Gallstone disease (GSD) is a multifactorial disease of the hepatobiliary system, which goes through several stages of development. The causes of cholelithiasis are disturbances in the metabolism of cholesterol and bilirubin with the formation of stones (calculi) in the gallbladder and its ducts. Recently, there has been an increase in incidence in men and even at a young age, although statistically more often the diagnosis is made in women. However, after 70 years, signs of gallstone disease are recorded in both women and men equally often.
Principles of treatment
Active treatment measures begin only when stones provoke acute inflammation or exacerbation of chronic inflammation, blocking the ducts of the bladder. There are several approaches and methods for treating cholelithiasis: conservative and surgical. Cholecystectomy (surgical removal of stones) is the second most common operation in the world, followed by appendectomy (removal of the appendix due to its inflammation - appendicitis). According to statistics, every year in the USA the operation is performed on more than half a million patients, in Russia - more than 110 thousand people.
Why is bile needed?
TANACECHOL® tablets
herbal choleretic drug
It is used as a choleretic and antispasmodic agent for:
- chronic noncalculous cholecystitis
- hypomotor type biliary dyskinesia
- postcholecystectomy syndrome
ADVANTAGES:
- choleretic effect combined with antispasmodic effect
- affordable price
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation required
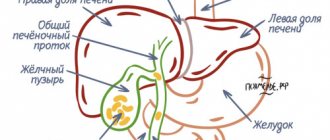
Bile is produced in the liver by hepatocytes, then accumulates in the gallbladder and is excreted through the common bile duct into the duodenum along with pancreatic secretions. That is, the gallbladder acts as a reservoir and transfers bile to the duodenum.
The chemical composition of bile is represented mainly by bile acids. The composition of bile “in numbers” looks like this:
- bile acids - 35.0 mmol/l;
- bile pigments - 0.8–1.0 mmol/l;
- cholesterol ~ 3.0 mmol/l;
- phospholipids - 1.0 mmol/l.
About 22% of bile is phospholipids. In addition, bile contains proteins (immunoglobulins A and M) - 4.5%, cholesterol - 4%, bilirubin - 0.3%, mucus, organic anions (glutathione and plant steroids), metals (copper, zinc, lead, indium, magnesium, mercury, etc.), as well as lipophilic xenobiotics [1].
The synthesis of these substances occurs during the breakdown of cholesterol and its removal from the human body.
Bile performs two important functions in the body:
- removal from the body of lipophilic components that cannot be excreted by the kidneys in the urine;
- secretion of bile acids, which are involved in the digestion of dietary fat and the absorption of its hydrolysis products.
In addition, bile acids found in bile improve intestinal motility, which naturally prevents constipation. Bile acids also have antiseptic properties and reduce the risk of intestinal infections [2]. Thanks to bile, toxins are removed from the body. In general, any failure in bile transit can cause a lot of trouble. Most often this is:
- nausea;
- pain after eating;
- repeated moderate pain localized in the epigastrium;
- vomit.
What should a pharmacist know?
First of all, which choleretic drugs have a stimulating mechanism of action, which have a contractile mechanism. Depending on the leading mechanism of action, choleretic agents are divided into:
- Choleretics - drugs that enhance bile production;
- cholekinetics - stimulating the flow of bile from the gallbladder into the intestines.
Conservative treatment methods
Conservative methods are aimed at relieving pain, as well as other symptoms and disorders.
After diagnosis and examination, during the acute period of the disease, medications are prescribed to relieve pain: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics, as well as drugs for the relief of dyspeptic and other disorders. If the pain syndrome does not stop within 5 hours, then inpatient treatment is indicated, where further treatment tactics will be determined.
In the chronic course of the disease, antispasmodics are the main drug for treating acute pain attacks, even between attacks. They will not only relieve pain, but also restore the ducts for the normal outflow of bile into the duodenum. This, by the way, will relieve dyspeptic disorders.
Diet for gallstone disease
Previously, recommendations were limited to sharply limiting fats to prevent the development and growth of gallstones. However, recent studies have shown that such recommendations are not as useful as previously thought, since rapid weight loss is a possible cause of complications. Today, doctors recommend maintaining a balanced and regular diet. This will not eliminate the presence of stones, but may have a positive effect on symptoms and pain. Limiting foods high in saturated fat will help reduce your risk of developing gallstones, as cholesterol is involved in their formation. The diet should include plant foods that will cover all the body's needs for vitamins, minerals and other nutrients that are necessary to maintain metabolic processes.
We must not forget about the proteins the body needs for recovery. But animal protein sources can be harmful because they put more strain on the gallbladder. Therefore, it is recommended to include easier-to-digest proteins in the diet; their sources can be:
- bird;
- fish;
- dairy products;
- nuts, etc.
For normal functioning of the digestive tract, you need to include fiber in your diet. Even outside of an exacerbation, you need to adhere to the same nutritional principles. Moderate consumption of natural ground coffee will help protect gallbladder function. Caffeine has various benefits for normal organ function. We must not forget the sources of calcium, vitamin C, folic acid and magnesium.
Methods and means that “break” stones
If the stones are made of cholesterol, the doctor will prescribe medications that will literally help dissolve the stones. Taking medications is long-term, it may take more than one month. For some patients, this is the only possible treatment. There are other techniques that will help break up stones and remove them from the body - lithopsy.
These are ultrasonic shock waves aimed at stones.
If the manipulation is successful, the stones are crushed and safely passed along with the feces. However, this procedure is not performed by everyone; it has a lot of indications and contraindications. Another surgical, but not radical, treatment method is retrograde cholangiopancreatography,
which is performed under local anesthesia. During the procedure, a flexible fiber-optic camera and endoscope are inserted through the mouth and directed into the gallbladder. Special probes at the end of the tube apply current to the ducts of the bladder, expanding them, and this also allows you to remove or break up stones so that they can pass into the intestines.
Surgical methods of treatment
Surgery to remove the gallbladder is called cholecystectomy. And most often it is performed using endoscopic methods, but in the presence of large stones, pronounced inflammation that cannot be stopped, open abdominal surgery is recommended. The advantages of the endoscopic technique are that it is a less invasive operation and the postoperative recovery period is shorter. If it is decided to undergo abdominal surgery, the patient spends a long time in the hospital, followed by a long course of rehabilitation and treatment.
Possible complications
Blocked ducts can cause acute pancreatitis and jaundice, and this is a direct indication for surgery. In the postoperative period, some patients may complain of frequent bloating, dyspeptic disorders, and digestive disorders, especially if the diet contains foods high in fat. It is important to be able to promptly recognize possible symptoms of complications of gallstone disease:
- Biliary colic
When a calculus clogs the duct, it prevents contraction of the gallbladder, which causes severe pain - this is colic. The pain is felt in the upper abdomen, but radiates to the central part of the abdomen. It usually appears after eating and persists for several hours and then subsides. In some cases, the pain may persist for a day, but more often the attack is wave-like: the pain arises and then subsides.
- Infection
Blocked ducts can cause inflammation and infection. As a result, the following symptoms appear: fever, chills, severe pain, dyspeptic disorders, etc.
- Obstructive jaundice
Requires surgical removal of a stone in the gall bladder, which disrupts the flow of bile into the intestines.
- Pancreatitis
Even small stones can block the pancreatic duct or cause the backflow of bile into the duct, which predisposes to the development of pancreatitis, that is, inflammation of the pancreas.
Prevention
Age, nutrition, gender are predisposing factors for the development of cholelithiasis, and these factors cannot be controlled, however, there are recommendations that will reduce the likelihood of its development.
First of all, this is nutrition: balanced, rich in vegetables and fruits. It is known that people who adhere to a vegetarian diet have a lower risk of developing cholelithiasis. It is recommended to control weight, because rapid weight loss increases the risk of developing the disease and even complications. Text: Yulia Lapushkina.
Medicines for the gallbladder
The gallbladder performs an important function - it stores and removes bile from the body. Bile is a special substance that is directly involved in the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as in other digestive processes. Gallbladder diseases are quite common. What medications are most often prescribed by specialists for the treatment of the gallbladder?
Antibacterial drugs
In the complex treatment of gallbladder pathologies, antibiotics are often used, which are divided into several groups depending on the mechanism of action on the body:
- Antibacterial drugs acting at the cellular level destroy the walls of bacteria:
- Cephalosporins,
- Penicillins.
- For the treatment of diseases caused by Escherichia coli or streptococci, the following are prescribed:
- Ampicillin,
- Gentamicin,
- Lincomycin,
- Tetracycline,
- Cefazolin,
- Cephalexin,
- Erythromycin.
If the patient has allergic reactions, sulfonamides are used:
- Sulfalene,
- Sulfadimezin.
In the process of taking antibacterial drugs, the development of a fungal infection is often observed. Therefore, in order to prevent the development of candidiasis, doctors prescribe antifungal drugs in parallel with antibiotics.
Antispasmodics
To relieve pain, experts prescribe antispasmodics for the treatment of the gallbladder, which are divided into two groups:
- Broad-spectrum drugs (affect all areas of the body where smooth muscles are present):
- Papaverine,
- Drotaverine.
- Drugs that have a selective effect (promote relaxation exclusively of the gastrointestinal tract muscles):
- Bromide,
- Mebeverine hydrochloride.
Choleretic agents
Choleretic medications for the gallbladder are of two types:
- Medicines containing bile enhance the movement of bile along the bile ducts, reduce the amount of precipitated cholesterol, and prevent the formation of stones. In addition, these drugs stimulate intestinal motility:
- Allohol,
- Vigeratin,
- Dekholin,
- Livamin,
- Liobil,
- Holenzim,
- Hologon,
- Tanacehol.
- Treatment of the gallbladder with medications involves the use of drugs that stimulate the formation and excretion of bile from the body:
- Olimethine,
- Sorbitol,
- Magnesium sulfate,
- Tykveol.
- Synthetic drugs have a pronounced choleretic effect:
- Nikodin,
- Odeston,
- Oxafenamide,
- Cholestil,
- Holonerton.
Hepatoprotectors
Hepatoprotective drugs are divided into 5 groups:
- Medicines of animal origin:
- Hepatosan - available in tablet form, provides tissue protection from the effects of toxins, stimulates the production and activity of enzymes, promotes the removal of toxins from the gastrointestinal tract and prevents the absorption of harmful substances in the intestines.
- Preparations of plant origin have a healing effect due to the content of essential oils, phytoncides, resins:
- Berberine,
- Convaflavin,
- Liv-52 – reduces the amount of fatty deposits in the liver, improves the digestive process, stimulates intracellular metabolism in affected tissues,
- Flacumin.
- Essential phospholipids:
- Essentiale Forte helps restore damaged liver and gallbladder cells.
- Amino acids have a restorative and detoxifying effect:
- Arginine,
- Gepa-Merz,
- Heptor,
- Heptral.
- Drugs that restore damaged liver cell membranes:
- Ursosan,
- Ursofalk.
Antiviral drugs
Treatment of the gallbladder with antiviral drugs is advisable for viral hepatitis:
- Velferon,
- Intron A,
- Reaferon,
- Roferon.
Sedative drugs
Patients with gallbladder diseases often experience various disorders of the nervous system. In such cases, doctors prescribe sedatives:
- Hawthorn,
- Valerian,
- Corvalol,
- Persen,
- Motherwort,
- Seduxen.
Related products View all products
Allohol, table.
p/o No. 10 9.60 ₽
More details
Allohol, table. p/o No. 25
49,90 ₽
More details
← Previous article Medicines for high blood pressure
Next article → Medicines for alcoholism
Part 2. The most important things about cholekinetics
Cholekinetics are also divided into two groups:
- Actually, cholekinetics, which include:
- magnesium sulfate;
- polyhydric alcohols (sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol);
- sunflower, olive oils, essential oils;
- herbs and plants containing bitterness;
- juices of lingonberries, cranberries, etc.
- Cholespasmolytics:
- hyoscine butyl bromide;
- papaverine;
- drotaverine
Indications for the use of cholekinetics:
- atony of the gallbladder with stagnation of bile;
- gallbladder dyskinesia;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- chronic hepatitis;
- anacid and strong hypoacid gastritis;
- carrying out duodenal sounding.
Cholespasmolytics are prescribed for the hyperkinetic form of biliary dyskinesia and for cholelithiasis. They are used to relieve pain of moderate intensity, often accompanying pathology of the biliary tract [6, 7].
Such drugs are contraindicated
in acute liver diseases, with exacerbation of hyperacid gastritis and peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. In this case, taking cholespasmolytics will only worsen the situation.