as a result of which it will stagnate, and this will sooner or later cause cholestasis.
Gallbladder removal surgery
With a traditional cholecystectomy, a fairly large incision of about 15-20 cm is made on the anterior abdominal wall, through which the gallbladder is removed.
Laparoscopy of the gallbladder has a number of advantages compared to traditional cholecystectomy:
- The gallbladder is removed through small, neat punctures instead of a large incision: after the operation you are left with almost imperceptible spots instead of an extensive scar
- You recover quickly: up to 2-3 days in hospital and up to 7 days outpatient
- Laparoscopy of the gallbladder occurs with virtually no blood loss
- The risk of complications after surgery (suppuration, formation of adhesions, etc.) is practically zero
- After surgery, you will need much less or no pain medication
Preparing for surgery
Preparation for surgery is the most important stage on which the success of the future operation largely depends. Preliminary diagnosis helps assess the general condition of your body, exclude infections, allergic reactions and other pathologies for which surgery is contraindicated.
These are the key tests and examinations you undergo before gallbladder removal:
- . General and biochemical blood and urine tests.
- . Tests for syphilis, hepatitis B and C.
- . Coagulogram.
- . Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
- . Ultrasound of the gallbladder, biliary tract and abdominal organs.
- . ECG.
- . X-ray of the lungs.
- . Fibrogastroscopy or colonoscopy – if necessary.
If necessary, other specialists are also involved for a comprehensive diagnosis - gastroenterologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, allergist. This approach helps to understand your condition in detail, select anesthesia and properly monitor the body’s functioning during surgery.
How to prepare your bowels?
3 days before gallbladder laparoscopy, exclude bread, vegetables, and fruits. To cleanse the intestines, on the eve of the operation it is necessary to give an enema (about 1.5 liters of liquid) or take the drug Microlax. The evening before surgery, you can eat a light dinner, for example, porridge or dairy products - cottage cheese, yogurt or kefir. Important: Do not eat or drink for 8 hours before surgery.
How is the gallbladder removed?
Laparoscopy of the gallbladder is performed under general anesthesia and takes from 20 minutes to 1.5 hours:
- The doctor makes several small punctures in the abdominal wall and inserts instruments through them - trocars, an endoscope and special manipulators
- Gas is injected into the abdomen, which improves visibility
- The doctor clamps the cystic duct and artery with a special tool and cuts them off
- After this, the doctor removes the gallbladder from the abdominal cavity, removes the instruments and sutures the holes.
Sometimes a drainage (a thin tube to drain fluid) is installed in the wound, which is removed the next day if there is no discharge. After removal of the gallbladder, you are transferred to the recovery room, where you are under the supervision of specialists for 1 to 3 days.
Rehabilitation
The patient spends the first postoperative hours in intensive care, then he is transferred to the ward. After a few hours you can get up. The drainage is removed the next day. Recovery takes place within a month after surgery:
- You need to follow a daily routine;
- Take prescribed medications.
- Gradually introduce physical activity.
The need to follow a diet exists only in the first months after surgery, while the body adapts to new conditions. Within six months the restrictions will be lifted.
Speaking about the results of laparotomy cholecystectomy, it is worth noting that the operation is considered the standard treatment method. The main advantage is rapid recovery. The technique is safe, the frequency of conversions to open surgery is minimal.
Possible complications after surgery
In most cases, there are no complications after laparoscopy of the gallbladder, since there are no large incisions, stitches, and blood loss during the operation is minimal. But, like any surgical intervention in our body, this operation can cause a number of rare complications, including:
- Supuration of sutures
- Bleeding in the abdomen
- Leakage of bile
- Formation of adhesions
- Bile duct injuries during surgery
- Allergic reactions
- Thromboembolic consequences
- Exacerbation of another chronic disease
These complications are extremely rare. As a rule, this occurs in elderly people, or when there is severe concomitant pathology or severe damage to the biliary tract. If you feel unwell after surgery, tell your doctor immediately, who will help prevent further complications.
Do stones form after gallbladder removal?
Surgery to remove the gallbladder does not change the composition of bile. Hepatocytes continue to create abnormal bile, which can cause stones to form again. That is why, even after surgery to remove the gallbladder, you need to regularly undergo bile composition testing.
Types of cholecystectomy
If therapeutic treatment of gallstones does not bring results or there are clear indications for surgical intervention, doctors at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow will give recommendations on the choice of surgical method. This can be a classic open cholecystectomy, endoscopic gallbladder surgery, or surgery through a mini-access.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is an intervention that is characterized by low surgical trauma, fast and fairly easy recovery. Instruments and a video camera are inserted through punctures in the abdominal wall. As a result of air injection, visibility is provided for carrying out the necessary operations. In some cases, upon completion of the operation, the doctor ensures drainage of fluid from the subhepatic space. After 2-3 days, the patient leaves the department on his own and recovers at home.
- Operation from a mini access (3-7 cm incision) - the objective desire of most patients is to undergo laparoscopic cholecystectomy of the gallbladder. However, this type of surgical treatment is not suitable for all clinical cases. In order to reduce the degree of trauma during gallbladder removal, a decision may be made to perform the operation from a mini-access under the right costal arch - this is a compromise option between traditional abdominal surgery and laparoscopic surgery.
If you are indicated for a planned operation (laparoscopic cholecystectomy), contact the specialists of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. In a modern hospital, we carry out any operations to remove the gall bladder at a high level - single-port, retrograde (from the neck), antegrade (from the fundus). You can find out the cost of the operation in the price list on the clinic’s website. However, it is better to obtain all information about the assessment and recommendations for the type directly at the consultation of specialists from the Central Clinical Hospital.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive operation to remove the gallbladder using laparoscopic technology through a centimeter incision. Today this is the only method of planned treatment of chronic cholecystitis.
The operation is considered the most frequently performed of all those performed on internal organs.
Rehabilitation after gallbladder removal
4-6 hours after gallbladder removal, you can eat light food, drink water, get out of bed and walk. The main thing is to do this carefully, as after anesthesia you may feel weak and dizzy. Pain after surgery is minimal and does not require large amounts of analgesics. And many people do not need painkillers at all. You will be discharged in 1-4 days. And in 15-20 days you will be able to return to work. Limit physical activity: do not lift more than 2-3 kg and do not do exercises that involve the abdominal muscles. Please note: proper nutrition after gallbladder removal is one of the most important factors in recovery.
Reviews
Almost all reviews from our patients are positive - the operation is considered effective, fast and low-traumatic. Unpleasant points that patients pay attention to:
- Abdominal pain due to bloating;
- Difficulty breathing because the lungs have been compressed;
- You have to fast at first.
All these sensations pass quickly. Operated patients agree that these symptoms can be tolerated; they are incomparable to the benefits of surgery.
Nutrition after gallbladder removal
Without a gallbladder, bile constantly flows into the intestines from the liver. Proper nutrition will reduce its toxicity and help protect the intestinal mucosa. For the first month after surgery, eat 5-6 times a day, but not much, and drink up to 1.5 liters of water per day. During this period, you can eat white bread, boiled meat and fish, porridge, jelly, fermented milk products, stewed or steamed vegetables. Take your time and chew your food thoroughly: this will help activate the necessary enzymes and “turn on” the liver. Six months after surgery, you can gradually expand your diet. Eat berries, fruits and vegetables, except onions, garlic, radishes and lemons. You can eat honey and dried fruits. Alcohol, sweets, pickles, fatty and fried foods will have to be limited forever. Fermented milk products with live bifidobacteria, which improve intestinal microflora, will also be beneficial for you. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe choleretic herbs and medications with the necessary enzymes.
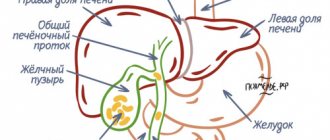
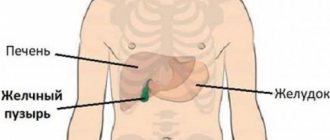
Functions of the gallbladder. Norm and pathology.
A healthy gallbladder plays an important role in the digestive process. When food enters the duodenum from the stomach, the gallbladder contracts and bile flows from it through the common bile duct into the small intestine. Mixed with food, it promotes the digestion process and also removes certain products from the body (mainly hemoglobin and excess cholesterol).
A pathologically altered gallbladder, in addition to disrupting its main function of participating in digestion, causes pain, becomes a reservoir of chronic infection, and leads to dysfunction of both the biliary (bile) system and the functioning of the pancreas.
Drug treatment and gymnastics
After removal of the gallbladder, it is vital to restore normal functioning of the body and adapt all systems. To do this, the doctor will select individual drug therapy for you, consisting of choleretic and enzyme drugs, as well as drugs that restore intestinal microflora. Several months after surgery, physical activity is necessary. Several months after surgery, physical activity is necessary. Take half-hour walks every day and do gymnastics in the morning. This will help saturate the body with oxygen and activate the abdominal organs.
Removal of the gallbladder in the Stolitsa network of clinics means:
High tech
To effectively carry out low-traumatic operations to remove the gallbladder, we use modern premium PENTAX video equipment. Thanks to a powerful optical system, it allows the doctor to examine the condition of the gallbladder in detail and safely remove it.
Professionally
The experience and professionalism of the doctor is the key to a successful operation. After all, without a highly qualified specialist, even the most premium equipment is just devices. Only an experienced doctor can perform laparoscopic surgery professionally and safely for your health. Over the years of successful practice, our specialists have performed a huge number of laparoscopic operations to remove the gallbladder and have restored health to hundreds of people. By contacting us, you can be sure that our specialists will thoroughly understand your situation: they will conduct a detailed preliminary diagnosis and determine exactly how necessary it is to remove the gallbladder. Before the operation, we enter into a formal contract with you. You receive all the necessary documents. The contract price includes payment for the operation itself, the cost of anesthesia and postoperative observation in the clinic. After the operation, you will receive a sick leave certificate from the first day of hospitalization, which you can extend if necessary either in our clinic or at your local clinic. After discharge, you receive a discharge summary with a protocol of the operation and detailed recommendations from the doctor for treatment during the rehabilitation period.
Comfortable
In our cozy rooms you will feel comfortable, because they have everything you need: a button to call a nurse at any time of the day, a separate bathroom, air conditioning, refrigerator, TV, microwave and Wi-Fi. After the operation, your condition will be continuously monitored by our specialists. Good nutrition and rehabilitation procedures will help you quickly regain strength after surgery and return to a full life. Get your health back. Make an appointment now.
Types of operations using laparoscopy
- One of the unique techniques is the NOTES technology - removal of stones transvaginally, without incisions in the abdominal wall. For access, the posterior vaginal vault is used, where an incision about 1 cm long is made. During transvaginal laparoscopic surgery to remove the gallbladder, after introducing instruments and optics into the intervention area through an incision on the vaginal vault, cholecystectomy is performed in a standard way. After removing the bladder through the same access using a plastic container, a single suture is placed on the incision, which resolves after 3-4 weeks. Among the advantages of this technique: painlessness in the postoperative period;
- hospitalization takes one day;
- after the operation, the patient’s activity is not limited;
- excellent cosmetic result.
The only restriction is the exclusion of sexual relations in the first month after the operation. However, the intervention does not affect sexual function, since the reproductive organs are not affected. But it should be noted that this technique is not recommended for patients who have a history of multiple surgeries on the pelvic organs.
However, there are contraindications for performing surgery using this technology:
- acute cholecystitis;
the presence of pronounced adhesions in the area of the neck of the gallbladder and Calot’s triangle;
In patients over 45 years of age or who are overweight, the possibility of surgery using this technique is decided individually.
Due to the low-invasiveness of the techniques, in our clinic it is possible to perform simultaneous operations - simultaneous performance of several interventions during one anesthesia. Thus, a patient who has several diseases of the abdominal and pelvic organs requiring surgical treatment can be treated with one operation. At the same time, the load on the body is much lower. Unlike operations performed with a 5-6 week interval between each one, hospitalization and recovery with simultaneous surgery take much less time.
To perform a cholecystectomy, the surgeon must be fluent in all techniques, since every person’s body is unique. Each patient who turns to me for help can count on an individual approach. I select the surgical treatment method taking into account the state of health and individual characteristics of the body. For better diagnostics and selection of the optimal solution, we have developed a special program, which is already registered on Russian territory.
As for laparoscopy, in this case manipulations are performed in a limited space, which also requires experience from the surgeon. Since 1994, I have personally performed more than 6 thousand laparoscopies for the treatment of cholelithiasis, of which more than 100 were performed using the transvaginal technique. The results of treatment are summarized in more than 30 scientific publications: both domestic and foreign. I described in detail the indications and technique of all types of operations for cholelithiasis in a monograph published in 2017 - SURGERY FOR GALLSTONES: laparoscopy, minilaparoscopy, single port, transvaginal access, simultaneous operations. -M.: Publishing House "MEDPRACTICA-M", 2021, 312 p.
I also regularly conduct seminars on laparoscopic removal of the gallbladder, which are attended by specialists from medical institutions of various importance: from regional hospitals to large research centers.