psychosomatics and the stomach connected ?
Did you know that stomach ulcers belong to the class of psychosomatic diseases?
It follows from this that the impact of psychological factors on the formation and formation of this disease has been proven by the vast majority of researchers. Like every psychosomatic illness, a stomach ulcer is directly related to the specific psychological characteristics of the victim’s consciousness.
Thus, the sources of ulcers are located not only on the physical plane of a person - the body, but also in more subtle planes invisible to the eye: in the soul, consciousness, and mind of a person.
And we will be able to understand these reasons in more detail thanks to the findings of the most famous researchers in the field of psychosomatics.
Causes of stomach ulcers
In our example, the protection consists of:
- high ability of cells to regenerate;
- sufficient supply of cells with “building” material and energy (which is ensured by adequate blood supply);
- timely cleansing of toxins, waste products and dead cells;
- mucus discharge;
- synthesis of acid “neutralizers” - the so-called. bicarbonates (salts of carbonic acid);
- timely leaving of food from the stomach;
- healthy nervous and endocrine regulation of the digestive process.
The main damaging factor is hydrochloric acid, which the stomach itself produces (rarely it can be an acid from the outside - the vinegar essence mentioned above). The reasons for its hypersecretion top the list of etiological factors of peptic ulcer disease.
- Bacteria Helicobacter pylori. Its way of surviving in the aggressive environment of gastric juice (“alkalization” of its environment) forces the body to increase acid production. In addition, this “parasite” also damages the wall of the stomach, facilitating its destruction.
- Hormonal medications that directly increase acid formation.
The third “leader” from the list of causes of peptic ulcers - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - slowly but surely “destroy” the protective system of the stomach, violating the functional integrity of its mucous barrier.
But let us emphasize once again that damage to the gastric mucosa, up to the appearance of an ulcer, is the result of several factors. The same Helicobacter pylori is found in almost all people. But its numbers are normally strictly controlled by our main defense system - the immune system. And healthy digestion guarantees that the walls of the stomach and duodenum will not allow this potential aggressor to multiply. The conditions for its unhindered reproduction are often created by man himself. First on the list of predisposing factors are poor diet, smoking, chronic stress, lack of water, exercise, etc.
Do not forget about the mental causes of the disease . No wonder peptic ulcer disease is officially included in the list of psychosomatic disorders. Acid, a very aggressive substance, reflects a different type of aggression on a physical level. Moreover, it is directed not outward, but towards oneself. An ulcer is a vivid example of auto-aggression, “self-criticism,” the inability to “digest” one’s reactions to life’s troubles and turn “negative” into “positive.” That is, in one sense, allow yourself to react, act, actively solve the current situation. And try to direct energy to creation instead of destruction.
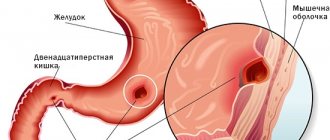
Peptic ulcer disease: familiar and so many-sided
Peptic ulcer
– a chronic, cyclically relapsing polyetiological disease, the main morphological substrate of which is an ulcerative defect and/or a scar within the gastroduodenal zone, manifested mainly by abdominal pain syndrome and gastric dyspepsia syndrome.
Exacerbation of the disease: when the ulcer is localized in the cardial and subcardial parts of the stomach - early pain, with ulcers of the antrum, pyloric canal and duodenum - late pain, as well as “hungry” and “night” pain. Appetite usually does not decrease, and often even increases, especially with duodenal localization of the ulcer (“painful feeling of hunger”). The general condition of patients worsens, increased fatigue, weakness, sweating, loss of ability to work appear, depression or, on the contrary, agitation is observed. Pain syndrome can be typical (pain is characterized by rhythm and frequency of occurrence, often appearing at a strictly defined time for a given patient - an alarm clock symptom) and atypical. Pain in the epigastric region is the most characteristic clinical symptom of peptic ulcer disease. Early – pain that appears in the first 1 – 1.5 hours after eating. Late – pain that appears 2 to 5 hours after eating. Hungry - pain that, occurring several hours after eating, quietly disappears or weakens after a new meal. Nocturnal – pain that occurs at night and causes the patient to wake up. Early pain often suggests concomitant esophagitis. There is some peculiarity of the pain syndrome. Pain of a constant nature - the involvement of the pancreas. The paroxysmal nature of the pain is due to the involvement of the gallbladder. Combination with symptoms of gastric dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting) - there is a noticeable violation of gastric evacuation of functional or organic origin.
The following types of pain syndrome in peptic ulcer disease can be distinguished:
Visceral
- pain is dull, pressing, aching, relieved by eating, antacids, pronounced periodicity, of uncertain localization in the epigastrium, does not radiate, symptoms of peritoneal irritation, local muscle tension on superficial palpation, tension of the anterior abdominal wall and skin hyperesthesia are absent, but there is local soreness in the location of the affected organ with deep palpation, which does not coincide with the subjective localization of pain;
Visceral pain syndrome with irradiation
- the pain is dull, diffuse, at the height of the pain it is acute, relieved by eating food, antacids, pronounced periodicity, irradiation is characteristic, Mendel's symptom is positive, most often only when the ulcer is localized on the anterior wall, there is local muscle tension on superficial palpation, there is no tension in the anterior abdominal wall, skin hyperesthesia in the Zakharyin-Ged zones, local pain in the area of the affected organ with deep palpation, which usually coincides with the subjective localization of pain;
Visceral-somatic pain syndrome
- the pain is acute, not relieved by food intake, antacids, there is no periodicity, characterized by pronounced irradiation, point pain in the area of the affected organ, Mendel's symptom is positive, there is local muscle tension on superficial palpation, there is no tension in the anterior abdominal wall, skin hyperesthesia at the site of the ulcer and local pain at the site of the affected organ with deep palpation, which coincides with the subjective localization of pain;
Somatic pain syndrome
with perforation into the free abdominal cavity - sharp pain, “dagger-like”, diffuse, no periodicity, irradiation, point pain in the area of the affected organ, positive Mendelian, Shchetkin-Blumberg symptoms, diffuse pain in the anterior abdominal wall, the anterior abdominal wall is tense, there is diffuse skin hyperesthesia at the site of the ulcer and local pain at the site of the affected organ with deep palpation, which coincides with the subjective localization of pain.
Atypical pain syndrome in peptic ulcer disease: cholecyst-like
pain syndrome
- right hypochondrium localization of pain, more often characteristic of women, with one or another involvement of the gallbladder; retrosternal pain, as with angina pectoris, aggravated by physical activity (with “high” ulcers and in the presence of perivisceritis with the formation of adhesions), however, unlike true angina, they are provoked or reduced after eating; pain in the heart area (if the ulcer is localized along the greater curvature of the stomach), appearing 30-40 minutes after eating and relieved by eating, antacids, etc. Cramping pain, reminiscent of attacks of hepatic or renal colic, occurring acutely and periodically recurring regardless of food intake and its nature. Pain localized in the umbilical region and slightly below it, reminiscent of intestinal colic, appendicitis and other diseases of the abdominal organs, often causing diagnostic errors, including appendectomy. Ossalgic variant – irradiation of pain in the back (left or right scapula, interscapular space, thoracic spine).
Gastric dyspepsia syndrome:
heartburn, belching (food, sour, air), changes in appetite (fear of eating with stomach ulcers due to provoking pain, frequent eating with duodenal ulcers to relieve pain), nausea and vomiting (hypertonicity n.vagus: hypersecretion, dysmotility and spasm of smooth muscles, including the pylorus), inflammatory swelling of the mucous membrane or cicatricial deformation of the pylorus and duodenal bulb, nausea precedes vomiting, sour vomiting, brings relief, a feeling of heaviness, fullness in the epigastrium (equivalent to pain syndrome, with motor evacuation violations).
Intestinal dyspepsia syndrome.
Constipation (more typical for duodenal ulcers): vagotonia (peristalsis, sphincter tone), dietary restrictions (fiber), taking medications (aluminum, bismuth). Diarrhea (more typical for stomach ulcers): against the background of hypochlorhydria, impaired bile secretion, impaired functioning of the pancreas, the influence of eradication therapy.
Astheno-vegetative syndrome:
general weakness, increased fatigue, emotional lability. It is necessary to exclude complications: bleeding, anemia, electrolyte disturbances with frequent vomiting, malignancy.
Clinical variants of peptic ulcer
Subcardial ulcers:
age – 40-60 years, mild and atypical pain syndrome, burning, pressure under the xiphoid process, irradiation behind the sternum, to the heart area, early pain (including during eating), insufficiency of the cardiac sphincter. Difficulties in diagnosis, cardiac masks, left-sided pleurisy. High incidence of complications.
Ulcers of the body of the stomach:
Middle age, polymorphic clinical picture, moderate pain syndrome, early pain, to the left of the midline, nausea, belching, less often - heartburn, vomiting. Complications: bleeding 15%, often massive, perforation – 4%, malignancy – 8-10%, pay attention to ulcers along the greater curvature of the stomach!
Antral ulcers:
young and middle age, clinically similar to duodenal ulcer, late pain, heartburn, belching, vomiting, bleeding 10-15%.
Pyloric canal ulcers:
Intense pain syndrome, late pain, paroxysmal, radiating to the back, persistent nausea and vomiting, feeling of fullness, rapid satiety, difficulties in X-ray diagnostics, malignancy 3-8%.
Ulcers of the duodenal bulb:
young and middle age, hereditary history, hypersecretion of HCl, pain syndrome, late and night pain, heartburn, vomiting of acidic contents, brings relief, cyclical and seasonal course, interest of the pancreas when localized on the medial wall.
Postbulbar ulcers:
persistent, long-term course, frequent recurrence, prolonged exacerbations, often multiple, hypersecretion of HCl, persistent pain syndrome, late (after 3-4 hours) and night pain, does not stop immediately, localized in the navel area, heartburn, frequent bleeding, lesions of the papilla of Vater , it is necessary to exclude symptomatic ulcers, including gastrinoma.
In adolescence:
duodenal localization, beginning with dyspeptic syndrome, vomiting, reflex nausea, weight loss, pale skin, autonomic imbalance (red dermographism, sweating, hypotension, bradycardia, constipation, low-grade fever), hypovitaminosis, often in the form of “mono-pathology” ", rare involvement of neighboring organs in the pathological process, often due to functional changes, often starting with complications.
In old age:
often - low-symptomatic and atypical course, against the background of concomitant pathology (vascular bed: hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, respiratory system - hypoxia), taking ulcerogenic medications, multiple organ lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, the role of trophic factor, high localization, large size, long-term scarring, frequent complications.
Rare causes of peptic ulcer
Stomach ulcers:
adenocarcinoma, carcinoid, penetration of tumors of other organs, sarcoma, leiomyoma, foreign bodies, endocrine diseases, Crohn's disease, syphilis, tuberculosis, HIV.
Duodenal ulcers:
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, portal hypertension, Crohn's disease, celiac enteropathy, lymphoma, lesions, CNS injuries - Cushing's ulcers, hypercalcemia, systemic mastoidosis, amyloidosis, polycythemia, HIV.
The goal of treating peptic ulcers is:
accelerate the scarring of the ulcerative defect, quickly stop the clinical manifestations of the disease (pain, dyspeptic syndromes, etc.), prevent complications and relapse of the ulcer.
Symptoms (signs) of gastric ulcer
An ulcer is a significant damage to the integrity of the tissue. The body does not remain indifferent to it and reacts to a significant danger with very pronounced pain. Pain occurs in the epigastric region.
- When? It depends on the location of the ulcer. If it occurs in the upper part of the stomach, the pain appears immediately after eating. If in his body, then after thirty to sixty minutes. If the pain is delayed and comes later than an hour and a half later, or appears at night, on an empty stomach and is satisfied with food, the duodenum is affected.
- Where? The pain can radiate to different areas of the body: in the back, under the ribs, in the left nipple. These features also help the doctor more accurately determine the location of the ulcer.
- With what intensity? The strength of the pain varies: from dull and aching to sharp and sharp. And “dagger” pain is already an SOS signal from the body, since it is a consequence of “perforation” of the wall of the stomach or intestines and the release of its contents into the abdominal cavity. By itself, this condition can no longer end happily; very urgent help from a surgeon is needed.
Peptic ulcer disease has other, less specific signs: heartburn, belching, heaviness and a feeling of fullness that quickly comes during eating, nausea, vomiting, and bowel movements.
Traditional medicine recipes for stomach ulcers, psychosomatics of the disease.
- An effective remedy for stomach ulcers is the following mixture : mix honey, strong alcohol and crushed aloe branch in equal proportions. Let it brew for a day. Use a tablespoon three times a day for 4-5 weeks.
- Plantain decoction . Brew dried or fresh plantain leaves with boiling water. For brewing, take an arbitrary amount of raw materials. You can not use the prepared decoction according to the norm.
- Pumpkin seed tea . Brew pre-crushed pumpkin seeds with skins in a ceramic teapot. Drink pumpkin tea at any time, both with and without honey.
Research shows that the psychosomatics of the stomach is very sensitive to any negative emotions.
Therefore, the best prevention of his diseases will be control of the psycho-emotional state of the individual.
If you have already allowed these diseases to occur, then do not despair. Methods of Spiritual Integration will help you get rid of them forever.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. Treatment
Returning to the topic of psychosomatics, it is better to voluntarily radically solve psychological problems than to be forced to radically (i.e., surgically) deal with their consequences in the stomach. The same choice towards prevention is also relevant for the physical plane. It includes:
- daily routine (including the recommendation not to go to bed for two to three hours after eating);
- diet and quality of food;
- timely treatment of teeth and ENT diseases (places where Helicobacter pylori awaits an opportunity);
- working with bad habits;
- walks and physical therapy (sharp and prolonged exercise, especially during an exacerbation, is not advisable);
- drinking enough water.
By the way, there are cases where successful treatment of stomach ulcers was carried out exclusively by drinking enough plain water.
It is also worth paying attention to the modern world’s excessive enthusiasm for medicines. In many cases, you can do without many of them or at least reduce the dose. If this is not possible, you should look for a replacement that will not further destroy stomach tissue.
Alternative methods of holistic medicine: traditional Chinese medicine, osteopathy, herbal medicine, classical and resonant homeopathy will help to increase the body’s nonspecific defense, taking into account a person’s individual situation (the combination of causes and conditions for the development of peptic ulcer disease that are characteristic of him).
Stomach on psychosomatics, explanation by popular authors.
The world-famous Louise Hay explains the occurrence of stomach ulcers with the following possible reasons: horror, fear of the new, helplessness to perceive new things.
To heal the psychosomatics of stomach ulcers, Louise Hay recommends repeated repetition of a positive statement: “My life does not harm me. I always absorb new things throughout the day. Everything is going positively."
Louise Hay also names the following emotions and feelings as the reasons for the formation of psychosomatic ulcers: a firm belief in one’s own inferiority, the victim’s feeling that something is bothering him. A positive statement for the patient in this case: “I am lovingly full of self-approval. Everything flows in a positive way. I have peace of mind."
In general, Louise Hay explains stomach diseases and psychosomatics by the fact that the stomach, as a vessel for food, is responsible for the “digestion” of ideas and thoughts. To heal stomach diseases, Louise Hay recommends the following statement: “I easily “digest” being.”
Luule Viilma explains the problems of psychosomatics of the stomach with the following mental traumas (see table):
| Diseases | Mental trauma | Book | Page no. |
| Stomach (diseases) | Fear of being guilty. | Stay or go | 60, 61 |
| Duty to start. | Bright source of love | 249 | |
| Forcing yourself to work; the desire to have a lot, to be an example. | Pain in your heart | 177-179 | |
| Bleeding stomach ulcer | The desire to rise above others (“if I don’t do it, no one will”). Self-confidence, belief in one's own infallibility. | Pain in your heart | 247, 265, 270-279. |
| Prolapse of the stomach and gastritis | Fear “no one needs me” (passive person). | Pain in your heart | 264 |
| Stomach (increased acidity) | Guilt. | Pain in your heart | 220 |
| Stomach (low acidity) | Forcing yourself to work out of guilt. | Pain in your heart | 281 |
| Stomach (pyloric spasm until complete blockage) | Fear of trusting another. | Pain in your heart | 284-289 |
| Ulcer of any kind | Suppressing the sadness that comes from not wanting to be helpless and show your helplessness. | Pain in your heart | 156 |
Similar to Louise Hay, the psychosomatics of ulcers, V.V. Zhikarentsev sees in the patient a feeling of fear, a belief of inferiority, and concern. To heal stomach ulcers, he recommends using af.
Dr. R.G. Hamer, the author of “New German Medicine”, who confirmed the connection between diseases and mental trauma using the biological laws of the root causes of diseases, explains the occurrence of psychosomatic stomach pathologies (gastritis, ulcers, high acidity) by a conflict of territorial anger or a conflict of identity (depending on the dominant hand, hormonal status and previous conflicts). These conflicts are characterized by the following stages:
- Active stage : Disintegration of cells of the gastric mucosa in areas with squamous epithelium. The longer the conflict lasts, the deeper the mucosal defects (ulcers).
- Healing stage : Restoration of the squamous epithelium of the gastric mucosa. Bleeding stomach ulcer.