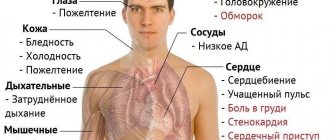
A gastroscope is a flexible tube with a complex optical system. It is injected into the stomach and allows you to see the condition of its mucous membrane and take material for microscopic examination.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy: what is it?
FGDS (endoscopy, gastroscopy) is considered a classic procedure in medicine, carried out to detect and also study diseases of the stomach and esophagus.
Prescribed by a specialist for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
The essence of the method is for the patient to swallow a special diagnostic device - a gastroduodenoscope (endoscope) . It is in most cases presented in the form of a flexible fiber optical tube. It is based on a bundle of glass threads (rod) and a head with a built-in lens or video camera.
When the device is inserted into the esophagus, a thorough examination (including photo and video recording) of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out, revealing not only inflammatory processes, but also erosion, ulcers and even tumors . The procedure also makes it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of the patient’s course of treatment or to identify the cause and source of bleeding and eliminate it.
The procedure is performed by a specialized doctor - endoscopist .
The method is unique in a large number of positive features:
- High information content ;
- Painless;
- Safety for gastric tissue;
- Possibility of performing several diagnostic procedures ;
- Possibility of performing the procedure without hospitalization.
the disadvantages of gastroscopy, perhaps only slight discomfort directly during swallowing of the probe.
Diagnostic results
As a rule, video gastroscopy makes it possible to make a final diagnosis during the examination. More accurate data become known after examining the biopsy specimen. Based on them, the doctor writes a conclusion. It is accompanied by digital materials: endophotography, video recording of research. They will help in the future to monitor the effectiveness of treatment or the progress of pathology. Also, the results are presented in the form of a form that describes the condition of the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach, and any existing pathological changes are noted.
Indications for use
FGDS is indicated in many cases, and there are a number of specific symptoms in which the procedure is performed as planned, and there are also individual situations when the patient requires emergency gastroscopy.
So, planned is provided for when the patient complains of:
- Moderate/severe pain in various areas of the stomach (upper section, hypochondrium, etc.), occurring either in the morning before eating or immediately after eating;
- Problems with swallowing;
- Frequent heartburn;
- Frequent vomiting;
- Sudden and severe weight loss;
- Problems with appetite or lack thereof;
- Anemia of unknown origin;
- Frequent bloating or belching after eating.
Based on the symptoms, FGDS is prescribed as a control procedure to identify the following diseases:
- Gastric polyps are pathological growths on the inner wall of the stomach. They do not manifest themselves symptomatically, can be detected and removed using FGDS;
- Gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which manifests itself in frequent heartburn, stomach pain, weight loss, etc. FG;
- Pancreatitis – dysfunction of the pancreas and compaction of parenchymal tissue;
- An ulcer is a deep lesion of the gastric mucosa, manifested in the form of severe pain and nausea after eating, sour belching, a feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- Cholecystitis - manifests itself as an inflammatory process in the gallbladder;
- Duodenitis is a change in the duodenal mucosa, which manifests itself in frequent nausea, weakness, pain in the epigastric region;
- Esophageal cancer is the formation of a tumor of the gastric mucosa. It manifests itself in the form of frequent vomiting, impaired swallowing function, chest pain, putrid odor from the mouth.
In addition, the procedure is often prescribed as a preparatory stage before abdominal or long-term operations , to control gastric pathologies, after removal of polyps, for diseases of the liver, pancreas, and in cases of suspected oncology.
Please note: In a number of situations, FGDS becomes not a desirable, but a necessary procedure: in the presence of foreign bodies, bleeding in the stomach, or to determine the causative agent of an ulcer.
Types of gastric endoscopy
FGDS is conventionally divided into several main types:
- Video FGDS . The simplest and most unpleasant option for the patient is the procedure. A special probe is used with a small video camera at the tip , which allows you to display an enlarged image of the internal organs on the monitor screen, which makes it possible to clearly examine the gastric mucosa in great detail. But the method is not the most pleasant and is done without anesthesia.
- Transnasal FGDS . This is the best option for those patients who, due to certain circumstances, cannot undergo classical FGDS (for example, with an irritated root of the tongue or strong vomiting). The transnasal method of guiding the probe is a real salvation in situations where the risk of organ perforation is high (for example, burns, tumors, narrowed esophagus, etc.) and the standard size probe used for conventional FGDS is simply contraindicated for use.
- Endosonography . This is a modern endoscopy method with ultrasound capabilities. This research method allows , using an ultrasound probe, to study in detail a previously detected and confirmed pathology , for example, damage to stomach tissue by a tumor, namely: the degree and depth of damage to the walls of the organ. This allows you to adjust actions during surgery.
Capsule endoscopy . One of the most technologically advanced, but also expensive methods of diagnosing the gastric region. The instrument uses a tiny capsule with a mini-color camera and a built-in radio transmitter , which the patient needs to swallow with water. During its “journey,” the pill examines the gastrointestinal tract in detail and reports the results to the reader.- short-term sedatives A method that is suitable for those who want to undergo a painless examination. The procedure is most often prescribed for children and the elderly. During its implementation, the patient falls into a light doze , sees and understands everything, but feels nothing. Drowsiness goes away within 30 minutes.
Testing without swallowing the tube and probe
If it is absolutely impossible to perform a classic gastroscopy, if the patient has contraindications, there is an alternative method of visual examination of the gastrointestinal tract. This is a capsule FGDS - the patient swallows not a tube, but a small chamber in the form of a capsule. It sequentially passes through all parts of the gastrointestinal tract and leaves the body naturally. The data recorded by the camera is then transferred to a computer where the doctor can study it.
This lightweight method is no less informative than classic gastroscopy; it allows you to study not only the upper gastrointestinal tract, but also the entire intestine from the inside. However, it is not performed on all patients. The cost of such a study is very high - together with the capsule itself, the price of the procedure is within 50 thousand rubles.
As with classical gastroscopy, there are several contraindications:
- swallowing disorder;
- installed pacemaker;
- epilepsy;
- intestinal obstruction.
The preparation required is the same as for conventional FGDS. The capsule passes through the entire gastrointestinal tract in 12-14 hours, so the test result is issued the next day.
Capsule FGDS
Preparation: some important tips
You should prepare very seriously for gastroscopy, as for any other research method, since the comfort and effectiveness of the procedure depends on this. The following is a reminder for the patient that will help simplify the process of fibrogastroduodenoscopy:
You should not eat at least 8 hours before the procedure, as your stomach must be empty. If you neglect this rule, doing the test may be pointless because either the results will end up being inaccurate or the procedure will cause vomiting.
- On the day of FGDS, you must be careful about taking medications (it is advisable to consult with a gastroenterologist first).
- Some time before gastroscopy, you need to give up cigarettes and alcohol , as they irritate the stomach and create a feeling of nausea.
- Do not use perfume before the procedure .
- It is important to warn the specialist before the procedure about all concomitant diseases and medications taken (this point is especially important for allergy sufferers, chronically ill patients, and pregnant women).
- It is necessary to come to the procedure in loose clothing and with the appropriate attitude (in a calm, relaxed state) .
- You can drink water an hour before the procedure . No more than half a glass of water.
- You can brush your teeth before the examination . But you should refrain from chewing gum.
If acidity is to be determined, then it is necessary to stop taking medications that affect it . We are talking about several types of drugs:
- Antisecretory (lowering pH). These include proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Lanzoprazole), anticholinergics, bismuth preparations , etc.
- Stimulating/replacing pH . Pentagastrin, Lemontar, preparations based on plantain, etc.
- Antacids . Neutralizers that maintain normal acidity or reduce it (Rennie, Tams, Maalox, Gastrocid, Gaviscon, etc.).
To make the examination comfortable and easy, it is important to follow a special diet for several days before the examination, while temporarily changing your rhythm of life. So, in 3-4 days you should exclude from the diet :
- Liquid food;
- Fatty, spicy, salty foods;
- Pickles;
- Some drinks (sparkling water, juices, alcohol);
- Nuts, seeds;
- Vegetables/fruits with a high content of acids (tomatoes, peaches, plums, apples, etc.);
- Legumes;
- Baking;
- Dairy products.
As dietary foods, you can eat baked vegetables, low-fat fish, boiled chicken, eggs (except fried), herbal teas (without sugar), water . In the evening the day before the test, have a light dinner at least 2 hours before bedtime .
Please note: If you follow a diet before gastroscopy, you need to eat 5-6 times a day (little by little). If discomfort occurs in the stomach even while taking certain dietary foods, you should also avoid them.
It is worth noting that endoscopy is completely safe for pregnant and lactating women . If gastroscopy is performed on a child, it is very important to first prepare him for diagnosis by describing in detail the essence of the procedure, as well as practicing measured breathing through his nose with his mouth open.
It is equally important for mothers to behave correctly during the procedure : the voice should be calm and quiet, since babies always feel any changes in their mother’s mood.
Three ways to perform gastroscopy
Modern medicine can offer three ways to perform gastroscopy.
Option one “Inexpensive, traditional, but improved”
Not everyone is destined to force themselves to swallow the proposed flexible hose, but gastroscopy is a must. However, doctors today suppress all gag reflexes, calm the nervous system and drive away all fears. We are talking about swallowing an ordinary probe.
However, endosonography, which is an ultrasound, has also been added to this procedure. If a tumor is suspected and the diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy samples, all further studies are already carried out using ultrasound. X-rays are not required in this case.
Option two “During sleep”
Let’s admit right away – it’s extremely expensive. It all comes down to the fact that the necessary manipulations are performed not under anesthesia, but during sleep, which is achieved by using short-term sleeping pills. In this case, no painkillers are used and no ultrasound is required.
Option two “Nowhere more expensive”
Since this process of gastroscopy is crammed with modern advances in science and technology, it is very expensive. It involves swallowing a disposable capsule, which is a tiny device that travels through the patient’s digestive system. During such a run, everything is recorded and recorded. A miniature color video camera is built into a pill no larger than 1.5 cm. In offline mode, the device operates from 6 to 8 hours.
This capsule is swallowed with a glass of water and forgotten until it is released naturally. After this, the material goes into the hands of a doctor for examination. In many cases of gastroscopy, this option is more than justified; for example, it has no equal for detecting intestinal cancer. However, a biopsy cannot be performed using the capsule.
More details about all methods of gastroscopy in the next video clip.
Photo
Fig.1. Endoscope image
Fig.2. Insertion of the device after surgery
Fig.3. Scheme of gastroscopy
Fig.4. Passing the device through internal organs
How do they do it?
Traditionally, the procedure is carried out in the morning. First, the patient goes to the specialist’s office to sign an agreement in which he consents to the procedure.
It is important to understand that FGDS can be completed completely painlessly and without sedation. The doctor will not intentionally hurt you. As long as you are relaxed and maintain a calm breathing rhythm, the endoscope will advance without causing pain or discomfort.
The procedure is done in a certain way, depending on the type of research. So, for standard manipulation, the patient is asked to lie on the couch (on his left side) and the gastroenterologist irrigates the patient’s nasopharynx with an anesthetic. A couple of minutes after the anesthesia begins to take effect, the patient should grab the mouthpiece with his teeth, which will help avoid injury to the teeth and mucous membranes of the lips.
Then the most important stage begins - inserting the tube through the pharynx into the esophagus. The process takes a few seconds and as the probe passes through the esophagus, the person experiences the urge to vomit, which must be overcome. To make it easier to endure the insertion of the endoscope, breathe calmly, measuredly, without strong swallowing movements . Try concentrating on your breathing and counting your exhalations and inhalations. Afterwards, it is important to relax and the doctor will begin to examine the internal organs.
How long you relax and let the doctor do his job will determine how long the examination will take. On average, the whole process takes 5-10 minutes.
Some time after the FGDS, the patient is given a conclusion with the diagnosis (or to his attending physician).
Please note: When performing pediatric gastroscopy, a smaller probe is used than for an adult. If the standard length of the probe is about 120 cm, devices with a length of about 50-70 cm are used for children. The diameter of the tube is 13 mm.
Transnasal gastroscopy does not differ from the standard procedure in any way, except for the location of the probe insertion - through the nasopharynx.
First, the patient also lies on his left side, then his nasopharynx is treated with an anesthetic, and after a few minutes a probe is inserted through the nostrils.
In this case, there is no discomfort or gagging . After the end of the manipulation, the patient can receive a conclusion.
When using the pill, the patient does not need to do anything at all except take the pill with water. It will independently go the entire “path” through the gastrointestinal tract and transmit the results to the reader.
FGDS with the help of sedatives is the simplest of the presented options using an endoscope. The positive side of this diagnostic method is the absence of anesthesia as such, because drug-induced sleep is easily tolerated : after the procedure is completed, there is no lethargy or lethargy , and literally after 40 minutes you can leave the clinic. However, it is advisable not to drive a car during the day.
Additional Research
FGDS allows, in addition to diagnosis, to do a number of tests for the purpose of treating/detecting concomitant diseases.
Thus, it is possible to eliminate venous bleeding of the esophagus by injecting a special “gluing” solution into its veins. The procedure also helps remove small tumors (or take a tissue sample for analysis), polyps or foreign bodies from the stomach , if any are present.
When performing a gastroscopy, you can take several tests:
- Detection of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori , which destroys gastric tissue and provokes the development of serious gastrointestinal pathologies (from gastritis to stomach cancer);
- pH-metry to study acid-forming/neutralizing gastric function (especially relevant for acid-related gastrointestinal disorders);
- Biopsy . A sample of mucous tissue is taken using endoscopy for the purpose of histological examination for the presence of cancer cells.
Some of the tests that are taken during FGDS are specified by the specialist in advance, but a biopsy can be carried out without the consent of the patient , depending on the condition of the gastric mucosa.
Advantages and disadvantages
Fibrogastroscopy has a number of positive and negative aspects, taking into account which the need for it is determined.
The pros and cons of gastroscopy are presented in the table:
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
Consequences of the procedure
Complications rarely occur after FGDS (less than 1% of patients). Most often, you may experience an unpleasant sore throat , which usually goes away after 2 days . The most important thing is that after the procedure, for 2-3 days, protect the stomach and throat from exposure to coarse, hard food : it is better to eat light liquid cereals, purees, light soups, eat liquid dairy products, etc.
Help In very rare cases, after gastroscopy, allergic reactions (to the anesthetic), perforation of the esophagus or bleeding (against the background of an existing disease) are possible.