New inhabitants of the skin
Skin neoplasms are quite common diseases. If you look closely, for example, at random fellow travelers on a bus, you will probably notice that there are almost no people without any formations - moles, warts, subcutaneous “bumps”... Tumors can be benign and malignant. Some benign tumors do not change their character during their existence, although it happens that they exhibit the ability to increase, sometimes to significant sizes. There are a huge number of forms of benign tumors of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: warts, keratoses, cysts, hemangiomas, lymphangiomas, lipomas, fibromas, keloids, ganglia. Unfortunately, we will not be able to talk about all these types and methods of their treatment in the format of one article; we will only touch on those problems that most often concern our patients, in particular, we will talk about lipomas, atheromas, fibromas and hemangiomas.
"Lump" under the skin
The prerequisites for the occurrence of lipomas, or as they are popularly called - wen, in the vast majority of cases are created during the period of embryonic development. When the adipose tissue of the embryo is formed, islands of cells are formed in which metabolic processes are absent or sharply slowed down. Lipomas grow from such cells - most often single, less often multiple. Often this disease is hereditary. Wen can also occur as a result of a bruise or constant mechanical irritation of some part of the body. Lipomas develop mainly in the subcutaneous tissue of the head, neck, back, and armpits. Wen are usually painless. However, sometimes when they grow, the nerve endings are compressed and pain occurs. Lipomas grow very slowly, taking decades. Although these tumor formations are only a cosmetic defect, doctors usually recommend removing them. The fact is that sometimes lipomas begin to grow rapidly, reaching enormous sizes, put pressure on surrounding tissues and can fester.
Hidden in the “thicket” of hair... are atheromas
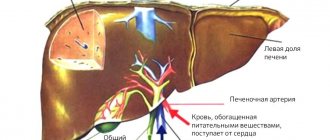
Atheroma is a benign tumor that occurs as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland duct. The mushy contents of the tumor (hence the name) consist of fatty substances and epithelial cells. The size of atheroma can be from a pea to a chicken egg and larger. Atheroma usually occurs on any part of the body where hair grows, but most often occurs on the scalp, face, and back. Externally, atheroma looks like a painless, round, dense formation with clear contours, while the skin above the atheroma does not fold. The contents of the tumor can become infected, resulting in pain, redness, swelling, tenderness, and fever. When suppuration occurs, the contents of the atheroma soften. Treatment is opening the abscess with subsequent drainage of the cyst cavity. Complete excision of the atheroma in this case is possible only after the inflammatory changes have subsided.
Ball on a leg
Fibroma consists of fibrous connective tissue. If smooth muscle fibers are mixed with this component, the tumor is called fibromyoma. This benign formation grows slowly, over the years, has a dense consistency, in most cases it is spherical in shape; sometimes “sits” on a stalk (polyp). Treatment for atheroma is surgical only. In our Center, surgery to remove such a formation is performed on an outpatient basis, and it is completely painless. The wound heals very quickly (if the atheroma is really small and shallow). The formation of scars primarily depends on the individual properties of human tissue; usually, after such an intervention there are practically no noticeable marks.
Causes of polyps and papillomas of the anus
The anus is an area in which the growth of tumors is quite often observed. Polyps may form inside the rectum. Condylomas (a type of papillomas that resemble cauliflower in appearance) may appear in the perianal area (around the anus). In some cases, condylomas can also occur inside the anal canal.
Sometimes you may not even suspect the existence of such formations in yourself. A common situation is when their presence is established during an examination (or during an endoscopic examination) when treating for other diseases.
Polyp
- This is the growth of the mucous membrane in the form of a mushroom body. With its thin stalk, the polyp maintains contact with the wall of the rectum, and the body itself hangs freely inside the canal.
Papillomas (genital warts)
are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a widespread disease; according to various sources, from 70 to 90% of people carry this infection. However, in most cases, the virus “sleeps” and becomes active when immunity decreases. This is when active growth of papillomas occurs.
In the perianal area, HPV manifests itself in the form of genital warts, which usually also affect the human genitals. Often condylomas become injured and bleed. The virus can be transmitted through blood from damaged condylomas.
Swollen vessels
Hemangioma is a benign neoplasm, or, simply, a tumor, which is a collection of abnormally overgrown blood vessels. Despite their benign nature, hemangiomas are characterized by rapid progressive growth. As they grow, they destroy the tissues surrounding them. This becomes dangerous if hemangiomas are localized on the oral mucosa, ears, and eye area. Vascular tumors located in these places can disrupt the most important functions of the body - vision, hearing, breathing. A characteristic feature of hemangiomas is the unpredictability of their behavior. Sometimes a small, punctate hemangioma turns into a large tumor in 2-3 months, requiring treatment. Hemangiomas disappear just as spontaneously. When dealing with hemangiomas, doctors previously used wait-and-see tactics. They preferred to start treatment when it was finally clear that the tumor would not go away on its own. Today, surgeons recommend removing hemangiomas as early as possible. There is no universal method for treating hemangiomas. The doctor chooses a tactic based on the type of vascular tumor, its complexity, size, and location.
Don't be afraid of the word "tumor"!
“Is it necessary to remove benign tumors of the skin and soft tissues?” — surgeons quite often hear a similar question at outpatient appointments. Patients are interested in whether the tumors are benign, whether they should resort to surgery, but on the other hand, the very word “tumor” in the diagnosis frightens a person. In the vast majority of cases, these tumors are not dangerous to human health, since these tumors are benign. However, we must not forget that malignant tumors of a primary or metastatic nature can be localized in the same areas where benign ones and often have the same shapes and sizes.
BENIGN TUMORS OF MUSCLE TISSUE
Tumors of muscle tissue are divided into smooth muscle tumors - leiomyomas, and striated muscle tumors - rhabdomyomas. Tumors are quite rare.
Leiomyoma
Mature benign tumor. Occurs at any age in both sexes. It is often multiple. The tumor can become malignant. Treatment is surgical.
Leiomyoma, developing from the muscular wall of small vessels - small, often multiple, poorly demarcated and slowly growing nodes, often with ulcerated skin, is clinically very similar to Kaposi's sarcoma.
Genital leiomyoma is formed from the muscular lining of the scrotum, labia majora, perineum, and nipples of the mammary gland. May be multiple. Cellular polymorphism is often observed in the tumor. Hormone dependent. Treatment is surgical.
Angioleiomyoma from the trailing arteries
Clinically, a sharply painful tumor that can change size under external influences or emotions. The sizes are usually small, more often found in older people, on the limbs, near the joints. It is characterized by slow growth and a benign course.
Rhabdomyoma
A rare mature benign tumor based on striated muscle tissue. Affects the heart and soft tissues. It is a moderately dense node with clear boundaries, encapsulated. Metastases of rhabdomyoma have not been described. Relapses are extremely rare. Microscopically, 3 subtypes are distinguished - myxoid, fetal cell and adult. Rhabdomyoma of the female genitalia is also distinguished. The adult type mainly recurs.
Diagnosis via injection
The diagnosis of a benign neoplasm is usually made on the basis of a clinical examination. In difficult cases, cytological puncture with a thin needle can be used to distinguish them from other tumors. Such a puncture is practically painless; on the other hand, it can provide very valuable information for the diagnosis. Due to the fact that our Center has its own clinical and biochemical laboratory, puncture results can be obtained in the shortest possible time. Timely ultrasound examination, which is used in our Center along with other diagnostic methods, can also be of great importance for making an accurate diagnosis.
How to prepare for surgery to remove colon polyps?
To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Sigmoidoscopy – examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the large intestine.
- Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity - if intestinal obstruction is suspected.
Among the laboratory tests, the patient must undergo a general blood and urine test, electrocardiography, chest x-ray, examination by a therapist, and also receive consultation from specialists if there are concomitant chronic diseases.
At least 5 days before surgery it is necessary to cleanse the intestines. A slag-free diet is prescribed, and laxatives and cleansing enemas are used for 3 days. 6-8 hours before surgery you are not allowed to eat any food.
Accurate diagnosis, competent treatment!
The only possible treatment for benign tumors is their surgical removal. As a rule, people resort to surgery in two situations: if the tumor causes a cosmetic defect, and if it is located near important organs, blood vessels, nerve trunks, compresses them, and prevents them from functioning normally. Often, patients are not aware that benign soft tissue neoplasms can be facultative or obligate diseases, that is, they are more or less likely to transform into a malignant tumor, while their localization may not cause a cosmetic defect or disrupt the function of the organ. Taking this into account, if you discover a tumor-like formation on your skin or subcutaneous tissue, you must consult a specialist. Our Center provides patients with all the necessary methods for diagnosing benign soft tissue tumors. Experienced doctors will be able to advise you and choose an adequate treatment method. If the tumor is small, it can be removed using the Surgitron radio wave device at an appointment with a dermatologist. This method is as gentle as possible and allows for the removal to be as gentle as possible. If surgical intervention is necessary, on the basis of the CELT surgical service, the patient can undergo the necessary preoperative laboratory diagnostics, undergo surgery under local or general anesthesia, and be provided with a comfortable room for postoperative observation.
BENIGN TUMORS OF PERIPHERAL NERVES
Traumatic or amputation neuroma
Arises as a result of post-traumatic hyperregeneration of the nerve. It is a small painful node.
Neurofibroma
A single, slowly growing benign tumor of the mesenchymal sheath of the nerve trunk of any location, but most often develops on the sciatic nerve and intercostal nerves. Occurs in people of any age. Clinically defined as a small, densely elastic consistency with a smooth surface of the tumor node, upon palpation of which the pain radiates along the nerve. Some tumors can reach large sizes. Tumor growth can occur both to the periphery of the nerve and in the thickness of the nerve trunk, which is revealed during its morphological examination.
Treatment is surgical. The prognosis is good. A special disease is multiple neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen's disease), which belongs to the group of dysplastic processes. Cases of malignancy of one of the multiple neurofibromas in this disease have been described.