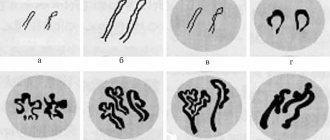
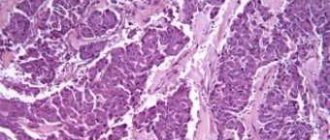
Lipoma is painless lumps or tubercles, called wen, since by their nature they are benign neoplasms from adipose tissue. Sometimes they are enclosed in a capsule of connective tissue.
Lipomatosis is multiple tumors on the body that require mandatory consultation with a surgeon.
The Miracle Doctor clinic uses a modern method of removing lipomatosis, which is much more effective than the laser and radio wave method.
General information
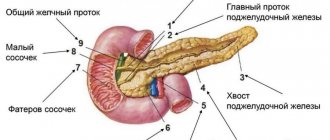
The pancreas is a digestive organ, produces digestive enzymes, and also has endocrine (produces the hormone insulin ) activity. Very often, its defeat is associated with obesity . In overweight patients, non-alcoholic fatty pancreatic disease is diagnosed, which can have two morphological variants - lipomatosis and steatopancreatitis .
They represent different stages of the pathological process. What is pancreatic lipomatosis? Pancreatic lipomatosis is fatty degeneration of the organ (synonyms: pancreatic steatosis, fatty degeneration, non-alcoholic fatty disease of the pancreas). The most acceptable term is pancreatic steatosis, and if it is associated with metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty pancreatic disease. The terms “lipomatosis” and “fatty gland” are used to refer to all types of fat accumulation in the gland; steatosis refers to the accumulation of fat in the cells of the gland (they are called pancreacytes) and intercellular tissues. The accumulation of fat is accompanied by a gradual disruption of gland function, but without signs of inflammation. Steatopancreatitis is the second, more advanced stage of fatty disease of this organ and additionally includes an inflammatory component (lymphomonocytic-plasmacytic infiltration of the gland tissue occurs).
The prevalence of steatosis increases with patient age. The accumulation of fat in cells is associated with weight gain , insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome . A direct connection has also been recorded between diabetes mellitus and this gland pathology, and vice versa - patients with fatty infiltration of the organ have a high risk of diabetes mellitus . At the initial stage, steatosis is reversible and a decrease in its severity is noted with weight loss.
Fatty infiltration of the organ is more common in men over 40 years of age, with elevated levels of cholesterol , triglycerides and glucose . Previously, fatty infiltration of the gland was considered a harmless condition, but observations of patients and studies have shown a high risk of developing diabetes mellitus, gland failure, acute pancreatitis and cancer of this organ, and therefore more attention has been paid to this condition.
Treatment of pathology
The choice of treatment method depends on the degree of damage to the body, the age and well-being of the patient. The disease cannot be completely cured due to a structural disorder of the tissue layer of the pancreas. The actions of doctors are aimed at restoring the functioning of the organ. To do this, they resort to methods of conservative therapy:
- The patient is prescribed a special diet that will reduce the load on the pancreas and other organs of the digestive tract. It will also help reduce weight and alleviate the patient’s condition.
- Painful spasms can be relieved with medications based on painkillers - No-shpa, Baralgin or Spazmalgon.
- Fermenting drugs that improve the functioning of the digestive system are prescribed - Pancreatin or Creon. The products relieve unnecessary stress and alleviate the patient’s condition.
- Treatment of the pathology requires completely quitting smoking and drinking alcohol.
- You can stop attacks of nausea and vomiting with Loperamide or Domperidone.
Conservative treatment is used in the first and second stages of the disease. At the third stage, drug therapy does not have a positive effect, since there are serious disturbances in the structure of the pancreas, which lead to complete dysfunction of the organ.
At the last stage of the disease, surgical intervention to remove the pancreas is required. During the operation, the ducts of the organ are also removed. The process of replacing healthy tissue with fat is irreversible. During the last stage, atypical cells penetrate inside the pancreas, causing severe complications. New methods are required for the functioning of the digestive tract.
After surgical removal, the patient requires a rehabilitation course, including diet and lack of exercise. After a course of therapy, you need to follow all the recommendations of your doctor - this will speed up the recovery process.
Pathogenesis
Fatty infiltration is formed against the background of obesity, which creates the prerequisites for the intracellular accumulation of fats (mainly triglycerides) in the gland cells. This process causes the death of β-cells (they are the endocrine part of the gland and produce insulin), which are replaced by adipocytes (fat cells). The constant influence of high concentrations of free fatty acids on β-cells (lipotoxicity) causes their secretory dysfunction: first, the level of fasting blood glucose increases moderately, then after a food load, and, ultimately, diabetes mellitus develops. And hyperglycemia further impairs β-cell function, completing a vicious circle.
Many authors consider the initial development of fatty infiltration of the liver, and then the pancreas.
This is explained by the fact that a diet rich in fats and carbohydrates, as well as hyperinsulinemia, cause the development of changes in the liver and the flow of very low-density lipoproteins into the islets of the pancreas. Insulin resistance at one time causes the release of free fatty acids from adipose tissue, therefore their concentration in the blood increases. If the accumulation of fat in the gland cells exceeds the permissible threshold, then hyperglycemia , which closes a vicious circle of glucose metabolism disorders.
During hyperglycemia, free oxygen radicals are formed from glucose, which triggers free radical oxidation reactions of proteins and lipids. Increased free radical lipid peroxidation causes cell apoptosis, including β-cells, and dysfunction of the gland. At stages II and III of lipomatosis, its function is significantly impaired and the process of autolysis of the gland is started. As a result, inflammation of the parenchyma develops, necrosis , which invariably leads to fibrotic changes and fibrolipomatosis .
Treatment approaches
Treatment of the pathology is aimed at slowing down the replacement of its active cells with adipose tissue. Medications are designed to support the remaining cells and cope with the symptoms of enzyme and endocrine deficiency. The following remedies are used for treatment.
- Diet and lifestyle correction. A split diet with low fat and high-calorie foods will help slow down the progression of the pathological process. Alcohol consumption should be avoided. Moderate physical activity will help you lose excess weight and stop the progression of the disease.
- Medications. There are no drugs that stop the progression of lipomatosis. Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms and alleviating the patient’s condition: • for abdominal pain - antispasmodics (No-shpa, etc.); • for frequent stools – antidiarrheal drugs (Loperamide); • for severe nausea and vomiting – antiemetics (Metoclopramide); • if digestion is difficult - enzyme preparations (Pancreatin, etc.); • in case of insulin deficiency, insulin therapy is carried out depending on the blood glucose level.
- Surgery. This method is used for fatty tumors of the pancreas, when they reach an impressive size and compress the surrounding tissue.
The dosage, choice of treatment regimen and specific drug are selected by a specialist, taking into account the clinical picture of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Classification
The most common ultrasound classification of glandular lipomatosis is:
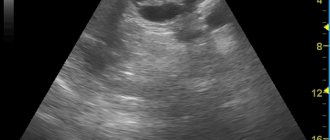
- I degree. The size of the gland is not enlarged, the splenic vein and pancreatic duct are clearly visible. The echogenicity of the gland is uniformly increased and is equal to the echogenicity of the adipose tissue located in the area of the mesenteric artery.
- II degree. Indistinct edges of the splenic vein and pancreatic duct. The superior mesenteric artery is almost invisible. Increased echogenicity, but signal attenuation behind the posterior surface of the gland.
- III degree. Reduced ultrasonic conductivity.
According to the prevalence of fatty infiltration, according to the ultrasound picture, there are:
- Diffuse infiltration - fat cells are evenly distributed in the gland tissue.
- Nodular fatty infiltration - limited fat deposits are noted, which are surrounded by a connective tissue capsule and are often located symmetrically.
- Diffuse nodular infiltration - two types of changes are detected simultaneously.
In accordance with MRI data, the clinical course of lipomatosis has the following degrees:
- Pancreatic lipomatosis stage 1. This is the initial stage, when one third of the organ is replaced by adipose tissue. At grade 1 there are no symptoms. The function of the organ is compensated.
- At grade 2, half of the parenchyma of the gland is replaced by adipose tissue, which is accompanied by dysfunction of the gland and clinical manifestations. A patient at this stage of the disease most often seeks medical help.
- The 3rd degree is characterized by the replacement of more than 2/3 of the gland with adipose tissue. In this case, there is a violation of exocrine and endocrine function. The patient experiences digestive disorders and increased blood glucose levels.
The combination of pancreatic steatosis and hepatic steatosis occurs in 50-68% of cases of obesity . Liver lipomatosis (steatosis) and pancreas lipomatosis (pancreas) have the same development mechanism - the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver and pancreatic cells. Fatty liver disease is distinguished as an independent entity and also includes two forms: fatty steatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis .
The amount of fat in cells depends on the balance between intake, synthesis and use for the body's needs. In both organs, changes can be focal or diffuse. In the diffuse form, fats are located over the entire surface, and in the focal form, grouped fat deposits are determined. In both cases, the condition of the organ worsens due to an increase in adipose tissue and a decrease in functioning parenchyma. Initially, excess fat in the form of triglycerides is located inside the cells, shifting the nucleus to the periphery. If fatty deposits accumulate in large quantities, the cells rupture and the fats move into the intercellular space, forming a kind of cysts that change the structure of the organ and its function. In most patients, changes at the level of steatosis can remain throughout life, while in others they progress with the development of spaatohepatitis and steatopancreatitis with the transition to fibrosis.
Skin lipomatosis has a completely different genesis and is not associated with general obesity, so these terms should not be confused. Skin lipomatosis (lipomas) is the occurrence of multiple fatty formations in the subcutaneous tissue, which may have a connective tissue capsule or transform into normal adipose tissue without a clear boundary.
Skin lipomatosis occurs more often in men. Lipomas are painless formations and histologically have the composition of adipose tissue. Lipoma fat cells are resistant to lipolytic factors, so they do not shrink even if a person loses a lot of weight.
A type of lipoma is Dercum's disease ( neurolipomatosis ), which is characterized by the appearance of lipoma-like formations in the subcutaneous tissue of the arms, back, mammary glands, abdominal wall, buttocks or thighs. This is a chronic disease that is more common in women aged 30 to 60 years. Subcutaneous tumors from adipose tissue have an irregular shape and are detected simultaneously in different parts of the body.
Characteristic is the pain of the formations with slight pressure and touch, which distinguishes this disease from ordinary lipomas. Pain syndrome has varying degrees of severity in different patients - from moderate intensity to severe. Sometimes pain also occurs in areas where there are no fatty tumor-like formations.
Dercum's disease occurs with compression neuropathy of the nerve branches, resulting in a pain syndrome that is not eliminated by classical analgesics, amitriptyline and carbamazepine . The lack of effective treatment leads to a decrease in quality of life. Other symptoms include: numbness in the fingers, spontaneous swelling in different parts of the body, stiffness in the morning, sleep disturbances, anxiety-depressive syndrome, weakness, aggravated by light exertion, pain in the joints (wrist, elbow, hip) and in long tubular, headache (classic migraine and tension headache), memory impairment, possible fever. The disease is systemic and the localization of fatty formations in the lungs or heart is deadly. The course of the disease varies - the condition can slowly worsen over several years or quickly, under the influence of various factors (surgeries, pregnancy, influenza). More than half of the patients lose their ability to work.
The cause of the disease has been little studied. It is believed that the cause of the disease is a disorder of lipid metabolism and endocrine disorders. A hypothesis is put forward about the autoimmune nature of the disease. Dercum's disease is inherited through the grandmother-mother-daughter line.
A variant of Dercum's disease is Gram syndrome . It is found in older women and is characterized by rapidly increasing obesity with fat deposition in the area of the knee joints and arthrosis of the knee joints. It is also a hereditary disease.
Stages of pathology development
Lipomatosis occurs in three stages, which are characterized by certain symptoms:
- At the first stage, the level of atypical cells is within 30%. The fat layer occupies a small area of the organ, which is characterized by the presence of mild symptoms. In some cases, the disease may be asymptomatic at this stage. Mostly there are mild sensations of discomfort in the stomach area.
- At the second stage, the fat layer increases to 50%, i.e. The pancreas is half occupied by atypical tissue. Neoplasms grow inside the organ, which is accompanied by painful sensations that intensify during or after eating. No serious violations in the activities of the body are recorded at this stage.
- The third stage of the disease is characterized by the active progression of the spread of the fat layer to 60-70%. Here, pronounced symptoms of pathology are observed - painful spasms, diarrhea or constipation and bouts of vomiting. There are serious disturbances in the functioning of the organ.
Modern advances in medicine make it possible to identify the disease at the initial stage of its formation, so doctors advise not to postpone a visit to the clinic when the first suspicious symptoms appear. Early initiation of treatment guarantees recovery without complications.
Causes of lipomatosis
The main cause of this disease in various age groups is obesity , which is a leading risk factor for pancreatic pathology.
- Obesity is accompanied by hyperlipidemia and promotes fatty infiltration of the gland and liver. In addition, eating fatty foods causes excess production of pancreatic enzymes and cholecystokinin and disrupts the outflow of pancreatic juice.
- Atherosclerosis . With it, the fat content in the gland exceeds the norm by 25%.
- Fatty degeneration of the pancreas also develops due to the toxic effects of alcohol . Ethanol also negatively affects the progression of the disease and stimulates fibrotic processes.
- Consumption of foods high in animal fats and proteins, as well as alcohol abuse, are the main risk factors for this disease.
- Toxic effects of corticosteroids , gemcitabine and rosiglitazone .
- Presence of diabetes mellitus .
- Hemochromatosis . Iron overload during blood transfusions also causes fatty replacement of the organ parenchyma.
- Kwashirkor.
- Metabolic syndrome (includes abdominal obesity , hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance ).
- Hereditary diseases ( cystic fibrosis , and Johanson–Blizzard syndromes , lysosomal acid lipase mutations).
- Viral diseases ( viral hepatitis , HIV/AIDS).
Surgical methods
Most often, fat removal is performed under local anesthesia. Traditional anesthetics are used (lidocaine, novocaine in low concentrations of 0.25% - 0.5%). The operation is performed on an outpatient basis; hospitalization is not required. Immediately after the operation the patient goes home.
Contraindications to removal of a wen on an outpatient basis may be its large size (more than 10 cm), depth of location (intermuscular, in internal organs), and close proximity to large vessels and nerves. In this situation, the operation must be performed in a hospital setting, with the participation of an anesthesiologist and a team of surgeons, with the possibility of postoperative observation in the ward.
Currently, only surgery can reliably get rid of lipoma. The following methods of lipoma removal are distinguished:
- Excision of the formation is the most common and effective method - a small incision is made on the skin under anesthesia. The fatty tissue is isolated from the surrounding tissue and removed. Hemostasis is performed - stopping bleeding from small vessels in the wound, which reduces the risk of postoperative hematomas. Stitches are placed on the wound. Both regular interrupted sutures and intradermal (cosmetic) sutures can be applied. Cosmetic stitches are characterized by the absence of transverse “stripes” on the scar. Regular sutures are removed on the 8th - 9th day, and cosmetic sutures - on the 12th - 14th.
- Laser and radio wave methods. Practically no different from conventional excision. The skin incision is made with a regular scalpel, but on deeper tissues they use radio waves or lasers, which allows for more careful separation of tissues, reducing bleeding and the risk of postoperative hematomas. There are myths that the use of radio waves and lasers allows you to avoid leaving scars and not requiring stitches - all this is not true. Laser and radio waves, due to a more gentle effect on the tissue, can minimize the scar, but to one degree or another, the scar still remains after removal, and sutures also need to be applied.
- Puncture-aspiration method for lipoma removal. A small incision is made in the projection of the formation, through which a suction resembling a thick needle is inserted. Using a special vacuum device, the lipoma is “sucked out” through suction. At its core, the procedure is liposuction. The problem is that liposuction is good for removing unchanged fat tissue. Lipoma is a tumor. For its complete removal, visual control is required, which the puncture-aspiration method cannot provide. If, after “sucking out” blindly, at least a small fragment of the formation remains under the skin, this will lead to an inevitable relapse, and in some cases, malignancy (malignancy) of the tumor. So most surgeons do not use this method. The puncture-aspiration method is only well suited for the treatment of Bichat lipoma (located in the area of the 7th cervical vertebra). This is due to the fact that the cells of this formation are essentially not tumor cells, and even with incomplete removal there will be no negative consequences.
Our clinic has extensive experience in removing fatty tissue. In our practice, we use both conventional excision and radio wave excision.
During the initial appointment, the doctor finds out the medical history, complaints, examines the patient, and, in doubtful cases, performs an ultrasound. If you have severe concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, anemia, cardiopulmonary pathology), you must inform your doctor about this - additional examination may be required. It is also necessary to report any allergies to non-medicinal products. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then removal can be performed immediately, on the day of treatment. There is no need to collect any additional tests before surgery. If liposarcoma is suspected, a preliminary consultation with an oncologist is recommended.
The operation is completely painless, takes 10-15 minutes and eliminates lipoma forever. With lipomatosis, a large number of formations can be removed at once (10–15). In the postoperative period there is practically no pain. Immediately after the operation, patients go home, and the next day they can live a normal life, work, and do everyday activities.
Reception and operations are performed by Dr. Elshansky Igor Vitalievich, a surgeon with more than 20 years of experience, candidate of medical sciences. The doctor knows all methods of removing wen. After the operation, it is possible to apply either a regular suture or a cosmetic one. When contacting Dr. Elshansky I.V., you will encounter high professionalism at affordable prices for treatment. Removing a wen in our clinic costs from 2000 rubles, including anesthesia and the use of radio waves. When removing several formations, a discount is provided, which can reach 50%.
Symptoms
Clinically, lipomatosis of the gland can be asymptomatic or have a pronounced picture. With a slight accumulation of fat in the gland cells, there are no clinical symptoms and the disease is discovered accidentally during instrumental examination (ultrasound, MRI). Only sometimes Tuzhilin’s symptom - the appearance of small red spots (vascular aneurysms) that do not disappear with pressure. They are located on the abdomen and upper half of the body, but this symptom is not specific to this disease.
With pronounced fatty infiltration, signs of exocrine insufficiency appear: diarrhea , steatorrhea (the presence of an excess amount of neutral fat in the feces), hypovitaminosis . The patient also experiences nausea, bloating, pain or discomfort in the left hypochondrium. Disruption of the endocrine function of the gland manifests itself in impaired carbohydrate metabolism ( fasting hyperglycemia , insulin resistance , impaired glucose tolerance). Since dysfunction of the pancreas always leads to dysfunction of the biliary system, the patient experiences bitterness in the mouth and pain in the right hypochondrium. If we talk about steatopancreatitis , it often appears as a moderately severe pain and dyspeptic syndrome (belching, nausea, tendency to frequent vomiting, bloating, aversion to fatty foods).
Tests and diagnostics
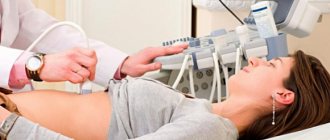
- Transabdominal ultrasound. Signs of steatosis of the gland are: an increase in its echogenicity while maintaining the homogeneity of the structure, possibly a slight increase in the size of the organ. Such changes are referred to as diffuse changes in the pancreas. Its echogenicity is assessed indirectly by comparing it with the echogenicity of the liver and kidneys. The echogenicity of a healthy gland is the same as that of the liver. In fatty liver disease, the echogenicity is higher than that of the kidneys. The information content of ultrasound is quite low, since patients have abdominal obesity and flatulence .
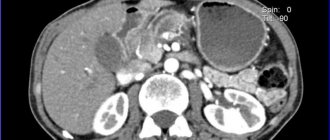
- Multislice CT. Accurately determines the presence of fatty inclusions, layers, and allows you to detect fibrosis. The examination also gives a picture of the condition of the peripancreatic tissue.
- MRI. It is considered the best diagnostic method. Modern MRI technology determines homogeneous changes in the structure of the gland; with proton MR spectroscopy, the content of triglycerides is assessed quantitatively.
- Endosonography. It is an invasive procedure and allows you to obtain highly accurate images, as well as reliably confirm steatosis. The resolution of this method is superior to CT and MRI, but there is a risk of complications.
- From clinical and biochemical examinations, determination of the level of glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins.
Diet
Diet 8 table
- Efficiency: weight loss to the required level
- Time frame: long-term, until the expected effect is achieved
- Cost of products: 1120 - 1230 rubles per week
Fatty infiltration of the organ has a direct connection with nutrition, so diet takes a leading place in treatment. For patients with normal weight, the main goal of nutrition is to reduce the load on the gland, so Diet No. 5 . In case of obesity, it is important to reduce weight, so the basic principles of nutrition of table No. 5 are preserved, but in addition, patients are recommended to reduce calories by reducing fats and carbohydrates ( Diet 8 table ), while the diet should contain a normal amount of proteins. Daily calorie content is no more than 1500-1700 kcal. In case of disruption of the endocrine function of the gland, dietary Table No. 9 with a significant restriction of carbohydrates.
Saturated fats and fructose cause the progression of steatohepatitis and steatopancreatitis . At the same time, choline, a protein diet, unsaturated fats and antioxidants have a preventive effect. With lipomatous lesions of the pancreas, the digestion of dietary fat worsens. In the diet of such patients, the fat quota is reduced, and given the obesity of all patients suffering from this disease, this is all the more necessary. It is also important to avoid heating fats, since the substances formed when heating fats are difficult to digest. High-calorie, fatty, fried foods and smoked foods are excluded from the diet. At the same time, phospholipids, fat-soluble vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids are additionally introduced.
Dishes should be easily digestible, low-fat and steamed or baked. Such dishes do not require stress on the enzyme systems of the gastrointestinal tract. Recommended are cereal and vegetable puree soups, vegetable purees, stewed vegetables, meat and fish balls, boiled meat, steamed cutlets, non-sour cottage cheese, curd casseroles, omelettes, and fermented milk products. The volume of dishes should not cause discomfort. To prevent flatulence , dishes made from legumes and white cabbage are excluded.
Carbohydrates are the second component of nutrition, an excess of which in the diet leads to impaired lipid metabolism and the development of fatty infiltration of the pancreas. In this regard, the consumption of simple carbohydrates and sugary drinks is significantly limited. It has been established that sucrose and fructose influence the development of fatty infiltration of organs - they increase lipogenesis, cause insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridemia .
Malt and maltodextrose are widely used in the food industry (confectionery, dairy products, sauces), and their glycemic index is higher than sugar. If carbohydrate metabolism is impaired, carbohydrates should be evenly distributed throughout the day to avoid sudden fluctuations in glucose levels. Sources of carbohydrates for such patients are whole grain cereals (buckwheat, oatmeal), bran and whole grain bread, unsweetened berries and fruits, baked apples.
The third main point of nutrition is to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages!
Treatment of diffuse changes in the pancreas such as lipomatosis: medications and diet
Basic fat (lipoma)
The pancreas is a vital organ, the functional disorders of which lead to disorder of the entire organism. Lipomatosis or fatty degeneration are diseases that disrupt the functioning of the digestive system. Treatment of pancreatic lipomatosis requires compliance with rules and lifestyle changes.
The mechanism of occurrence of pancreatic pathology
Lipomatosis is a disease leading to a functional disorder (ICD-10 code K86). Due to various factors, pancreatic cells gradually die. Adipose tissue is formed - a compensatory reaction of the body aimed at restoring the missing volume of the organ. Fat cannot perform the functions taken over by glandular cells.
The replacement process is benign. The growth of a fatty tumor does not lead to the development of malignant tumors, but treatment is necessary.
Pancreatic lipomatosis goes through 3 stages of development:
- First degree. No more than 30% of the digestive system organ was affected.
- The second stage affects 30-60%. There are clinical signs of the disease.
- Third degree. More than 60%. Pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus develop through the destruction of insulin-producing cells.
Methods of treating the disease
Treatment of changes in the type of liposomes is carried out by conservative and surgical methods.
Do you need to consult an experienced doctor? Ask your question right now.
Ask your free question
- The therapeutic method includes the use of medicines and local residents, a special diet.
- The surgical method is a surgical procedure.
- Indications for surgery: significant damage to the pancreas, adipose tissue puts pressure on the ducts and neighboring organs (liver, duodenum).
- Prevention of surgical interventions - timely diagnosis of pancreatic lipomatosis.
Pharmacy drugs
Drug therapy allows the affected organ to adapt, eliminates symptoms of discomfort and improves well-being.
| Drug group | Effect | List of effective remedies |
| Fermenter | Remedy for enzyme deficiency. Normalize the digestion process. Eliminate the feeling of heaviness after eating, flatulence, flatulence. Fill hormone deficiency. Prevention of the development of concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system. |
|
| Antispasmodic | Eliminates spasms, stops chronic pain. Normalize the patient’s condition during treatment, eliminate discomfort in the stomach and left hypochondrium. |
|
| Symptoms | Treatment of associated symptoms caused by glandular and digestive disorders. Helps cope with attacks of nausea and vomiting. Regulates bowel movements, prevents the development of diarrhea and constipation. |
|
When diagnosed with pancreatic lipomatosis, self-medication with medications is possible only if there is medical evidence. The problem is especially acute when the disease is diagnosed in a child.
Folk remedies
At an early stage, lipomatous growth can be stopped, and the function of the gland can be partially restored with decoctions and tinctures.
Recipes:
- Oat decoction. The drug helps fight tumors, restores secretion function, establishes metabolic processes, and digestive function. Daily use. Daily dose: 500 ml.
- An infusion of blueberry leaves has regulating properties. Used for treatment 100 ml twice a day before meals.
- Fresh cranberries prevent further development of pancreatic lipomatosis and improve metabolic processes.
- A decoction of blackberry leaves is effective for diffuse lesions. The drink is taken 4 times a day for 1 month, 30 milliliters per drink.
- Tincture based on the collection: calendula root, St. John's wort, valerian, mixed with nettle leaves. Treatment lasts 21 days, after which a 7-day break is required. Daily dose: 250 ml.
Treatment of pancreatic lipomatosis using folklore methods is allowed only after consultation with a doctor.
The use of folk remedies is combined with pharmacological drugs in complex therapy.
Sample menu for lipomatosis
The diet should be balanced and low in calories. Unhealthy foods are excluded. Following a diet in the early stages of the disease allows you to stop the degenerative process, and in later stages it helps to maintain the body’s performance. The “Table 5” diet is recommended.
A sample diet for one week in the case of pancreatic lipomatosis allows you to prepare your own diet based on a list of desired foods and dishes. This is combined with drug treatment.
Monday
- Breakfast - liquid semolina.
- Lunch - buckwheat soup with vegetable broth, thin mashed potatoes, steamed rabbit meatballs.
- Dinner - steamed omelet. Tuesday
Tuesday
- Breakfast: low-fat cottage cheese.
- Lunch - grated wheat soup in broth, vegetable puree with cod.
- Dinner - rice porridge with chicken fillet.
Wednesday
- Breakfast - steamed omelet.
- Lunch - chicken broth with grated vegetables, steamed porridge, meat chops without fat.
- Dinner - mashed potatoes or turnips with boiled, lean fish.
Thursday
- Breakfast - Thin milk bread.
- Lunch - grated vegetable soup, durum wheat noodles with steamed meatballs.
- Dinner - oatmeal with fish chops.
You may be interested in: Removal of a polyp in the bladder: how does the operation proceed, what is the cost?
Friday
- breakfast - rice porridge.
- Lunch - thick soup of vegetables and rice, boiled vegetables with rabbit meat.
- Dinner - steamed chicken soufflé.
Saturday
- Breakfast - Hercules porridge liquid.
- Lunch - soup with vegetables, meat casserole, boiled vegetables.
- Dinner - light porridge with steamed fish chops.
Sunday
- Breakfast - an egg with a dent.
- Lunch - rice soup with lean meat broth, vegetable puree with meatballs.
- Dinner - durum wheat noodles without oil, vegetable stew.
For proper nutrition, you should consult a doctor or nutritionist.
List of permitted and prohibited products
When developing diseases of the digestive system, it is important to remember that the diet depends on permitted and prohibited foods.
List of approved foods for pancreatic lipomatosis:
- dietary meat - chicken, turkey, rabbit, beef;
- low-fat fish - cod, pike, pike perch, bream, site;
- skim milk and fermented milk products;
- cereals - buckwheat, barley, rice, oatmeal;
- hard wheat noodles;
- dried eggs (chicken, quail), steamed omelettes;
- jelly, herbal tea, dried fruit compote.
Alcoholic drinks, smoked products, pickles, spices, beans, mushrooms, cabbage, baked goods and flour products should be excluded from the diet. Fatty broths, fish and meat are prohibited. This helps treat pathologies.
Reduce or give up sweets completely.
Contraindications: sweet carbonated drinks, all “street” products.
Prognosis and duration of treatment
Diffuse changes in the pancreas with atrophy such as lipomatosis are irreversible. Timely treatment helps stop the development of pathology. If left untreated, the organ completely atrophies, which leads to consequences. When the disease is diagnosed in the early stages, the chances of remission increase and the process of tissue replacement completely stops.
A patient with pancreatic lipomatosis must get rid of bad habits, lose excess weight, and balance her diet. When performing surgical operations to remove atrophied tissue, the patient must recover for a long time. It is necessary to constantly take special medications, robot, to replace the activity of the glands.
Digestive obesity and related complications can be prevented. Prevention - good nutrition, mobile lifestyle, abstinence from alcohol and smoking. It is necessary to undergo a routine medical examination.
The article was checked by the site editors
Didn't find any suitable advice?
Ask your doctor a question or view all questions...
Classify the article:
Download…
Prevention
Primary prevention of this disease includes:
- A balanced diet that prevents weight gain.
- Elimination of alcohol, which is one of the risk factors for steatosis of the liver and pancreas.
- An active lifestyle, which is the prevention of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- If the disease occurs, it is important to adhere to a low-calorie diet that promotes weight loss. A weight loss of even 8% leads to a significant reduction in pancreatic fat. A healthy lifestyle and avoiding alcohol consumption are also important.
Disease prognosis
With an adequate attitude of the patient to the existing problem and the correct organization of the lifestyle, the capabilities of the pancreas are compensated - its healthy areas continue to secrete a sufficient amount of hormones and enzymes to ensure the vital functions of the body.
Long-term remission is possible, but requires close attention of the carrier of lipomatosis.
With insufficient attention to the disease, new disorders are added to the problem (diabetes mellitus, complete indigestion, liver and intestinal diseases, general intoxication).
It is important to know and remember that lipomatosis is a chronic incurable disease, slowly but steadily progressing. The task of patients and doctors is to stop progress and achieve stable remission. Preventive measures and public education can reduce the number of newly ill patients - a healthy lifestyle is increasingly becoming fashionable.
Consequences and complications
The following complications of pancreatic lipomatosis are possible:
- Development of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
- High risk of diabetes mellitus , since the accumulation of fat in the islets of the gland reduces the number and functional activity of β-cells, which leads to impaired carbohydrate metabolism.
- Generalized atherosclerosis .
- Acute pancreatitis .
- Development of adenocarcinoma of the gland. Many scientists believe that it is likely that cancer of this organ will develop as a result of fatty infiltration. They draw an analogy with fatty liver, the outcome of which is hepatocellular carcinoma .
Pancreatic lipoma: how to recognize and how to treat
The pancreas is an endocrine and digestive organ. It produces substances that regulate a number of processes in the body.
Insulin normalizes blood sugar levels and is therefore responsible for carbohydrate metabolism. Enzymes secreted by PJ are essential for normal digestion and absorption of food from GIT.
Every change that occurs in the gland leads to a chain of disorders in other organs.
Pancreatic lipomatosis can be one of the pathologies that a person may encounter. This is the progressive replacement of healthy organ tissue with fat.
The accumulation of adipose tissue in a separate area forms a benign lipomatous tumor that does not form metastases. This disease is also known as fatty degeneration.
Its progression gradually leads to gland dysfunction, which causes certain unpleasant symptoms. It is very important to recognize and treat lipomatosis in time.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Inflammatory and infectious processes in the PG lead to tissue degradation and necrosis in certain areas. If treatment is carried out on time and completely, the growth of pathogenic microflora stops and the organ stops working. At the site of the damaged infection, new areas are formed.
Often the resulting lumen is filled with adipose tissue. This means that lipomas (fats) are formed. In most cases, the trigger for the formation of lipomas in the pancreas is an inflammatory process in the organ (pancreatitis). This causes damage and destruction of the cellular structures of the pancreas.
They are gradually replaced by adipose tissue.
Factors contributing to the formation of lipomas:
- hereditary predisposition,
- chronic liver diseases, hepatitis,
- alcohol abuse,
- hypothyroidism,
- Diabetes,
- Abdominal injury
- Taking drugs that destroy PG cells
- Overweight.
Which organ produces insulin and what role does the storage hormone play? Check out useful information.
For symptoms and treatment of an isoechoic thyroid with a hypoechoic rim, read this article.
Characteristic symptoms
The pancreatic lipoma did not appear for a very long period of time. It develops slowly over the years. Fatty degeneration is often accidentally discovered during ultrasound examination.
The primary signs of fatty degeneration are minor and often overlooked. Their severity directly depends on the size and degree of replacement of healthy tissues with fat.
If less than 30% of the organ is damaged, the patient may feel little or no change.
Symptoms of pancreatic lipoma:
- Pain in the left hypochondrium, pancreas,
- Feeling of heaviness after eating
- Injuries to intestinal motility,
- Steatorrhea (fecal fat),
- Nausea, vomiting,
- General malaise,
- Loss of appetite,
- Apathy.
Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism are observed when glucose levels increase due to a decrease in insulin synthesis. As the fatty tumor grows, it begins to put pressure on glandular ducts, blood vessels and nerve fibers. As a result, a number of associated symptoms may occur.
Classification
Many experts define 3 degrees of lipomatosis:
- 1 1 less than 30% of PG tissue is affected. The disease does not manifest itself through severe symptoms.
- 2 Adipose tissue replaced 30-60% of the organ tissue. There are characteristic dyspeptic disorders.
- 3 More than 60% of the pancreas tissue is damaged. Disturbances become noticeable in the functioning of the whole organism.
This classification of lipoma is not shared by all specialists. In some cases, the disease may be more dangerous than in others already at stage 1.
There is another classification, where the severity of the process is determined by the amount of damage:
- Holes (focal) Lipoma fat replaces healthy fat in a certain part of the PG. Such a formation is very dangerous if it is located in the area of glandular ducts and vessels.
- Diffuse foci of fat degeneration are scattered throughout the body, they are usually small.
For the record! Sometimes fibrolipora are found in the PJ. These are areas where healthy tissue is replaced not only by fatty tissue, but also by fibrous (connective) tissue. The progression of this type of formation is more severe than with a simple lipoma.
Effective treatments
Although pancreatic lipoma is not classified as a dangerous pathology, it is constantly progressing and leads to significant organ dysfunction. Therefore, early diagnosis of changes and treatment of lipoma is very important. Depending on the stage and severity, conservative or surgical treatment may be offered.
Conservative therapy
For diffuse lipoma, a therapeutic diet and taking certain groups of medications are recommended. Nutritional correction is necessary in order to free the affected organ and provide the body with all nutrients.
For diseases of the pancreas, a diet similar to Table 5 is recommended. The diet requires a complete rejection of fatty, fried, spicy, and salty foods.
You cannot drink alcohol, coffee, chocolate or cakes. Food should be steamed or cooked. You should eat small meals 5-6 times a day.
In the case of lipoma, it makes sense to eat buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, pumpkin, cabbage, and fermented milk products.
There are no specific medications that can cure lipomatosis. Medicines are prescribed by a doctor to relieve symptoms of the disease:
- antispasmodic (drotaverine, No-Spa),
- antidiarrheal agent (loperamide),
- enzymes (Festal, Creon),
- in case of deficiency of insulin synthesis, its synthetic analogues.
Where is the thymus gland and what hormones are produced by this important endocrine organ? We have the answer!
In this article you can read about the causes of hemorrhagic ovarian cysts and treatment options for neoplasia.
Read on the website https://fr-dc.ru/vnutrennaja-sekretsija/shhitovidnaya/gormony-zhelezy.html about the standard of thyroid hormones and the role of important regulators in human life.
Surgical intervention
Surgery may be performed when the lipoma reaches a large size and puts pressure on nearby organs. Surgical removal of the lipoma is indicated for the island form of the pathology.
Non-functioning areas of the pancreas must be excised; in some cases, the organ is completely removed.
In case of complete pancreatectomy with subsequently prescribed lifelong use of PS enzymes and insulin injections as replacement therapy.
Forecast
Lipomatosis is a chronic, slowly progressive disease that ends with fibrosis of the gland tissue. The danger of the disease lies in the reduction of functional cells. The main goal of treatment is to stop progression. With adequate treatment, elimination of risk factors and lifestyle changes, the prognosis is favorable. If the recommendations are followed, the progression of fatty changes in the gland often stops and does not reach pronounced changes in the organ.
Definition of disease
Any inflammation of the pancreas is accompanied by decay and necrosis of tissue in a certain area. If further destruction is stopped and the infection is defeated, the spread of microbes stops, the organ recovers and restores function. But nature does not tolerate emptiness, so new ones are formed in place of areas destroyed by pathogenic agents. Most often, this is adipose tissue that fills the resulting gap in the flesh of the pancreas. Each such area is a lipoma (fat). The presence of lipomas on the body of the gland or in its flesh indicates lipomatosis - irreversible changes in the structure and functioning of the pancreas. Adipose tissue replaces normal cells of the organ, interrupts their work, and weakens the functionality of the gland.
List of sources
- Ivashkin V.T. Pancreatic steatosis and its clinical significance // Ros. Journal of gastroenterology, hepatology, coloproctology. 2006. T. 16. No. 4. P. 32–37.
- Bokova T. A., Ursova N. I. Morphofunctional state of the pancreas in children and adolescents with obesity and metabolic syndrome // Experimental and clinical gastroenterology. 2008. No. 7. pp. 24–29.
- Ivashkin V.T., Shifrin I.A., Sokolina I.A. Chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic steatosis and steatopancreatitis. M.: Litterra, 2014. 240 p.
- Kucheryavyi Yu.A., Moskaleva A.B., Maev I.V. Baranskaya E.K., Sviridova A.V. The relationship of chronic pancreatitis with fatty liver disease and carbohydrate metabolism disorders in obese patients // Effective pharmacotherapy. 2011, no. 6. pp. 44–48.
- Kosyura S.D., Pavlovskaya E.V., Starodubtseva A.V. Damage to the pancreas in obesity // Medical Affairs. 2006. No. 3 P.23-26