Consultation with a proctologist – 1,750 rubles.
- Symptoms of colon polyps
- Risk factors
- Diagnosis of neoplasms
- Treatment
- Popular questions
Colon polyps
- these are benign formations, which are usually asymptomatic and are most often found in patients complaining of discomfort, intestinal dysfunction, pain in the anus, pathological discharge from the anus, which also occurs in other diseases (hemorrhoids, paraproctitis, anal fissure , colitis, rectal cancer, etc.).
The prevalence of formations increases with age and ranges from 25 to 35% among the population over 50 years of age.
The clinical significance of this pathology is due to the fact that from 70 to 95% of colorectal cancer cases develop in the “polyps-cancer” sequence Source: Vladimirova A.A. The use of aquascopy in the diagnosis of colorectal polyps / A.A. Vladimirova [and others] // Bulletin of the All-Russian Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. - 2006. - No. 6 (52). — P. 32-35. .
There is a disease, there are no symptoms
Colon polyps are often asymptomatic, but can cause rectal bleeding, mucous discharge with feces, constipation or diarrhea, discomfort in the intestinal area, and rarely pain (without clear localization).
It should be borne in mind that a dangerous symptom - frequent rectal bleeding - may indicate a high risk of the polyp degenerating into a cancerous tumor. In this case, bleeding, as a rule, is chronic.
But these symptoms are not specific, that is, characteristic only of this disease. Diagnostics is of decisive importance.
How does an intestinal polyp appear?
Cancer in the intestine begins, as a rule, not out of nowhere, but against the background of a benign tumor, popularly called a “polyp.” All benign tumors are divided according to their structure into:
- adenomatous polyps
- and adenomas: tubular, villous and tubular-villous.
Adenomatous polyps are the most common, accounting for almost a third of all tumors.
The risk of cancer due to a polyp is about 15%, maybe more, so all polyps are removed. A quarter of all existing villous adenomas can become cancer, so they are considered the most “harmful”. Of course, not all adenomas become malignant, but the chance of cancer cells appearing in one or another part of the polyp increases with the polyp, its size and age.
A polyp is a tumor that is benign for the time being. They should be distinguished from hyperplastic polyps, which are not polyps at all, but the result of inflammation of the mucous membrane. This name has been preserved since the time when in medicine everything was determined by eye without histological examination, so they were mistaken for true tumors.
Real polyps consist of connective tissue and irregular and deformed glands of the mucous membrane; they are not just a growth, like a hypertrophic polyp, but a complex tumor. And not just a benign tumor, but a precancer that can become a real cancer.
It is not known why polyps occur in the colon; it is assumed that diet, life and genetic factors are to blame. The intestinal mucosa consists of villi and depressions - crypts; for each villi there are several crypts. At the bottom of each crypt, intensive division of stem cells occurs, replenishing the lost cells of the villi and the crypts themselves. A polyp on the villus appears when the balance between proliferation—replenishment of cells—and their differentiation—specialization of newborn cells by function—is disturbed.
The size and shape of polyps vary even in one intestine; they can look like warty protrusions, or they can be a ball on a thin stalk or a fungus sitting on a fold. They can cluster in one place, forming a cluster, or they can be located a meter from each other. It is believed that adenomatous polyps accumulate additional mutations in genes that should normally suppress emerging cancer cells, or in genes responsible for regulating proliferation, and the polyp becomes malignant - becomes malignant, and this is early colon cancer.
Recognize in time
To identify polyps, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination. After examination by a coloproctologist, the following types of instrumental diagnostics may be prescribed:
- sigmoidoscopy (examination of a section of the intestine (up to 30 cm) using an endoscope);
- colonoscopy (comprehensive endoscopic examination of the intestines);
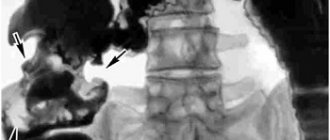
- irrigography (x-ray examination of the intestine using a contrast agent);
- biopsy of the polyp to clarify its histological structure and assess the risk of degeneration into cancer;
- and other studies (according to the testimony of a coloproctologist).
Modern diagnostic methods are available to all patients of the ON CLINIC medical center.
Symptoms and diagnosis of adenomatous polyps
At the onset of the disease, rectal polyps do not manifest clinical symptoms. Adenomatous polyps of the rectum during their growth can cause intestinal bleeding, which proctologists detect using a special test. People over the age of 50 are recommended to undergo a sigmoidoscopy procedure once every 3-5 years using a flexible instrument to identify any abnormal growths that may be an adenomatous polyp.
If adenomatous polyps are found during this procedure, the patient will also have to undergo a colonoscopy procedure. Proctologists recommend this procedure as an important part of the examination for the early detection of colon cancer, since adenomatous polyps can be found in any part of the large intestine. As methods for removing an adenomatous polyp of the rectum identified during colonoscopy, a loop or cauterization is used. Doctors at the proctology department prefer colonoscopy to sigmoidoscopy for the reason that the first procedure allows you to examine the entire cavity of the colon. This is very important because more than half of colon polyps are located in the upper part of the colon, which is inaccessible to sigmoidoscopy.
Adenomatous polyps of the rectum are also detected in the absence of symptoms of the disease during screening examinations or when the study is carried out for other reasons (gastrointestinal bleeding), endoscopic examination (sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy) or x-ray method (irrigoscopy).
If small polyps (less than 1 cm) are detected during sigmoidoscopy, a biopsy is performed followed by a morphological examination. If the polyp is larger than 1 cm, a biopsy is usually not required, as the patient will need a colonoscopic polypectomy. If the histological structure of the polyp detected during sigmoidoscopy corresponds to an adenoma, the patient needs a colonoscopy.
Who is at risk of getting sick?
It has been established that people living in a metropolis mainly consume high-calorie foods with a high content of animal fats and a small amount of fiber.
All this helps to reduce the contractile activity of the intestine, the release of toxic substances that negatively affect its mucous membrane, disruption of the intestinal microflora and changes in the composition of enzymes of microbial origin.
One of the main factors in the development of polyps is heredity .
Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases contribute to the development of painful changes (dysplasia) of the colon mucosa.
A sedentary lifestyle and associated constipation are a secondary factor contributing to long-term exposure to toxic substances on the colon mucosa.
It is worth remembering that only timely diagnosis and treatment of polyps give the patient the opportunity to prevent the development of cancer.
Diagnosis of intestinal tumors
Among non-invasive methods for diagnosing colon polyps, the stool occult blood test
. At the same time, the hemoccult test is characterized by a high percentage of false negative results and is not very informative in the presence of polyps less than 2 cm and when the formations are localized in the right half of the colon.
Quite common in the diagnosis of polyps is digital examination of the rectum.
. The method allows you to evaluate the shape and consistency. mobility, presence or absence of a polyp stalk. Low-lying polyps are always detected by digital examination. Small adenomatous polyps located above 5-6 cm from the anus are difficult to determine using the finger method.
Sigmoidoscopy is an important method in the diagnosis of villous tumors.
. This research method is more informative and makes it possible to detect most colon polyps, because more than 50% of them are localized in the rectum and sigmoid colon, i.e. within reach of the rectoscope.
Irrigoscopy
allows you to diagnose most polyps more than 1 cm in diameter; smaller formations can be detected much less frequently.
The most accurate and affordable method for detecting colon polyps is currently colonoscopy.
. During the procedure, the condition of the colon mucosa is visually assessed. Also during colonoscopy, it is possible to perform various therapeutic procedures: removal of benign tumors, stopping bleeding, removal of foreign bodies, recanalization of intestinal stenosis.
Virtual colonoscopy
allows you to obtain three-dimensional computer sections of the colon mucosa even with a small lumen diameter. The sensitivity of this method for diagnosing polyps larger than 1 cm is 90%; for polyps measuring 0.5-0.9 cm 80%; 67% when the size of the polyp does not exceed 5 mm. The disadvantages of the method are the rather expensive cost of the procedure and the impossibility of performing a biopsy of the formations.
For a targeted study of the condition of the rectum and colon and if a tumor lesion is suspected, special ultrasound
, which are associated with filling with air or diagnostic medium.
All types of modern diagnostic tests are available at the SM-Clinic. Currently, diagnosing polyps does not require much time and is carried out quickly and painlessly.
The disease can be prevented
A special focus of the work of the coloproctologist at ON CLINIC is preventive research. For this purpose, a colonoscopy is performed.
After 40-50 years, an examination by a coloproctologist is necessary once a year, a colonoscopy – once every three years. But you should approach this issue more individually.
It is necessary to undergo regular examinations at an earlier age:
- if the patient’s family had cases of polyps or colon cancer;
- if the patient was previously diagnosed with chronic intestinal disease;
- with eating disorders, sedentary lifestyle, frequent constipation;
- when discomfort in the intestinal area, pain and other unpleasant symptoms occur.
The basis for the prevention of colon cancer is the early detection of asymptomatic polyps and timely surgical treatment.
Any detected polyp requires, first of all, a thorough examination and subsequently immediate surgical intervention to avoid life-threatening complications.
Surgical treatment is carried out using endoscopic equipment, with the help of which the stalk of the polyp is captured and compressed. This is followed by a mandatory histological examination of the taken material.
Polyposis of the colon
Diffuse polyposis of the colon is multiple polyps. This disease is considered a precancer of the colon. The following forms of colon polyposis are distinguished:
1. Proliferating diffuse polyposis: stage I - hyperplastic polyposis; the size of the polyps usually does not exceed the size of a millet grain; in most cases, patients complain of frequent loose stools, often mixed with blood; anemia with corresponding symptoms may develop; the disease may be asymptomatic. The average age of patients is 30 years, malignancy develops in approximately 35% of cases. Stage II - adenomatous polyposis, the size of the polyps is 5-8 mm, a more pronounced clinical picture is observed. The average age of patients is 34 years, malignancy is observed in 45% of cases. Stage III - adenopapillomatous polyposis: large glandular polyps transform into villous ones (from 1.0 cm or more). Patients are concerned about abdominal pain, repeated diarrhea with blood and mucus, weight loss, and anemia. The average age of patients is 39 years. Malignancy develops in 80% of cases. With diffuse familial polyposis of the colon, several members of the same family are often affected, and the disease is inherited. Almost all untreated patients develop colon cancer. 2. Juvenile diffuse polyposis. Patients complain of abdominal pain without clear localization, frequent loose stools with mucus and blood. Diagnosis of polyps of the small intestine is helped by x-ray examination, biopsy, endoscopy; when polyps are located in the colon - colonoscopy with biopsy. These patients also have other developmental anomalies - heart defects, hydrocephalus. Characterized by metabolic disorders arising from disorders of digestion, absorption, and intestinal motility. The probability of malignancy is 20%. With timely surgical treatment, the prognosis is favorable. Patients after surgical treatment require long-term follow-up. 3. Hamartomatic polyposis or Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a hereditary disease characterized by a combination of pigmentation of the mucous membranes and skin with polyposis of the stomach and intestines. Symptoms of this type of colon polyposis: attacks of abdominal pain, gastrointestinal bleeding. It is believed that malignancy of Peutz-Jeghers polyps occurs rarely, but with widespread polyposis the likelihood of malignancy increases. The prognosis depends on complications (bleeding, intestinal obstruction, malignancy), timely diagnosis and treatment. Colonic polyposis also includes Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract, nail dystrophy, baldness, hyperpigmentation of the skin. Symptoms of this type of colon polyposis: loose, watery, copious stools up to 4-6 liters per day, swelling due to protein loss (which can spontaneously decrease and increase), muscle atrophy, changes in the fingers in the form of drumsticks are more often observed after 40 years. Due to calcium deficiency, patients often experience cramps. The diagnosis is made based on the detection of polyposis during endoscopic and radiological studies with appropriate symptoms. A family predisposition to the disease has not been proven. Malignant degeneration of polyps is not observed in Cronkhite-Canada syndrome.
Share link:
Effective treatment of polyps at ON CLINIC
Modern diagnostic equipment and gentle methods of surgical treatment allow coloproctologists of the Multidisciplinary Medical Center ON CLINIC to diagnose and effectively treat polyps of any size, multiple types (including villous adenomas).
Thanks to the introduction of a modern endosurgical treatment method (transanal endoscopic microsurgery), operations are performed on an outpatient basis, and the patient’s performance is restored in the shortest possible time.
After the operation, the patient is observed in a comfortable day hospital at ON CLINIC under the supervision of the attending physician. Control endoscopy is carried out every year, for preventive purposes - every three years.
Coloproctologists at ON CLINIC will help each patient prevent the development of a dangerous disease. And with the help of preventive studies, the disease can be recognized in time (including asymptomatic polyps), and highly effective treatment will be carried out in accordance with international standards.
ON CLINIC – modern standards of diagnosis and treatment!
Polyps of the colon and rectum
- Home /
- Branches /
- Proctology /
- Polyps of the colon and rectum
The Clinical Hospital on Yauza carries out the necessary diagnostics (endoscopic, histological) and radical treatment of all types of polyps of the rectum and large intestine using modern endoscopic and surgical equipment, including an ultrasonic scalpel, laser and radio waves.
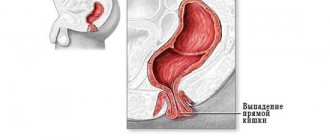
Polyps of the colon and rectum are one of the most common diseases of the outflow tract of the large intestine, caused by a benign growth of its mucous membrane. It occurs at any age, in both men and women. Intestinal polyps tend to progress and, if they exist for a long time, can degenerate into a malignant tumor, therefore they are subject to surgical removal in the absence of contraindications.
Using a modern colon and rectoscope, endoscopic removal of a polyp of the mucous membrane of the rectum or colon is performed, followed by postoperative monitoring of the condition of the intestine.
Symptoms of rectal polyps
Polyps, as a rule, irritate the intestinal wall, thereby causing a number of unpleasant symptoms: false urge to defecate, frequent stools in small portions, often mixed with mucus and blood, poor health.
Frequent chronic bleeding from polyps and inflammation in the area of glandular growth are an absolute indication for their removal.
Removal of polyps at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
Our surgeons remove polyps in the lumen of the rectum and colon through a recto- or colonoscope. This is a painless procedure, since the glandular tissue of the polyp is devoid of nerve fibers that perceive pain. The operation lasts literally a few minutes. The formation is removed by an endoscopic diagnostic doctor during a colonoscopy. Preparation for the diagnostic procedure is required over several days according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor.
Anal canal polyps and hypertrophied anal papillae (small formations on the crypts (folds) of the rectum in the anorectal area) are removed in our medical center using modern equipment: ultrasonic scalpel, laser or radio waves. These are bloodless and non-traumatic methods that are used in outpatient surgery and promote rapid healing.
Radio wave and laser methods themselves contribute to the disinfection of the surgical wound and the bloodlessness of the operation. An ultrasonic scalpel additionally protects tissue from thermal burns, which promotes faster healing. Therefore, patients recover quickly after surgery. But, a prerequisite for the postoperative period is to follow a diet and avoid heavy physical labor and heavy lifting for two weeks.
We perform polypectomy of the anal canal and removal of hyperplastic anal papillae by an experienced coloproctologist. The doctors of our clinic work according to modern standards of high-tech medical care and carry out all the treatments for rectal and colon polyps known in the world today.
You can see prices for services