Burns of the esophagus occur as a result of exposure to alkalis or acids. In this case, damage most often occurs due to accidental use of a dangerous substance. Less commonly, people swallow acid or alkali on purpose: for example, during suicide attempts.
Acids and alkalis are found in household chemicals, including products intended for cleaning water pipes. Of course, measures should be taken to prevent such emergencies, but, unfortunately, the number of such accidents is always high.
Types of burns
The main culprits of serious injuries are:
- Chemical burn of the esophagus. It happens due to inattentive or intentional ingestion of strong acids (fluorophosphoric, hydrochloric, sulfuric), alkalis (caustic soda, caustic), as well as when consuming ammonia, iodine, glue, a strong solution of potassium permanganate and other substances. Esophageal injury is especially common when swallowing vinegar or vinegar essence due to improper storage of it in the kitchen.
- With a thermal burn of the esophagus, injury to the mucous membrane of the mouth and esophagus occurs due to the consumption of very hot foods. Such damage is dangerous for those who already have erosive lesions in the esophagus.
- A radiation burn can occur during the treatment of cancer tumors during a course of radiation therapy. Such damage is considered a complication of radiation treatment.
- A separate category includes burns resulting from the consumption of counterfeit and surrogate alcoholic beverages, as a result of which the esophagus and other organs are damaged.
According to statistics, in 70% of cases, burns to the esophagus occur in children who, due to their curiosity, put into their mouths everything that attracts their attention.
Responsibility for injuries lies with the parents who keep the chemicals accessible. That is why they must know how to provide assistance for burns of the esophagus.
Causes
You can burn your esophagus either accidentally or intentionally. According to statistics, more than 70% of the victims are preschool children who accidentally tasted a chemical liquid with a pleasant smell and in bright packaging. About 50% of adults also burn their esophagus with chemicals. The rest of the people, ending up in the hospital with damage to the tissues of the larynx and esophagus, are victims of suicide. The following chemicals can cause the most severe damage to the esophagus:
- Acids;
- Alkalis (caustic soda, sodium hydroxide);
- Vinegar essence;
- Alcohol;
- Ammonia;
- Hydrogen peroxide.
Classification of the degree of burns
Burns of the esophagus are classified according to severity:
- In grade I, the upper layer of the epithelium is injured. The patient's mucous membrane turns slightly red and a slight pain appears. Typically, this type of burn does not require medical attention, and burn symptoms go away within two weeks.
- In degree II, the mucous membrane and deep layers of muscle tissue of the esophagus are damaged. As a result of damage, ulcers form on the surface of the mucosa and swelling appears, making swallowing difficult. If the victim receives timely medical care, the burn will heal within a month without consequences for the body.
- III degree is the most severe type of burns of the esophagus and stomach, which affects the layers of these, as well as adjacent internal organs. The patient is in a state of shock and experiences excruciating pain. With a successful outcome and timely assistance provided, scars will remain at the site of the injury, and complete healing may take a long time. If timely medical care is not provided, the likelihood of death increases.
With a high degree of burn to the esophagus, tissue breakdown products enter the bloodstream and cause intoxication of the body, having a negative impact on the functioning of the heart, kidneys, liver, and other organs. Intoxication in combination with painful shock can cause death.
Diagnostics
Alcohol burns of the esophagus occur as a result of oral intake of 70 or 90% alcohol, as well as alcohol tinctures. In this case, the patient experiences a white coating on the mucous membranes, swelling and redness. Large volumes of alcohol-containing liquids can cause corrosion of the stomach walls. Poisoning is accompanied by general symptoms of intoxication (nausea, vomiting, dizziness); in this case, the stomach is immediately washed with plenty of water to avoid the appearance of ulcerative wounds caused by alcohol.
Symptoms of damage
Symptoms of esophageal burns are local and general. General symptoms occur against the background of severe intoxication. Due to the fact that there are a large number of nerve endings in the esophageal mucosa, the patient experiences severe pain as the potent chemical spreads. Excruciating pain and muscle spasms appear in the oral cavity, larynx, sternum, and epistragal region. In the future, the resulting injury can cause the development of chemical gastritis.
Signs indicating a burn are:
- swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth, lips and tongue, which causes the victim to experience hoarseness;
- sore throat, impaired swallowing function caused by swelling and damage to the larynx;
- inability to eat food, intestinal spasms;
- increasing shortness of breath, cough, respiratory problems;
- vomiting mixed with bloody discharge, the presence of particles of the esophageal mucosa in the vomit.
In especially severe cases, perforation of the walls of the esophagus, as well as the formation of tracheal-esophageal fistulas, can occur. Characteristic signs of general intoxication include general weakness, disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, increased temperature, and impaired consciousness.
Anatomical features
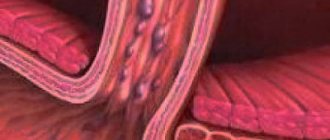
The esophagus itself is a tube made of smooth tissues and muscles, the length of the passage part is 27-30 cm. The main functionality is the delivery of food from the oral cavity to the stomach. If you look at the esophageal tract in section, you can see its star-shaped shape. This design is necessary for the body to quickly push food and liquid through.
Basic shells:
- Mucous membrane - located inside, produces a viscous liquid that allows food to pass easily.
- Muscular – located between the mucous membrane and the connective membrane (in the middle). Consists of two types of smooth muscles (some run transversely, others lengthwise). The main function is to push food to the stomach.
- Connective tissue – regulates the diameter of the lumen of the esophagus.
- The esophagus also has peculiar valves (at the beginning and end), which serve to allow or limit the passage of food, and also act as a blockage valve (do not release food from the stomach cavity into the esophageal tract).
How to provide first aid for a burn of the esophagus
For first-degree burns of the esophagus, no medical attention is required; second- and third-degree burns are treated in a hospital setting.
Before the ambulance arrives, the victim of a burn to the esophagus needs to be given assistance. It is necessary to perform a gastric lavage, first numbing the mouth and throat. First, you need to rinse your mouth and throat with a 0.5% solution of novocaine, and then give the victim to drink at least a liter of clean water and induce vomiting to remove the chemical reagent from the stomach. This procedure must be repeated 8-10 times.
After washing, you need to weaken the effect of the chemical. The acid is neutralized with a 2% sodium bicarbonate solution, which can be found in every kitchen. To prepare the solution, dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda in 200 ml of clean water. The effect of alkali is weakened by a 1-2% solution of citric or acetic acid. In cases where the substance that caused the injury is unknown, the patient needs to drink 1-2 cups of milk to reduce the concentration of the reagent.
Most common burns
Vinegar
The vinegar liquid itself is not a factor in severe injuries that need to be treated in the hospital. Vinegar is dangerous because, when absorbed into the blood, it destroys its components (proteins, red blood cells), which in turn will lead to a decrease in the functioning of the immune system and diseases of the kidney system. Damage to the epithelium of internal organs is possible when acetic essence gets on them. A large dose of vinegar can cause shock and abnormalities in the functioning of the heart and liver.
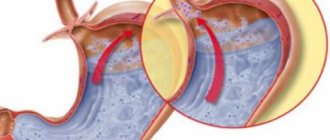
Gastric secretion
Characteristic for people suffering from reflux gastroesophageal disease. The peculiarity of the disease is that it provokes the release of gastric juice into the esophagus. The digestive secretion, in turn, gets on the mucous membranes of the esophagus, burns them, all this leads to ulcerative formations, stenosis and even cancer.
How is treatment carried out in a hospital?
After the patient is admitted to the hospital, treatment of a burn of the esophagus begins with gastric lavage with a soft probe.
The presence of blood discharge and vomit is not a contraindication to the procedure. Washing is carried out under anesthesia until traces of the caustic substance disappear in the rinsing waters. After completing the procedure:
- relieve spasm of the esophagus with the help of medications;
- carry out anti-shock therapy measures;
- carry out infusions of drugs and saline solutions to prevent the occurrence of renal and hepatic failure;
- to prevent re-infection, antibiotic treatment is prescribed;
- painkillers and sedatives are prescribed, as well as hormonal medications to maintain the body.
In particularly severe cases, patients may need surgery to excise damaged tissue or eliminate internal bleeding resulting from perforation of organs.
Consequences of a burn to the esophagus
If treatment of the victim was started in a timely manner, then after 2-3 days his condition stabilizes, swelling of the esophagus begins to subside, and the resulting wounds gradually heal through scarring and granulation. If immediately after receiving a burn, patients refuse to eat due to severe pain and swelling, then as the wounds scar, the fear of pain goes away, and they begin to eat liquid and pureed food.
The scarring process lasts about three months. During this time, difficulty and discomfort when swallowing, nutritional dystrophy, and increased secretion of the salivary glands may again occur. If the scars are not corrected during the scarring process, the patient's esophagus narrows and stenotic obstruction appears. To prevent it, bougienage is carried out. It consists of gradually introducing probes of different diameters into the esophagus. The procedure must be performed by an experienced surgeon under the control of special equipment.
Traditional medicine
After discharge from the hospital, you can treat the esophagus and stomach at home using folk remedies. The most effective of them are:
- Fresh egg white. It needs to be mixed in a small amount of water. The protein film promotes rapid healing of the burned surface.
- A decoction of flax seeds. It has an enveloping and healing effect, relieves pain. To prepare the drink, pour 10 spoons of seeds into 1 liter of boiling water and leave in a thermos for 2-3 hours. Drink in small portions throughout the day.
- Chamomile flower tea. It is an anti-inflammatory agent and relieves pain. To prepare the infusion, pour 2 teaspoons of the herb into 200 ml of boiling water and infuse for 10 minutes.
Treatment of the esophagus can last for several years, so when storing chemicals and household chemicals, you should be careful, hide them in places inaccessible to small children, do not tear off the labels and do not pour them into other containers.