Diseases of the duodenum are a fairly common pathology, but cancer here accounts for only about 1-1.5% of all malignant tumors of the digestive tract. Despite the rarity of this pathology, if a patient has duodenal cancer, its treatment is quite complex and should be started as early as possible. Specialists from the I. Medvedev Medical Center will conduct a detailed diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Duodenal cancer: first symptoms
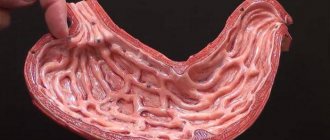
The initial segment of the small intestine is called the duodenum. In this segment of the small intestine, the acidic environment is converted into an alkaline one, which allows for further intestinal digestion. During the digestion process, amino acids, triglycerides, fatty acids, and glucose are formed in the small intestine, which are then absorbed through the mucous membrane of the small intestine. The small intestine plays an important role in maintaining the balance of the internal environment of the body; the quality of absorption of water and electrolytes depends on it. The duodenum consists of four sections - upper, descending, horizontal and ascending.
Duodenal cancer is common, accounting for approximately 4% of all intestinal malignancies. Malignant lymphoma develops most often. Benign tumors of the small intestine are less common. Duodenal cancer affects men and women equally often and is more common in people over 50 years of age.
It can be difficult to distinguish duodenal cancer from cancer of the head of the pancreas, the common bile duct. The most common secondary form of duodenal cancer is caused by the growth of a malignant tumor into neighboring tissues or organs.
About 70% of cases of malignant tumors of the duodenum are localized in the descending segment, in the peripapillary region. It is believed that most tumors originate from the mucosal epithelium of the common bile duct or pancreas, which is very difficult to determine accurately. The upper horizontal segment of the duodenum is affected by suprapapillary cancer, the incidence of which is 16-17%. Cancer of the lower horizontal part of the duodenum is very rare.
Reviews from our patients
- Chemotherapy - review by Svetlana Vyacheslavovna
Chemotherapy - review by Svetlana Vyacheslavovna May 12, 2021Svetlana Vyacheslavovna arrived at the clinic on the 17th with ovarian cancer, a classic for women, but already with an early pre-treated condition. She was treated and had a long remission. But, based on her general health, she suspected a return of symptoms and contacted our clinic. After further examination, unfortunately, the progression of the disease was discovered. We held a consultation and decided to start...
read more
- Feedback on chemotherapy
Feedback on chemotherapy March 30, 2021
The patient was admitted in serious condition for chemotherapy courses. A comprehensive examination was carried out. Treatment tactics have been developed. Port system installed. The first course of chemotherapy was completed. A positive effect was achieved: the patient can eat independently, speak normally and even sing.
read more
- Feedback on treatment. A united team that helped get on its feet
Feedback on treatment. A united team that helped get back on its feet March 29, 2021
The patient shares her impressions of hospitalization at the Medicine 24/7 clinic: “I am very grateful. Many thanks to this huge, close-knit team that helped me get on my feet. I am pleased to thank Alexander Valerievich and his assistants. Wonderful medical staff. Very good technical staff. Of course he is mute, but he does his job. Thank you all very much."
read more
- Feedback on treatment. Gratitude to the medical staff of the clinic
Feedback on treatment. Gratitude to the medical staff of the clinic March 26, 2021
This was not the first time the patient was hospitalized. The treatment was carried out in full. A positive effect has been achieved. The patient is happy with everything and thanks the medical staff of the Medicine 24/7 clinic.
read more
- Feedback on chemotherapy and subsequent rehabilitation
Feedback on chemotherapy and subsequent rehabilitation March 24, 2021
The patient was hospitalized for another course of chemotherapy and subsequent rehabilitation. During treatment, the number of lymphocytes and erythrocytes was stabilized. Other blood parameters are restored. The patient notes the high organization of all work and the professionalism of the medical staff. In particular, he notes the efficiency of the nurses.
read more
- Comparison of treatment in Israel and at the Medicine 24/7 clinic
Comparison of treatment in Israel and at the Medicine 24/7 clinic March 24, 2021
The patient was hospitalized for examination, as well as a second course of chemotherapy followed by detoxification. Before that, she had experience of treatment in an Israeli clinic. The patient notes the efficiency and timeliness of solutions to all emerging issues. "I like it here. Everything is fine here. Everything is compact. All examination issues are resolved according to programs and duration, as it should be... The equipment is modern, imported, I looked at it all. Me…
read more
- Treatment of anemia
Treatment of anemia March 23, 2021
The patient was hospitalized at the Medicine 24/7 clinic for blood transfusion. It was necessary due to the state of anemia that arose against the background of multiple courses of chemotherapy. Continuing treatment became impossible for her. During hospitalization, blood transfusion was performed. Hemoglobin level is increased. Anemia corrected. Further treatment is ahead.
read more
Radiation therapy for duodenal cancer
Radiation therapy is prescribed in the following cases:
- For inoperable malignant tumors in late stages.
- To combat symptoms and complications of cancer: intestinal obstruction, bleeding.
- After surgical removal of cancer, as an adjuvant treatment. However, as with chemotherapy, the benefit of radiation therapy in this case has not been proven.
The procedure is similar to an x-ray, but it uses higher doses of radiation and exposes the patient to radiation for a slightly longer period, usually for several minutes.
Get an in-person consultation with an oncologist
Leave your phone number
To summarize: general approaches to the treatment of duodenal cancer, depending on the stage
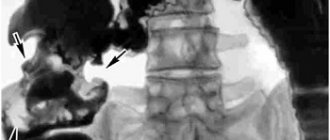
So, in order to decide on treatment tactics, first of all, the doctor must decide whether the malignant tumor in the duodenum is resectable, that is, whether it can, in principle, be removed surgically. To do this, an examination is carried out, which includes endoscopic examination (fibrogastroduodenoscopy), radiography with barium contrast, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and biopsy.
For resectable cancer, the Whipple procedure is most often performed. If it turns out that the tumor has spread to regional lymph nodes, adjuvant chemotherapy or radiation therapy is given after surgery.
Contraindications to radical surgery may include: too much spread of the malignant tumor into neighboring tissues, the presence of distant metastases, or the patient’s poor condition, due to which he will not be able to undergo surgery. In such cases, chemotherapy becomes the main treatment. Radiation therapy is most often used for metastases in the brain and spine.
If the tumor blocks the lumen of the duodenum, palliative surgery is performed to restore its patency.
In some patients, in the presence of certain genetic markers, treatment of duodenal cancer involves the use of immune drugs from the group of checkpoint inhibitors. Molecular genetic analysis is performed to detect relevant genetic changes. It can be carried out at the Medicine 24/7 clinic.
If the malignancy has resulted in peritoneal carcinomatosis, hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) may be performed. A surgical intervention is performed during which all large tumor nodes in the abdominal cavity are removed, after which the abdominal cavity is washed with a heated chemotherapy solution to destroy small tumor foci. HIPEC can sometimes prolong life by years, but this technique can only be used for localized lesions in the abdominal cavity without metastases beyond the abdominal cavity, in patients whose condition allows major surgery, and if all large lesions in the abdominal cavity are resectable.
Duodenal cancer, symptoms and treatment
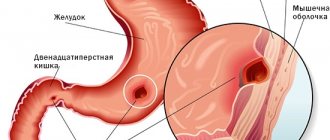
A tumor located in the area of the large duodenal nipple, as it grows, leads to compression and narrowing of the lumen of the nipple, compression of the common bile duct. The common bile duct begins to expand above the tumor, delaying the flow of bile into the intestine and making it difficult to exit.
During this period of tumor development, symptoms of the disease appear - pain in the right hypochondrium, decreased or loss of appetite, pain in the epigastric region, severe nausea, jaundice, which gradually increases. If the patient has previously suffered from diseases of the liver and gallbladder, the doctor assumes the development of a tumor in the area of the duodenal nipple. It is more difficult to determine the site of origin of a malignant tumor, which during growth leads to the appearance of inflammatory changes in the pancreas. The tumor can lead to severe pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis with peritonitis.
Cancer of the upper horizontal part of the duodenum manifests itself as symptoms of stenosis as the tumor grows. The scirrhous form of the tumor leads to deformation and narrowing of the lumen of this segment of the intestine, which is manifested by certain symptoms: discomfort in the stomach, bloating, nausea, heartburn, belching, vomiting, dull pain in the right hypochondrium, often in the epigastric region. Often, with such symptoms, the doctor makes a diagnosis - a complication of peptic ulcer disease, if the history indicates that the patient suffers from such a disease.
Cancer of the lower horizontal part of the duodenum also leads to a narrowing of the intestinal lumen as the tumor grows. Symptoms indicate the development of intestinal obstruction: vomiting, nausea, bile is present in the vomit, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, a feeling of strong pressure.
Duodenal cancer leads to the gradual development of anemia, loss of appetite, then to loss of body weight, weakness and fatigue. The growth of the tumor into other tissues and organs reduces the patient’s chances of recovery. Symptoms of duodenal cancer in women are similar to those in men. The disease is often accompanied by pain of varying intensity.
Screening will help identify tumors at an early stage; it is also recommended that people over 50 years of age undergo a colonoscopy every 5 years; people with a serious medical history need to undergo such tests more often.
Diagnostics
Endoscopy remains the preferred diagnostic method today. Assessment by an experienced endoscopist is essential because it allows both imaging and biopsy to be performed simultaneously. Particular attention should be paid to the condition of the relevant structures, such as the papilla of Vater.
Lesions in the third or fourth portion of the duodenum may be technically challenging to view endoscopically. Therefore, clinics in Belgium now use modern endoscopes with an elongated thin tip that has increased flexibility. Such devices make it possible to examine the entire duodenum.
Lesions in the distal duodenum may be missed during initial endoscopic evaluation if outdated equipment is used or the endoscopist is insufficiently skilled. This leads to further diagnostic delays.
Endoscopic ultrasound may be performed concurrently with direct imaging to evaluate local expansion or lymphadenopathy. In addition, it may facilitate diagnosis if attempts at percutaneous biopsy are unsuccessful.
Computed tomography with contrast is important for assessing damage to adjacent structures, determining resectability (possibility of removal) and planning surgery. However, MRI can provide more information to the doctor in the initial stages of diagnosis, and therefore its appointment is a priority.
Treatment of duodenal cancer with chemotherapy
Clinical manifestations of a malignant process in the duodenum depend on the stage of cancer development. In most cases, several years pass from the onset of cancer development to the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. Duodenal cancer is treated by resection of the affected part of the intestine, chemotherapy, which is prescribed in the preoperative period and after surgery according to indications.
Cancer cells are characterized by a very fast metabolism and are sensitive to cytostatics (chemotherapeutic drugs). Chemotherapy helps to cope with tumor metastases and reduces the risk of cancer recurrence. With the help of preoperative influence on the tumor, it is achieved to reduce its size and reduce the risk of metastasis. In advanced stages of cancer, chemotherapy is used for palliative treatment and helps relieve the patient's suffering.
Classification and stages
A cancerous node is formed from mucosal cells and has many varieties according to histology. There are exophytic and endophytic forms. Education may be located:
- in the bulb - closer to the stomach;
- in the peripapillary zone - about 75% of all cases of oncology of this organ;
- in the upper part of the intestine;
- in the horizontal area.
Our expert in this field:
Ivanov Anton Alexandrovich
Medical director, oncologist-surgeon, candidate of medical
sciences Call the doctor
Call the doctor
As with most malignant tumors, there are 4 main stages of disease development:
I - small size, clear boundaries, within the mucosa and submucosa;
II - the formation increases to a diameter of 5 cm, grows into other layers of tissue;
III - regional lymph nodes are affected, the tumor grows into nearby organs;
IV - metastases reach distant organs and lymph nodes.