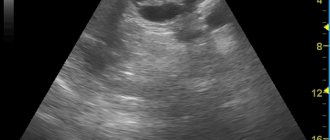
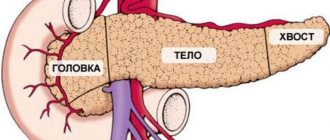
Approximately 75% of pathological cystic formations that are found in the pancreas are pseudocysts. They are cavities that appear after an attack of acute pancreatitis. This usually occurs 6 weeks after its manifestation.
- Why do pseudocysts occur in the pancreas?
- Symptoms and possible complications
- Diagnosis of pancreatic pseudocysts
- Benefits of endoscopic drainage
The prefix “pseudo” is used to distinguish these formations from true cysts and cystic neoplasias. However, the difference between them is small. The main difference is that the wall of a true cyst is lined with epithelial tissue.
At the Euroonko clinic in Moscow, modern endoscopic techniques are used to treat pseudocysts in chronic pancreatitis. Compared to classical interventions, they are less traumatic and more effective. They are also accompanied by a lower risk of complications. After such interventions, patients quickly return to their normal lives and get rid of the causes that led to the symptoms caused by the pseudocyst for a long time.
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
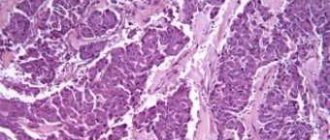
Types of pancreatic cancer include tumors of different etiologies, the most common of which is adenocarcinoma. This is a malignant formation, which includes glandular tissue. If the tumor is benign, then a pancreatic adenoma is diagnosed. Symptoms of a benign pancreatic tumor do not appear until the tumor is large.
As education grows:
hormonal balance is disrupted;- there is a feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- a bursting sensation on the left side of the hypochondrium;
- nausea, which is accompanied by a gag reflex;
- A large tumor puts pressure on the nerve endings, causing quite severe pain.
Adenocarcinoma that develops in the interlobular ducts of the gland is called ductal (ductal, canal). In terms of prevalence, this tumor ranks third among the total number of gastrointestinal cancers.
Causes of pancreatic cancer:
- family history;
- a large amount of animal fats in the diet;
- long smoking history;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- development of chronic pancreatitis;
- obesity.
Often, a ductal tumor is localized in the head of the gland - up to 70% of cases. Using ultrasound and tomography, it is possible to detect a formation as small as 1 cm, that is, the early stage of pancreatic cancer. In practice, adenocarcinomas ranging in size from 2 to 5 cm are diagnosed when signs of the disease are already present. Ductal formations are grayish-yellow and do not have clear boundaries.
Often, a developing tumor puts pressure on the bile duct that passes through it. Stenosis of the main excretory duct of the pancreas may develop. It serves to transport digestive juice to the duodenum, and tumor growth into the intestinal wall is possible.
Further spread of the tumor passes through the vascular structures, affecting:
- aortic opening;
- portal vein;
- inferior vena cava.
In order for pancreatic cancer treatment abroad to be as effective as possible, diagnosticians need to accurately determine the path of tumor spread. During the diagnostic process, the histological structure of the formation is also assessed. Ductal adenocarcinomas are characterized by atypical ductal glandular structures that are well differentiated and accompanied by mucous discharge.
Types of pancreatic cancer in the context of ductal adenocarcinomas:
- adenosquamous carcinomas - such formations include flat stratified epithelium of the pancreas;
- mucinous non-cystic carcinomas - this type of carcinoma is characterized by the formation of mucinous or folded formations;
- Anaplastic or undifferentiated carcinomas - during the development of tumors, cells and tissues become undifferentiated.
The prognosis of pancreatic cancer depends on the stage of the disease, namely the presence of a metastatic process. There is no definite answer to the question of how long people live with pancreatic cancer, because the prognosis is affected by various factors, including not only the extent of the prevalence of the formation, but also the type of tumor and the age of the patient. Moreover, if proper cancer treatment is organized abroad, then doctors will take all measures to ensure the greatest possible life, even if it is stage 4 pancreatic cancer.
The process of metastasis begins with damage to nearby lymph nodes. The spread of metastases through the bloodstream leads to metastatic liver damage. With further spread, all digestive organs are affected, so treatment of stomach cancer abroad may become a necessity.
Adenocarcinomas that affect the tail and body of the gland are diagnosed less frequently. But they are the ones who pose the greatest danger, as they develop to large sizes and often affect the liver with metastases. The entry of tumor cells into the peritoneum leads to the development of peritoneal carcinosis.
Why do pseudocysts occur in the pancreas?
Most often, the cause is an inflammatory process and a violation of the patency of the pancreatic ducts.
In 75–85% of cases, pseudocysts are preceded by pancreatitis associated with excessive alcohol consumption, cholelithiasis, or other causes. Blunt and penetrating abdominal injuries lead to pathology much less frequently. Sometimes the causes of pseudocysts are unknown, so they are called idiopathic.
Some numbers and facts:
- Pancreatic pseudocysts can be single or multiple. Multiple occur in 15% of cases - most often in people suffering from alcoholism.
- The size of pseudocysts can range from 2 to 30 cm.
- In 2/3 of cases, these formations appear in the tail of the pancreas, in 1/3 of cases - in the head.
- In general, the reasons for the development of pseudocysts are the same as for pancreatitis.
Intraductal papillary mucinous pancreatic cancer (IPMT)
This type of pancreatic tumor accounts for about 2% of the total number of cancers affecting the gland. Men over 60 years of age are often susceptible to the development of IPTM. The tumor is localized inside the ductal ducts, mainly affecting the pancreatic duct of the head of the pancreas. It is possible for a tumor to develop in the branches of the duct, as well as simultaneous damage to the main line and the branches.
Healthy ductal epithelium consists of columnar neoplastic cells that cluster and form finely nodular papillary structures. These structures are characterized by the production of mucinous mucus of a viscous consistency, which is very difficult to wash out. As a result of structural changes in the tissues, the ducts periodically expand by about 2-3 cm. Sometimes a pathology is diagnosed in which both the ductal tissue and the gland are lined with tumor cells. In 25% of cases, the formation develops aggressively and metastasizes.
IPTM can be recognized by pain in the upper abdomen, similar to pain during the development of pancreatitis. An undetected tumor in time causes exocrine insufficiency - a condition in which tumor mucus accumulates in the excretory ducts, and the production of digestive enzymes by the pancreas is blocked. The occurrence of such a complication causes the development of chronic obstructive inflammation, symptomatically similar to pancreatitis.
The treatment offered by Israeli hospitals involves surgical removal of the tumor and is associated with a good prognosis. Even if colloid carcinoma with aggressive growth is diagnosed, treatment will be successful, provided that the formation is located within the pancreas.
Symptoms of hormonally active pancreatic tumors
Depending on the hormone released into the blood by tumor or (less often) hyperplastic cells scattered in the tissues of the organ, certain clinical manifestations of the disease are observed.
Three types of tumors have been studied better than others:
- g lucagonoma,
- insulinoma (insuloma),
- gastrinoma.
Symptoms of hormonally active pancreatic glucagonoma:
Glucagonoma is a tumor of the a-cells of the pancreas. It manifests itself as gynerglucagonemia (glucagon is an insulin antagonist) and diabetes mellitus. Due to the catabolic properties of glucagon, the following develops:
- cachexia,
- anemia
- and peculiar necrotic changes in the tissues of the oral cavity and on the skin, simulating pellagra.
Symptoms of hormonally active insulinoma:
Insuloma (insulinoma) comes from the β-cells of the islets of Langerhans and manifests itself as hyperinsulinism - recurrent hypoglycemia, leading to seizures and organic changes in the brain.
Manifestations of hormonally active gastrinoma of the pancreas
A peculiar syndrome has been described, which was characterized by gastroduodenal ulcerations resistant to routine therapy. They occurred with pronounced clinical manifestations, excitable gastric hypersecretion, and often with severe complications.
Mucinous cystic pancreatic cancer
In mucinous cystic cancer, a fibrous capsule is formed, the size of which is from 10 to 12 cm. This capsule is divided into at least six cysts, each approximately 2 cm in diameter. The inside of the cyst is lined with cylindrical cells that produce mucins (mucus). Women aged 40 to 60 years are susceptible to the development of tumors of this type.
Good differentiation of mucinous cystic tumors allows for effective surgical treatment of pancreatic cancer in Israel. If tumor cells are poorly differentiated, treatment becomes more complicated.
Mucinous cystic formation can be diagnosed by elevated levels of carcinoembryonic antigen and specific antigen CA 19-9 in the blood.
Acinus cell carcinoma of the pancreas
The acini is the structural and functional unit of an organ. In the case of the pancreas, the acini is a small round-shaped formation, not exceeding 0.15 mm in size. The acini consists of a secretory section and an intercalary duct, from which the ductal system of the pancreas begins.
The acini consists of ductal and secretory cells. When secretory cells are affected by a tumor, excessive production of lipase begins, which is involved in the digestion of fatty acids, fats, and acid-soluble vitamins. The presence of lipase in large quantities causes necrosis of adipose tissue and inflammation of the joints in the arms and legs.
Acinus cell carcinomas grow rapidly, increasing to 5-6 cm. At the stage when there is no metastatic liver damage, the tumor is amenable to surgical removal. Men at risk are in the age group from 55 to 65 years. Approximately at the same age there is a peak in the development of prostate cancer tumors, so men from this age group often turn to foreign specialists to undergo treatment for prostate cancer abroad.
Tumor Papilla Vateri of the pancreas
This formation can affect both the pancreas and duodenum. The tumor received its name because of its formation in the place where the bile and pancreatic ducts adjoin the duodenum. This border zone is called Papilla Vateri.
In development, the Papilla Vateri tumor is similar to ductal adenocarcinoma, with the only difference being that against the background of this formation, jaundice develops faster. In this case, the disease can be detected earlier than ductal adenocarcinoma.
Prognosis for pancreatic cancer in terms of lifespan depends on the stage of the tumor. It should be borne in mind that any delay in diagnosis and treatment leads to a significant reduction in life expectancy. If at stage 1 life expectancy is calculated in years, then at stage 4 it is calculated in months.
Competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2020/2021
This work was published in the “Free Topic” category of the “Bio/Mol/Text” competition 2020/2021.
The general partner of the competition is the annual biotechnology conference BiotechClub, organized by the international innovative biotechnology company BIOCAD.
The sponsor of the competition is SkyGen: a leading distributor of life science products on the Russian market.
Competition sponsor: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"