- Published by: Laima Jansons
This symptom is not a separate disease, but just one of the signs of dysfunction of one or another internal organ. The feeling of a “dry mouth”, which occurs as a result of a reduction or 100% cessation of salivation, is a pathology called xerostomia.
Photo 1: In order to find out why your mouth is dry, you need to visit a doctor who will prescribe the appropriate tests, and possibly a full medical examination of the body. Source: flickr (Laura).
Diseases that provoke xerostomia
What diseases create a feeling of constant dry mouth:
- Adenoids. The growth of the nasopharyngeal tonsil forces breathing through the mouth. The otorhinolaryngologist diagnoses the stage of the disease. Enlarged lymphoid tissue is removed surgically.
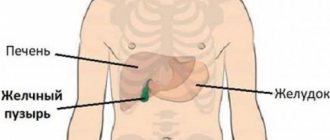
- Dehydration. Poisoning leads to low moisture content, which is dried out by attacks of vomiting and diarrhea. Abdominal pain is caused by cholagenic diarrhea. Pathology occurs due to diseases of the gallbladder and ducts, causing increased water loss. After vomiting during intoxication, temporary relief occurs.
- Orthostatic hypertension. Low blood pressure, weakness, headache and vertigo (circling) are symptoms of hypotension. Fatigue and slight lack of oxygen lead to dysfunction of organs. The salivary glands cause the hypotensive patient to feel xerostomia. Nausea and gastrointestinal disorders also cause inconvenience due to a malfunction of the body.
- Diabetes. Thirst, dry mouth, frequent urination, uncontrollable bouts of hunger - this is an incomplete list of signs of the disease. A common symptom of diabetes is fluctuations in body weight. The patient is constantly thirsty, regardless of eating sweet or salty foods. The disease is accompanied by itching of the skin, cracks in the corners of the mouth, and inflammatory rashes of the epidermis.
- Dental diseases. A feeling of dryness, burning on the gums and tongue, a metallic taste, bitterness in the mouth are symptoms of damage to the tissues of the oral cavity, caries.
Viral infections
Influenza conditions and infectious diseases are accompanied by a symptom of dehydration. A person loses a lot of water during rotavirus and norovirus infections with diarrhea and vomiting. Temperatures above 38-39 degrees dry out the mucous membranes. The patient experiences photophobia and pain in the eyes. What factors characterize viral intoxication:
- Headache, mainly in the temples;
- Nausea and gag reflex;
- Prostration;
- A sore throat;
- Dizziness;
- Thirst and dry mouth;
- Apathy.
Signs require urgent medical attention. If the question concerns a child or a pregnant woman, then go to an ambulance.
Diseases of the respiratory system.
Diseases of the respiratory system are a large group of diseases and conditions that can cause dry throat and require mandatory treatment under the supervision of an ENT doctor. Typically, such diseases are accompanied not only by dryness, but also by other symptoms: runny nose, frequent pain, cough and sore throat. If these symptoms appear, you should definitely contact an ENT doctor for an examination.
What diseases of the respiratory system cause dry throat?
- Acute respiratory viral infections, flu, colds. In addition to a dry throat, the patient has the following symptoms of colds and acute respiratory viral infections: fever, cough, nasal congestion, pain in muscles and joints, weakness, loss of appetite. Treatment is symptomatic: lowering the temperature, eliminating cough and runny nose with medications, as well as drinking plenty of warm fluids.
- Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Pharyngitis can be acute or chronic. Based on the nature of the changes in the mucous membrane, catarrhal pharyngitis is distinguished, when swelling of the tissues is observed, hypertrophic, when the mucous membrane thickens, and atrophic pharyngitis, when the mucous membrane, on the contrary, becomes thinner. Attacks of dry cough, red throat, discomfort during swallowing, sore throat - all these symptoms are signs of pharyngitis. Pharyngitis can simultaneously be paired with tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils) or laryngitis (inflammation of the larynx). In this case, the patient is diagnosed with tonsillopharyngitis and laryngopharyngitis. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drugs, gargling, irrigation with antiseptics and physiotherapy (to consolidate the positive results from the action of the drugs and speed up the recovery process).
- Tonsillitis. The acute form of tonsillitis is called tonsillitis. If a sore throat is not treated in time, the disease will become chronic, with exacerbations occurring up to several times a year. Unlike pharyngitis, tonsillitis affects not the pharyngeal mucosa, but the palatine tonsils (tonsils). A sore throat occurs with acute pain in the throat, high body temperature, and a white coating or purulent accumulations appear on the tonsils. An effective means of combating sore throat is high-quality antibiotic therapy prescribed by an ENT doctor and physiotherapy performed in an ENT clinic. Chronic tonsillitis is not as severe as a sore throat, but its symptoms also cause the patient considerable discomfort: elevated body temperature, bad breath, sore throat. On the tonsils, purulent plugs are noticeable - accumulations of compressed streptococcus. Plugs support inflammation in the tonsils, so it is imperative to get rid of them. Effective therapy for chronic tonsillitis should be comprehensive and include treatment with medications, rinsing the tonsils from plugs and physiotherapy. In the absence of proper treatment, tonsillitis causes complications in the heart, kidneys and joints.
- Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx, which is accompanied not only by dryness, but also by severe itching, barking cough, hoarseness in the voice and itching in the throat, as if the throat is being “teared” from the inside. The treatment regimen for laryngitis includes taking antibacterial or antiviral agents, antiseptic drugs, antitussives, and physiotherapeutic procedures. Also, during treatment it is necessary to give up alcohol, smoking and avoid overstraining the vocal cords. Moisturizing and softening the throat is achieved by drinking plenty of fluids (herbal teas, fruit drinks, compotes, etc. are suitable)
- Pharyngomycosis (or fungal pharyngitis) is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, the causative agent of which is a fungal infection. Often the disease occurs due to uncontrolled use of antibiotics. The disease occurs with dryness, severe burning, discomfort and pain in the throat. A cheesy coating is noticeable on the mucous membrane of the throat. Therapy consists of taking antifungal, anti-inflammatory drugs, gargling and irrigating the throat with antiseptic drugs. Physiotherapy is an excellent addition to drug therapy.
Possible reasons
For your information! A set of symptoms such as dry mouth, nausea, weakness and drowsiness, as well as dizziness can bother a person for the following reasons:
- Osteochondrosis (usually the cervical or thoracic spine). In this case, accompanying symptoms will be a crunch when turning the head or the entire body, numbness of the extremities. A headache, fainting, decreased joint flexibility may appear. A feeling of chronic fatigue occurs (especially after performing physical activities) and etc.
- Spasm of blood vessels in the head caused by impaired blood flow. Associated symptoms: ringing or noise in the ears, disorientation in space, speech impairment, pain in the eyes.
- Poisoning with food, chemicals or alcoholic beverages. In case of poisoning with various substances, dry mouth, nausea, weakness and dizziness are complemented by symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting. Possible rapid shallow breathing, dilated pupils, pale skin, chills, convulsions, drowsiness and etc.
- Head injuries (for example, received in a fall or during a fight). In this case, the main symptoms will be supplemented by the following signs: short-term but frequent loss of consciousness (literally for a few seconds), acute or aching headache. Noise or ringing in the ears appears, vomiting, bleeding from the nose and ears (with severe traumatic brain injuries). There may be clouding of consciousness (including hallucinations, delusions, etc.), and the presence of bruises on the face and neck.
- Pregnancy or menstruation. Both of these phenomena are accompanied by hormonal imbalance. They are characterized by additional symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen or lower back, vomiting, fatigue and lethargy. Characterized by swelling of the mammary glands, high blood pressure (not observed in all cases) , bloating, slight increase in body temperature, mood swings, etc.
- Overdose of drugs. Associated symptoms: bowel problems (constipation or diarrhea), headache of varying intensity, skin rash, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, lethargy, etc.
- Severe physical fatigue and stressful situations. Such conditions may be accompanied by headaches, insomnia, an increase or a sharp decrease in blood pressure. They may be accompanied by trembling in the limbs, deep breathing, excessive sweating and exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- Hypotension (low blood pressure). In this case, dry mouth, nausea and weakness are complemented by symptoms such as acute headache or migraine. Possible paleness of the skin (especially on the face), a pre-fainting state (up to loss of consciousness).
- Brain tumors of various types. In this situation, it is possible to have either an asymptomatic course of the disease (in the initial stages) or with a full set of characteristic symptoms (in addition to dry mouth, nausea, etc.). For example, the patient may have convulsions, severe headaches , impaired coordination of movements, double vision and vision problems.
- Meningitis. Associated symptoms: acute headache, lack of appetite, persistent feeling of thirst, sudden fever. There may also be increased photosensitivity, skin rashes, inability to straighten the legs, complete impotence.
- Stroke and pre-stroke condition. A stroke is most often accompanied by symptoms such as numbness in the arms or legs, vomiting, “spots” before the eyes. Temporary blurred vision, numbness of half the face, slowed speech rate, and impaired muscle tone may occur.
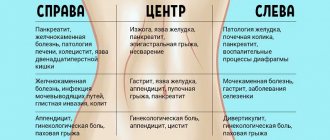
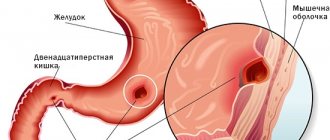
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, etc.). Gastrointestinal pathologies are characterized by the following symptoms: vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, bowel disorders (constipation, diarrhea), etc.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Black plaque - causes, removal at home and at the dentist
But this is only a small list of diseases accompanied by dry mouth, dizziness, nausea and weakness. In reality there are many more.
One way or another, only a doctor can establish the true cause of this pathological condition.
Stay up to date! Dry mouth combined with a bitter taste in most cases indicates the release of bile into the gastrointestinal tract, some of which penetrates the esophagus.
Also, dryness in combination with weakness and dizziness can be a sign of hypoglycemia (severe decrease in plasma glucose), anemia, vegetative-vascular dystonia, autoimmune diseases (Sjogren's syndrome, etc.).
Diseases of other human organs and systems.
Dry throat does not always indicate inflammatory processes in the ENT organs. It happens that discomfort in the laryngopharynx occurs against the background of diseases of other human organs and systems. The treatment of these pathologies will no longer be carried out by an otolaryngologist, but by related specialists.
The cause of a dry throat can be a simple allergy to dust, pollen, pet hair, food and other irritants. An allergic reaction is also usually accompanied by mucus discharge, itching in the eyes, and in especially severe cases, asphyxia. To cope with allergies you will need to take antihistamines and treatment with an allergist.
Dry throat may be a sign of gastrointestinal diseases, such as gastritis, peptic ulcers or reflux esophagitis. With pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, gastric juice can be thrown into the laryngopharynx, irritating the mucous membrane and causing a feeling of dryness in it. Patients also complain of abdominal pain, nausea, bloating, bitterness in the mouth, etc. A gastroenterologist deals with the treatment of such diseases.
Another cause of dry throat is diseases of the endocrine system. Hormonal disturbances due to malfunction of the thyroid gland negatively affect the condition of the mucous membranes, which causes a feeling of dryness. A similar symptom occurs against the background of diabetes. Both disorders are treated under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
If dry mouth occurs, you may need to consult an oncologist, since this is one of the symptoms of benign and malignant oral tumors.
In medicine, there are a number of diseases that affect not a specific organ, but the entire body. Such diseases are called systemic, and they can also cause discomfort in the throat. These diagnoses include scleroderma, cystic fibrosis, Sjogren's syndrome, etc.
Whatever the cause of dry throat, this condition cannot be ignored. It is necessary to begin an examination of the body with a visit to an ENT doctor, who, after examination, if necessary, will refer the patient to the right specialist, or prescribe effective therapy if dry throat is a consequence of an ENT disease.
Intoxication disorders
A defeat of this kind very often provokes dry mouth, dizziness and general malaise.
The etiology of poisoning is often:
- alcohol;
- food products;
- medicines;
- chemicals.
To decide on the required amount of therapy, it is important to first determine the root cause of the lesion.
The patient can only overcome a mild degree of intoxication on his own. If you suspect the development of complications or progression of the pathology, it is important to immediately call an ambulance.
We must not forget that the female body is indeed considered more delicate and sensitive.
Thus, weakness and dry mouth can be caused by infectious agents, blood loss, or sunstroke.
Brain pathologies, hypotension
With any disturbances in the functioning of the brain, accompanied by apathy and nausea, the head begins to spin. Even with a minor injury, a deterioration in the condition is felt, however, if in addition the mouth becomes numb, then there is a risk of the following pathologies:
- stroke;
- meningitis;
- benign and malignant tumors.
If, in addition to the listed signs, pale skin, frequent fainting are observed, and the headache develops into a migraine, then the examination, as a rule, reveals hypotension. The danger of the disease lies in the gradual decrease in the tone of blood vessels, a reduction in the flow of oxygen and nutrients into the blood, which leads to disruptions in the production of saliva.
We suggest you read about Pus in the throat without fever, how to treat it. Causes of pus in the throat and plugs in the tonsils | Human health
Treatment of hypotension and brain pathologies is carried out exclusively under the supervision of a doctor.
Pathologies of the respiratory system
Among the diseases of the respiratory system, which are usually associated with inflammatory or tumor processes in the lungs and bronchi, there are:
- Pneumonia is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the lungs. In this case, it is difficult for a person to inhale and exhale. Plus, the process is accompanied by a severe cough, weakness, dry mouth and a sharp increase in body temperature.
- Bronchitis is a disease of the lower respiratory tract. It is characterized by an inflammatory process in the bronchial mucosa. The symptoms in this case are almost the same as in the case of pneumonia. However, the person feels much lighter and does not suffer from high fever (with rare exceptions).
- Lung tumor - in addition to the above symptoms, it is characterized by hemoptysis and severe cough.
Remember! Pathologies that cause shortness of breath and fever are not limited to this list.
Inflammatory cardiovascular diseases, as well as pneumonia and lung tumors (or suspicion of them) require immediate medical attention or calling an ambulance. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Physiological factors.
Physiological are so-called household, non-infectious causes that are associated with the impact of unfavorable external factors on the body or with a person’s lifestyle. In this case, there is no need to treat the throat: by eliminating the influence of such a factor, the discomfort in the throat disappears. Physiological reasons include:
- Too dry air in the room, which occurs at the height of the heating season or during prolonged use of the air conditioner. Buying a humidifier usually solves the problem.
- Polluted or dusty air. This problem is faced by people living in places with poor environmental conditions or working in “harmful” industries, who are forced to constantly inhale fumes, gases, dust, etc.). This also includes passive smoking.
- Overstrain of the vocal cords. If you regularly subject your vocal apparatus to excessive stress, a dry throat is a typical situation for you. Typically, this problem is faced by representatives of speech professions - artists, singers, teachers, announcers, tour guides, call center employees, etc. To learn how to safely use and not overstrain your vocal apparatus, it is recommended to visit a phoniatrist. A phoniatrist is an ENT doctor who specializes exclusively in the human vocal apparatus. The phoniatrist will show you effective exercises for the vocal cords and give the necessary prescriptions.
- Insufficient fluid intake. Eating foods that are too salty, sweet or spicy.
- Long-term use of certain medications (cough suppressants, antibacterials, antihistamines, diuretics, etc.).
- Uncontrolled use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops greatly dries out the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
- Difficulty in nasal breathing caused by structural features of the nasal cavity (deviated nasal septum, enlarged nasal turbinates, adenoids).
- Advanced age. In older people, the mucous membranes become thinner as they age, leading to a feeling of dry mouth.
- Nervous overstrain. Stressful situations provoke a decrease in saliva production, which causes discomfort. Dry mouth is not the only unpleasant consequence of stress. A person may also feel a lump in the throat and problems swallowing. This condition is temporary. After the person has calmed down or taken a sedative, the discomfort goes away.
- Tobacco smoking. The substances that make up cigarettes negatively affect the condition of the laryngopharyngeal mucosa. If you do not stop in time and do not say goodbye to the bad habit, chronic pharyngitis, chronic rhinitis, as well as malignant tumors of the larynx may develop.
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, women's hormonal levels change, which can directly affect the appearance of an unpleasant symptom.
These conditions do not require specific treatment. In most cases, it is enough to eliminate or eliminate the irritating factor.
Brain pathology causes dry mouth and weakness
Even a slight blow to the head can cause a slight attack of dizziness. And more serious pathologies of the brain immediately provoke complete weakness, impotence, severe headaches, thirst and dry mouth. These are the following anomalies:
- head injuries of varying severity;
- stroke;
- meningitis;
- brain tumors of various types, etc.
It is difficult to list the entire list of pathological processes that can affect the brain, but any of them can lead to serious consequences.
Important! Protect your head from injury, and if you suspect more serious problems, consult a doctor immediately. For example, meningitis is a rapidly progressing disease that, if not treated in a timely manner, leads to sudden death.
Methods and causes of manifestation of the disorder
In medical practice, the feeling of dry mouth is called xerostomia. It is associated with a decrease in the amount of saliva production and leads to serious complications. Changes in the microflora of the mucous membrane can be identified by the following signs:
- there was an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- constant feeling of thirst;
- saliva becomes viscous, viscous;
- taste perception is dulled;
- pain in the nose and throat when swallowing;
- hoarseness of voice;
- redness of the tongue;
- the corners of the lips are cracked;
- discomfort during the conversation.
The disorder is temporary due to changes in a person’s lifestyle. Thus, the oral cavity is negatively affected by fatty, salty and fried foods. Strong tea and coffee, alcoholic drinks, and cigarettes have a similar effect. Failures are possible as a result of disorders in the respiratory system, for example, with a runny nose, nasal congestion, and night snoring.
Dry mouth occurs due to an adverse reaction to taking medications or dehydration of the body for a number of reasons (diarrhea, excessive sweating, high body temperature during infectious diseases). In old age, saliva is produced in smaller volumes, so xerostomia is considered normal.
If symptoms persist for a long period, you should consult a doctor to prevent the development of a serious illness.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Alveolitis - a complication after tooth extraction
Along with a feeling of discomfort in the mucous membrane, headache and nausea often occur, which indicates pathologies. The most common are:
- chronic fatigue;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- brain tumors;
- impaired blood flow, vascular spasms;
- poisoning – food, alcohol, chemical;
- meningitis;
- head and neck injuries;
- in women – pregnancy, menstruation, menopause;
- in men – disorders of the genitourinary system.
Symptoms of xerostomia
- dry throat and mouth as a result of insufficient salivation;
- difficulty swallowing;
- slurred speech;
- the appearance of erosions, cracks, wounds in the corners of the lips, as well as on the mucous membrane (accompanied by severe discomfort, burning, pain);
- constant desire to drink;
- dry tongue, turning bright red;
- distortion of taste, the feeling that some kind of foreign taste is always present;
- smell from the mouth;
- hoarse voice;
- sore throat.
Note! If dry mouth is observed for a long time, the risk of developing periodontal disease, damage to the oral cavity by fungi, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms increases. The body becomes more susceptible to viral diseases, including sore throat, tonsillitis and stomatitis.
Dry mouth, dizziness
Dizziness and dry mouth are signs of hypotension, that is, low blood pressure. A lot of people have low blood pressure and still feel normal, this is a variant of the norm. But when low pressure leads to weakness, dizziness, headache in the back of the head, especially when bending forward or lying down, this is an alarming sign, since a sharp drop in pressure is a hypotonic crisis, shock, this is very dangerous for health and even life.
People with hypotension often feel dizzy and have dry mouth in the morning, and weakness and lethargy returns in the evening. Poor circulation affects the functions of all organs and glands, including the salivary glands. Therefore, headaches, dizziness, and dry mouth are observed. The cause of hypotinia should be determined in consultation with a cardiologist and therapist, who can prescribe maintenance therapy.
Reasons Why Your Mouth and Throat Sometimes Dry
There are a lot of factors that provoke drying of the mucous membranes of the larynx and oral cavity. The exact cause of the disease can be determined by the nature of xerostomia. Each type can be triggered by various disorders in the body.
Photo 2: Dry mouth can occur periodically or be a constant problem, occurring at night or in the morning. Source: flickr (albori2003).
Dry mouth in the morning
A feeling of dry mouth in the morning can be caused by:
- taking certain medications,
- smoking;
- increased ambient air temperature;
- eating fatty, too spicy or salty foods;
- dry mouth in the morning as a result of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (hangover);
- poor-quality oral care products (toothpastes, rinses, etc.) or their improper use;
- insufficient amounts of group A vitamins in the body, which causes blockage of the salivary glands;
- lack of potassium;
- too much magnesium content.
Dry mouth at night
- forced mouth breathing (for allergies, colds, etc.);
- snoring, which leads to a dry throat;
- too dry air in the bedroom;
- diabetes mellitus, which almost always causes sleep disturbances;
- itchy skin rashes that prevent you from sleeping.
Dry mouth and thirst
- Often, the oral cavity dries out in females due to changes in the functioning of hormones, for example, during menopause or pregnancy.
- Diabetes. In this case, it dries out due to an increase in glucose levels, resulting in the need to drink more fluid.
- Dryness and severe thirst are provoked by severe vomiting, diarrhea, severe sweating, diuretics, and insufficient water consumption during the day.
Dry mouth and frequent urination
This is one of the symptoms of diabetic disease. In addition to thirst, the functioning of almost all body systems, including the salivary glands, is inhibited. Frequent urination also leads to dry mouth in the presence of chronic kidney disease.
Dry mouth, nausea, headache
The cause of nausea accompanied by dry mouth may be a consequence of a disease of the endocrine system. The likelihood is especially high if there is irritability, a feeling of unreasonable fear, the person sweats a lot and profusely, trembling and loss of appetite bother him.
If, in addition to dryness and nausea, there is heartburn, and the tongue is coated, this may be the cause of a gastrointestinal tract disease.
Headache and dryness can be caused by hypotension, when along with dryness there is weakness, increased drowsiness and frequent dizziness.
Coated tongue and feeling of dryness
Often dryness is accompanied by heartburn and nausea, and a thick coating appears on the tongue. The bitter taste may be disturbing. All this speaks of gastrointestinal diseases.
Other causes of dry mouth
- Systemic diseases (Parkinson's, Sjögren's, Alzheimer's, HIV, artiritis, scleroderma).
- Innervation. As a result of problems with the nerve endings in the cervical spine and head, the salivary glands begin to work incorrectly, which causes xerostomia.
- Stress, depression. With psychological and nervous disorders, a person is constantly tense, which can cause dry mouth. These symptoms do not disappear on their own and quickly, so observation by a doctor in this case is a prerequisite.
- Low blood pressure causes drying of the oral mucosa.
- Abnormal proliferation of lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes behind the ears or under the lower jaw are affected, salivation is often impaired. These are signs of cancer, so you need to visit a doctor urgently!
- Various infectious diseases, which may result in dehydration.
This is interesting! The daily rate of saliva production by the body is 1.5 liters. Its main purpose is to protect the mucous membranes from drying out, as well as from the appearance of caries on the teeth. With the help of saliva, food debris is washed away, acids are neutralized, chewing and swallowing of food is facilitated, and the risk of proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms is reduced. Saliva contains a special enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates during food consumption.
Factors not related to diseases
Why does a person’s mouth become dry if he is definitely not sick?
- Foods high in salt. Over-salted food, dried fish, pickled vegetables force the body's cells to replenish the water-salt balance by drawing moisture from their own resources.
- Too sweet foods. Sweets change the osmotic pressure in organs and tissues, causing the brain to signal a lack of fluid. The process is accompanied by dryness of the oropharynx.
- Tea, coffee, energy and carbonated drinks. Dehydration develops due to the increased content of tannins, sugar, and stimulants. The feeling of thirst is eliminated by drinking clean water.
- Exercise stress. During intense exercise, a person loses moisture through sweat. The deficiency is compensated by drinking mineral and plain water.
- Bad habits. Dry mouth. In addition, they cause dizziness, cerebral vasospasm, and nausea. Alcohol poisoning is accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea.
- Taking antibiotics. A side effect of antibacterial medications is dry mouth. The person feels nauseous, has a headache or discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Physiological changes in women. During menopause, amenorrhea, menstruation and pregnancy, organs undergo hormonal changes. This is reflected in the level of moisture in the mucous membranes. A feeling of nausea may occur before hot flashes.
- Neuroses, mental disorders. Nervous shocks and panic attacks provoke drying of the oral cavity and dysfunction of the salivary glands.
Dental causes of burning sensation in the mouth
When the first symptoms appear, you should contact your dentist, because most often the reasons are related to his profile:
- Oral candidiasis
A burning sensation in the mouth and tongue after prosthetics or filling in most cases indicates poor quality of the procedure. The dentist could damage the mucous membrane during the operation or incorrectly manufacture the prosthesis itself. Some patients are allergic to the filling composition.
- With candidiasis, the tip of the tongue stings the most, there is a feeling that the palate is burned, and there is a bitter taste. Sometimes there is pain in the throat area. The disease manifests itself due to the active proliferation of yeast fungus against a background of weakened immunity.
- Stomatitis
The cause of the disease can be glossitis. With this disease, due to the action of viruses and bacteria, the entire mucous membrane of the tongue experiences a strong burning sensation.
- Aphthous stomatitis is another disease that causes a burning sensation in the mouth. With it, small ulcers form on the mucous membrane, which hurt when touched. There is an unpleasant sensation in the mouth, like a burn from hot drinks.
Exogenous factors
To determine the possible cause of nausea, weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, previous events should be analyzed. Such symptoms may appear as a result of the influence of unfavorable factors:
- recent head contusions;
- stressful situation;
- emotional stress;
- long concentrated painstaking work or physical activity;
- inhalation of harmful fumes, for example, during hair dyeing or perming, when carrying out finishing work, when working in gassy or dusty rooms;
- long trip in transport, air travel;
- taking medications: sedatives, antihistamines, hormonal and painkillers.
The causes of dizziness, drowsiness, nausea and weakness may be fasting, hypothermia or overheating.