Often, a child’s lack of bowel movements for several days does not cause any concern. Especially if such an incident happens to an adult. Sometimes this symptom really does not pose any threat. But there are cases when persistent constipation leads to harmful changes in the intestines, its expansion and retention of feces. This condition, known as megacolon, can be caused by congenital abnormalities or a number of associated factors. In any case, this condition requires immediate treatment, otherwise it threatens with dangerous complications.
- 2 Types of disease
2.1 Photo gallery: manifestations of megacolon in adults and children - 2.2 Video about Hirschsprung's disease
- 4.1 Differences in the manifestations of congenital and acquired forms of the disease - table
4.1.1 Symptoms of pathology in the photo
- 5.1 Diet
5.1.1 Photo gallery: basic nutrition during illness
- 5.2.1 Agents used for the symptomatic treatment of megacolon - table
Definition and classification
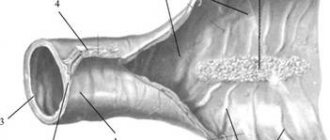
Megacolon is said to exist if the x-ray shows a pathological increase in the diameter of the colon:
- blind – more than 12 cm;
- ascending – 8 cm;
- descending and sigmoid - 6.5 cm.
In clinical practice, there are three types of megacolon:
- spicy,
- chronic,
- toxic.
Acute megacolon (Ogilvie's syndrome) is an enlargement of the colon that occurs in patients with severe surgical diseases. The chronic version lasts for several months or more. It is caused by persistent intestinal dysfunction, such as in Hirschsprung's disease or muscular dystrophies. Toxic megacolon is provoked by various infections: bacterial or pseudomembranous colitis, Chagas disease, etc.
What is megacolon?
This is a concept that combines a complex of similar symptoms from the large intestine, resulting from various congenital and acquired causes. Megacolon is characterized by an increase in length or proliferation (hypertrophy) of the intestinal wall in one area of the colon or throughout the entire colon.
The condition occurs among adults and among children of various age groups. Megacolon in an adult is a disease that occurs as a result of the action of damaging factors on the intestines from the outside (infection, toxins, etc.); megacolon in children is, as a rule, a congenital pathology.
Megacolon is a congenital or acquired disease that manifests itself as an enlargement of the colon
Interestingly, megacolon was identified in 1886 by pediatrician G. Hirschsprung, who noticed an “unusual disease” of the colon in some children, manifested by persistent constipation. This pathology was unlike any other intestinal disease previously known. Since the development of the disease was based on the “large colon,” the pathology was called megacolon (mega (Greek) - large, colon (Latin) - colon). Subsequently, to this day, it is the congenital form of megacolon that is called Hirschsprung's disease.
Causes
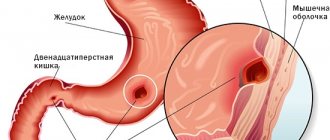
Depending on the etiology, megacolon is divided into primary (congenital) and secondary (acquired). The primary form is Hirschsprung's disease. This is a congenital pathology, which is based on the absence of intramural (inside the intestinal wall) nerve plexuses. Because of this, functional obstruction occurs due to distal narrowing, often in the rectal area. The direct cause of Hirschsprung's disease is a genetic mutation on four chromosomes.
Megacolon is said to be acquired if no congenital gastrointestinal pathology (aganglinosis, stricture or atresia) is detected. Typically, the pathology develops against the background of atonic constipation. The latter, in turn, provoke various diseases, including the gastrointestinal tract:
- mechanical intestinal obstruction (tumor, helminthic infestation);
- infectious and inflammatory bowel pathologies (Chagas disease, pseudomembranous colitis, etc.);
- surgical operations;
- Parkinson's disease;
- myotonic dystrophy;
- diabetic neuropathy;
- collagenoses (for example, scleroderma);
- hypothyroidism;
- hypokalemia;
- porphyria;
- pheochromocytoma.
Acquired megacolon can also be idiopathic. That is, there are clinical manifestations of the disease, but its exact cause has not been established.
The prevalence of chronic megacolon, such as Hirschsprung's disease, is 1 in 5000 births. The congenital form of the disease is more often diagnosed in boys than in girls (4:1). Secondary megacolon occurs with equal frequency in both men and women.
Complications and prognosis
The main complication of the pathology is intestinal obstruction due to fecal impaction or volvulus. Idiopathic megacolon has a favorable course. With conservative therapy, patients' well-being improves.
Hirschsprung's disease often leads to complications, so timely diagnosis and surgical treatment of the disease is important. The results of the operation depend on the severity of the condition, the correct choice of technique, and the qualifications of the doctor. In 50-90% of cases the prognosis is favorable.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Rectal cancer: symptoms, stages, treatment and prognosis for life
- Causes of bloating and increased gas formation, treatment methods
- More about hemorrhoids: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
- Irritable bowel syndrome: symptoms and treatments
- Details about bowel cancer: stages, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
- Sigmoiditis (inflammation of the sigmoid colon): symptoms and treatment methods
- Typhlitis (inflammation of the cecum): symptoms and treatment methods
- Intestinal stenosis: symptoms, treatment and prognosis for life
- Diverticulitis: symptoms and treatments (diet, medications, surgery)
Symptoms
Megacolon is characterized by nonspecific symptoms:
- abdominal pain;
- bloating and rumbling;
- constipation
Congenital megacolon (Hirschsprung's disease) usually develops immediately after birth. The baby passes a small amount of feces (meconium) in the first few days after birth, but the abdomen remains enlarged. Stool occurs only after a cleansing enema or the use of laxatives. If intestinal obstruction develops, vomiting, abdominal pain, and bloating occur.
Prolonged constipation is one of the signs of chronic megacolon Photo: shutterstock.com
If the disruption of intestinal innervation is partial, then symptoms may appear later, after several months. Frequent constipation is common, even despite taking medications. Due to digestive disorders, anemia and malnutrition (physical underdevelopment) develop. The child is often sick and has a weakened immune system.
The acquired form of the pathology is diagnosed in older children and adults. Chronic megacolon manifests itself with the same symptoms, but they are less pronounced than with a congenital disease. The process of nutrient absorption is disrupted to a lesser extent, so the patient’s general condition is usually not impaired.
Constipation with secondary megacolon lasts more than a week. Sometimes it is possible to palpate compressed stool in the lower abdomen. In some patients, fecal incontinence occurs due to reflex atony of the anal sphincter.
If the disease develops acutely, for example, against the background of infectious colitis or obstruction, a clinical picture of intestinal obstruction develops. Sharp abdominal pain, cessation of gas discharge, vomiting, nausea, and increased body temperature occur. In this case, you should immediately seek medical help.
Megacolon - symptoms and treatment
Diagnosis of megacolon begins with examination of the patient. On examination , an enlarged abdomen is usually noticeable. Muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall may be present. Percussion (tapping) usually produces a tympanic sound (loud, medium-high or high-frequency sound, similar to the sound of beating a drum).
A digital examination of the rectum reveals dense stool above the anorectal ring. Digital examination of the rectum in patients with Hirschsprung's disease may be accompanied by the release of large amounts of fecal content.
In patients with megarectum, the rectum may be filled and distended with fecal matter, which often leads to a gaping anus due to secondary dysfunction of the internal anal sphincter. In such patients, incontinence (failure to retain feces) and leakage of liquid stool may be present.
Differential diagnosis of megarectum must be carried out with various types of intestinal obstruction:
- malignant neoplasms of the large intestine;
- fecal blockage is a complication of chronic constipation, in which the intestines do not empty for a long time, and the feces become compacted and subsequently turn into stones;
- intussusception is a pathological condition in which one part of the intestine invades another, resulting in intestinal obstruction;
- rectal prolapse - partial or complete prolapse of the rectum beyond the anus;
- anal atresia - absence of the anus.
Laboratory research:
- Determination of blood electrolytes (potassium, sodium, chlorine, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus). It is necessary to exclude intestinal obstruction of another etiology, for example, acute pseudo-obstruction of the colon (Ogilvie's syndrome), which is accompanied by electrolyte disturbances, primarily potassium loss.
- Determination of thyroid function. Hypothyroidism, caused by decreased thyroid function, can cause slower bowel movements. Laboratory indicators for hypothyroidism:
- thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) - increased;
- total and free triiodothyronine (T3) - reduced;
- total and free thyroxine (T4) - reduced.
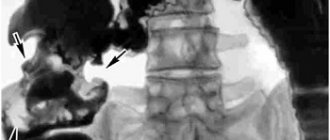
For primary diagnosis, a plain radiography of the abdominal cavity . This helps to clarify the situation and assess its severity.
After a plain X-ray of the abdominal cavity indicating the presence of megacolon, in most cases it is recommended to perform irrigography (irrigoscopy) (X-ray examination of the abdominal cavity using a contrast agent) [12]. This study allows you to safely assess the size of the large intestine and the location of its anatomical sections, as well as find out which area is pathologically dilated. Irrigography is also used to assess the potential ability to empty the large intestine using conservative methods [24].
It is possible to make a differential diagnosis between a total slowdown in the functioning of the large intestine and a functional obstruction at the exit (rectosigmoid obstruction) by monitoring the passage of a radiocontrast substance through the intestine. At least two days before the test, the patient is recommended to take 30 g of dietary fiber daily, and also avoid taking laxatives and performing enemas. The patient drinks a contrast agent and then has a plain abdominal x-ray on days one, three, and five to accurately determine bowel patency and the location, shape, and function of the colon.
In patients with a total slowdown in the functioning of the large intestine, the passage of the contrast agent through the intestine slows down and spreads from the cecum to the rectum. While in patients with a functional obstruction at the outlet (rectosigmoid obstruction), the contrast agent moves through the intestines at a normal pace and then accumulates in the rectum.
Anorectal manometry can help in the differential diagnosis of congenital and acquired megacolon This is a research method that allows you to evaluate the tone of the anorectal muscle complex, as well as the coordination of contractions of the walls of the anal sphincters and rectum. The test is carried out by inserting a rectal tube connected to a device that measures the pressure exerted by the anal sphincters. If, in response to stretching of the rectal wall, the internal sphincter of the anus relaxes and the external sphincter contracts, the patient does not have Hirschsprung's disease. If this reflex is absent, a rectal biopsy is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of Hirschsprung's disease.
Testing for conduction delay along the pudendus (pudendal nerve) may reveal problems related to intestinal motility, as well as mechanical and/or anatomical problems with defecation. The study is carried out using electrodes that are attached to the skin at the site where the nerves being studied pass through. An electrical current stimulates nerve activity, and electrodes measure the speed and strength of electrical signals passing through the nerve. If the nerve is damaged, the current will flow slowly and weakly.
Colonoscopy is necessary to exclude an obstructive cause of intestinal dilatation (narrowing or closing of the intestinal lumen). During colonoscopy, the large intestine is examined using a special optical device - a colonoscope, which allows you to examine the walls and lumen of the intestine.
Histological examination allows us to determine the etiology (cause) of the disease. Fine needle biopsy is the established standard for diagnosing Hirschsprung's disease. However, in most cases, aspiration biopsy of the mucous membrane is sufficient to establish the diagnosis. The disease is characterized by the absence of nerve cells, so Hirschsprung's disease cannot be excluded or confirmed by routine manometric studies. In other cases, a biopsy is not indicated, since the presence of nerve cells is normal.
Diagnostics
If stool retention occurs in a newborn, then Hirschsprung's disease is first ruled out. In the secondary form of the disease, it is necessary to identify the etiological factor leading to intestinal dilatation. It is important to differentiate between congenital and acquired forms of megacolon. The treatment approach and prognosis depend on this.
Diagnostics includes the following instrumental research methods:
- irrigoscopy (x-ray of the intestines with the introduction of contrast);
- computed tomography;
- colonoscopy;
- anorectal manometry.
To confirm Hirschsprung's disease, aspiration biopsy of intestinal tissue is necessary. The absence of nerve ganglia on histological examination confirms the diagnosis.
In case of toxic megacolon, a bacterial examination of the stool is additionally performed to identify the causative agent of the disease. In this case, it is not recommended to do a colonoscopy due to the high risk of intestinal perforation.
Classification
Stages: compensation, subcompensation, decompensation.
There are congenital megacolon and acquired
. The pathological process is also classified as follows: Congenital underdevelopment of the intramural nervous system in areas of the large intestine - Hirschsprung's disease.
Obstacles of a mechanical nature, which are expressed by stenosis, atresia, scars, postoperative deformities - obstructive or functional type
. Stagnation of food gruel initially provokes hypertrophy of the muscle layer due to increased peristaltic movements, then the tone weakens and the intestine undergoes expansion. Functional tissue is replaced by sclerotic tissue. Obstructive type of megacolon is diagnosed in 10% of patients. Mental disorders and associated incorrect eating habits, suppression of the urge to defecate lead to the fact that the colon is in an overstretched position for a long time due to the accumulation of a large volume of feces - the psychogenic type, occurs in 2-5%.
Endocrinological diseases, most often isolated mexidema and cretinism, lead to the development of endocrine megacolon
in 1% of cases.
Toxic megacolon
- one of the manifestations of pathology, occurs against the background of abundant damage by pathogenic microflora, taking laxatives.
Organic damage to the central nervous system (for example, meningoencephalitis) disrupts the motor-evacuation function of the colon due to pathological innervation due to disease - neurogenic megacolon
.
If the cause of colon gigantism cannot be determined, idiopathic megacolon
.
Classification of megacolon in accordance with the anatomical structure:
• rectal option; • rectosigmoidal; • segmental; • subtotal; • total.
ICD-10 code – K53.3
Treatment
Acquired megacolon is treated conservatively or surgically. As a rule, they begin with therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating constipation and normalizing intestinal activity:
- laxatives;
- cleansing enemas;
- prokinetics (Itomed).
A high fiber diet is prescribed. The menu must include the following products:
- vegetables and fruits;
- nuts;
- seeds;
- whole grain cereals;
- dried fruits;
- legumes;
- sea kale.
Vegetable oils (olive, flaxseed) and avocado improve intestinal function. You can add wheat bran or psyllium (psyllium husk) to your dishes.
For toxic megacolon due to enterocolitis, gastroprotectors (Rebagit), probiotics (Bifiform), and steroids or antibiotics, if indicated, are prescribed. At the same time, correction of water and electrolyte balance and detoxification therapy are carried out.
If there is no effect from conservative treatment, surgery is recommended. It is also indicated for congenital megacolon (Hirschsprung's disease). In the toxic form, the indication for surgery is the lack of effect of drug therapy within 24-48 hours.
The choice of technique is based on the degree of intestinal dysfunction. The following types of operations are possible:
- Ileostomy. Indicated for slow intestinal motility. Usually performed on middle-aged and older patients.
- Ileorectostomy. It is carried out with the defecation mechanism preserved. Recommended mainly for older people.
The following operations are recommended for children with Hirschsprung's disease:
- Colon decompression with colostomy;
- Resection of a section of intestine without nerve ganglia and formation of an anastomosis.
Treatment for intestinal hypertrophy
If the disease does not lead to acute intestinal obstruction, then it is treated with conservative methods. These include the use of a cleansing enema, abdominal massage and physiotherapy. Also, the prescription of enzyme preparations and drugs to enhance gastrointestinal motility (medicine “Cerukal”, “Maalox”) is indicated. It is important to follow a diet to prevent constipation.
In acute megacolon caused by Hirschsprung's disease, a section of the colon is resected. If total organ damage is observed, a colostomy is installed.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment, the prognosis for megacolon is favorable. After radical surgery for Hirschsprung's disease, improvement is observed in 90% of patients. If left untreated, life-threatening conditions may occur: infectious-toxic shock, water-electrolyte imbalance, sepsis.
Prevention of megacolon is aimed at preventing the etiological factor. To prevent constipation, you need to eat more foods with fiber (vegetables, fruits, whole grain bread, nuts). At the same time, exclude from the diet foods that slow down intestinal motility: sweet pastries, potatoes, rice, chocolate. To prevent congenital megacolon, pregnant women should adhere to a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits and unnecessary medications.
Intestinal megacolon: causes
The causes of the disease in question can be very different. It's worth considering some of them.
Toxic
Toxic causes of megalocon include inflammatory processes in the intestines under the influence of viruses or parasitic pathogens. Swelling of the digestive tract and irritation in some cases occurs. In this case, the large and small intestines are greatly irritated, pain and severe swelling may occur.
Toxic causes are always factors that additionally cause the development of inflammation processes. The intestines do not remove gases or fecal matter. If the permissible concentrations of gases in the intestines are exceeded, it may rupture.
Idiopathic
In such cases, patients complain of constipation tormenting them. Such conditions can develop due to intestinal expansion as a side effect of a number of other diseases. The causes may be toxic lesions of the small and large intestines, lesions of the plexuses of the small intestine in the area of infection, as well as malfunctions of the central nervous system. Other factors can cause disruption of the functioning of the small intestine, as well as a significant decrease in the lumen of the small intestine.
Functional
The functional causes of the described condition are considered to be those that do not entail fundamental changes in the functioning of the intestine. These can be considered the effects of certain diseases on the body, side effects from taking a number of drugs and medicines. In all such cases, there is no direct disruption of the effect on the stomach and intestines, but its general condition may sharply worsen. Lethargy and drowsiness appear, and a sharp deterioration in the person’s condition occurs. In such cases, it is recommended not to aggravate the situation, but to seek help from a specialist for a quality solution to the problem that has arisen.
Congenital
Congenital causes of the described condition include impaired conduction along nerve endings, disorders or differentiation of peripheral receptors, as well as their possible complete absence. The reason may be hidden in disturbances in neuron migration during embryogenesis. In addition, congenital disorders of the motor activity of the large intestine may occur, manifested in narrowing of the intestinal lumen and innervation disorders.
Prevention
Preventing the disease is not only a relief of subsequent symptoms, but also protection of one’s own body from all kinds of pathologies. Prevention of megacolon consists of a balanced diet. To do this, the diet must contain enough products that can dilute feces (although you should not get too carried away with this) and have a lot of fiber, which actively stimulates the nerve processes of the intestinal walls, forcing them to work much more actively. Recommended dishes include raw or stewed vegetables, as well as fruits and fermented milk dishes. There is a sharp need to reduce the amount of viscous porridges, sweets, jelly and fresh baked goods eaten.
It is advisable to behave actively, since physical inactivity is an ally of megacolon. Therapeutic exercise, supplemented by massage manipulations, will significantly strengthen the abdominal muscles along with the intestinal muscles.
Approximate price tags for treatment in major centers
| Sigmoidoscopy | average cost |
| Moscow | 1800 rub. |
| St. Petersburg | 1500 rub. |
| Omsk | 1200 rub. |
| Novosibirsk | 1100 rub. |
| Samara | 950 rub. |
| Chelyabinsk | 1300 rub. |
| Volgograd | 1000 rub. |
| Kyiv | 600 UAH. |
| Kharkiv | 520 UAH |
| Dnepropetrovsk | 490 UAH |
| Minsk | 48 bel. rub. |
| Almaty | 5000 tenge |
Megacolon: treatment
Treatment of megacolon is divided into several main types and is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
Traditional treatment
Traditional methods of treatment involve establishing a diet that includes a high content of plant fiber, as well as installing cleansing enemas to cleanse the intestines, performing abdominal massage, and using bacterial-based drugs. In addition, medications are used that can provide high-quality normalization of intestinal microflora, enzyme agents, as well as modulators of colon motility and stimulation of the rectum using electrical stimulation methods.
Operation
Surgical intervention in the treatment of the disease is possible in the event of the onset of Hirschpung's disease. In such cases, resection of the aganglionic zone is performed, as well as that part of the colon that has undergone the greatest expansion. As a rule, this occurs in children under 3 years of age; in adults, such treatment methods are much less common. When an obstructive form of megacolon occurs, a colostomy is applied and surgical intervention is prepared.
The actual volume of colon removed during surgery is determined by the severity of the disease, as well as the total duration of the affected intestine. In each individual case, the scope of work performed is determined strictly individually.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment involve drinking herbal decoctions that weaken the effects of the disease and have a general calming effect. These include infusions of valerian and mint. It is recommended to drink three times a day, half an hour before meals. If the desired effect does not occur, it is recommended to extend the period of use of herbs for drinking.
An infusion of black currant and horseradish also has a good effect. The proportion in each case is individual and is determined by the total volume of the affected area of the intestine. You should drink in slow sips, without rushing. It is imperative that before prescribing a course of treatment using traditional medicine methods, you should obtain advice from a competent specialist.
Symptoms
The severity of clinical signs is directly dictated by the extent of the lesion. Symptoms common to all age categories are:
- chronic disturbance of the bowel movement process, which is expressed in constipation - the act of defecation is carried out only with the help of a cleansing or siphon enema;
- distension of the lower abdomen;
- severe pain syndrome;
- nausea with frequent vomiting - often bile is present in the vomit;
- rounded abdomen or “frog belly”;
- displacement and deformation of internal organs, which are anatomically close to the colon;
- change in the shape of the chest - it becomes barrel-shaped;
- dyspnea;
- increased heart rate;
- pale skin.
In addition to the above clinical manifestations, the child also has the presence of the following signs:
- severe bloating;
- loss of appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- increased gas formation;
- attacks of diarrhea - expressed in rare cases;
- blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle;
- the ability to feel the presence of feces in the intestines;
- formation of a “pit” when pressing on the abdomen;
- increased tearfulness and anxiety.
With megacolon in adults, additional symptoms may include the following:
- headache;
- weakness and apathy;
- constant drowsiness;
- anemia;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- tachycardia;
- a sharp decrease in body weight.
In any case, it is very important at the first signs of megacolon, namely the appearance of constipation and flatulence, to seek qualified help as quickly as possible.