Home » Rectal fistulas
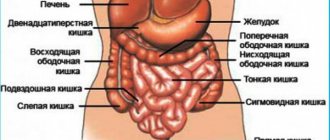
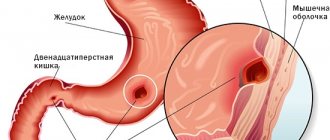
Rectal fistula is a chronic form of paraproctitis. Characterized by the appearance of deep fistulas or canals. Neoplasms are located between the perirectal tissue and the rectum. The main symptoms are bloody and purulent discharge from the anus. Maceria appears, itching and burning in the anal canal, the skin becomes irritated.
The following studies are carried out as diagnostics:
- probing pathological passages;
- anoscopy;
- fistulography;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- irrigoscopy;
- ultrasonography;
- sphincterometry;
Surgical treatment is also used, which includes excision of the fistula in the rectum. Treatment depends on the stage of paraproctitis.
The fistula is formed due to chronic inflammation of the anal crypt, pararectal tissue and intersphincteric space. These areas lead to the formation of a fistula tract. The anal crypt is also an internal fistulous opening. Recurrence of rectal fistula is extremely common. The patient notices a general deterioration in his condition, stomach pain, and gastrointestinal disorders.
If there is no timely treatment, the fistula enlarges and leads to rectal cancer and other complications. Timely detection of pathology and initiation of treatment reduces the risk of relapse to zero.
Causes
According to medical statistics, 95% of fistulas located in the rectum are the result of acute purulent paraproctitis. A dangerous infection penetrates deep into the walls of the rectum, which surrounds the tissue. A perirectal abscess forms. Over time, it opens, and as a result, a fistula forms. A rectal fistula is formed if the patient does not consult a doctor on time and ignores the symptoms that appeared in the early stages of the disease.
The cause of acute paraproctitis is also non-radical surgical intervention, which was performed by incompetent doctors.
In some cases, neoplasms appear after injury or after surgery. Occur due to resection of the rectum. In women, proctological pathology is diagnosed much more often. Fistulas that connect the rectum and vagina are the result of birth injuries. This occurs with pelvic recumbency of the fetus, with ruptures of the birth canal, with prolonged labor, and with the use of obstetric aid.
Acute paraproctitis occurs in people who suffer from rectal cancer, tuberculosis, chlamydia, AIDS, Crohn's disease, diverticular intestinal disease, actinomycosis and other diseases.
Classification
Based on the number of formations and location of openings, rectal fistulas are:
- full;
- incomplete;
The entrance hole of a complete fistula is located on the wall of the rectum. The outlet is located in the soft tissue around the anus. In most cases, proctologists find several inlet openings that merge in the perirectal tissue and form one canal. The exit hole in this case is located on the skin.
An incomplete fistula has only one entrance hole. Located on the perirectal tissue. The purulent processes that occur during the disease contribute to the fistula getting out, after which it turns into a complete one.
According to the location of the internal opening on the wall of the rectum, fistulas are distinguished:
- anterior localization;
- posterior localization;
- lateral localization.
According to the location of the fistula tract relative to the anal sphincter, rectal fistulas are:
- intrasphincteric;
- transsphincteric;
- extrasphincteric.
Intrasphincteric fistulas are called marginal subcutaneous-submucosal fistulas. A direct fistulous tract is diagnosed, which has an external opening in the anus. The internal hole is located in the crypt.
Transsphincteric fistulas are located in the subcutaneous, superficial or deep portion of the sphincter. Fistula tracts become branched, have purulent pockets in the tissue, which are expressed by a scarring process in the soft tissues.
Extrasphincteral fistulas are located in the rectum and affect the external sphincter. The neoplasms open with an internal opening in the crypt area. This type of fistula is the result of lack of treatment for acute paraproctitis. The fistula tract becomes long and tortuous. It forms purulent streaks, mucous discharge, scars, and fistula openings.
What is a rectal fistula and how does it form?
The formation of a fistula occurs when suppuration during paraproctitis is opened, but the cavity in which the contents were located has not healed. Through the formed channel, an infection penetrates into the perirectal tissue space, which maintains inflammation in the tissues. At the same time, pus begins to form again, melting the tissue located next to the lesion. The outlet of such suppuration often forms outside - on the surface of the skin.
Types of extrasphincteral fistulas
There are several types of extrasphincteral fistulas according to the degree of complexity:
| Degree of difficulty | Characteristic |
| Fistulas 1st degree | There is a narrow opening inside and a straight course of the rectum. There are no purulent accumulations, scars or cracks in the tissue. There are no infiltrates. |
| Fistulas 2nd degree | The inside of the anus is surrounded by cracks and scars. There are no inflammatory or infectious processes. In general, the patient's condition is satisfactory. |
| Fistulas 3rd degree | There are no scars in the narrow internal opening. A purulent-inflammatory process is observed in the fiber. The patient suffers from itching and burning in the anus. |
| Fistulas 4 degrees | The internal opening of the purulent fistula is surrounded by scars. A large number of inflammatory and infectious infiltrates and purulent streaks appear in the tissue. |
Each stage of the disease is dangerous in its own way, so it is worth starting treatment immediately.
Our specialists
Tolstykh Vladimir Sergeevich
Proctologist, surgeon, coloproctologist of the highest qualification category. Member of the European Association of Coloproctology (ESCP). Member of the Russian Society of Surgeons ROH. Member of the Russian Society of Colorectal Surgeons ROKH.
Medical experience since 2005.
Trained at the Agency for Medical Innovation Technologies (Austria). Proficient in all modern methods of treating diseases of the colon and rectum. Author of publications in Russian and foreign scientific publications.
Certificates Tolstykh V.S.
Kharabet Efim Igorevich
Coloproctologist. Doctor of the first qualification category.
Medical experience since 2000.
Specialization: minimally invasive surgical techniques for the treatment of hemorrhoids. Instrumental diagnostic methods in coloproctology.
Certificates of Kharabet E.F.
Garanina Anna Stanislavovna
Coloproctologist surgeon, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Medical experience since 1991.
Specialization: minimally invasive surgical techniques for the treatment of hemorrhoids. Instrumental diagnostic methods in coloproctology.
Diplomas and certificates of A. S. Garanina
Paraproctitis: symptoms and treatment
In the early stages of the disease there are no symptoms. In some cases, the patient develops wounds on the skin of the anal area that bleed after defecation. Pus, mucous and bloody brown discharge appear on the affected area. The patient notices discharge on underwear, on the bed and on toilet paper. There is a need to use sanitary pads. The patient should rinse the anus several times a day and use disinfectants.
Pain occurs during bowel movements, coughing and walking. Severe discomfort occurs if an incomplete internal fistula is formed after chronic inflammation in the anal sphincter. The patient feels spasm and cutting pain as stool passes through the rectum.
Rectal fistulas are known for their undulating course. Exacerbation of proctological disease occurs due to blockage of the fistula tract with granulation tissue and purulent-necrotic mass. This process forms an abscess after the purulent fistula has opened. Painful sensations disappear, the amount of purulent and mucous discharge decreases. The wound heals, soft tissues are regenerated. Without treatment, the pain subsides, however, the source of the disease. A relapse soon occurs.
During remission, the patient's general condition worsens, pain and burning appear in the anal area. If the patient follows the rules of personal hygiene, the symptoms disappear for a while. Lack of diagnosis and medical supervision leads to asthenia. Sleep deteriorates, regular headaches appear, temperature and blood pressure rise, performance and potency decrease. The patient becomes irritated and nervous.
Features of the rehabilitation period
After recovery from anesthesia, pain appears for a short period. The patient is prescribed painkillers and antispasmodics. To avoid postoperative complications, treatment with antibacterial agents is used. For seven days after the operation, the patient takes broths, cereals, and drinking water. The consumption of fried and salty foods, baked goods, carbonated and alcoholic drinks is excluded.
After a few days, the transition to fractional meals occurs. The patient eats 5 times a day in small portions. You should include foods with a lot of fiber in your diet. Intestinal function will be normalized, constipation and diarrhea will disappear. For a quick recovery, you need to walk in the fresh air for thirty minutes every day. Exercising in the morning is welcome, as it will improve muscle tone.
The recovery period takes 4 weeks. You should avoid physical activity and heavy lifting. It is recommended to visit your doctor to monitor the condition of the wound. Every day, the affected area is washed with warm water and disinfected with antiseptics. It is necessary to establish a daily routine, including proper sleep.
To receive expanded information about the operation and complex studies, fill out an application on the official website of the proctology clinic. An employee of the medical institution will call you back and tell you in detail about the procedures being carried out.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, the patient visits a proctologist. During the consultation, the medical specialist asks the patient about complaints, symptoms, nature and intensity of pain. A clinical examination and instrumental examinations are carried out. Among them:
- probing;
- fistulography;
- ultrasonography;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- irrigoscopy;
In the absence of contraindications, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography or ultrasound diagnostics are performed.
A complete rectal fistula is located in the perianal region. The proctologist notices the external opening during palpation and visual inspection. When you press on the tumor, mucous fluid and pus are released. Fistulas that occur after acute paraproctitis have one external opening.
Two holes are located on the sides of the anus and indicate a horseshoe fistula of the rectum. A large number of external holes are observed during specific processes. In acute paraproctitis, discharge from the anus has a toxic yellow color. There is no odor in purulent discharge. With actinomycosis, the discharge is called scanty and cheesy. The presence of bloody mucus may indicate the appearance of a malignant neoplasm.
With an incomplete internal fistula of the rectum, only an internal opening is observed. The presence of a formation is determined only by a rectal digital examination by a proctologist. Female representatives are required to undergo a gynecological examination, which will exclude the presence of a fistula in the vagina.
For diagnosis, the following diagnostic studies are carried out:
- probing of the rectal fistula - a medical specialist examines the fistula and its direction. The branching of soft tissues, the appearance of purulent pockets, and the state of the passage to the sphincter are examined;
- anoscopy and dye tests - the length and shape of the pathological canal is determined. Dye tests are carried out using a methylene blue solution. If the dye test is negative, fistulography is indicated;
- sigmoidoscopy - allows you to assess the condition of the rectal mucosa and soft tissues, detect benign and malignant neoplasms, the presence of inflammatory processes;
- irrigoscopy with barium enema - has a differential value and examines the rectum as a whole;
- sphincterometry - carried out to assess the condition of the anal sphincter in case of complications or relapse;
- ultrasonography - carried out for comprehensive diagnostics of the intestines;
- differential diagnosis of rectal fistulas - carried out to assess the condition of adirectal tissue cysts, epithelial coccygeal tract;
The diagnostic method is selected for each patient individually.
Treatment of chronic paraproctitis
Treatment of acute paraproctitis is carried out only with the use of surgery. During remission or with closed fistula openings, it is not recommended to perform operations, since there are no clear visible landmarks of the neoplasm or the possibility of complete excision of the fistula. Increased risk of soft tissue damage. In case of complications of paraproctitis, the abscess is opened, thereby eliminating the source of the disease and suppuration. The patient is prescribed massive antibiotic therapy, physiotherapy, namely ultraviolet irradiation and electrophoresis. After this, surgery is performed.
At various stages of treatment of paraproctitis, dissection or excision of the purulent fistula into the lumen of the rectum is performed. Additional opening and drainage of purulent areas is carried out. The anal sphincter is sutured, and a mucous or muscle flap is moved to close the internal fistula opening. The choice of treatment method depends on the location of the fistula, the degree of scarring, the presence of infiltrates, and purulent pockets in the anus.
After surgery, relapses may occur due to the fact that the anal sphincter is insufficient. To avoid such complications, you should contact experienced surgeons at the private proctology clinic “Proctologist 81”. Treatment will be effective even in advanced cases. The disease can be detected even at an early stage, when there are no symptoms.
Advantages
Radio wave excision of rectal fistula in Moscow is carried out at the Proctologist 81 clinic. The operation is performed by experienced surgeons and coloproctologists. The cost of excision of a rectal fistula depends on the severity of the pathology. Before surgery, the patient is consulted by an anesthesiologist who selects individual anesthesia. General or epidural anesthesia is used.
The following are the advantages of radio wave excision of a tumor:
- minimally invasive, which guarantees the absence of blood;
- fast healing;
- no risk of relapse or complications;
- absence of swelling and inflammatory processes after surgery;
- painlessness;
- speed of the rehabilitation period;
In addition, after the operation the patient goes home and returns to his usual lifestyle. There is no need for observation in a hospital. Minimally invasive interventions relieve the patient of rectal fistula even in advanced stages.