Home » Intestinal adenoma » Tubular adenoma of the colon
What is tubular villous adenoma of the colon? This is a benign neoplasm that instantly affects the intestinal mucosa. The size of the neoplasms is 2 centimeters, after which growth stops. If the volume of adenoma grows rapidly, then the disease progresses and affects neighboring healthy organs. Tubular adenoma of the colon with dysplasia is considered the first stage of low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia of the colon. The pathology turns into a malignant tumor if timely treatment is not provided.
When the first signs of adenoma appear, you need to contact a proctologist to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the body and begin treatment. The private proctology clinic “Proctologist 81” employs highly qualified specialists who use modern treatment methods and new equipment that can diagnose the disease even at an early stage.
Types and their features
Depending on the location, adenoma is distinguished:
- thyroid gland – follicular, papillary nodes formed from Hürthle cells and toxic with hyperfunction of the organ;
- prostate – benign prostatic hyperplasia BPH in men;
- mammary glands – phylloid, near-ductal, growing into the lumen of the flow and mixed type;
- salivary glands - rare encapsulated tumors near the ear glands with accumulations of lymphoid tissue;
- sebaceous glands;
- adrenal glands – adenocortical, pigment and oncocytic;
- pituitary gland;
- bronchial mucosa;
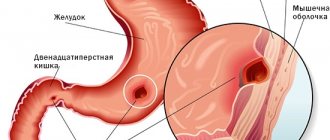
- gastrointestinal mucosa;
- liver - solitary, localized in the right lobe, found mainly in women.
Depending on the structure, neoplasms are distinguished:
- cystic – sac-like;
- papillary - with papillary growths into the lumen of the gland;
- polypoid - polyps of glandular tissue;
- solid - with a poorly developed supporting connective tissue structure and continuous glandular epithelium;
- tubular - from narrow epithelial canals and intercellular supporting stroma.
Depending on the number of nodes, they can be single or multiple (adenomatosis).
Adenomatous polyps
All types of polyps have their own signs that the patient notices. The following characteristics are distinguished:
- there are no inflammatory reactions;
- polyps are located in the final section of the large intestine;
- have the appearance of single polyps from the epithelium;
- have a smooth and even surface;
- the structure is considered dense;
- placed on a thin stalk that grows rapidly;
- redness and irritation appear on the mucous membrane;
- cracks form;
The characteristic of the formation is the size of the polyp. It is small and increases if left untreated. To diagnose tubular villous adenoma of the sigmoid colon, studies are carried out, including rectoscopy and irrigoscopy. The procedures allow us to assess the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and diagnose the presence of tumors and cysts. Determination of the type of polyp is carried out without histological examination.
Tubular papillary adenoma of the colon and tubulovillous adenoma of the colon are similar in appearance, so you should contact a proctologist who can make a clear diagnosis for the patient.
Reasons for development
Most adenomas exhibit primary hormonal imbalances. For example, hormone-dependent prostate hyperplasia occurs due to an imbalance of testosterone, and mammary glands due to an imbalance of estrogen.
Sometimes the formation of adenomas of the thyroid gland is associated with mechanical lesions, and of the pituitary gland - with head injuries or previous infections. The risk of developing adrenal hyperplasia is higher in smokers.
Breast adenoma can be caused by a large number of abortions, taking oral contraceptives, unfavorable pregnancy, pathologies of the female reproductive system. Hepatic hyperplasia is associated with taking OCs or steroids.
Symptoms of adenoma
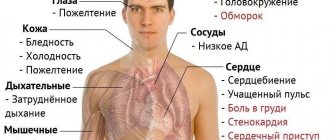
After a long asymptomatic course, the disease begins to manifest itself only if the tumor grows: it begins to compress surrounding organs, nerves, blood vessels, urinary tract, etc. Signs of adenoma appear depending on the location of the pathological process:
- Bronchial tumors are characterized by shortness of breath and wheezing cough.
- When the prostate gland is damaged, urination disorders, frequent urge to go to the toilet, intermittent urination, and constipation occur. According to the severity of manifestations, 3 stages of prostate adenoma are identified.
- An adenoma of the pituitary gland or thyroid gland is characterized by headache, irritability, tearfulness, fatigue, decreased libido, and excess weight.
- Cystic can be located in the pancreas, bile duct or appendix. When it opens spontaneously, a person feels severe attacks of pain.
- With adenoma of the lymphatic system, the lymph nodes increase in size and become denser.
- With adrenal adenoma, bone fragility and the risk of developing osteoporosis increase.
- With adenoma of the salivary glands, recurrent otitis is possible.
- Hepatic adenomas cause severe abdominal pain.
Diagnosis of adenomas
Diagnosis is made using:
- biopsy of a tissue sample – allows you to determine the type of neoplasm;
- CT and/or ultrasound, including transrectal TRUS, help determine the exact size and location of the tumor;
- Clinical blood and urine tests allow you to assess the overall picture and identify foci of inflammation.
Prostate adenoma is detected using digital examination, radiography and contrast urography, cystometry of the bladder and uroflowmetry of the urinary tract, determination of the level of the prostate-specific hormone PSA and a biochemical blood test. Palpation and mammography are also used to diagnose breast adenoma.
Diagnosis of the disease
The presence of tubular adenoma is extremely difficult to detect in the early stages. There are no symptoms, and the size of the tumor does not exceed a few millimeters. According to medical statistics, for many years the pathology occurs without clinical manifestations and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
For diagnosis, the patient visits a proctologist, who conducts an initial examination and learns about the medical history. Clinical and biochemical studies are being carried out. The patient takes a general blood, urine and stool test. It is mandatory to conduct a stool test for occult blood, which will determine the presence of disorders in the intestines. Tests such as irrigoscopy and colonoscopy are popular.
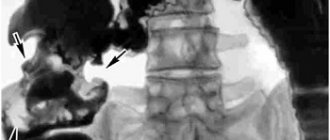
Irrigoscopy is considered an X-ray examination of the colon, which is performed using contrast fluid. For example, barium sulfate. The procedure reveals the contours of the mucous membrane in the affected area and suggests the nature of changes in the body. Diagnostic testing is not carried out for allergic diseases, pregnancy and the lactation period. Contrast agents are considered allergens.
Colonoscopy is most effective in identifying and diagnosing adenomas. Allows a medical expert to identify a formation on the mucous membrane and perform a biopsy for morphological examination of the affected tissue. During a colonoscopy, the surgeon can identify an existing polyp or coagulate it using a medical device.
The results of the examination are interpreted by a specialist who will clearly make a diagnosis and prescribe an effective course of treatment.
Treatment methods for adenomas
At the first stage, hormonal levels are adjusted using drug treatment. Then surgical intervention is performed - the main method of effective treatment of the pathology. During the operation, the tumor is completely removed. Preference is given to laparoscopic techniques with mini-access without incisions.
How are some types of adenomas treated?
In addition to surgery, alternative methods for removing prostate adenoma are often used:
- expansion of the narrowed area by inflating a special balloon;
- installation of expanding stents;
- thermo- or MV coagulation;
- UZT;
- cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen;
- transurethral needle ablation.
Drug treatment of the disease is additionally aimed at improving blood circulation in the pelvis, eliminating stagnation of urine and constipation, reducing inflammation, inhibiting hyperplasia and preventing infection.
With breast adenoma in young women, reverse development (resorption) of the tumor is possible. Therefore, if the tumor does not cause fear of malignancy and inconvenience for the patient, dynamic observation is recommended.
In the first weeks after discharge from the hospital, it is recommended to avoid any heavy physical activity and sudden movements, which may disrupt the healing of the postoperative wound.
Removal of tubular adenoma of the colon
Removal is the only treatment for tubular adenoma of the colon. Surgical treatment of benign tumors of the colon as an effective measure for the prevention of colorectal cancer is an important area of activity at the European Oncology Clinic in Moscow. Therefore, its specialists have extensive experience in removing tubular adenomas. In the vast majority of cases, operations are performed here:
- endoscopic method during fibrocolonoscopy. Often this is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure, since single polyps are removed during the same colonoscopy when they were discovered. No more than 4 tubular adenomas are usually removed at one time, so that the operation does not become too traumatic. The rest, if any, are removed after the intestinal mucosa has healed after the first intervention.
In experienced hands, this is a simple, minimally invasive intervention, during which the neoplasm is cut off from the mucous membrane with a special loop with an electric current passing through it. As a result, a tiny non-bleeding scab remains at the site of the adenoma, the mucous membrane under which quickly recovers;
- by transanal resection - when the tubular adenoma is located in the rectum not far from the anus, in the area of direct vision when the passage is widened with special instruments. For adenomas of this localization, which almost always show signs of severe dysplasia or non-invasive stage of cancer (in situ) during histological examination, this method is preferable, since in this case they are excised together with the underlying part of the rectal wall.
Endoscopic removal of a single tubular adenoma is an outpatient procedure; in other cases, the duration of hospitalization does not exceed 1-2 days.
The need for abdominal surgery usually arises if:
- tubular adenomas recur repeatedly, and after many operations difficulties arise in carrying out the next endoscopic intervention;
- Many tubular adenomas have been discovered, when the only solution is resection of part of the intestine with them;
- Histological examination of the removed tubular adenoma revealed its malignant degeneration. The patient then undergoes a more extensive resection, consistent with colorectal cancer treatment protocols.
Prevention
Prevention of pathology - undergoing regular preventive examinations and screenings - for example, monthly self-examinations and annual visits to a mammologist, as well as proper wearing of a bra to prevent breast adenoma. Prevention of prostate adenoma - timely treatment of prostatitis, monitoring PSA levels at the age of 50 years or more, control cholesterol and BMI, quitting smoking and alcohol abuse, balanced nutrition and physical activity.
After removal of the adenomasmal glands, medical supervision is necessary, since the disease is associated with Muir-Torre syndrome, which increases the risk of developing cancer. To consult with a specialized specialist in St. Petersburg, fill out the online appointment form.
Sources:
- Clinical guidelines of the European Association of Urology, 2017. https://urologi.kiev.ua/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/EAU_2017.pdf
- Urology. Russian clinical recommendations / ed. SOUTH. Alyaeva, P.V. Glybochko, D.Yu. Pushkar. — 2021.
- Colorectal adenomas - A.D. Borsuk, E.G. Malaeva: Problems of health and ecology, 2011.
- Thyroid adenoma. Pinsky S.B., Beloborodov V.A.: Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk), 2010.
- Aggressive pituitary adenomas (literature review and clinical observation. Kalinin P.L., Trunin Yu.Yu., Fomichev D.V., Chernov I.V., Ryzhova M.V.: Head and neck tumors, 2021.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Expert opinion
The chief physician of the European Oncology Clinic in Moscow, surgeon, oncologist, candidate of medical sciences Andrei Lvovich Pylev explains: “Not all colon polyps have the same malignant potential. Tubular adenoma, for example, degenerates in 60% of cases. The risk increases even more if the polyps are multiple, large, have a wide base, and are located in the rectum.
Therefore, the diagnosis of tubular adenoma is a direct indication for its removal in all cases. This is done here by Doctor of Medical Sciences, one of the most experienced specialists in Russia in the field of diagnostic and surgical endoscopy, Mikhail Sergeevich Burdyukov.”