What happens to a person after gastric resection? Gastric resection is a surgical treatment of certain stomach diseases (complicated gastric ulcers, stomach tumors, etc.).
Depending on the nature of the operation, there may be total removal of the stomach, Billroth I resection, Billroth II resection and other modifications of operations. In the early stages after surgery, various medical and dietary measures are carried out in the hospital.
We will talk about the lifestyle of patients who underwent gastric surgery 5-6 months ago. I’ll say right away that stomach surgery is not a death sentence. Life after gastrectomy means many years of careful attention to yourself, a good quality of life, and proper nutrition. After the operation, the anatomical features of the gastrointestinal tract change, and the digestive processes in it also change.
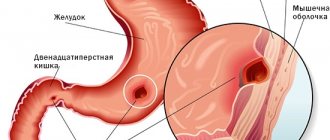
Let me remind you that the stomach is the organ where food enters from the oral cavity. It is subjected to deposition, mechanical and chemical processing and evacuation of stomach contents into the intestines. The duration of food in the stomach is from 1 to 3 hours, depending on its nature. After the operation, all functions of the stomach are lost. Nitrogenous substances in protein foods are quickly absorbed into the blood, which leads to disruption of the absorption of nitrogen by the tissues of the body, and nitrogen is excreted in the urine. The nitrogen balance in patients after surgery is disturbed; it becomes negative, i.e. More nitrogen is excreted in the urine than is taken in from protein foods. This leads to weight loss and weakness.
Surgeons should always warn a patient undergoing gastric surgery that the body weight lost before and after the operation cannot be restored, it will remain reduced, but this is not the main thing, the basis is a good quality of life and work capacity.
Progress of the operation
In LCRYGB surgery, the size of the stomach is reduced using a surgical staple. This bariatric procedure cuts the stomach so that it leaves a reservoir the size of a walnut. Then the so-called “biliopancreatic branch” (50 cm) is measured. The distal intestinal loops are connected to the reservoir (GEA gastrojejunostomy). This results in food being transported from the stomach directly to the small intestine. The junction of the small intestine (jejuno-jejunal anastomosis EEA) is formed at a distance of 120-150 cm from the GEA.
Laparoscopy as a method of treating stomach cancer
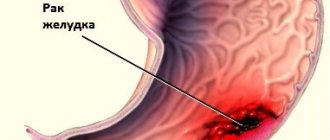
Gastric cancer (GC) is a malignant form of tumor that affects the stomach. The danger of cancer lies in its aggressive progression, destruction of the immune system, damage to other organs and a high probability of death. Surgery for cancer is a mandatory stage of treatment.
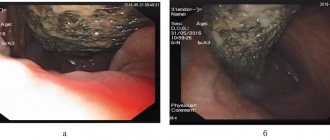
Laparoscopy is a surgical method used to diagnose or perform surgery for pathologies of internal organs. Access to the internal organs is gained through small incisions into which special instruments and a laparoscope are inserted. When diagnosed with stomach cancer, laparoscopy is performed to remove the organ partially or completely.
The Yusupov Hospital provides treatment in various areas, including oncology. The clinic has an oncosurgery department, where gastric cancer is treated by laparoscopy.
Indications for gastric laparoscopy
Stomach cancer is accompanied by multiple pathologies: uncontrolled bleeding, perforation of the gastric walls, neoplasms, and others. to eliminate the effects of cancer. Minimally invasive surgery is also performed to treat the underlying disease. Laparoscopy allows, without opening the abdominal cavity, to perform a full-fledged operation for resection and complete removal of the stomach
Laparoscopy for stomach cancer is performed to:
- determining the location, size and extent of tumor spread;
- clarification of the nature of the pathology;
- choice of treatment tactics.
The decision to perform laparoscopic surgery is performed solely according to indications and after preliminary diagnosis.
After operation
The patient must follow a special diet and take vitamins to lose weight in a controlled manner.
Diet after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or loop gastric bypass (BII)
Gastrobypass is a bariatric procedure with a small malabsorptive component as the stomach is reduced and connected to a subsequent segment of the small intestine. It is used in patients who have failed other methods (diet, exercise, medications) and whose BMI is around 35 kg/m2. The stomach volume is 15-20 ml after the procedure; over time it grows again to 125-250 ml. Before surgery, the patient must learn to eat healthy and eat mindfully, and accept a limited eating plan. Only then can he be satisfied with the job later. In addition, each patient must undergo physical therapy, receive psychological assistance and follow the advice of an endocrinologist.
After the procedure and, as a result, the patient cannot adequately provide his body with vitamins and microelements. He must supplement his diet with appropriate medications available in pharmacies.
General principles
A high protein, low calorie, low fat, low fiber, low carbohydrate diet.
Protein
Protein (protein) is one of the most important components of the diet and is essential for life. Our body needs proteins to strengthen tissue. It cannot be replaced with other components. Adequate intake is vital to our health. High quality protein is found in animal products such as meat, fish, low-fat dairy products and eggs. Constant protein deficiency leads the body to degradation and depletion of body tissues; restoration is then impossible.
Carbohydrates, sweets
This includes all sweets (chocolate, candies, cookies), confectionery, ice cream, sweet milkshakes and sweetened juices. The diet after biliopancreatic bypass should not contain any of the above for the following reasons:
- These foods are high in calories and are easy to digest. Weight loss can hardly be achieved
- Foods in this group are low in nutrients such as vitamins and minerals and have no health benefits.
Fats
After surgery, fat digestion is more difficult. A high-fat diet can slow stomach emptying, leading to the symptom of reflux esophagitis. Vegetable fats and unsaturated fatty acids, such as those found in fish, should dominate the diet.
Cellulose
Foods such as whole grain oatmeal, baked goods, raw vegetables and fruits, or dried legumes are high in fiber. They increase in volume in the intestines. For this reason, these foods should only be consumed in small portions immediately after surgery.
Vitamins and microelements
These vital substances are involved in many biochemical reactions in the body. Please note that many vitamins are destroyed during cooking or long-term storage of foods. Since the quantity and quality of food is significantly limited after surgery, there is a shortage of these substances. Especially: vitamin B12, iron, folic acid and calcium.
Iron-containing products
Liver, red meat, fish, poultry, seafood, especially oysters, vegetables, whole grains, grains, green vegetables (especially spinach and broccoli), dried fruits such as figs, raisins, cherries and dates.
Foods Rich in Vitamin B1
Whole grain products, yeast, red meat, legumes (peas, beans), nuts.
Vitamin B12 Rich Foods
Animal products (especially liver), eggs, fish. Vitamin B12 is also produced by bacteria in the intestinal flora. After surgery, the patient must receive vitamin B12 injections once a month for the rest of his life.
Foods rich in folic acid
Liver, green vegetables (raw or blanched), especially spinach, Brussels sprouts, white beans, green peas, cauliflower, broccoli, yeast, wheat germ, egg.
Water
Water is vital because absolutely every process in our body requires water. We should drink at least 1.5 liters per day. The need for fluid increases after physical activity or on hot days.
Important Tips:
- Drink a glass of water, tea or low-calorie vegetable or fruit juice between meals.
- Drink at least six glasses of liquid.
- Drink one hour before meals.
Diet after gastric bypass surgery (step by step)
First phase:
Only liquid - usually during the first two days after surgery.
Start with small sips of water. Later, weak tea.
Followed by oatmeal and low-fat broth.
Second phase:
Protein-rich liquids and cereals - up to three weeks after discharge from the hospital. Protein preparations from the pharmacy are useful (for example, Protifar - Nutricia).
Third stage:
Four weeks after surgery, the diet should be expanded to include some specific foods. Do not forget that food should be easily digestible, pureed in a blender (“well chewed”) and, above all, should be rich in protein (crushed soft-boiled or hard-boiled eggs, mashed, low-fat cottage cheese, grain cottage cheese, pureed chicken in a blender or low-fat fat content fish products, potato and vegetable puree, natural yogurt). For variety, you can buy baby food at a health food store. Grinding (pureeing) as well as low fat content is always important. Vitamins and microelements are important if not prescribed by a doctor (usually one tablet per day).
Benefits of laparoscopy
Laparoscopic surgery for the treatment of stomach cancer has many advantages over laparotomy. The modern method of surgical intervention is characterized by a high rate of efficiency and preservation of the organ.
The advantages of laparoscopy also include:
- minimally invasive - minimal tissue trauma;
- no scars - small incisions on the abdomen remain almost invisible;
- rapid physical recovery;
- less severe pain;
- accuracy of manipulations - the ability to visualize and magnify images allows the surgeon to perform all actions with maximum precision;
- reducing the risk of heavy blood loss - thanks to the precise actions of the surgeon, damage to blood vessels is minimized, or they are immediately blocked;
- air from the space almost does not enter the abdominal cavity, which facilitates postoperative recovery;
- low risk of tissue infection, development of purulent wounds and hernia.
Patients diagnosed with stomach cancer, even in the initial stages, are in serious condition. Laparoscopy, as a minimally invasive operation, allows surgical intervention with minimal complications and quick recovery. Thus, the patient has the opportunity to begin the next stage of treatment much faster than with laparotomy.
Why is it worth undergoing gastric resection surgery at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency?
Federal Scientific Center FMBA is one of the leading multidisciplinary clinics in Russia, where you can undergo all the necessary preoperative and postoperative examinations, which significantly saves time and money. Thanks to an integrated approach, the clinic offers the optimal price for gastric reduction surgery in Moscow.
Since 2011, the Bariatric Surgery Department of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia has been performing surgeries on patients with a high body mass index. Many years of experience in the fight against obesity have allowed us to:
- develop a system of preoperative preparation that reduces the risk of complications during and after surgery;
- optimize the surgical technique and reduce its duration (on average, longitudinal gastrectomy lasts about 1 hour);
- perform the operation laparoscopically (the size of laparoscopic punctures is about 1 cm), due to which the incisions heal quickly and there are no obvious cosmetic defects;
- reduce the level of postoperative complications;
- include in the patient rehabilitation program a unique complex “Postoperative examination of a bariatric patient”, in which each operated patient is observed for several years.
Depending on the program, for at least a year after surgery, patients of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center FMBA have access to consultations with a bariatric surgeon and doctors of other specialties, which facilitate the rehabilitation period. Patients who have undergone gastrectomy in other clinics can also join this program.
Our team of endoscopic doctors
Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of cancer patients requires high precision, mastery of techniques and considerable experience from the surgeon.
The team of Euroonko doctors under the leadership of the head of the endoscopy department, MD. M. S. Burdyukova completed:
- More than 1500 endoscopic operations on the bile ducts;
- More than 250 endoscopic stenting for esophageal tumors;
- More than 150 stentings for stomach tumors;
- More than 170 stentings for duodenal tumors;
- More than 150 stentings for colon tumors;
- More than 75 endoscopic operations in patients who had previously undergone major surgery.
Endoscopic treatment is highly effective with a minimum of complications. Patients recover as quickly as possible, their quality of life improves significantly, and the functions of the stented organ are preserved.