Home » Polyps in the intestines
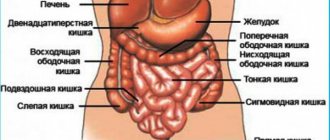
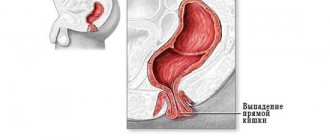
Polyps are abnormal growths of tissue on the intestinal mucosa. Pathology manifests itself on the genitals. Neoplasms are also found in the digestive tract. Polyps form in the large intestine, rectum and cecum. In the early stages of the disease, there are no signs of polyps in the intestines. To diagnose the pathology, an endoscopic examination and tests should be performed.
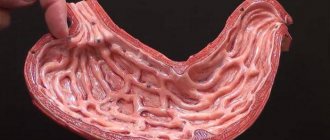
Colon polyps externally resemble fleshy growths that form in the cavity of the gastrointestinal tract or in other internal organs. Consists of a cluster of small cells. The polyp is attached by a stalk or other base to the soft tissues and presses into the cavity.
In advanced cases, many polyps are diagnosed in the human body, which are located throughout the intestine. Small neoplasms are up to two millimeters in size. They are growing daily. As polyps enlarge, they are injured by feces. Internal bleeding opens, which leads to anemia.
If the size of the growths exceeds the norm, then they block the intestinal lumen. As a result, the patient suffers from constipation, feces stagnate in the body, thereby causing discomfort. This proctological disease is diagnosed in both young and elderly people. Both men and women are susceptible to the appearance of polyps.
The risk group includes genetically predisposed people and those who have previously suffered intestinal polyposis. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease becomes malignant. The polyp is constantly injured, and cancer cells form in it. The appearance of polyps is a precancerous condition.
Types of intestinal polyps
Medical experts identify several types of intestinal polyps. Depending on the form of the neoplasm, multiple and single growths are distinguished , on a stalk or on a thick base. The upper part of the polyp looks like a ball or a mushroom cap.
Based on the reasons for their occurrence, the following varieties are distinguished::
| Inflammatory bowel polyps | This type of pathology is formed during acute and inflammatory diseases. Often such polyps are diagnosed with ulcerative colitis and duodenal ulcers. |
| Hyperplastic intestinal polyps | Polyps form during the growth of soft tissues. It is the most common form of the disease. |
| Neoplastic intestinal polyps | Polyps appear due to an increase in atypical cells. Such cells are divided into benign and malignant. This form of the disease is dangerous to health and can be fatal. |
Neoplastic intestinal polyps are divided into the following types:
- tubular;
- tubular-villous;
- villous adenomas;
According to medical statistics, the risk of transition to a malignant disease is high with villous adenomas and tubulovillous polyps. With other types, the risk of cancer cells is reduced to zero.
Treatment of cecal polyps
The only way to get rid of a polyp of the cecum and any other part of the colon quickly and reliably is polypectomy, that is, its removal.
In most cases, the doctor does this during a colonoscopy - painlessly and practically invisible to the patient, and only the largest and most complex of them require surgery, which doctors try to perform using a laparoscope - a long thin tube with a light source and a camera. The procedure is minimally invasive, that is, during its implementation very little tissue is damaged - the device is inserted into a small incision in the abdominal cavity and eliminates the suspicious formation. Upon completion, the person is left with a tiny, quickly healing scar, and the body quickly recovers.
The removed material is sent to a laboratory, where specialists examine it - determine the type of formation and check whether it contains cancer cells.
Doctors recommend that each patient undergo repeated examinations, since there is a risk that polyps will develop again. This should be done once a year if there were several formations, or at least one of them turned out to be larger than 2 centimeters, or less often - with small single growths.
The first signs and symptoms of oncology February 3, 20211678 1
Intestinal polyps: symptoms and manifestations
Intestinal polyps are diagnosed in ten percent of people. According to medical data, men are more predisposed to proctological disease than females. Symptoms of polyps in the intestines appear when the size of the tumors rapidly increases. In most cases, treatment begins when the disease is at an advanced stage.
To reduce the risk of proctological diseases, you should pay attention to even isolated symptoms and promptly contact medical specialists. The help of a proctologist is needed if the following signs appear :
- pain in the abdominal area;
Do polyps in the intestines hurt? When polyps appear, the patient experiences constant abdominal pain. Unpleasant sensations intensify with movement, coughing and sneezing, and with the slightest physical exertion. The pain increases sharply and disappears completely after a few minutes.
- problems with bowel movements;
The patient suffers from problems with defecation. Constipation and diarrhea are observed, regardless of food intake. With diarrhea, the intestinal mucosa is irritated, intra-abdominal pressure increases, which leads to the formation of anal fissures. With constipation, the patient strains, trying to defecate, which also provokes the formation of anal fissures.
- stagnation of feces in the body;
With regular constipation, feces stagnate in the body, accumulate and grow in volume. An infectious process develops, intoxication occurs, which leads to complications.
- impurities in feces;
Impurities of blood, mucus and pus are found in the stool. This sign indicates an inflammatory process.
- frequent urge to defecate;
The patient suffers from frequent urge to go to the toilet, but bowel movements never occur. The functioning of the esophagus is disrupted.
- lack of appetite;
The patient has no appetite throughout the day. There is rapid weight loss, anemia or anemia. Due to a lack of vitamins, the patient feels severe weakness and drowsiness.
- itching and burning in the anus;
Due to the frequent urge to defecate, the soft tissues of the anus become inflamed. Itching and discomfort appear in the affected area.
- symptoms of the cardiac system;
When polyps appear in the intestines, the patient is also concerned about symptoms from the cardiac system. Blood pressure increases, tachycardia and dizziness appear.
Symptoms of polyps in the intestines in women are accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen , so patients often confuse the appearance of polyps with inflammation of the appendages. We are talking about a gynecological disease if vaginal discharge appears before menstruation.
Diagnosis of cecal polyps
Early detection of polyps is an extremely important task, since the doctor can not only examine a tumor found in time, but also remove it if he considers it necessary, which allows a person to avoid the fate of becoming an oncologist’s patient.
How are such formations found and studied?
- The most popular method is a colonoscopy
- an examination of the digestive tract using a flexible tube at the end of which there is a camera with good resolution. First, its contents are qualitatively removed, then, at the patient’s request, so-called sedation is carried out - they give him sedatives, after the onset of which the not most pleasant of procedures is perceived quite easily. The colonoscope itself is inserted into the anus and passes through all the bends of the rectum, colon, descending, transverse, ascending and cecum, and the doctor examines and evaluates the condition of their walls. Modern equipment makes it possible not only to look at, but to remove polyps without incisions or surgical operations. After removing the formation, it is sent to the laboratory for examination, where specialists determine its malignancy, that is, danger to the body, and determine whether there is a need for other interventions. - Virtual colonoscopy
allows you to see what is happening in the body without penetrating it or damaging the tissue - in fact, a computer or magnetic resonance imaging scan allows you to get an accurate image of the desired part of the digestive system without inserting tubes and other hoses into it. True, first, air is injected into the patient’s rectum, straightening all the intestinal walls, and if polyps are detected, they are removed using the same classic colonoscopy. - Stool testing
is another important diagnostic method that can detect blood in the feces, which indicates the likelihood of the presence of formations or diseases in the intestines.
Signs of polyps in the intestines in children
In childhood, polyps in the intestines appear much less frequently, but such cases still occur. Children do not pay attention to the symptoms and will not be able to determine the presence of the disease, so parents should pay attention to the child’s nutrition, the process of bowel movements and general well-being.
If you have problems with your stool or blood is found in your stool, you should immediately contact a medical specialist. The private proctology center “Proctologist 81” employs experienced doctors who can cure the disease even at an advanced stage.
There are such types of polyposis in a child:
| juvenile polyposis; | The disease is diagnosed in preschool children. The pathology does not manifest itself in any way and disappears on its own. |
| lymphoid polyposis; | The pathology develops from six months to puberty. This type of polyposis must be treated urgently to avoid the chronic stage, the opening of bleeding and the disease becoming cancerous. There are constant problems with bowel movements and stomach pain. |
| Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; | The disease is considered hereditary. People with a genetic predisposition are susceptible. Neoplasms form in the small intestine or rectum. |
| adenomatous polyposis; | We are talking about neoplasms that appear in the colon. The disease develops en masse in all family members. |
| Gardner's syndrome; | A large number of polyps appear in the intestines. Neoplasms are also found in the sigmoid and duodenum, and in other internal organs. |
Why do polyps grow?
The process of their growth is quite simple - our body constantly creates new cells that are needed to replace old, damaged or unnecessary cells that have expired, and this procedure is clearly regulated. This is exactly how everything happens with correct, healthy cells - they appear in a strictly defined tissue, live and die as it is “written” in their genetic “program”. But sometimes, due to illness, injury, damage, exposure to harmful substances or simply random failures, they change and begin to work differently from normal ones - they quickly develop and create growths that gradually turn into polyps growing anywhere in the intestines.
Causes of polyps in the intestines
The reasons for the formation of polyps in the intestines are quite different. The etiology depends on the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases. To date, medical experts and scientific researchers have not identified factors that could cause tumors. However, there are several theories that explain the causes of polyps in the intestines:
- Inflammatory theory;
This theory suggests that benign neoplasms are an intermediate stage between the appearance of cancer cells and between acute inflammation in the intestine.
- Disregenerative theory.
According to this theory, proctological disease is considered a pathology or regenerative process of affected cells in the intestine. This process provokes an increase in tumors in the internal organs.
- Embryonic theory.
According to the embryonic theory, the appearance of polyps in the intestines is influenced by improper formation of the mucous membranes following injury or inflammatory processes.
There are also several reasons that could affect the formation of polyps in the gastrointestinal tract:
- genetic predisposition;
People whose relatives have previously been diagnosed with polyps are predisposed to the appearance of neoplasms. In some cases, the pathology is considered congenital.
- poor nutrition;
Diet directly affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If the menu contains fatty, fried, smoked foods, then the stomach and intestines cannot cope with processing. The presence of animal fats and carbohydrates has a negative impact on intestinal function. With a lack of fiber, polyps form in most cases.
- sedentary lifestyle;
With a sedentary lifestyle, feces stagnate and the stomach works more slowly. Intra-abdominal pressure increases, which provokes the appearance of neoplasms.
- impaired functionality of the gastrointestinal tract;
With constant constipation and diarrhea, the intestinal mucosa is irritated, the functioning of the digestive tract is disrupted, and this provokes the growth of polyps. With alcohol abuse, intestinal function slows down, thereby causing the formation of polyps.
A weakened immune system and the presence of reflux diseases can also affect the development of pathology. It is worth changing your diet, leading an active lifestyle and getting rid of bad habits to reduce the risk of developing diseases.
For patients: Flat “invisible” #polyps #colon.
Full text of the article:
Hello, dear readers!
I am often approached by patients who have undergone a colonoscopy in the past 1-2 years and are firmly convinced that there are no polyps or tumors in their intestines, but in fact the situation turns out to be completely different. This publication will provide just such an example.
The reasons for differences in colonoscopy results are differences in the approach to quality.
I will not dwell in detail on the quality criteria for colonoscopy in this publication; I will simply list them:
— The examination must include the cecum, the colonoscopy protocol must contain a photograph of the mouth of the appendix - taken into account in the CIR indicator. If the cecum is not reached, then the colonoscopy is considered incomplete and should be repeated as soon as possible.
— The quality of intestinal cleansing must be at least 6 points according to BBPS (residual fluid is allowed in the intestine, which can be pumped out and the intestinal walls washed). If the quality of preparation is insufficient, the colonoscopy is stopped and repeated as soon as possible.
— The screening colonoscopy time should be at least 30 minutes, and in case of a positive stool occult blood test, at least 45 minutes. This time includes insertion, removal of the colonoscope, and therapy. Removing the colonoscope from the colon
— ADR ⩾ 25% – frequency of detection by an endoscopist of adenomas (except serrated) in patients 50 years of age and older. THIS IS A KEY INDICATOR. Leading experts have an ADR of 60-65%. The lower the ADR, the higher the adenoma missed rate (AMR). A 1% decrease in ADR results in a 3% increase in the risk of interval colon cancer.
— Removal of polyps up to 10 mm immediately during primary colonoscopy, their extraction for further pathomorphological examination.
— Photo protocol of colonoscopy.
— High-resolution equipment, with NBI optical narrow-spectrum technology, with high-quality HD image quality, Enhancement structural detailing function and the possibility of preliminary freeze-frame. Today, OLYMPUS equipment of the 170, 185, 190, 290 series meets these requirements. It is also extremely important to have optical magnification, which is provided by the DualFocus technology: optical magnification of 60-70 times - these technical characteristics are possessed by the 190 series endoscopes together with the endoscopic system OLYMPUS EXERA III.
Those interested can study in detail the ESGE colonoscopy quality criteria using the link.
As you can see, there are many requirements and it is not so easy to comply with them, so not every colonoscopy can be considered high-quality.
At #CenterExpertEndoscopy, we comply with all quality criteria for endoscopic examinations within the framework of the ESGE guidelines and remove intestinal polyps on an outpatient basis, immediately when they are detected.
So, a clinical case. The patient is 60 years old. Repeated colonoscopies in 2021, 2021, 2021 in different clinics. Several polyps in the sigmoid colon were discovered and removed.
During examination at #CenterExpertEndoscopy, dozens of flat epithelial neoplasms and lateral creeping tumors, up to 25 mm in size, were identified in all parts of the colon, belonging to the category of high risk of malignant transformation. These polyps have not been described in any previous studies. Of course, this situation is very unpleasant for the patient, who had undergone colonoscopy several times and was sure that she had no serious problems in her intestines.
You can see that in white light the polyp is really not striking, but with the use of NBI we clearly see its borders and microrelief, and we can determine that it is most likely a tubular adenoma with low-grade dysplasia, up to 10 mm in size. This adenoma was removed using cold loop polypectomy.
In the next photo you can immediately see flat polyps, covered with a thick layer of mucus, which, in fact, indicates their presence. After removing the mucus, we see the microrelief of these neoplasms in the form of wide open rounded pits, which is typical for serrated adenomas.
We removed some of these tumors, and some are planned to be removed during a subsequent colonoscopy.
Images were obtained using an OLYMPUS EXERA III system and a CF-H185I colonoscope with NBI optical narrow-spectrum technology.
At #CenterExpertEndoscopy, we remove polyps during the initial examination, on an outpatient basis, according to the international recommendations of ESGE, ASGE.
Only a combination of the doctor’s knowledge and his compliance with the criteria for the quality of colonoscopy, the quality of patient preparation, and expert-class video endoscopic equipment can ensure high quality colonoscopy!
Be healthy! Focus on results!
#Let'sStopCRC
#AlexeyKorneev
#cornevendoscopy
How to get rid of polyps in the intestines
First of all, you should immediately contact a proctologist or gastroenterologist. The doctor will review your medical history and conduct a survey regarding complaints and symptoms. After this, the patient is sent for tests and diagnostic tests.
A colonoscopy is performed, with which you can most accurately examine the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and detect the presence of polyps, even if the size of the formations is too small. After the examination, each patient is individually prescribed a course of treatment.
When treating intestinal polyps, surgery is performed. Conservative treatment is ineffective in such cases and makes no sense. Drug treatment is prescribed only to elderly people and children whose bodies are too weak to undergo surgery. Drugs are prescribed that relieve the patient of symptoms.
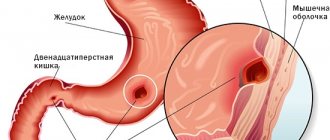
What is a cecal polyp and how dangerous is it?
Polyps are formations that grow on the inner wall of the intestine.
They occur quite often - according to various studies, at least 30% of residents of civilized countries over 50 years of age, and about 6% of children, become their owners.
Most of these growths in the cecum, colon, and rectum are harmless, but some can develop into cancer. The transformation from a harmless growth into a fatal disease usually takes many years, which makes it possible to avoid a terrible diagnosis for those who undergo timely examinations and monitor their health.
The very fact of having a polyp does not mean at all that a person will definitely develop cancer, but it is important not to forget that some of them do become dangerous tumors, and this probability is most increased by:
- growths larger than 1 centimeter;
- or their quantity – from 3 pieces;
- and detection on the intestine itself or in a distant formation of dysplasia - a precancerous condition, that is, altered cells that differ from normal ones.
Recommendations
In advanced stages, alternative medicine will not be effective, but traditional treatment methods will help prevent the formation of new polyps. The patient is given enemas of medicinal herbs , which have an anti-inflammatory effect and improve intestinal microflora. To improve intestinal motility, it is recommended to drink a decoction of yarrow, St. John's wort, and oak bark . A decoction of viburnum is considered effective, as it has a beneficial effect on internal organs.
Sea buckthorn oil, celandine tincture , pumpkin seed infusion, and chamomile herb infusion are considered anti-inflammatory agents It is recommended to drink a mixture of butter and natural honey daily before meals. This remedy improves the digestion process, helps with constipation and makes bowel movements easier. In addition, intestinal pain and bloating disappear.
Polyps and cancer of the cecum - how does one turn into the other?
Alexander Korotaev,
thoraco-abdominal surgeon, oncologist, head of the department of surgery, “Medicine 24/7” clinic
“Simply altered cells are not always oncology. Only a part of the formations consisting of them still undergo malignancy, that is, they turn into a life-threatening tumor. If this happens to the tissues of the polyp itself, over time they grow into the intestinal wall, and cancer begins to develop in its inner layer, its cells gradually grow into vessels - blood and lymphatic, draining waste and fluid. From there they can get into the lymph nodes - our “filters” that retain harmful substances, and anywhere in the body, attach there, multiply, and create a new tumor - metastasis.”
Hyperplastic processes of the endometrium (hyperplasia, polyps)
Primary appointment/consultation with a gynecologist—RUB 1,700. Repeated appointment/consultation with a gynecologist—RUB 1,200. See all prices
+7 (499) 400-47-33
Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells in any tissue (except tumor) or organ, resulting in an increase in the volume of this anatomical formation or organ. Histologically (according to cellular composition), several types are distinguished: glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium; glandular cystic hyperplasia; atypical endometrial hyperplasia (synonym - adenomatosis, adenomatous hyperplasia); endometrial polyps.
According to most authors, the first two types of hyperplasia are not a precancerous disease. The third type, atypical hyperplasia, is a precancerous disease. If present, the risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor (endometrial cancer) in the absence of therapy ranges from 1 to 14% and is most often observed during menopause (cessation of menstrual function due to age).
Precancerous hyperplastic processes develop into endometrial cancer in approximately 10% of patients (according to various authors, from 2 to 50%), they often persist for a long time, and sometimes undergo reverse development. However, taking into account the real threat of the process progressing to endometrial cancer, a doctor’s attentive attitude towards patients with endometrial adenomatosis and adenomatous polyps is necessary. There are opinions about the possibility of considering glandular hyperplasia and hyperplastic processes that arise again (recur) after endometrial curettage or are not amenable to hormone therapy as precancer of the endometrium. The risk of malignancy (malignancy) of hyperplastic processes increases with metabolic disorders caused by extragenital disease (obesity, impaired carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system and gastrointestinal tract), concomitant with the development of endometrial pathology.
A localized, localized form of endometrial hyperplasia is called an endometrial polyp. Histologically, they are also divided into several types depending on the cells that predominate in their structure: glandular; glandular fibrous and fibrous polyps.
Cause and mechanism of development of the disease
Risk factors for the occurrence of this pathology are:
1. The occurrence of hyperplastic processes in the endometrium is facilitated by hereditary burden (uterine fibroids, genital and breast cancer, hypertension and other diseases), damaging effects during intrauterine life, diseases during puberty and associated disorders of menstrual and subsequently reproductive function . In mature women, the appearance of hyperplastic processes is often preceded by gynecological diseases and surgical interventions on the genital organs.
2. Hyperplastic processes of the endometrium are often accompanied by obesity, hypertension, hyperglycemia (this triad of symptoms is especially often combined with atypical and hyperplastic processes recognized as precancer of the endometrium), uterine fibroids, mastopathy, endometriosis, which are largely hormonal-dependent diseases, as well as dysfunction of the liver, responsible for the metabolism of hormones. The leading factor in the cause of occurrence and further development belongs to hyperestogenia - an increase in the level of the hormone estrogen.
Clinical picture
In the clinical picture of the pathology, the following symptoms are most often noted:
1. Uterine bleeding that occurs after a delay in the next menstruation. They can be either long in duration with moderate blood loss, or short in time but abundant;
2. Bloody intermenstrual discharge;
3. Primary or secondary infertility, which is based on the process of lack of formation of a normal egg;
4. The most common, almost constant symptom of endometrial polyps is menstrual irregularities. With polyps against the background of a normal functioning endometrium, women of reproductive age experience scant intermenstrual and premenstrual blood discharge with a preserved menstrual cycle, as well as an increase in menstrual blood loss.
5. In women of reproductive age, glandular fibrous and fibrous polyps can cause menorrhagia. With anovulatory cycles and the presence of polyps of the glandular structure against the background of hyperplastic processes of the endometrium, metrorrhagia is observed, the cause of which is not polyps, but dystrophic, necrotic changes in the endometrium and hormonal disorders. Such clinical manifestations are more typical for premenopausal women (after 45 years).
Diagnostics
1. Ultrasound using a transvaginal sensor;
2. For diagnostic purposes, diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the uterine body and subsequent histological examination of the resulting material are widely used.
It is recommended to scrape the endometrium on the eve of the expected menstruation or at the very beginning of the appearance of bleeding. In this case, it is necessary to remove the entire mucous membrane, including the area of the uterine fundus and fallopian tube angles, where foci of adenomatosis and polyps are often located. For this purpose, endometrial curettage is performed using hysteroscopy. The removed mucous membrane is sent for histological examination.
Hysteroscopy is the most informative method and allows not only to diagnose endometrial polyps with a high degree of accuracy, but also to specifically remove them, and to monitor the bed of the polyp after its removal. With hysteroscopy, polyps have an oblong or round shape, pale pink, yellowish or dark purple (poor blood circulation) color. Polyps can be single or multiple, often located in the fundus or tubal corners of the uterus and, unlike stationary myomatous nodes, fluctuate in the stream of washing fluid.
The so-called recurrent endometrial polyps are of interest to clinicians. With the introduction of control hysteroscopy after curettage and removal of polyps, there was a firm belief that the “relapse” is the unremoved parts of the polyps.
Histological examination is the most reliable method for diagnosing hyperplastic processes and determining the nature of this pathology (glandular cystic hyperplasia, atypical hyperplasia - diffuse, focal adenomatosis, polyps - glandular, adenomatous, fibrous).
It should be especially noted that separate (separately - the cervical canal, separately - the uterine cavity) curettage of the uterine mucosa is the first stage of treatment for the hyperplastic process of the endometrium. It allows you to obtain a sample of endometrial tissue and make an accurate diagnosis: what kind of hyperplasia, and whether there are any precancerous changes. Further treatment depends on this. The changed endometrium can only be removed mechanically.
Treatment
Treatment of endometrial hyperplastic processes is carried out taking into account numerous factors - the patient’s age, the causes of hyperplasia and the nature of this pathology, clinical manifestations, contraindications to a particular treatment method, tolerability of medications, concomitant extragenital and gynecological diseases. The main treatment is hormonal (selected individually). When prescribing hormone therapy, certain conditions and strict consideration of contraindications are required. After 3 and 6 months, a control ultrasound is indicated. For hyperplasia associated with polycystic ovary syndrome, the first stage of treatment is wedge resection of the gonads. This operation is especially indicated for recurrent hyperplasia, which is alarming for endometrial precancer.
If the clinical effect of ovarian resection is insufficient (control - biopsy and histological examination of the endometrium), hormone therapy is carried out according to the guidelines adopted for various types of endometrial hyperplastic processes.
Surgical methods are preferable for recurrent glandular cystic hyperplasia that has developed against the background of diseases of the endocrine glands (diabetes, prediabetes, etc.), obesity, hypertension, liver and vein diseases. Surgical treatment is indicated for precancer (adenomatosis, adenomatous polyps) of the endometrium, especially when this endometrial pathology is combined with adenomyosis and uterine fibroids, and pathological processes in the ovaries.
Patients with fibrous polyps are not subject to hormonal therapy.
Women of reproductive and especially premenopausal age who have glandular and glandular-fibrous polyps against the background of endometrial hyperplastic processes are advised to remove the polyp followed by hormonal therapy.
For adenomatous polyps in premenopausal women with metabolic and endocrine disorders, an alternative is removal of the uterus with a thorough revision of the ovaries (hyperplasia of the tissue body, the presence of hormonally active tumors). Adenomatous polyps in postmenopausal women are an indication for removal of the uterus and appendages.
When to see a doctor?
As we have already said, most polyps are harmless, and their owners do not even know about the existence of such formations in their own body. Regardless of whether a person is aware of the growths he has or not, he should consult a doctor immediately after discovering the following symptoms:
- unexplained changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea lasting more than a few days;
- blood on toilet paper, underwear, or in stool;
- nausea, vomiting and fever;
- unexplained exhaustion;
- and bruises appearing literally out of the blue.
Even if one or more polyps have already been removed, be wary and
- You should consult a doctor if:
- the appearance of weakness and dizziness;
- severe abdominal pain;
- temperature;
- and any bleeding.