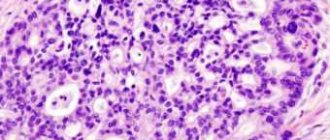
Malignant tumors are a group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of cells, their spread in the body, the formation of primary and metastatic tumor foci (with the exception of leukemia, in which solid tumors do not form). Oncologists are involved in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of these pathologies.
Our expert in this field:
Sergeev Pyotr Sergeevich
Deputy chief physician for medical work, oncologist, surgeon, chemotherapist, doctor of the highest category, Ph.D.
Call the doctor
The prevalence of cancer in the modern world continues to grow, primarily due to an increase in the average life expectancy of the population, as well as the spread of risk factors associated with lifestyle and the environment. Malignant tumors occupy the second place among the causes of mortality after cardiovascular pathologies, but in developed countries they are already gradually taking leading positions. Thus, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2021, cancer caused the death of 9.6 million people. Every sixth death in the world occurs from cancer.
But there is also a positive dynamic. Modern medicine is increasingly successfully fighting cancer pathologies, and the survival rate among patients is increasing. Oncology is one of the most rapidly developing areas of medicine; new technologies, treatment approaches, and antitumor drugs appear regularly. Although the complete victory over cancer is still very far away, the capabilities of oncologists are constantly growing.
Types of neoplasms
The content of the article
The type of benign tumors depends on the cells that formed them. Papillomas and warts form from the upper layer of skin, condylomas from mucous membranes, nevi (birthmarks) from pigment, fibroids from connective tissue, and fibroids from muscle tissue.
Atheromas form in the ducts of the sebaceous glands, and syringiomas in the sweat glands. There are vascular neoplasms - hemangiomas and lymphatic ones - lymphomas. Cysts, cavities filled with fluid, can form in any layer of the skin.
All tumors are schematically divided into two types - benign and malignant (cancerous). These neoplasias differ:
- The nature of growth
. Benign neoplasms grow by pushing tissue apart, while malignant neoplasms grow into neighboring structures and are transferred (metastasize) to distant organs. - Damage to the lymph nodes
- with the growth of benign tumors, the lymph nodes do not suffer, but malignant ones quickly affect them. - Violation of the general well-being of the patient
. Benign tumors do not cause intoxication, and the person feels well. During oncological processes, the body is poisoned by the products of tumor decay and exhaustion - cachexia. - The prognosis
is that for cancerous tumors it is much more serious.
Types of malignant tumors
Many people use the terms “malignant tumor” and “cancer” interchangeably. This is not entirely correct. Cancer (carcinoma) is just one type of malignant neoplasm. This is the name for tumors that develop from epithelial (integumentary) tissues - the skin and mucous membranes of various internal organs, exocrine glands.
Cancer is the most common type of malignant tumor. But there are others:
- Sarcomas are tumors of bones and connective tissue: fat, muscle, tendons, ligaments, blood and lymph vessels.
- Leukemias are malignant diseases of the hematopoietic system. Their peculiarity is that there is no solid (dense) tumor in the body. With leukemia, many pathologically altered leukocytes appear in the blood and red bone marrow, which crowd out normal cells.
- Lymphomas are tumors that arise in the lymph nodes and other organs in which lymphoid tissue is present: tonsils, spleen, thymus gland, etc. There are two main types of lymphomas: Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin.
- Multiple myeloma develops from plasma cells, a specific type of immune cell. The disease affects the red bone marrow and appears as tumors in the bones throughout the body.
- Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm that is often called skin cancer, but this is incorrect. This tumor originates from pigment cells—melanocytes; it can develop not only in the skin, but also in other organs.
- Brain and spinal cord tumors are a heterogeneous group and can develop from different types of cells.
- Germ cell tumors (germ cell tumors) come from the cells that give rise to sperm and eggs. They most often develop in the male and female gonads, but can occur in any part of the body.
- Neuroendocrine tumors develop from hormone-producing cells. Their peculiarity is that often the most prominent symptoms are those caused not by the tumor itself, but by the influence of hormones on the functions of various organs.
- Carcinoid tumors are a special type of neuroendocrine tumors. Typically, these slow-growing tumors are found in the gastrointestinal tract.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Why do you need to remove benign tumors?
Non-cancerous tumors can grow to enormous sizes. Wen (lipomas) and fibroids weighing several kilograms have been described. During the growth process, large tumors put pressure on tissues, blood vessels and nerves.
Neoplasia becomes inflamed and suppurates. The accumulation of pus can lead to cellulitis and blood poisoning. If accidentally injured, the tumors “get wet” and heal poorly.
Papillomas, warts and condylomas grow, forming large lesions. Growths located in the intimate area, on the edges of the lips and nasal mucosa, create inconvenience.
A benign tumor, especially located in open areas, often looks unaesthetic, causing problems with appearance.
Stages
Depending on the extent of the process, there are 4 stages of the disease:
- Stage 1 – the tumor is limited to the uterine cavity;
- Stage 2 – the tumor spreads to the appendages, cervix and vagina;
- Stage 3 – metastases appear in the lungs;
- Stage 4 – metastases in other organs.
* interval between the end of the previous pregnancy and the start of chemotherapy;
** low levels of β-hCG can occur with a trophoblastic tumor at the placenta site.
If the score is ≤ 6, there is a low risk of developing tumor resistance; ≥ 7 points – high.
How does cancer occur?
Neoplasia has a tendency to malignancy (malignancy), when a harmless formation begins to grow, degenerating into cancer. Frequent causes of degeneration:
- Mechanical damage.
Neoplasms injured by clothing, linen and jewelry become malignant. - Tanning abuse
. Under the influence of UV rays, harmless moles turn into melanomas. - Hormonal changes.
The degeneration of tumors often occurs during pregnancy and menopause, when the body undergoes serious changes. - Endocrine disorders
- problems with the thyroid and other endocrine glands. - Working with harmful substances
that cause the growth of cancer cells. Tobacco has a strong carcinogenic effect, so in smokers benign tumors often degenerate into malignant ones. - Exposure to viruses
, especially papillomavirus.
Under the influence of unfavorable factors, cell mutation occurs and defective cellular structures form. But not all such cases lead to cancer. In most cases, protective immune mechanisms are triggered, and the body copes with the problems. Atypical (irregular) cells undergo destruction (apoptosis) and the oncological process does not develop.
But sometimes malignant cells, from which the structures familiar to the body have not formed (have not differentiated), begin to multiply. Dysplasia occurs - areas with signs of beginning cancerous degeneration.
The division of atypical cells that form a tumor gradually accelerates. The lower their differentiation (incomplete formation), the more aggressive the cancer. Its first stage is cancer in situ - a tumor that has not grown deeper and has not metastasized. But, since malignant cells develop faster than normal cells, the tumor grows quickly, penetrating into neighboring tissues and metastasizing.
All types of benign neoplasms have their own characteristics and degree of danger.
Causes and signs of malignancy
The causes of malignancy are extremely varied. As a rule, a combination of several factors is required for the occurrence of a malignant tumor. The most significant of them are the following:
- Chemical carcinogens are chemicals that can cause cancer). It has certainly been proven that polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (substances that are formed in huge quantities during the processing of petroleum products, including automobile fuel, at some industrial enterprises), nitrosamines, which are found in large quantities in tobacco products, mineral fibers, etc., have a malignant effect. .h. asbestos and even some medications (in particular cytostatics, which are used to treat the same malignant tumors).
- Ultraviolet radiation, sunlight. They are the main provoking factor in the development of melanoma and other malignant skin tumors.
- Obesity. It is a risk factor for colorectal, breast and ovarian cancer.
- Poor nutrition - a large amount of fast carbohydrates, meat, smoked meats, marinades, canned foods and alcohol abuse are risk factors for the development of malignant neoplasms of the digestive system and liver.
- Ionizing radiation. Radiation can provoke the development of leukemia, thyroid cancer, and bone sarcomas. Patients who have undergone radiation therapy, as well as workers associated with the source of ionizing radiation - medical staff of radiation diagnostics (CT, X-ray), medical staff of radiation therapy departments, nuclear power plant employees, etc. are at greatest risk.
- Some viruses. For example, the well-known human papillomavirus can lead to the development of cervical cancer. The Nobel Prize was awarded for this discovery. The Epstein-Barr virus provokes the development of lymphomas, ATLV provokes the development of leukemia, and the hepatitis C virus can cause liver cancer.
- Hormonal dysfunction. Some hormones can stimulate cell growth and reproduction; breast and prostate cancer cells are hormonally dependent. In addition, hormones can influence the immune system and change the metabolic activity of certain carcinogens.
- Genetic predisposition. Today, many diseases and hereditary syndromes are known in which the likelihood of developing cancer is very high. For example, hereditary colon polyposis is complicated by colorectal cancer; a mutation in the BRCA genes is highly likely to lead to the development of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer.
Papillomas
These soft growths, mistaken for moles, are manifestations of a viral infection, which, as it spreads, leads to the formation of new growths. When injured by clothing and jewelry, the soft “pendants” can come off, ulcerate, and bleed. But the most dangerous complication of papillomas is degeneration into cancer. Therefore, these formations need to be removed.
Because the virus affects the entire body, cancerous tumors can occur in the genital tract, colon, and rectum. Patients suffering from papillomatosis (multiple papillomas) undergo a comprehensive examination and are prescribed antiviral treatment.
Causes
Conventionally, the reasons for this process can be divided into external and internal.
External reasons:
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- A dose of x-ray radiation that significantly exceeds the norm.
- Chemically active substances that have a long-term effect on the body.
- Nutritional disorders, namely consumption of carcinogens, prohibited stabilizers and dyes, transgenic products, etc.
Internal reasons:
- Decreased immunity.
- Chronic inflammatory diseases.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Fungal and viral diseases.
- Prolonged stress.
- Severe psychological shock.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Burdened heredity.
Warts
This is another viral type of skin tag that needs to be removed by combining topical treatment with an antiviral one. Warts spread over the surface of the skin, merging into large lesions. Contrary to ancient belief, the infection is “caught” not from frogs and toads, but from sick people, therefore, without removing the warts, a person infects those around him. Children are especially often infected.
Early diagnosis methods
Each person should regularly examine their skin for the presence of suspicious nevi. Paying attention to your body is a simple and effective diagnostic method. However, a person who does not understand medicine cannot always distinguish a healthy mole from a dangerous neoplasm - a sign of oncology.
At the hospital, doctors use the following diagnostic methods.
- History The collection of information by a doctor allows you to determine the root cause of the malignancy. The doctor will ask about sun exposure, injuries to the mole, and any actions taken with the neoplasm.
- Dermatoscopy Examination of the skin with dermatoscopes is an effective diagnostic method. The doctor will examine the color of the nevus, examine the relief and structure of the integument.
- Histological examination Examination of a skin sample under a microscope.
Pigmented nevi (moles, birthmarks)
Every person has several moles of different sizes on their body, but it is not necessary to remove them. There are nevi that need to be gotten rid of because of the risk of cancerous degeneration. To make it easier to remember, the signs of a “bad” mole are described by the AKORD system.
- A
- asymmetry. - K
- edge unevenness, scalloping. - O -
coloring. Malignant degeneration is indicated by the dark, almost black color of the neoplasm and the presence of areas of a different shade. - R
– size. Rapid growth of a mole is an unfavorable sign. You should consult a doctor if the nevus becomes more than 6 mm in diameter. - D
- dynamics, Dangerous signs - changes in the appearance of the mole, loss of hairs growing on it, bleeding, the appearance of nodules, crusts or ulcers, itching, burning and inflammation of the surrounding skin.
After removing the tumor, the tissue is examined for cancer cells.
Signs of malignant tumors
In the early stages, there are usually no symptoms of a malignant tumor. A person may not know for a long time that he has cancer. This is one of the reasons for late diagnosis, which leads to a worse prognosis.
But even when symptoms have already appeared, it is very difficult to diagnose cancer pathology from them. All of them are nonspecific and are most often caused by other diseases. For example, discomfort after eating and heartburn in stomach cancer can easily be mistaken for manifestations of gastritis, and cough and shortness of breath in lung cancer can be easily mistaken for signs of smoker’s bronchitis.
The clinical picture in each specific case depends on which organ is affected by the tumor and its metastases. In addition, there are some common symptoms:
- Constant feeling of tiredness, increased fatigue.
- Unreasonable weight loss.
- Increased body temperature.
- Loss of appetite.
Any unusual symptoms that persist for a long time should be a reason to visit a doctor and get tested. In most cases it turns out that they are not caused by cancer, but there is always a small chance.
For early diagnosis of malignant tumors at an asymptomatic stage, there are several types of screening:
- Mammography - x-ray of the breast - is recommended once a year or every two years for all women from 40-45 years of age.
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the colon. It is recommended for every person to undergo it upon reaching the age of 50 years. Subsequently, the study, if no pathologies are detected in the intestine, is repeated after 5 years. Also, for screening purposes, a stool test for occult blood and other studies, “virtual colonoscopy” (multispiral computed tomography of the intestine) are performed.
- HPV testing and cytology smears are recommended for all women of reproductive age for the purpose of early diagnosis of cervical cancer.
- Low-dose computed tomography of the chest is used for early diagnosis of lung cancer. This study can be administered to people with a long history of smoking, who are current smokers or who quit the bad habit less than 15 years ago.
Come see a doctor at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, he will assess your personal risks and tell you what types of screening you need to undergo.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Atheromas
These benign tumors are formed due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. Inside the formation there is a sebaceous secretion and skin particles. Sebaceous secretion is an excellent breeding ground for microbes that cause suppuration. Therefore, the tumor turns into an abscess, which can develop into a purulent tissue lesion - phlegmon, requiring urgent surgical intervention.
There are many methods for treating atheroma using compresses and ointments described on the Internet. These methods are harmful and dangerous because they increase the growth of tumors and provoke suppuration. The ruptured atheroma will not disappear as long as its capsule remains inside the tissue. After “home treatment,” a fistula forms on the skin, which has to be excised along with the tumor. When removing a tumor as planned, gentle methods are used - laser and radio knife, which leave no traces. This approach is more rational and safer.
How are malignant tumors diagnosed?
The examination for suspected cancer can be divided into three stages.
Stage I. Detection of the tumor.
If the tumor is located close to the surface of the skin, it can be detected by the patient himself or the doctor during an examination. Typically, tumor formations are initially detected using diagnostic methods such as ultrasound, radiography, and endoscopic examinations.
Stage II. Making an accurate diagnosis.
A biopsy helps determine which tumors are malignant and which are benign. The doctor removes a sample of pathologically altered tissue or the entire formation and sends it to the laboratory for histological or cytological examination. In the laboratory, you can not only study the material under a microscope, but also carry out immunohistochemical, molecular genetic and other tests. This will help to better understand the characteristics of tumor cells and select the optimal treatment.
Stage III. Clarification of the diagnosis.
When there is no doubt that the detected tumor is malignant, it is necessary to assess how far it has spread in the body and establish the stage. For this purpose, chest and bone radiography, CT, MRI, PET/CT scanning are used.
They also prescribe studies and laboratory tests that help assess the patient’s condition and properly plan treatment.
Hemangiomas
These tumors arising from vascular tissue are:
- flat – red and or bluish birthmarks;
- cavernous - having the appearance of purple or bluish growths. When tension occurs, blood flows to the tumor, it increases in size, becoming more noticeable;
- combined and combined - consisting of convex and flat sections.
Cavernous hemangiomas, which grow, hurt, bleed and suppurate, must be removed. Other options are eliminated only for aesthetic reasons.
Malignancy of stomach ulcer
Statistics show that the degeneration of a stomach ulcer into a cancerous tumor occurs in 4-15% of cases. The reasons for this process have not been reliably identified. But it is known that poor nutrition plays a significant role in this transformation. First of all, this is the intake of too spicy, fried or smoked food. In sick people with a history of stomach ulcers, who abuse alcohol and smoking, the risk of malignancy increases many times.
Symptoms of ulcer malignancy include:
- Changes in taste preferences, such patients often refuse meat dishes.
- Decreased appetite.
- The connection between pain and eating is no longer observed.
- The pain in the stomach area becomes constant.
- Painful sensations do not disappear from medications that previously helped.
- Nausea is added, which is present almost constantly.
- There is belching with a foul odor.
- There are bouts of vomiting.
- There is a feeling of heaviness in the stomach area.
- The patients are exhausted.
- Pallor of the skin is observed.
- Vitality decreases.
Malignancy is diagnosed in the same way as a gastric ulcer. It is enough to do fibrogastroscopy (FGS), during which a biopsy will be taken and sent for research.
Lipoma
This tumor is composed of fatty tissue. Wen formations can be single or multiple. Lipomas can grow, reaching a weight of several kilograms. Such large formations compress blood vessels and nerves, interfering with blood and lymph flow. Huge fatty tissues create many everyday problems - they impede movement and interfere with the selection of clothes. Cases of degeneration of wen into a malignant tumor - liposarcoma - have been described.
Therefore, if a lipoma is detected, you need to monitor it. Tumors that increase in size, cause pain, swelling, or are injured by clothing are removed. Small formations are cut off with a laser or electric knife, and for the resection of large lipomas, a surgical operation with suturing is performed. Therefore, it is recommended to remove wen before they reach an impressive size.
Symptoms
A woman should be alert to the following signs:
- painless vaginal discharge mixed with blood of varying intensity and severity;
- an increase in the size of the uterus, inappropriate for the duration of pregnancy with a complete hydatidiform mole;
- reduced size of the uterus, inappropriate for the duration of pregnancy with partial hydatidiform mole;
- toxicosis in late pregnancy.
With malignant trophoblastic disease, the nature of discharge during menstruation changes. Monthly bleeding is either absent or occurs longer than usual and is profuse. Along with this, complaints appear about changes in taste preferences, nausea and dizziness - symptoms that suggest pregnancy. Often there is a dull pain in the lower abdomen associated with compression of the walls of the uterus by the tumor.
The course of the disease depends on the provoking factor. So, after a normal pregnancy that ends in childbirth or abortion, the disease develops rapidly, disrupting the recovery of the female body. If the tumor formed after an ectopic pregnancy or transformed from a hydatidiform mole, then the course of the disease is more favorable.
The clinical picture can vary significantly depending on the location of metastatic foci:
- with metastases in the lungs, hemoptysis, persistent cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain occur;
- with metastases in the vagina, a compaction is palpated through the anterior wall of the abdomen;
- with metastases in the liver, pain appears in the right hypochondrium;
- with metastases in the brain, constant headaches, nausea, convulsions and loss of consciousness are possible.
Where to remove tumors in St. Petersburg
In St. Petersburg, at the Diana clinic, tumors of any type are removed using modern methods - laser and radio wave knife. The procedures take place without pain, scarring or other complications. Before removal, you can take tests for oncology and consult with an oncologist. All low-traumatic operations are performed by a dermatologist with the highest qualification category, confirmed in St. Petersburg.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Treatment options
In the early stages of malignancy, it may be sufficient to take measures to strengthen the immune system, as well as timely detection and treatment of inflammatory processes occurring in the body. As a rule, in healthy people the process does not develop beyond the first stage and fades away on its own if the irritating factor is eliminated.
Minimally invasive methods
This is one of the achievements of modern medicine. Such treatment methods are performed with minimal intervention in the patient’s body. In this case, the operation is performed through punctures or natural physiological openings. The process most often uses local anesthesia, and the duration of the procedure does not exceed one hour. Then the patient spends another three hours in the ward and can go home. Minimally invasive surgeries are also often performed using an endoscope or laparoscope.
With such operations, the risk of complications is sharply reduced, the patient recovers quickly, there is no need for long-term use of antibiotics before the procedure, no dressings, painkillers, etc. are required.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is one of the long-used methods of treating cancer. Drugs for its implementation are selected strictly individually, taking into account the characteristics of the tumor and the general health of each patient. The number of procedures and dosage are also selected by the attending physician, based on the test results.
Chemotherapy is one of the ways to treat malignancy
The main idea of chemotherapy is to “break” cancer cells enough to trigger the mechanism of apoptosis (their natural self-destruction). But, unfortunately, chemotherapy drugs are also dangerous for healthy cells; they affect overall well-being, reduce immunity, and can lead to brittle nails, hair loss and other unpleasant effects. However, this method is almost the only one for patients who, for some reason, are contraindicated for surgical intervention.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is also designed to trigger the process of apoptosis of cancer cells and also negatively affects healthy ones. Only in this case, chemotherapy drugs are not used for treatment, but exposure to radioactive substances is carried out. The decision about what type of therapy is optimal in each specific case is made by the attending physician, based on the medical history and general well-being of the patient.
Forecast
If malignancy is detected at the very initial stage, then the prognosis is favorable. Often, simply measures to strengthen the immune system and eliminate the irritating factor are enough for the abnormal cells to self-destruct naturally. The same goes for the second stage. This condition is more dangerous, but can still be treated without much difficulty.
With the beginning of the third stage and its transition to the fourth, they speak of the development of an oncological disease, and here the prognosis will depend on how early the tumor was detected, what biological properties it has, and where it is located. An important role in this case when predicting will be played by the general health of the patient, his age, the presence of concomitant diseases and many other factors.
All we can say for sure is that the sooner the tumor is discovered and treated, the greater the chances of survival, but a more accurate prognosis depends on a combination of many factors. It can only be done by the attending physician, and in some cases even he turns out to be wrong.
Preventive measures
To prevent malignancy, it can be advised to lead a healthy lifestyle and give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol. Monitor your diet, choosing a balanced diet and giving preference to natural products. You should not overuse spices, especially salt and pepper, as well as various herbs. It is advisable to process food by boiling or baking. Fried, fatty and smoked foods should not be overused. The protein content in the daily diet should not exceed 20%.
Proper nutrition is the prevention of malignancy
In addition to proper nutrition, it is important to try to protect the body from the harmful influences of the external environment. It is even possible to move to an area with a favorable environmental situation. It is advisable to avoid stress, overwork, and not to get nervous over trifles. It is also important to maintain a sleep-wake schedule and give the body moderate physical activity. It is also useful to be in the fresh air.
So that the disease does not take you by surprise, it is recommended to undergo regular scheduled medical examinations; if necessary, you can also undergo histological examinations for the presence of oncological markers; this is a simple and quick way to identify a precancerous condition or even a later stage at a time when symptoms have not yet appeared and treatment with favorable forecast is still possible.
In addition, routine medical examinations will help identify the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. Timely treatment of these disorders will also significantly reduce the risk of malignancy and degeneration of cells into malignant ones.