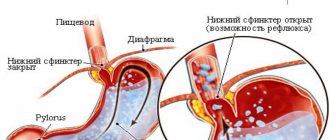
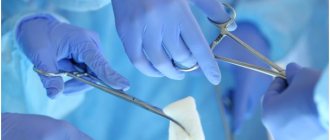
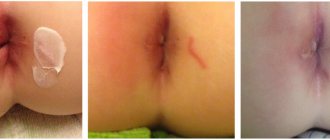
Colostomy is a surgical intervention that consists of creating an artificial opening that will perform the functions of the anus (ensure adequate passage of intestinal contents and gases). The course of the operation involves bringing out a section of the colon and suturing it to the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall. The stoma can be temporary (subsequently it is planned to stitch together the removed segments) or permanent (it is the final stage of surgical treatment). This operation is most widely used in oncology.
Indications
Colostomy is performed for the following cancers:
- Cancer of any part of the intestine associated with blocking of its lumen;
- Tumor of the peritoneum and retroperitoneal space that cannot be removed;
- Peritoneal cancer complicated by obstruction;
- Deformation of the lumen due to radiation therapy;
- Disintegration of a cancer focus due to radiation;
- Development of severe inflammation after radiation therapy.
In this case, the procedure is also carried out for non-cancerous tumors:
- Multiple polyps;
- Hereditary diseases;
- Adhesive pathology of the peritoneum, which leads to intestinal obstruction;
- Ineffective treatment of intestinal wall ulcers;
- Multiple intestinal injuries.
How is the operation performed?
In almost all cases, the formation of a colostomy is one of the stages of another, more extensive surgical intervention (resection of part of the intestine, elimination of intestinal obstruction). The operation can be carried out in different ways:
- laparotomy (open);
- laparoscopic (using video equipment).
The type and technique of colostomy is determined by the attending physician, taking into account the type of pathology, its volume and the degree of intestinal damage. Also, the price for providing this service will depend on the method of carrying out the operation.
Stages of surgery:
- The anesthesiologist performs endotracheal anesthesia.
- Access is provided to the desired area of the large intestine (depending on the location of the pathological process).
- If the operation is performed laparotomically, then one large incision is made and the surgeon performs all manipulations under control.
- If the laparoscopic method was chosen, then several small incisions are made through which special surgical instruments and optical devices are inserted, and the image is displayed on the monitor (this method is more gentle, but in some cases cannot be used). The location of the colostomy on the anterior abdominal wall also depends on which area was accessed and which part of the large intestine was operated on.
- The main stage of the operation is performed (removal of part of the intestine, extirpation of the rectum, etc.).
- The incision for subsequent colostomy formation is made separately from the main laparotomy incision. The skin at the site of the colostomy should be free of scars and inflammation. A layer-by-layer dissection of the tissue is carried out, then the surgeon sutures the parietal peritoneum to the tissues of the aponeurosis and muscles.
- Through the created hole, a loop of intestine is brought out into the wound and intersected (it may already be dissected if the stoma was preceded by an operation to resection part of the intestine).
- A colostomy is formed from the proximal end of the loop by suturing the intestine to the skin and aponeurosis. The intestinal wall should not be compressed too much by the edges of the incision, since excessive compression can lead to disruption of the blood supply and necrosis of part of the intestine.
- If an end stoma is planned, the diverting loop is sutured tightly and immersed back into the abdominal cavity.
- At the last stage, the surgeon closes the incision through which the main access was made layer by layer.
Kinds
In medical practice, colostomies are classified into temporary and permanent.
According to the level of localization, they are classified into small intestinal and large intestinal.
Small intestinal have three options:
- Jejunostomy (jejunum is removed);
- Ileostomy (ileal);
- Cecostoma (blind).
If we talk about the colon, there may also be options:
- Ascendostomy (region of the ascending section);
- Transversostomy (area of the transverse colon fragment);
- Descendostomy (output of the descending area);
- Sigmostoma (extraction of the sigmoid region).
According to visualization, colostomies are divided into:
- Single-barrel (in this case, only the upper part of the intestine comes out, the anus is sutured tightly);
- Double-barreled (both intestinal edges are located on the stomach, they are brought out autonomously or in a loop form).
The shape of the external output is:
- "Column";
- "Flat".
Closing the colostomy
Closing a colostomy is indicated after treatment of pathology of the lower intestine, which has led to the need to create a temporary opening for bowel movements. Surgery to close a colostomy can occur 3 to 6 months after the first surgery, although the time frame may vary. A colostomy can be removed after a shorter period of time. This will depend on the progress of treatment of the underlying disease.
Colostomy reconstruction surgery can be performed through a local approach or laparotomy. The double-barreled colostomy technique allows you to restore the integrity of the intestine through an opening in the abdominal wall. During colostomy closure surgery, the edges of the intestine are cleaned and sutured. The same surgical technique is provided for colostomy with mucous fistula. In this case, there is no need to perform a laparotomy. However, the operation is performed under general anesthesia.
To close a single-barrel colostomy, a repeat laparotomy is required using general anesthesia. To minimize patient trauma, colostomy closure can be performed laparoscopically. Closing a single-barrel colostomy is much more difficult than a double-barrel colostomy, so a double-barrel type is usually chosen for a temporary colostomy.
Closing a colostomy in the postoperative period is associated with the risk of complications. Quite often, fecal fistulas, strictures in the anastomotic area, intestinal obstruction, the formation of intestinal adhesions, intraperitoneal abscess, and extraperitoneal infections occur.
What to do next after colostomy removal? At the end of the recovery period after surgery, the patient undergoes a rehabilitation course. In the future, you need to take a very responsible approach to your diet and lifestyle. With proper attitude towards their body, patients return to a full life after some time. At the Yusupov Hospital, experienced rehabilitation specialists work with patients and use effective methods for the recovery of postoperative patients. A rehabilitation course at the Yusupov Hospital will help improve the quality of life in a minimum period of time.
Carrying out
The manipulation is carried out in the operating room using general anesthesia.
The surgeon selects the area where the colostomy will be removed. The choice of location depends on a number of factors: the location of the pathology, the characteristics of the patient’s fatty tissue, etc.
After the operation is performed, a colostomy bag is attached, which is a special plastic bag.
It simply attaches to the dermis as it has an adhesive backing. In some cases, the colocontainer is attached to the belt, which is less convenient.
It must be said that today, inhalation containers do not cause trouble for people, you can live and work with them, but caring for them is required.
conclusions
Colostomy is an operation in which part of the colon is brought out through an artificially created opening in the abdominal cavity and forms a colostomy, a kind of fistula that facilitates the removal of gases or feces. This operation is indicated for various intestinal diseases, and is also often a companion for cancer patients. Most often, for malignant neoplasms, permanent colostomies are placed, with which people live their entire lives.
Such an operation often helps save a person’s life, and with the availability of modern accessories and tools, people subsequently even forget about their delicate problem. Having a colostomy is not a death sentence; the main thing is to overcome the psychological barrier in this problem and take it for granted. People with a colostomy continue to live full, normal lives, get married, give birth and raise children. The main thing is to follow a healthy diet, do not forget about daily personal hygiene, and the problem will disappear on its own.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
What after?
Before starting to take any medications, a person with a colostomy bag should consult a doctor, otherwise you may experience intestinal dysfunction in the form of constipation or diarrhea.
It is equally important to follow the diet recommended by your doctor. It is worth visiting a nutritionist, he will be able to advise you on a diet in order to avoid troubles.
It is important to monitor the colostomy daily and change the stool collection tank on time. By doing this regularly, you will avoid unpleasant complications.
Some people experience psychological discomfort while having a colostomy. Try not to give in to despair and live a full life. Moreover, a colostomy does not interfere with work or household chores, and it is invisible under clothes.
Advantages and disadvantages of colostomy
In some cases, this procedure simply saves the patient’s life. This is the most important advantage of a colostomy. And with the use of modern devices, you can live comfortably even with such a diagnosis.
The main disadvantage of this procedure is the emotional and psychological factor, which often causes depression in patients. But this can also be overcome by listening carefully to the doctor, who is obliged to conduct explanatory conversations with the patient, tell him how to properly care for a colostomy, and what sensations may haunt the patient.
Many consider one of the main disadvantages to be the presence of an unpleasant odor. However, modern colostomy bags are equipped with powerful filters that eliminate odor, as well as special magnetic covers. Also, today there are various types of deodorants designed specifically for such purposes.
The availability of modern supplies and medications makes such a problem simply non-existent.
Care
Do not let the heat container overfill, otherwise it may come off and create a problem.
When changing the sterilizer container, thoroughly wash the part of the body where the sterilizer container is attached with soap and water. This is necessary to remove the adhesive substance. Shave your hair if necessary.
It is not difficult to install a new colostomy bag. Make a hole in the adhesive layer about half a centimeter in diameter larger than the colostomy.
After this, remove the protective film and glue the colocontainer to the body. The movement should be from bottom to top. And to peel it off you need to make movements in the opposite direction.
All this to the patient and his relatives before discharge.
Embolization
Stoma care at home
The stoma requires careful postoperative care. Typically, training in how to properly care for it is carried out by a nurse in the hospital, who is responsible for changing the patient’s colostomy bags and cleaning the colostomy. Afterwards, the patient must do this himself without fail.
To do this you need:
- Eliminate feces completely.
- Rinse the hole and the skin around it thoroughly with warm boiled water. Dry the colostomy with gauze pads.
- Treat the surface of the skin with Stomagesiv ointment or Lassara paste. Then apply gauze treated with Vaseline and cover everything with a sterile bandage. Then a gauze bandage is applied on top, which requires replacement every four hours.
- After the stoma has completely healed, it is allowed to use colostomy bags. We can talk about complete healing of the hole in the complete absence of inflammatory processes in this area, as well as when the mouth of the stoma does not protrude above the skin.
- Colostomy bags are changed in the evening or in the morning. To do this, you need to carefully remove the used fecal bag, remove any remaining fecal matter and thoroughly rinse the colostomy. Then it is necessary to treat the stoma with medications and fix the colostomy bag again.
To fix the fecal sac, in most cases, Coloplast paste is used, which has a small alcohol component. However, this drug does not cause any irritation and holds the colostomy bag well.
Sometimes, before gluing the fecal sac, a film is glued to the skin in order to prevent possible irritation or inflammation.
Once again about diet
Normal eating will return some time after the operation.
The first day you need to be patient, because you can’t drink or eat. But after a day you can drink water.
Liquid and soft food is what the patient can eat for the first two days after the intervention.
The main thing in eating now is not to provoke intestinal dysfunction, as well as increased gas formation. All nutritional recommendations are given by the attending physician.
You should try to eat little by little, but at the same time increasing the number of meals. It is important to strictly follow the regime. You need to eat slowly, chewing your food thoroughly.
Preparation, diagnostics
Since a colostomy is most often the final stage of another intestinal operation, preparation for its implementation is standard for all types of surgical interventions. The preoperative examination plan includes:
- Standard analysis package.
- Chest X-ray.
- ECG.
- Ultrasound or CT scan of the abdominal cavity.
- Colonoscopy.
You can undergo a comprehensive examination in our clinic in just a day.