Previously, it was believed that removal of polyps in the intestine was advisable only for large or multiple neoplasms.
However, statistics on the degeneration of these benign tumors into malignant ones (10-30% of cases) showed specialists that for cancer prevention it is important to get rid of even small polyps. Today, endoscopic treatment is used to remove polyps in the large and small intestine, except in cases where the tumor is located in parts of the intestine inaccessible to the endoscope. Large and multiple polyps with a high risk of degeneration into cancer are an indication for segmental resection surgery.
Types of benign intestinal tumor formations and their symptoms
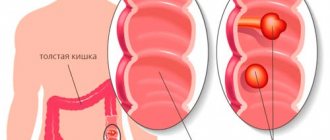
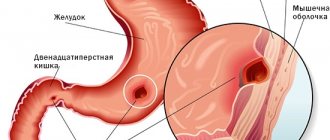
Typically, a polypous formation inside the intestine is benign, forming from epithelial tissue cells and growing into the intestinal lumen. Polyps vary in size, shape, they can “stand” on a stalk or on a broad base, single, multiple (polyposis), soft texture.
Intestinal pathology in the form of polyps is usually observed in older people, overweight people, diabetics, and heavy smokers; it can also be caused by genetic mutations.
Considering the frequency of occurrence of polyps in different parts of the intestine, you can notice that most of them develop in the sections of the colon and rectum, and less in the small intestine. In the duodenum, polyps are diagnosed quite rarely (approximately 0.2% of all endoscopic examinations).
A tumor-like growth in the form of a polyp is not oncology, but over time there is a possibility of its transformation into a malignant tumor.
There are many types of polypous formations in the intestines, but among them the most common are:
- Adenomatous , which are observed in approximately 70% of older patients. It is this type of tumor formation that is more likely than others to degenerate into a low-quality tumor.
- Serrated polyps, depending on their size and location, have varying degrees of malignancy. If small formations are located in the lower region of the colon, the risk is minimal, but if the polyp is large and located in the upper region of the intestine, then the risk of malignant transformation increases.
- Inflammatory polyps are formed when intestinal pathologies such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis occur. Although this type of tumor-like growth has a low percentage of degeneration into oncology, the treatment process should not be neglected.
The effectiveness of treatment of intestinal polyps abroad depends on an accurate diagnosis and determination of the type of pathology.
Clinical manifestations
As a rule, when polyps form in the sigmoid colon, there are no symptoms. A small percentage of patients may experience defecation disorders such as diarrhea, as well as pain in the left iliac region. Villous polyps bleed very often, so with a long course of the disease, such patients develop anemia. When analyzing stool, red blood cells are detected. If the bleeding is profuse, the stool will contain streaks of light blood. In addition, villous polyps are characterized by the production of large amounts of mucus.
Anemia manifests itself in the form of general weakness, headache, tachycardia and pallor of the skin. Abundant mucus production changes the water and electrolyte balance.
Polyps of gigantic size lead to disruption of the passage of feces through the digestive tract. Intestinal obstruction is a pathological condition that manifests itself in the form of cramping painful sensations localized according to the parts involved (in our case it will be the left iliac region). When questioned, patients suffering from obstruction note a violation of the passage of gases and feces. If such a condition is observed for a long time, then there is a possibility of reverse flow of intestinal contents up the digestive tract. In this case, patients will complain of nausea and foul-smelling vomiting.
If such a patient is not provided with timely medical care, then a sharp deterioration in health is possible, requiring emergency measures. Decompensation of the condition is associated with a decrease in circulating blood volume, a drop in pressure, intoxication and dehydration. In this situation, urgent surgery is required.
Article on the topic: Acute purulent inflammation of the appendix
Symptoms of polyps in the intestines
The presence of polyps in the intestines is difficult to determine by any specific clinical signs. The degree of symptomatic manifestation depends on the volume and location in the intestine, the number of formations, their structure, the transformation process and other factors.
However, among the key symptoms that may indicate polyps in different parts of the intestine, the following manifestations should be mentioned:
- the presence of bloody and mucous discharge;
- periodic pain in the lower abdomen, cramping in nature;
- abnormal bowel function (constipation, diarrhea);
- sensation of a foreign body in the anal area with large polyps;
- fullness of the stomach, belching, nausea;
- rectal bleeding;
- changes in stool color (from dark with blood streaks to black);
- anemia due to constant intestinal bleeding.
However, when the polyp is small in size, symptoms do not appear in any way. Tumor-like growths of this nature are detected during screening, which is an integral part of the cancer treatment program abroad.
Possible complications
The main danger of polyps is the likelihood of them turning into cancer. Also among the complications of the disease are:
- Rectal bleeding that occurs when a polyp is injured.
- Acute intestinal obstruction The cause is a large formation that closes the intestinal lumen.
- Enterocolitis . It is a dangerous condition in which the intestinal wall is affected by an inflammatory process. Lack of therapy causes death.
Against the background of regular bleeding, anemia develops over time. That is why, when sigmoid colon polyposis is diagnosed, immediate treatment is required.
Causes of intestinal polyps
It is quite problematic to unequivocally answer the question about the reasons for the appearance of polyps in the intestines. But there are factors that can lead to the formation of tumor-like growths of a benign nature, among them:
- heredity;
- elderly age;
- disorders associated with hormonal levels and metabolism in the body;
- gender (polyposis is more often diagnosed in men);
- inactive lifestyle;
- smoking;
- environmental degradation;
- poor nutrition with a predominance of foods high in fats and carbohydrates and lack of fiber in the menu;
- food allergies associated with gluten intolerance;
- chronic and inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract;
- predisposition to constipation;
- disturbances in the intestinal microflora;
- atherosclerosis.
Etiology
No one can still say reliably where polyps in the sigmoid colon come from. There are a number of theories suggesting the probable causes of these neoplasms. It was noted that people suffering from chronic intestinal inflammation are most susceptible to the appearance of polyps. In addition, a number of factors have been discovered that increase the risk of developing this pathology:
- Errors in diet and consumption of foods that contribute to the appearance of inflammatory reactions in the intestines;
- Chronic constipation caused by stagnation in the intestines;
- Permanent injuries to the mucous membrane with hard feces;
- Acute infection.
All of the above factors are to one degree or another associated with poor nutrition. Frequent consumption of low-quality and fatty foods, as well as the lack of foods containing fiber in the diet, can lead to improper formation of feces. Due to its anatomical features, the sigmoid colon is very vulnerable to such damage. The density of feces in the left parts of the colon is higher compared to the left, while the sigmoid colon has two bends that increase the likelihood of injury.
There is an embryonic theory, which suggests that polyps form in humans in the womb. During the formation of the intestine, improper formation of epithelial tissue occurs, which subsequently leads to the appearance of polyps on the mucous membranes. A relationship was noted between the formation of polyps and other gastrointestinal disorders (diverticulosis, circulatory failure). There is a family predisposition to the formation of polyps. The most common pathologies are Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and Gardner syndrome.
Article on the topic: Complex therapy of various forms of esophagitis
How are intestinal polyps diagnosed abroad?
In the early stages of the development of such a pathology in the intestines, there are no pronounced symptoms, therefore, in some foreign countries, in order to most effectively prevent cancer, annual special tests have been introduced for the population. One of them, the hemocult test, makes it possible to see, using certain chemical reactions, hidden blood in the stool, which occurs even with very small polyps and may indicate more serious diseases. Timely detection of pathology in a patient helps reduce the cost of cancer treatment abroad.
Digital examination is a traditional diagnostic method when the doctor detects tumor-like growths and other pathologies in the lower parts of the intestine.
The use of MRI and CT makes it possible to observe tumor-like formations in some parts of the intestine. But to diagnose them in the rectum or sigmoid colon, it is better to undergo sigmoidoscopy. A special device, a rectoscope, helps visualize the internal walls of the organ more carefully. Doctors recommend that people who have already crossed the 50-year mark undergo such an examination at least once every 5 years.
Irrigoscopy makes it possible to see polypous formations larger than 10 mm. It is performed using a contrast agent, which is injected into the colon. Then irrigograms are performed similar to X-rays.
Today, the most informative way to diagnose polyps is still a colonoscopy. This method allows you to learn about all intestinal pathologies. When examining a polyp, a biopsy may also be performed. The removed tissue sample is immediately sent for research (histology and cytology). Such an examination also precedes the start of treatment for intestinal cancer abroad.
The use of the latest laboratory testing techniques helps to diagnose polyposis as accurately as possible and find the most effective treatment method.
Treatment methods
When establishing sigmoid colon polyposis, drug therapy is not used, since drugs are not effective in this case.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Treatment is carried out only by surgery.
Today, the removal of tumors formed on the walls of the sigmoid colon can be carried out using several methods.
Polyectomy
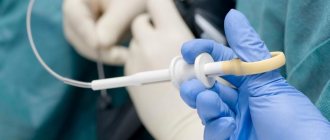
The procedure is performed using an endoscope. An electrode is inserted through the holes made. Then they wrap a special loop around the leg of the polyp, with the help of which the neoplasm is attached to the intestinal walls. After this, a current of high frequency is applied.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
The duration of exposure is only a few seconds. This time is enough for the tissue of the neoplasm to begin to die. The polyp is removed using special grab scissors. The bed where the formation was located is cauterized.
The procedure is performed only in cases where the polyp stalk is not very thick. If it is thick enough, coagulation is used. The tumor is cut off gradually.
If there is a large formation and a wide base, the operation is performed in stages. There should be 1 to 3 weeks between procedures. This time is enough for the wounds to begin to heal after the intervention.
Polyps in the intestines
According to statistics, polypous formations affecting the intestines are diagnosed in 10 percent of the population.
After the operation, the removed tumor is sent for histological examination to identify the presence of altered cells and confirm or refute cancer.
The operation is well tolerated by patients. After the procedure, there is no need for a rehabilitation period, and the patient can start working within 2-3 days.
Transanal resection
Type 3 polyps can be removed through the anus. The operation is performed using local anesthesia . After it has taken effect, the specialist, using a special mirror, expands the anus, intercepts the formation with a clamp and removes it. The resulting mucosal defect is sutured.
Transanal resection is currently used in exceptional cases, since after the procedure there is a high probability of re-formation of polyps.
Endoscopic method
Endoscopic operations have gained great popularity in medicine over the past few years. They have many advantages.
The procedure is performed using an endoscope equipped with instruments and a camera.
During the operation, it is possible to remove villous, adenomatous, hyperplastic polyps, which are located no further than 20 centimeters from the anus.
Abdominal surgery
The indication for this procedure is the presence of multiple polyps affecting the sigmoid colon. The specialist removes not only the tumors, but also part of the intestine.
The intervention is performed under general anesthesia. The disadvantage of the operation is the long rehabilitation period.
Treatment of intestinal polyps abroad
The most effective way to remove intestinal polyps is surgery. The desire to cure a tumor formation at home will not bring the desired results, but will only aggravate the situation, since the pathology can go into a malignant stage, and valuable time will be lost.
Nowadays, to remove polyps, they resort to a treatment method such as TAMIS (transanal minimally invasive surgery). Previously, it was first tested in cancer centers in Israel, but now high-tech equipment and qualified doctors allow this procedure to be performed quickly and painlessly in leading clinics in post-Soviet countries.
In some cases, a combined surgical intervention is used: excision of a tumor formation and electrocoagulation of small polyps. Foreign surgeons perform polypectomy on an outpatient basis using a proctoscope and an elastic ligature. In their opinion, this method is quite simple, low-traumatic, and occurs without side complications when removing even large polyps.
If malignant degeneration of a tumor-like formation in the intestine is suspected, resection of the membrane surrounding the polyp is performed. Next, the doctor sends these removed tissues for histological and cytological tests to confirm the diagnosis. This approach is actively used in the treatment of cancer in Israel and other countries.
Prognosis for intestinal polyps
It must be emphasized that the prognosis for intestinal polyps is favorable in most cases, provided they are removed in a timely manner. Long-term single or numerous polyps of large or small size have a tendency to transform into malignant formations, so treatment should not be delayed. Patients who have been diagnosed with tumor-like growths in the intestines should undergo an annual endoscopic examination in order to exclude the possibility of relapse even after the removal of a benign formation.
Can polyposis develop into cancer?
Polyps are benign formations. They can form in various organs.
But with abnormal division of tissue cells, neoplasms can transform into cancerous tumors, which is dangerous for the human body. That is why, in the case of diagnosing polyposis of the sigmoid colon or other organs, a thorough examination is required.
Patients should follow a special diet after removal of a sigmoid polyp. It will help reduce the load on the intestines and prevent the recurrence of the disease.