Esophageal hernia, causes and treatment methods
Among the most serious ailments of the gastrointestinal tract, hiatal hernia occupies one of the leading positions. For successful treatment, it is necessary to carry out timely diagnosis and establish an accurate diagnosis.
The type and methods of rehabilitation are selected depending on the stage of the disease, taking into account the general condition of the patient. In combination with medication and surgical treatment, a variety of folk healing recipes are allowed. After completing the treatment course, a gentle diet is prescribed and sports activities are limited.
Causes
As we initially noted, a number of reasons contribute to the appearance of a hiatal hernia. Meanwhile, most often the factors determining their appearance are the following:
- A certain type of endocrinopathy;
- A one-time chronic or, conversely, a systematic chronic sudden increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity. The reasons that lead to a pathological increase in pressure include blunt abdominal trauma, severe labor, chronic constipation, significant physical activity during which a heavy load is lifted while bending, etc.;
- Age-related changes provoked by certain degenerative processes, as a result of which the connective tissue ligaments become thinner;
- The presence of chronic diseases directly affecting the digestive system, in which the motility of the stomach, gallbladder, and duodenum is impaired;
- The presence of bad habits, as well as old age - these reasons are also identified as factors predisposing to the appearance of a hiatal hernia.
Classification
Depending on the characteristics, doctors distinguish several types of pathologies. Each type requires individual treatment. An incorrect diagnosis leads to ineffective treatment and the appearance of concomitant diseases.
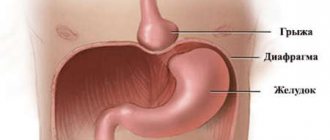
- Sliding (wandering) hernia. The organs that make up the hernial protrusion move to different planes with each change in body position. In this case, a thin shell of connective tissue (hernial sac) is formed.
- Paraesophageal (paraesophageal) hernia. The fundus of the stomach, a loop of intestine and the omentum move into the chest cavity.
- A mixed hernia is characterized by symptoms of sliding and fixed pathology.
- Congenital hernia. With congenital pathology of the short esophagus, the cardiac gastric section is located in the sternum. The gastric mucosa is located in the distal esophagus.
- Fixed (axial) hernia. Displacement of the entire stomach or a separate part of it occurs along the vertical axis. Changing the position does not affect the size; the protrusion does not reduce on its own.
Based on the volume of protrusion, the hernia is divided into 3 degrees:
- Hiatal hernia of the 1st degree - the stomach is slightly elevated, a small part of the lower esophagus enters the opening of the diaphragm;
- Grade 2 is characterized by a slight displacement of the cardia relative to the diaphragm; the entire lower intestine is located in the sternum;
- At stage 3, the cardia, lower esophagus, fundus and body of the stomach create a hernial protrusion.
Combined composition of fees
To relieve a number of symptoms characteristic of the pathology of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm, preparations are needed that have a multifaceted effect on the digestive tract. These include:
Recipe No. 1
2 parts flaxseeds are combined with 2 parts chamomile flowers, 1 part crushed licorice rhizomes and 1 part lemon balm leaves. To prepare the medicine, place 6 g of the resulting mixture in a container and pour 0.25 liters of boiling water. Using the water bath method, the liquid is heated for 5 minutes. After this, the container with the solution is placed in a warm place where it is infused. After 2 hours, the resulting mixture is filtered. The recommended amount per dose is 100 ml every 3 hours.
Recipe No. 2
10 g of oak bark is combined with 10 g of heather grass, watch leaves, wormwood, oregano and sage herbs, as well as linden blossom. All ingredients are taken 1:1. Then 10 g of the resulting collection is thoroughly crushed and steamed with 0.5 liters of boiling water. The mixture is boiled for about 3 minutes and left warm for 4 hours. The resulting broth is filtered. The recommended amount per dose is 100 ml 46 times a day.
The above recipes for the treatment of hiatal hernia are used between meals. The effect is noticeable on day 2 or 3, but therapy is recommended for 78 days until the symptoms of the disease disappear.
If the symptoms of inflammation predominate, the following combination of medicinal herbs is recommended.
Recipe No. 3
They combine medicinal plant materials of celandine, yarrow, St. John's wort, chamomile, serpentine, watch and mint. All ingredients, except the first two, take 2 parts each, and celandine and yarrow, 1 part each. To prepare the product, place 6 g of the resulting mixture in a container and pour 0.25 liters of boiling water. Heat in a water bath for 15 minutes and leave warm for 2 hours. Then filter thoroughly. The recommended amount per dose is 100 ml every 3 hours. You need to drink liquid 20 minutes before meals.
Symptoms
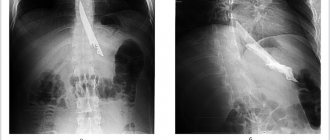
In 5–50% of cases, these hernias are completely absent of clinical manifestations; the pathology is discovered by chance (during an ultrasound, x-ray of the abdominal or thoracic cavity).
The main symptoms of a hiatal hernia:
- Pain is a clear symptom of a hiatal hernia. Most patients are familiar with pain syndrome, which most often manifests itself when bending over or horizontally positioning the body. The pain can be localized behind the sternum, in the hypochondrium, abdomen, and in the heart area. Painful sensations are usually aching in nature. After eating, they intensify, weaken after belching or taking a deep breath.
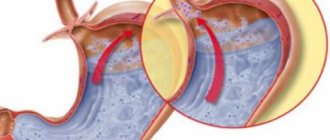
- The most common symptom that accompanies almost all known types of disease is heartburn. It can bother the patient when bending over, after eating, and often worsens at night. Heartburn attacks can be triggered by vigorous exercise, overeating, or drinking too much alcohol. Sometimes the symptom manifests itself in a mild form and does not affect the patient’s well-being. Severe heartburn is also observed, when the patient finds it difficult to tolerate a burning sensation in the chest. This condition may be accompanied by flatulence, nausea and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. When the stomach contents end up in the esophagus, heartburn becomes sour or bitter. All these manifestations affect a person’s psychological and physical health. Sleep is disturbed, the patient loses performance and appetite. (Read also: Causes and symptoms of heartburn, how to get rid of heartburn?)
- 35% of patients diagnosed with a hiatal hernia experience regurgitation. The reasons are the same: eating, bending, horizontal position. This symptom is typical for medium-sized formations and causes a lot of inconvenience. Ingoda, the volumes of vomit can be quite large, so the patient has to stock up and carry special containers for vomit.
- Common symptoms accompanying hiatal hernia include dysphagia or difficulty swallowing. This phenomenon can be provoked by haste in the absorption of food, too hot (cold) drinks, and neurogenic factors. Dysphagia may occur rarely or become permanent. This is usually associated with complications. With an exacerbation of the disease, complete or partial obstruction of consumed food is possible. This symptom usually accompanies heartburn. When the esophagus is full, the patient simply cannot swallow food. These unpleasant difficulties cause anxiety and nervousness. Over time, discomfort increases, which can lead to refusal to eat food and serious consequences.
- Belching. This symptom can be caused by spasms of the alimentary canal, active work of the stomach and increased intra-abdominal pressure. Involuntary release of air can occur during conversations and eating. Often an attack is accompanied by a characteristic sound and smell. When burping, not only air can be released, but also the contents of the stomach. Taking antispasmodics, which some patients use to relieve symptoms, rarely brings relief, so patients often induce belching on their own, thereby freeing themselves from discomfort. (
Individual symptoms
For intense pain and spasms, the most effective are medicinal herbs with an antispasmodic effect:
Recipe No. 4
50 g of alder fruits are placed in a container and 1 liter of water is poured. The resulting composition is placed on low heat. After boiling, cook it for another 20 minutes. Then cool it and filter thoroughly. The amount of medicine per 1 dose is 100-200 ml an hour after meals or for pain.
Recipe No. 5
To collect, take 5 g of dried herbs, St. John's wort and yarrow. Pour 0.4 liters of boiling water into it and leave it warm for 4 hours. Then filter. The amount of medication per dose is 1 glass on an empty stomach and 1 hour after meals 3 times a day.
Ulceration of the mucous membrane of a hiatal hernia is recommended to be treated as follows:
Recipe No. 6
Anise fruits are mixed with crushed serpentine rhizomes, oregano and marigold herbs, marigold flowers, fireweed leaves and lemon balm, all parts in equal quantities. To prepare the recipe, place 10 g of the collection in a container and pour 0.25 liters of boiling water. Heat the resulting mixture using a water bath for 10 minutes. Then place it in a warm place, where it is infused for at least 2 hours. The resulting liquid is filtered. The recommended amount per dose is 50 ml on an empty stomach, and then in the same volume an hour after each meal. The medicine can also be used for night pain.
To eliminate heartburn, you can use potato juice:
Complications
The disease sometimes leads to a number of complications, and this will not depend on the classifications and causes of its origin. This hernia may be accompanied by esophageal bleeding, transition of the esophagus into the so-called “hernial sac” or gastric mucosa, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, shortening of the esophagus, strangulation of the hernia (here surgical intervention will be inevitable).
A strangulated esophageal hernia is characterized by increased pain, bloating and severe tension of the abdominal walls, and the appearance of prolonged, uncontrollable vomiting. In such a case, emergency suturing of the diaphragmatic opening is performed to a normal size after repositioning the esophagus into the abdominal cavity.
Surgery
When conservative treatment does not give the desired result, the symptoms of hiatal hernia intensify, and against this background, severe damage to the esophagus occurs, gastroenterologists strongly recommend surgery.
(if the table is not visible completely, scroll it to the right)
The operation of suturing the hernial opening is carried out in three ways (the choice of method depends on the patient’s condition, his age, and the size of the hernia):
The recovery period directly depends on the method of surgery. After abdominal surgery, the patient spends a day in the intensive care unit, then he is transferred to a ward. You are allowed to stand up on the 5th day, and the stitches are removed on the 7th day. Full recovery of the body ends after 4 weeks.
After laparoscopy, recovery time is halved. Already in the evening on the day of surgery, the patient is allowed to get up, and he is discharged 35 days after the operation.
You must follow the diet and follow special doctor’s instructions for at least 6 months. Then the person gradually moves on to a normal lifestyle.
Diagnostics
The first step in detecting a diaphragmatic hernia is to look for the patient's characteristic symptoms and possible causes. After this, it is necessary to proceed with a direct examination, during which the following signs of the disease can be detected:
- Feeling the abdomen (palpation) - it becomes dense in the upper parts of the abdominal wall due to strong muscle tension. Pain on palpation is also possible;
- Inspection - with a hiatal hernia, the chest practically does not move during breathing, due to dysfunction of the diaphragm. If a person suffers from this pathology for a long time, the stomach becomes “sunken”. This symptom may not be observed in people who are overweight;
- Auscultation (listening with a phonendoscope) - a characteristic sign of a diaphragmatic hernia is the appearance of bowel sounds in the chest cavity. The normal sound of breathing is usually absent or significantly reduced.
The above signs are enough to suggest a diagnosis. However, the presence of a hiatal hernia can only be reliably confirmed using instrumental diagnostic methods.
Schmorl's hernia
Schmorl's hernias are very common - in every third person. These hernias, unlike intervertebral hernias, extremely rarely cause concern to their owner and are almost always an accidental finding during an X-ray examination. However, in some situations, these formations pose a serious health threat.
What is Schmorl's hernia?
Schmorl's hernia is the pushing of the cartilage plate of the intervertebral disc into the vertebral body, which is located above or below the disk. Unlike an intervertebral hernia, which is located in the horizontal plane, Schmorl's hernia is located along the vertical axis of the spine. This formation does not compress the nerve roots and blood vessels, but the spongy substance in the vertebral body, which has no pain receptors. That is why such hernias are almost always asymptomatic and are discovered by chance.
Why do Schmorl's hernias develop?
Most of these hernias appear in childhood due to the rapid growth of the child (the vertebrae do not keep up with the growth of the muscles and the rest of the skeleton, and voids appear in them). If there are a lot of hernias, then most likely we are talking about a hereditary predisposition.
Other causes include back injuries and osteoporosis (loss of bone tissue). The lower thoracic and upper lumbar spine are most often affected.
Is there any danger?
If a Schmorl's hernia is small in size and located in the center of the vertebra, then you most likely will not find out about it until you take an X-ray of the spine. Apart from a slight restriction of movement in the adjacent vertebrae and slight tension in the surrounding muscles, there are usually no symptoms even with a detailed examination. This situation is not dangerous and does not require treatment or lifestyle changes.
Read also: Protrusion of the spine. What it is?
If the hernia occupies more than a third of the volume of the vertebra or is located close to the anterior edge of the vertebra, then unpleasant symptoms may appear. You may feel pain in the area of the affected vertebra not only when moving, but also at rest. Limitation of movements in the spine becomes more pronounced.
Perhaps the most unpleasant consequence of a marginal or large hernia is a vertebral compression fracture. This occurs because the damaged vertebra can no longer cope with the load. This usually happens after lifting weights or jumping from heights.
Multiple small Schmorl's hernias in the thoracic region can lead to visible deformation of the spine - thoracic kyphosis increases, the person looks stooped. In addition to the cosmetic defect, restriction of movements in the thoracic spine and pain during exercise gradually increase.
What to do?
If you have single small Schmorl's hernias, then no special treatment or further examination is required.
If several Schmorl's hernias are detected, then it is necessary to do exercises that strengthen the back muscles to reduce the load on the affected vertebrae. Swimming, Pilates, yoga are suitable. Lifting heavy objects and jumping from heights should be avoided.
For large and marginal Schmorl's hernias, treatment tactics will depend on the severity of symptoms. A consultation with a neurosurgeon may be required to decide on surgery. Fortunately, such hernias are extremely rare.
Be healthy!
Maria Meshcherina
Photo istockphoto.com
Treatment methods
How to treat a hiatal hernia is decided jointly by a gastroenterologist and a abdominal surgeon. To draw up the correct method of therapy, the type and characteristics of the pathology are important (sliding or fixed hernia, whether there is any infringement of organs).
The main treatment takes place at home and includes four methods:
- diet,
- taking medications,
- exercise therapy,
- traditional methods.
For the following complications, surgical intervention is resorted to:
- strangulated hernia;
- bleeding;
- introduction of one hernia organ into another;
- A large number of organs have entered the chest cavity, and they are compressing the heart.
In other cases, the operation is carried out as planned (the duration is not limited, but it is recommended within several weeks) in a specialized department of “thoracic surgery”.
Breathing exercises
When faced with a hernia and receiving recommendations from a specialist regarding therapeutic, breathing exercises, many people think about whether it is really possible to eliminate the disease using this method. In fact, such exercises strengthen the muscle tissue of the abdominal cavity and diaphragm. And this allows you to speed up the healing process and improve the condition of the body with such a disease.
Breathing exercises should be performed only after three hours have passed since the last meal. You need to lie on your side, with your legs off the sofa or bed, take a deep breath and stick your stomach out as much as possible. Then you need to exhale and relax all your muscles. The stomach does not retract at this moment. This exercise is done in four sets of 10 minutes, and each time the breath should become deeper.
To perform the next exercise, you need to kneel down and slowly begin to bend in different directions. It is important to monitor your breathing. When the body bends, inhalation occurs, and when returning to its original position, the air is exhaled. Then this exercise is repeated, but standing.
To complete this small complex, you need to lie on your back and begin to turn your upper body in both directions. At the turn itself, you inhale, and in the starting position you exhale and completely relax the muscles. When performing such gymnastics at home, you need to ensure that each exercise is performed correctly. Otherwise, when the exercise is done incorrectly, a person can only aggravate the situation and worsen his condition, since even greater pressure begins to be exerted on the diaphragm, which causes complications to develop.
Drug treatment
Treatment of hiatal hernia without surgery, that is, with the help of medication, is justified in case of moderate symptoms or in advanced stages as a preparatory stage before surgical treatment.
To treat esophagitis with hernia, 3 main groups of drugs are used:
- Antisecretory drugs - proton pump blockers, histamine receptors.
- Antacids.
- Prokinetic drugs.
Gastroenterologists around the world have recognized the use of proton channel blockers as the gold standard in the treatment of inflammation of the esophagus and stomach. These are omeprazole, rameprazole, lansoprazole. The products are very effective with minimal side effects. They reduce the aggression of gastric contents and promote mucosal regeneration.
Antacids are an emergency treatment for severe heartburn and do not require systemic use. Prokinetics - Metoclopramide - treat motility disorders underlying the appearance of hernia and peptic esophagitis. The course of use is no more than a month.
Let's sum it up
Remember that conservative treatment of a hiatal hernia will be effective only if you strictly take all prescribed medications and follow a lifelong diet and daily routine. If you are not ready to constantly limit yourself, you should consider surgery.
Finally, good news: in modern pharmacology, drugs have appeared without side effects and are not addictive. This is a big step forward in the treatment of hiatal hernia, because during therapy many problems arise due to the body’s addiction to certain medications, for which it is necessary to look for an alternative.
Preparing for planned surgery
Before surgical treatment, the anesthesiologist/surgeon questions the patient in detail about his state of health, allergies, previous blood transfusions, etc. The patient is prescribed a series of tests that will allow him to evaluate the functions of the main organs: general blood and urine tests, biochemical analysis of venous blood, acid-base status, ECG.
If necessary, the patient’s condition is somewhat improved (pressure, heart activity, respiratory function are stabilized, etc.). Immediately before the operation, the intestines are cleansed (if there is no strangulation of the esophageal hernia), the bladder is catheterized and the necessary medications are administered.
Surgery for hiatal hernia
There are different surgical techniques:
- Operation Belsey. Performed if the hernia is large. It is performed through an incision in the sixth intercostal space, on the left side of the sternum. The essence of the operation is that the lower part of the esophagus and esophageal sphincter is attached to the diaphragm.
- Nissen fundoplication. One of the most common operations. It is performed using laparoscopic technique or the open method. In this case, the upper third of the stomach is wrapped around the esophagus. This “cuff” prevents stomach contents from entering the esophagus.
- Allison's technique. The incision is made in the seventh and eighth intercostal space. In this case, the hernial orifice is sutured.
- Gastrocardiopexy. It is performed through an incision above the navel, along the midline of the abdomen. The upper third of the stomach and esophagus are sutured to the subdiaragmal structures.
The goal of surgery is to restore the anatomical structure of the esophagus and create an anti-reflux mechanism that will prevent the reflux of gastric contents.
Purposeful action
The main groups of medicinal plants according to their medicinal effect against hernia:
- To relieve or reduce the severity of inflammation, aloe, birch buds, heather, serpentine, coltsfoot, fireweed, plantain, and chamomile are used.
- Anise, cumin, coriander, calamus, barberry, sweet clover, and St. John's wort are responsible for relieving pain and spasms.
- For flatulence, anise, fennel, oregano, angelica, lavender, immortelle, and rhubarb are added to the collection.
- Stimulation of motor skills is carried out through the use of buckthorn, lingonberry, joster, and wormwood.
- Marshmallow, flax, and sea buckthorn provide an enveloping effect that protects mucous membranes.
- To provide an astringent effect, oak bark, birch buds, large serpentine, pomegranate, and galangal are used.
- The production and separation of bile is facilitated by tansy, barberry, immortelle, centaury, and cornflower.
- To facilitate bowel movements, it is recommended to consume raw apples, carrots and other foods containing large amounts of pectin.
- To reduce the acid-forming function and aggressive effect on the mucous membrane, acacia, large serpentine, dubrovnik, and rowan are well suited.
- Alimentary bleeding can be stopped with the help of nettle, yarrow, burnet.
- Regeneration of damaged tissue is carried out by sea buckthorn, Kalanchoe, aloe, mullein, plantain, and licorice.
- Mint, valerian, thyme, St. John's wort, and motherwort have a calming effect.