Liver cirrhosis is accompanied by signs of functional liver failure and portal hypertension, which is the final stage of the development of chronic hepatitis, a consequence of difficulty in the outflow of bile or blood from the liver or genetically determined metabolic disorders.
It is more common in men, mainly middle-aged and elderly. The cirrhotic liver is enlarged or reduced in size, unusually dense, lumpy, and rough. At the initial stage of cirrhosis there are still no complications of the disease. It is at this time that it is very important to eliminate the cause of the development of cirrhosis, which will allow you to preserve the remaining healthy liver tissue and lead a normal lifestyle. The liver has very great regeneration (restoration) capabilities, and healthy cells can work for themselves and their injured comrades.
Some historical data
Since ancient times, the liver has been considered as important an organ as the heart. According to the inhabitants of Mesopotamia, the liver produces blood and the soul lives. Hippocrates also described the connection between liver diseases and jaundice, as well as ascites. He argued that jaundice and hard liver were a bad combination of symptoms. This was the first judgment about liver cirrhosis and its symptoms.
Cirrhosis of the liver and its causes were described in 1793 by Matthew Baillie in his treatise Morbid Anatomy. In his work, he clearly linked the consumption of alcoholic beverages with the occurrence of symptoms of liver cirrhosis. In his opinion, middle-aged and older men were more likely to get sick. The British dubbed cirrhosis the “gin plague” or “gin liver.”
The term cirrhosis comes from the Greek “kirrhos”, which means yellow and belongs to René Théophile Hyacinthe Laennec, a French physician and anatomist. Many scientists have worked and continue to work on the study of liver cirrhosis to this day. Virchow, Kuehne, Botkin, Tatarinov, Abelov and others proposed many theories about what liver cirrhosis is, its symptoms, causes, methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Reasons for the development of cirrhosis
Among the main reasons leading to the development of the disease are:
- Viral hepatitis, which, according to various estimates, leads to the formation of liver pathology in 10-24% of cases. The disease results in such types of hepatitis as , , D and the recently discovered hepatitis G;
- Various diseases of the biliary tract, including extrahepatic obstruction, cholelithiasis and primary sclerosing cholangitis;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. Many autoimmune diseases lead to the development of cirrhosis;
- Portal hypertension;
- Venous congestion in the liver or Budd-Chiari syndrome;
- Poisoning with chemicals that have a toxic effect on the body. Among such substances, industrial poisons, salts of heavy metals, aflatoxins and mushroom poisons are especially harmful to the liver;
- Diseases transmitted by inheritance, in particular, genetically determined metabolic disorders (anomalies of glycogen accumulation, Wilson-Konovalov disease, deficiency of α1-antitrypsin and galactose-1-phosphate-uridyltransferase);
- Long-term use of medications, including Iprazide, anabolic steroids, Isoniazid, androgens, Methyldopa, Inderal, Methotrexate and some others;
- Drinking large doses of alcohol for 10 years or more. There is no dependence on a specific type of drink; the fundamental factor is the presence of ethyl alcohol in it and its regular intake into the body;
- The rare Osler-Rendu disease can also cause cirrhosis.
In addition, it is worth mentioning separately about cryptogenic cirrhosis, the causes of which remain unclear. It occurs in the range from 12 to 40% of cases. Provoking factors for the formation of scar tissue can be systematic malnutrition, infectious diseases, syphilis (which can cause cirrhosis in newborns). The combined influence of etiological factors, for example, a combination of hepatitis and alcoholism, significantly increases the risk of developing the disease.
Features of male cirrhosis
Among men there are more patients with cirrhosis, as they pay less attention to their diet
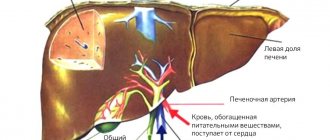
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic pathology in which liver cells (parenchyma) are replaced by connective tissue (stroma). This leads to the complete loss of the organ’s functions. As a result, toxic substances and breakdown products are not removed from the body, and intoxication begins.
The disease is more often diagnosed in men. For every sick woman there are three men. This is due to the fact that men consume more strong alcoholic drinks and fatty foods.
Mechanism of disease development:
- A person is affected by factors of various etiologies: alcohol, viruses, parasites, salts of heavy metals, radiation exposure.
- Ito cells are activated. These are stellate cells, in a calm state they are not dangerous, but in an active state they cause the formation of scars in the liver tissue. This starts the process of fibrosis, that is, the proliferation of connective tissue.
- Hepatocytes die, the blood supply to the parenchyma is disrupted.
- False lobules are formed in the liver, which do not have central vessels.
The following types of cirrhosis are found in men:
| Alcoholic | Necrosis of hepatocytes occurs due to alcohol poisoning. |
| Viral | Hepatitis viruses penetrate liver cells and cause their degeneration. |
| Stagnant | Cell death is the result of hypoxia and impaired venous outflow. |
| Primary | Develops as a result of genetic autoimmune pathologies. The main factor is impaired bile excretion. |
In the last stages of male cirrhosis leads to changes in hormonal levels. Testosterone production decreases and sexual dysfunction develops. Female type obesity and gynecomastia begin.
Classification
The modern classification of the disease in question is based on taking into account etiological, morphogenetic and morphological criteria, as well as clinical and functional criteria. Based on the reasons behind the influence of which cirrhosis of the liver developed, the following variants are determined:
- biliary cirrhosis (primary, secondary) (cholestasis, cholangitis);
- circulatory cirrhosis (arising against the background of chronic venous stagnation);
- metabolic and nutritional cirrhosis (lack of vitamins, proteins, accumulation cirrhosis resulting from hereditary metabolic disorders);
- infectious (viral) cirrhosis (hepatitis, biliary tract infections, parasitic liver diseases);
- toxic cirrhosis, toxic-allergic cirrhosis (food and industrial poisons, medications, allergens, alcohol);
- cryptogenic cirrhosis.
Depending on the clinical and functional characteristics, liver cirrhosis is characterized by a number of the following features:
- level of hepatic cell failure;
- general nature of the disease (progressive, stable or regressive);
- the degree of portal hypertension relevant to the disease (bleeding, ascites);
- general activity of the disease process (active cirrhosis, moderately active cirrhosis, as well as inactive cirrhosis).
Is it possible to be cured?
Biirin - a new medicine for cirrhosis
Until recently, the disease was considered incurable. With the help of therapy, doctors could only delay the onset of the terminal stage, but it was not possible to stop the process.
Now a unique drug Biirin, invented by Ukrainian scientists, has appeared on the pharmaceutical market. It is created on the basis of many medicinal herbs, so it does not have a toxic effect on the body.
The drug stimulates the production of liver enzymes, restores damaged hepatocytes, prevents the destruction of healthy liver cells, and removes dead cells from the body.
According to studies, complete restoration of the organ occurs within 3-8 months, depending on the stage of the process. In the third degree of cirrhosis, it takes about 2 years for the liver to fully recover.
Portal cirrhosis of the liver
The most common form of the disease, which is characterized by damage to liver tissue and death of hepatocytes. Changes occur due to poor nutrition and alcohol abuse. In 20%, portal cirrhosis can cause Botkin's disease. First, the patient complains of disorders of the digestive tract. Then external signs of the disease develop: yellowing of the skin, the appearance of spider veins on the face. The last stage is characterized by the development of ascites (abdominal dropsy).
Diagnosis of the disease
It is very difficult to diagnose such a disease at the initial stage. After all, the disease develops unnoticed. To identify it, specialists must conduct radionuclide, ultrasound, and x-ray examinations. Computed tomography is the best way to show the condition of the liver. The decisive stage in determining the disease is when the tissues of the organ are examined. To do this, a puncture biopsy is performed. It comes in two types: sighted and blind. Monitoring by laparoscopy or ultrasound is necessary during the procedure.
First signs
Early symptoms indicating cirrhosis include the following:
- A feeling of bitterness and dryness appears in the mouth, especially often in the morning;
- The patient loses some weight, becomes irritable, and gets tired faster;
- A person may be bothered by periodic stool disorders, increased flatulence;
- Periodically occurring pain localized in the right hypochondrium. They tend to increase after intense physical activity or after taking fatty and fried foods, alcoholic beverages;
- Some forms of the disease, for example, postnecrotic cirrhosis, manifest themselves in the form of jaundice already in the early stages of development.
In some cases, the disease manifests itself acutely and there are no early signs.
Symptoms of cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is characterized by general symptoms: weakness, decreased ability to work, discomfort in the abdomen, dyspeptic disorders, increased body temperature, joint pain, flatulence, pain and a feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen, weight loss, asthenia. Upon examination, an enlargement of the liver, compaction and deformation of its surface, and sharpening of the edge are revealed. At first, there is a uniform moderate increase in both lobes of the liver; later, as a rule, the increase in the left lobe predominates. Portal hypertension is manifested by a moderate enlargement of the spleen.
The detailed clinical picture is manifested by the syndromes of hepatic cell failure and portal hypertension. There is bloating, poor tolerance to fatty foods and alcohol, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, a feeling of heaviness or abdominal pain (mainly in the right hypochondrium). In 70% of cases, hepatomegaly is detected, the liver is compacted, and the edge is sharpened. In 30% of patients, palpation reveals a nodular surface of the liver. Splenomegaly in 50% of patients.
Low-grade fever may be associated with the passage of intestinal bacterial pyrogens through the liver, which it is unable to neutralize. The fever is resistant to antibiotics and resolves only when liver function improves. There may also be external signs - palmar or plantar erythema, spider veins, scanty hair in the axillary and pubic area, white nails, gynecomastia in men due to hyperestrogenemia. In some cases, the fingers take on the appearance of “drum sticks.”
In the terminal stage of the disease, in 25% of cases there is a decrease in liver size. Jaundice, ascites, peripheral edema due to overhydration (primarily swelling of the legs), external venous collaterals (varicose veins of the esophagus, stomach, intestines) also occur. Bleeding from veins is often fatal. Hemorrhoidal bleeding occurs less frequently and is less intense.
Consequences
Liver cirrhosis, in principle, alone does not cause death; its complications in the decompensation stage are deadly. Among them:
- Ascites in cirrhosis is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. A diet with limited protein (up to 0.5 grams per kg of body weight) and salt, diuretics, and intravenous administration of albumin (a protein drug) are prescribed. If necessary, resort to paracentesis - removal of excess fluid from the abdominal cavity.
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneum due to infection of the fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites). Patients have a fever of up to 40 degrees, chills, and intense abdominal pain. Long-term broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. Treatment is carried out in the intensive care unit.
- Hepatic encephalopathy. Manifests itself from minor neurological disorders (headache, increased fatigue, lethargy) to severe coma. Since it is associated with the accumulation of protein metabolism products (ammonia) in the blood, protein is limited or excluded from the diet, and a prebiotic is prescribed - lactulose. It has a laxative effect and the ability to bind and reduce the formation of ammonia in the intestines. For severe neurological disorders, treatment is carried out in the intensive care unit.
- Hepatorenal syndrome is the development of acute renal failure in patients with liver cirrhosis. Stop the use of diuretics and prescribe intravenous albumin. Treatment is carried out in the intensive care unit.
- Acute variceal bleeding. Arises from varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach. The patient becomes increasingly weak, blood pressure drops, pulse quickens, and vomiting appears mixed with blood (the color of coffee grounds). Treatment is carried out in the intensive care unit; if ineffective, surgical treatment methods are used. To stop bleeding, intravenous administration of octropide is used (to reduce pressure in the blood flow of the abdominal vessels), endoscopic treatment (ligation of varicose veins, sclerotherapy). Transfusion of solutions and blood components is carried out carefully to maintain the required level of hemoglobin.
- The development of hepatocellular carcinoma is a malignant neoplasm of the liver.
The definitive treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensated liver cirrhosis is liver transplantation. Replacing a patient's liver with a donor's liver.
Symptoms and stages
In the first stage, cirrhosis does not damage the liver much and can be easily cured
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the stage of the process. The following stages of the disease are distinguished:
The first (compensatory). It is asymptomatic, pathology can only be detected through clinical studies. The necrotic process is just beginning to develop, the patient develops weakness, fatigue, decreased appetite, and decreased ability to work. Most patients do not associate these symptoms with cirrhosis and do not consult a doctor.
Second (subcompensatory). In the parenchyma, the process of inflammation begins, the liver tissue is gradually replaced by connective tissue. However, the organ still functions normally, but is slightly increasing in size. At this stage the patient feels:
- heaviness in the right side;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- skin itching;
- decreased appetite.
Vomiting with bile often occurs. The feces become colorless and the urine darkens. This is explained by a violation of the outflow of bile; it is not excreted in the feces, but remains in the urine. Ascites may also develop - an accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, causing it to increase in size.
At the second stage, jaundice appears: the sclera and skin of the patient turn yellow due to the increased concentration of bilirubin in the blood.
At the third stage of cirrhosis, serious complications appear
Third (decompensated). It is characterized by the appearance of severe complications: portal hypertension, ascites, abdominal vein thrombosis. The patient experiences the following symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- protrusion of veins on the abdomen (cap jellyfish);
- weight loss, appetite;
- vomiting, diarrhea;
- bleeding (nasal, anal, stomach);
- dystrophy.
Toxins affect the nervous system and brain, which causes the development of hepatic encephalopathy. The patient's cognitive functions deteriorate and mental disorders may appear.
Fourth (terminal). This is the last stage of cirrhosis, in which the patient begins to experience serious complications: ascites, peritonitis, sepsis. Patients fall into a hepatic coma due to acute liver failure; they never recover from the coma and die.
Watch a video about the first signs of liver cirrhosis in men and women:
Diagnostics
Determining the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis takes place in several stages. The diagnosis itself is made on the basis of instrumental research data:
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography is the most accurate diagnostic method.
- Biopsy is a method of histological examination of material taken from the liver, which makes it possible to establish the type of large- or small-nodular cirrhosis and the cause of the development of the disease.
- Ultrasound – as a screening. Allows you to establish only a preliminary diagnosis, but is indispensable when diagnosing ascites and portal hypertension.
If, upon diagnosis, histological examination does not allow determining the cause of the disease, the search for it continues. To do this, perform a blood test to determine the presence of:
- antimitochondrial antibodies;
- Hepatitis C virus RNA and hepatitis B virus DNA using the PCR method;
- alpha-fetoprotein – in order to exclude blood cancer;
- copper and cerruloplasmin levels;
- level of immunoglobulins A and G, level of T-lymphocytes.
At the next stage, the degree of damage to the body due to liver damage is determined. For this use:
- liver scintigraphy - radionuclide study to determine working liver cells;
- biochemical blood test to determine indicators such as sodium and potassium levels, coagulogram, cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase, total and fractional bilirubin, AST, ALT, lipidogram, proteinogram;
- degree of kidney damage – creatinine, urea.
Absence or presence of complications:
- Ultrasound to exclude ascites;
- eliminating internal bleeding in the digestive tract by examining stool for the presence of hidden blood;
- FEGDS - to exclude varicose veins of the stomach and esophagus;
- sigmoidoscopy to exclude varicose veins in the rectum.
In cirrhosis, the liver can be palpated through the anterior wall of the peritoneum. On palpation, the tuberosity and density of the organ are noticeable, but this is only possible at the stage of decompensation.
Ultrasound examination clearly identifies foci of fibrosis in the organ, and they are classified into small ones - less than 3 mm, and large ones - over 3 mm. With the alcoholic nature of cirrhosis, initially small nodes develop; a biopsy determines specific changes in liver cells and fatty hepatosis. In later stages of the disease, the nodes enlarge and become mixed, and fatty hepatosis disappears. Primary biliary cirrhosis is characterized by an enlarged liver while maintaining the structure of the biliary tract. In secondary biliary cirrhosis, the liver becomes enlarged due to obstructions in the bile ducts.
Causes
In men, the main causes of cirrhosis are:
| Alcohol abuse | This type of disease occurs in 70% of cases. If a man drinks at least 100 g of ethanol every day for 5-7 years, then he develops alcoholic liver disease. The spread of the disease among alcoholics reaches 40%. |
| Hepatitis in the chronic stage | Hepatitis C is more destructive, therefore, if untreated, it contributes to the rapid development of the disease. |
| Stagnation | This group of cirrhosis is called biliary. The cause of primary biliary cirrhosis is a genetic disorder of metabolic processes. Among such diseases: cystic fibrosis, hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease. |
| Secondary biliary cirrhosis | They develop due to the toxic effects on the liver of drugs, toxic substances, radiation, and parasites. |
| Liver injury or surgery | This can trigger the degeneration of liver cells. |
Stages of liver cirrhosis
The course of the disease, as a rule, is characterized by its own duration, with the following main stages being distinguished:
- Compensation stage. It is characterized by the absence of symptoms of cirrhosis, which is explained by increased work of the remaining liver cells.
- Subcompensation stage. At this stage, the first signs of liver cirrhosis are noted (in the form of weakness and discomfort in the right hypochondrium, decreased appetite and weight loss). The functions inherent in the liver are performed in an incomplete manner, which occurs due to the gradual loss of resources of the remaining cells.
- Stage of decompensation. Here we are already talking about liver failure, manifested by severe conditions (jaundice, portal hypertension, coma).
Treatment
Liver cirrhosis in women cannot be treated independently or with folk remedies, because Such an attitude towards one’s own health can lead to dire consequences.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis occurs in a hospital inpatient setting or on an outpatient basis with a clear elimination of the root cause of the developed changes. Treatment aims not only to eliminate the cause, but also to prevent deadly complications.
It is generally accepted to divide the treatment of liver cirrhosis into three categories:
- A – treatment of the disease with outpatient support from a doctor;
- B – means hospitalization with possible continuation of outpatient treatment of the disease;
- C – definite hospitalization.
It is likely that patients with cirrhosis will be prescribed the following series of drugs:
- nitrates (for example, Nitroglycerin);
- a beta blocker;
- hepatoprotective drug;
- as well as products with bile acids.
It is also acceptable to individually prescribe treatment for the cause that provoked the cirrhotic process, for example, antiviral therapy or treatment sessions with a narcologist.
Drug treatment is necessarily supported by special nutrition, mainly table No. 5 is prescribed, which does not contain fried, smoked, canned, sour, spicy foods with an abundance of sauces and spices. Cream desserts, chocolate, coffee, cocoa and, of course, alcohol in any quantity and any strength are also prohibited.
A patient with cirrhosis should get useful substances from porridges, lean meat and fish fillets, fermented milk products, neutral-tasting vegetables, sweet fruits and ripe berries.
How to treat liver cirrhosis?
In general, the treatment of liver cirrhosis is selected on a strictly individual basis - therapeutic tactics depend on the stage of development of the disease, the type of pathology, the general health of the patient, and concomitant diseases. But there are also general principles for prescribing treatment.
These include:
- The compensated stage of liver cirrhosis always begins with eliminating the cause of the pathology - in this case, the liver is still able to function normally.
- The patient needs to adhere to a strict diet - even a slight violation can trigger the progression of liver cirrhosis.
- It is impossible to carry out physiotherapy or heat treatment for the disease in question. Physical activity is also excluded.
- If the disease is at the stage of decompensation, the patient is placed in a medical institution. The fact is that with this course of the disease, the risk of developing severe complications is very high and only medical workers will be able to promptly pay attention to even a slight deterioration in the condition and prevent the development of complications that lead to the death of the patient.
- Most often, hepatoprotectors, beta-blockers, sodium and ursodeoxycholic acid preparations are prescribed for treatment.
General advice for patients with liver cirrhosis:
- Rest as soon as you feel tired.
- To improve digestion, patients are prescribed multienzyme drugs.
- Avoid heavy lifting (this may cause gastrointestinal bleeding)
- Measure your body weight and abdominal volume at the navel level daily (an increase in abdominal volume and body weight indicates fluid retention);
- If there is fluid retention in the body (edema, ascites), it is necessary to limit the intake of table salt to 0.5 g per day, liquid intake to 1000-1500 ml per day.
- To monitor the extent of damage to the nervous system, it is recommended to use a simple handwriting test: write a short phrase, for example, “Good morning,” in a special notebook every day. Show your notebook to your relatives - if your handwriting changes, contact your doctor.
- Every day, count the fluid balance for the day (diuresis): count the volume of all liquid taken orally (tea, coffee, water, soup, fruit, etc.) and count all the liquid released during urination. The amount of fluid released should be approximately 200-300 ml more than the amount of fluid taken.
- Aim for stool frequency 1-2 times a day. Patients with liver cirrhosis are recommended to take lactulose (Duphalac) to normalize intestinal function and the composition of the intestinal flora in favor of “good” bacteria. Duphalac is prescribed in a dose that causes soft, semi-formed stools 1-2 times a day. The dose ranges from 1-3 teaspoons to 1-3 tablespoons per day, selected individually. The drug has no contraindications; it can be taken even by small children and pregnant women.
Treatment of pathological manifestations and complications of cirrhosis means:
- Reducing ascites using conservative (diuretic drugs according to the regimen) and surgical (removal of fluid through drains) methods.
- Treatment of encephalopathy (nootropics, sorbents).
- Relief of manifestations of portal hypertension - from the use of non-selective beta-blockers (propranolol, nadolol) to ligation of dilated veins during surgery.
- Preventive antibiotic therapy to prevent infectious complications during planned visits to the dentist, before instrumental procedures.
- Treatment of dyspepsia through nutritional correction and the use of enzyme preparations without bile acids (pancreatin). In such cases, it is also possible to use eubiotics - bactisubtil, enterol, bifidumbacterin and lactobacterin.
- To relieve skin itching, antihistamines are used, as well as drugs containing ursodeoxycholic acid.
- Prescription of androgens for men with severe manifestations of hypogonadism and correction of the hormonal levels of women to prevent dysfunctional uterine bleeding - under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
- The use of drugs containing zinc is indicated for the prevention of cramps during normal muscle activity and in the complex treatment of liver failure to reduce hyperammonemia.
- Prevention of osteoporosis in patients with chronic cholestasis and primary biliary cirrhosis, in the presence of autoimmune hepatitis with the use of corticosteroids. To do this, calcium is additionally introduced in combination with vitamin D.
- Surgical correction of portal hypertension for the prevention of gastrointestinal bleeding includes the application of vascular anastomoses (mesentericocaval and splenorenal) as well as sclerotherapy of existing dilated veins.
- In the presence of single foci of degeneration into hepatocellular carcinoma and the severity of the disease of class A, patients are advised to undergo surgical removal of the affected liver segments. In case of clinical class B and C disease and massive lesions, while awaiting transplantation, antitumor treatment is prescribed to prevent progression. To do this, they use both the effects of currents and temperatures (percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation) and chemotherapy by targeted injection of oil solutions of cytostatics into the vessels supplying the corresponding segments of the liver (chemoembolization).
Treatment of such a serious and fatal complication as acute massive bleeding from the veins of the esophagus includes:
- Local application of a Blackmore probe, with the help of which an air cuff is inflated in the lumen of the esophagus, compresses the dilated bleeding veins.
- Targeted injection of the esophageal wall with sclerosing substances.
- Blood replacement therapy.
Unfortunately, this condition becomes the main cause of death in patients with cirrhosis of the liver.
Relationship between causes of cirrhosis and mortality
The survival prognosis directly depends on the underlying cause of cirrhosis. The least favorable prognosis is observed with alcoholic cirrhosis. This is due to the toxic effects of ethanol on all organs. In alcoholics, not only the liver is affected, but also the kidneys, heart, blood vessels, etc.
Therefore, alcoholic cirrhosis is more difficult to treat. In addition, people who abuse alcohol rarely agree to treatment and follow recommendations. They continue to drink, which worsens the course of the disease.
If cirrhosis develops against the background of hepatitis, then the chances of cure are higher. Now there are many antiviral drugs that fight the main cause of the pathology.
A disease caused by the use of drugs or exposure to harmful chemicals is highly treatable, provided that the provoking factor is promptly eliminated. When the disease is a consequence of congenital gene mutations, the prognosis is directly related to the underlying disease.
Diet for liver cirrhosis
Following a diet for liver cirrhosis involves, first of all, avoiding foods that have a high protein content. After all, in patients with liver cirrhosis, the digestion of protein foods is disrupted, and as a result, the intensity of putrefaction processes in the intestines increases. The diet for liver cirrhosis involves periodic fasting days, during which the patient does not eat food containing protein at all. In addition, an important point is to limit the use of table salt with the main meal.
The diet for liver cirrhosis involves the exclusion of all products that contain baking soda and baking powder. You should not eat pickles, bacon, ham, seafood, corned beef, canned food, sausage, sauces with salt, cheeses, or ice cream. To improve the taste of products, you can use spices and lemon juice instead of salt.
The diet for liver cirrhosis allows the consumption of small amounts of dietary meat - rabbit, veal, poultry. You can eat one egg once a day.
Disease prognosis
Cirrhosis of the liver is incurable unless a liver transplant is performed. With the help of the above drugs you can only maintain a more or less decent quality of life.
How long people with liver cirrhosis live depends on the cause of the disease, the stage at which it was discovered and the complications that had appeared at the time of treatment:
- with the development of ascites they live 3-5 years;
- if gastrointestinal bleeding develops for the first time, from 1/3 to half of people will survive it;
- if hepatic coma develops, this means almost 100% mortality.
There is also a scale that allows you to predict life expectancy. It takes into account test results and the degree of encephalopathy:
| Parameter | Points | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Ascites | No | The abdomen is soft, goes away under the influence of diuretics | The abdomen is tense, its volume does not decrease well when taking diuretics |
| Changes in personality, memory, sleepiness | No | Mild degree | Strongly expressed |
| Total bilirubin | Less than 34 µmol/l | 31-51 µmol/l | More than 51 µmol/l |
| Albumen | 3.5 g/l or more | 2.8-3.5 g/l | Less than 2.8 g/l |
| Prothrombin index | More than 60% | 40-60% | Less than 40% |
| Sum of points | 5-6 | 7-9 | 10-15 |
| How long do they live? | 15-20 years | It is necessary to transplant the liver, but postoperative mortality is 30% | 1-3 years. If a transplant is performed at this stage, the probability of dying after the operation is 82 out of 100 |
Prevention
Liver cirrhosis is a rather long-term process that can be stopped and treated. The main key to success is to go to the doctor on time. However, it is one of those diseases that can be easily avoided by following certain preventive measures, including:
- vaccination against hepatitis B in childhood;
- rational and proper nutrition;
- avoiding starvation and overeating;
- giving up alcohol and smoking to exclude alcoholic cirrhosis and toxic liver damage;
- annual ultrasound and endoscopic examination;
- timely seeking medical attention from a doctor;
- adequate intake of vitamin and mineral complexes;
- strict suppression and treatment of drug addiction.
Preventive measures to prevent viral hepatitis will also help avoid the development of cirrhosis.