- home
- Gastroenterology
- Polypectomy of the stomach and gallbladder
Polyps are a common pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. They are benign neoplasms. If left untreated, they develop into malignant and pose a threat to life. Drug treatment is not effective in the presence of polyps, so surgery is used.
Endoscopic gastric polypectomy is a modern technique that is used at KDS Clinic for the treatment of polyps. During this procedure, soft tissues are not injured, only affected cells are removed. Interference with internal organs is minimized. Polypectomy is considered an outpatient procedure. After it is performed, the patient does not require long rehabilitation, and he can return to his usual lifestyle.
Endoscopic gastric polypectomy is performed in combination with gastroscopy. For surgical intervention, an operating gastroscope and pain relief using medicated sleep (sedation) are used.
Causes of polyps
The appearance of polyps is influenced by several factors. Benign formations in the stomach occur in people with chronic gastritis and duodenal ulcers. Lifestyle also influences the development of pathology. If you have bad habits, including smoking and alcoholism, the risk of the disease increases. Improper nutrition negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and contributes to the appearance of tumors.
Long-term use of antibiotics and other strong medications contributes to the appearance of benign tumors. The cause may also be genetic predisposition.
Principles of nutrition
The principles by which the patient’s nutrition is organized differ depending on the stage of recovery. In the first days after surgery, the patient is recommended to rest in bed and adhere to strict rules regarding food.
When moving to semi-bed rest, the principles change somewhat as the patient's condition improves. During the home recovery period, separate rules also apply.
During bed rest
On the first day the patient does not eat any food. To activate the gastrointestinal tract, the next day he is allowed to drink a glass of warm sweet tea.
You should not drink it immediately, but rather take a teaspoon every 15 minutes. This will help the stomach start working. If there are no adverse symptoms, then from the third day a diet with reduced energy value is prescribed.
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates begin to enter the patient's body, but in reduced quantities.
With semi-bed rest
At this time, foods that are easily digestible are recommended. They should not irritate the mucous membranes. It is necessary to control the amount of carbohydrates entering the body.
On this topic
- Digestive system
The role of hormonal contraceptives in the development of liver hemangioma
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2021
Fiber and complex carbohydrates are completely excluded. It is forbidden to consume hot or cold food. Salt is used in small quantities.
Food should be liquid, semi-liquid or pureed. Portions should be kept small to avoid overeating.
But at the same time there should be no hunger - this is also harmful to the stomach. To prevent dehydration, you need to consume about 2 liters of fluid.
Eating at home
It is organized according to the patient's condition, so there may be differences. But there are also general rules that everyone should follow.
Correct heat treatment
After removing a polyp in the stomach, the best options for preparing dishes are boiling and baking. Patients should not eat stewed or fried foods.
Reduced energy value
You need to eat fewer carbohydrates than usual. Products with complex compounds should be excluded from the diet. Proteins and fats are consumed in amounts normal for healthy people.
Fractional meals
You need to eat food 5-6 times. Portions are made small so as not to burden the stomach. But between meals you should not feel hungry. You should drink milk before going to bed.
Prevention of mucosal irritation
Patients during the recovery phase need food at a comfortable temperature, neither hot nor cold. There should be little salt in it (no more than 6 g per day).
You should not frequently consume foods that stimulate gastrointestinal secretion. These include raw vegetables, seasonings, and spicy foods.
Sufficient amount of liquid
To prevent dehydration, you should consume at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day.
In case of febrile syndrome, which sometimes occurs in patients after surgery, this amount must be increased.
This is interesting: Constipation: cause or consequence of hemorrhoids? How to deal with stool problems due to pathology?
Carrying out the procedure
Before endoscopic polypectomy, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination of the body, including ultrasound diagnostics. The patient is sent for testing. On the eve of surgery, you should follow a strict diet, give up alcohol and smoking.
Also, before the procedure, blood pressure, pulse, and general health are monitored. Removal of a polyp tumor is carried out under anesthesia using medicated sleep (sedation). A gastroscope is used, which captures the loop with the tumor. The procedure is absolutely painless for the patient and does not require rehabilitation. A few hours after recovery from anesthesia, the patient goes home.
Acceptable menu after polyp removal: what can you eat, what can’t you eat?
For the first two months after surgery, it is important to organize proper nutrition. Usually, table No. 5 according to Pevzner is prescribed, which is used for severe diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and during the postoperative recovery period.
The following foods are acceptable to eat:
- slimy porridges and soups;
- jelly, berry fruit drinks, dried fruit compotes;
- steamed meat or fish cutlets (minced meat is passed through a meat grinder 2-3 times);
- vegetables are steamed.
Sample menu for the day:
- Morning . Milk porridge, sandwich with butter, tea with milk.
- Second breakfast . Gingerbread and a glass of jelly.
- Dinner . Steamed fish cutlet, mashed potatoes, berry juice.
- Afternoon snack . Cookies with kefir.
- Dinner . Buckwheat without salt with a glass of berry jelly.
In the first weeks, you should not drink concentrated juices, strong tea or coffee. Under no circumstances should you drink alcohol or smoke!
A diet that requires only 100 grams per day will be effective. proteins, 500 gr. carbohydrates, 80-90 gr. fat The total daily calorie content should not be more than 3000 Kcal.
For a speedy recovery, you need to eat viburnum (berries, viburnum decoction, juice), oil or sea buckthorn juice (1 teaspoon before meals).
Preparation for the procedure
Before the procedure, the patient should quit smoking. It is advisable to take plenty of drinking water. It is important to follow a strict diet, eliminating fatty and floury foods. It is also advised to exclude foods that contain fiber. This substance affects the volume of the large intestine.
To cleanse the intestines, the patient is given an enema or prescribed laxative medications. A complete examination of the gastrointestinal tract will be required. The patient undergoes endoscopic examination and ultrasound diagnostics. You need to take a blood clotting test and determine your Rh factor.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient’s blood pressure is measured and the pulse is checked. The doctor should be interested in the patient's condition.
What not to eat
Any type of surgical intervention involves nutrition, when you should limit your usual food. After removal of polyps in the stomach, a number of dishes cannot be eaten for 6-12 months. This is due to their adverse effects on the digestive tract. Prohibited products include:
- carbonated drinks, alcohol, coffee, kvass, juices from sour fruits and vegetables - tomato, berry, citrus-based;
- decoctions of meat, mushrooms and fish, borscht, jellied meat;
- bread products based on rye flour and with bran;
- lard, sausages, sausage, offal - liver, heart, kidneys;
- full-fat milk, sour cream, fermented baked milk, full-fat kefir, cream;
- vegetables - onions, radishes, radishes, white cabbage, tomatoes, hot peppers;
- fruits and berries with a high acid content;
- barley, rice, pearl barley, millet porridge.
Results and reviews
Dietary nutrition after removal of gastric polyps allows you to restore full gastrointestinal function in a relatively short time, as evidenced by patient reviews.
- “... An ulcer sufferer with extensive experience. During the last exacerbation, examination revealed an adenomatous polyp in the antrum of the stomach. Two months later he was operated on as planned. I've been on the diet for almost six months now. And as I was told, I should be on this diet to prevent the regrowth of polyps at least 2 times a year, during the period of spring and autumn exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease”;
- “... An endoscopic examination diagnosed a polypoid tumor in the antrum of the stomach. Endoscopic surgery was recommended. While I am under clinical observation, I was prescribed Diet No. 1. I’m preparing mentally for the operation.”
Indications
- Diet No. 1 for polyps in the stomach with increased/normal secretion;
- Diet No. 2 for polyps in the stomach with secretory insufficiency.
After polypectomy :
- starvation diet (1-3 days);
- Diet 1A for 3-5 days;
- Diet 1B for 6-8 days;
- Diet No. 1 on day 12 for a period of 1-2 months with normo / hyperchlorhydria ;
- Diet No. 2 for hypo / achlorhydria .
General rules
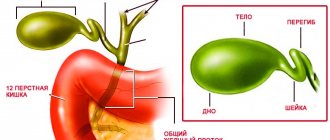
Gastric polyp refers to benign neoplasms on the mucous membrane, protruding into the lumen of the stomach and connected to its wall by a narrow stalk or a wide base. The shape, location in the stomach, size and quantity vary widely. As a rule, the leading factor in the occurrence and development of gastric polyps is chronic progressive gastritis .
Conservative therapy, regardless of whether these are single or multiple polyps, is practically ineffective, and given the high risk of malignancy of the polyp, the optimal measure for its treatment is polypectomy . However, in some cases, with small polyps of the hyperplastic type, in order to identify the dynamics of the growth of neoplasms, the nature of changes in their surface (the appearance of bleeding, erosions, the formation of irregularities), the formation of new growths, a wait-and-see approach is practiced, which consists in prescribing dietary nutrition with regular examination of the stomach.
The diet for polyps in the stomach is determined by the level of acidity. In case of increased or normal secretion, Diet No. 1 , and in case of secretory insufficiency - Diet No. 2 according to Pevzner.
The main goal of therapeutic nutrition is to maximize the sparing of the gastric mucosa from adverse factors, accelerate the evacuation of food from the stomach, and reduce/increase the secretion of gastric juice. The diet is physiologically complete, energy value is at the level of 2900-3000 kcal per day with a diet containing 95-100 g of proteins, 100 g of fats and 400 g of carbohydrates.
The principles of dietary nutrition are:
- Avoiding hot/cold foods that suppress acid-forming function and have an adverse effect on the mucous membrane.
- Limiting foods and dishes made from them that have a stimulating effect on the enzymatic secretion of the gastrointestinal tract (broths, seasonings, raw vegetables, spicy dishes).
- Exclusion from the diet of foods that are difficult to digest and linger in the stomach for a long time.
- For the purpose of mechanical sparing, dishes are boiled. When prescribing a pureed version of the diet, the food is ground, and when not pureed, it is served not pureed; baking without a crust is allowed.
- Salt is moderately limited (up to 6 g/day).
- Small meals, 5-6 times a day, including drinking milk before bed.
- Drinking regimen: 1500-2000 ml of free liquid.
The menu includes milk and vegetable soups. Vegetables and fruits are served only boiled. Fish and meat - low-fat varieties, in pieces. Legumes and pasta are not allowed in the diet. Barley, wheat and corn cereals are not included in the diet. Porridges are prepared crumbly. Fats (vegetable oils and butter) are added to prepared foods. The diet must include milk, cottage cheese, white dried bread/crackers, soft-boiled eggs, jelly, non-sour jam, tea, cocoa. Sweets: honey, sugar, marshmallows.
In case of secretory insufficiency with similar principles of dietary nutrition, the diet of Table No. 2 includes foods and foods that stimulate the production of gastric juice. These include various soups prepared in concentrated meat and fish broths, pasta, vegetables, and the use of seasonings is allowed. Foods that are difficult and take a long time to digest in the stomach are excluded from the diet. Almost all types of culinary processing are allowed (boiled, pureed, stewed, baked, fried without crust), and degrees of grinding. Table salt - up to 15 g/day.
Drinking regimen: 1.5 liters of free liquid. The menu allows first courses (soup, borscht, pickle), which are prepared in meat/fish, vegetable or mushroom broth with the inclusion of various cereals, potatoes, and vegetables. The range of second courses is expanding - baked, boiled, fried lump meat/fish, pancakes with meat, cutlets.
Boiled and baked vegetables (pieces and pureed) - white cabbage, potatoes, zucchini, carrots, beets, cauliflower, green peas, pumpkin. The diet includes cottage cheese, fermented milk products, cream, fruit/vegetable juices, bran decoctions, ripe berries and mashed fruits.
Diet after removal of a polyp in the stomach
Dietary nutrition after surgery to remove polyps ( gastric polypectomy ) is much more important. Typically, minimally invasive endoscopic polypectomy is used to remove single polyps. Gastric resection is performed in rare cases in the presence of multiple large neoplasms (with gastric polyposis), often recurrent polyps or complicated by gastric obstruction, massive bleeding, pinching, necrosis, or malignancy of the polyp. There is no specific drug treatment for stomach polyps. However, since this disease often occurs against the background of gastritis , treatment and diet are prescribed in accordance with the principles of treatment of gastritis ( peptic ulcer ).
Immediately after the operation, the patient is prescribed a full starvation diet for a day. On day 2, one teaspoon is given, after 15 minutes, 1 glass of sweet warm tea and rosehip infusion (50 ml); on the 3rd day, in the absence of abdominal bloating, normal peristalsis and the passage of gases, in order to maximize the sparing of the gastrointestinal mucosa from any impact and reduce inflammation, Diet No. 1A . Diet with reduced energy value. The consumption of mainly carbohydrates and, to a lesser extent, proteins and fats is reduced.
Meals during semi-bed rest. Prescribe pureed, semi-liquid and liquid food containing easily digestible foods and a sufficient amount of liquid. To prevent flatulence , foods containing complex carbohydrates, whole milk and fiber, as well as dishes and foods that stimulate secretion and irritate the gastric mucosa, are excluded from the diet. Hot/cold dishes are excluded. The amount of sodium chloride is limited.
Small meals (small portions 6 times a day) during bed rest. Patients often experience significant fluid loss after surgery. The daily requirement for free fluid during an uncomplicated postoperative period is approximately 2-2.5 liters. For complications ( intoxication , fever ) - 3-3.5 l.
On days 6-8, in order to stimulate mucosal regeneration processes, the patient is transferred to Diet 1B . The diet contains limited carbohydrates with an appropriate protein and fat content. Cold/hot dishes that irritate the mucous membrane and stimulate/inhibit the secretory function of the stomach are excluded. Food is steamed or boiled, served in puree form, soups with a mucous decoction. Drinking regimen: at least 1.5 liters of liquid. The amount of salt is limited. Milk is given at night.
One of the objectives of therapeutic nutrition is to eliminate, within 10-15 days after polypectomy , the deficiency of proteins, vitamins and minerals, which often develops in connection with blood loss, fever, malnutrition in the first postoperative days, and the breakdown of tissue proteins. Therefore, it is necessary, if possible, to transfer the patient to a nutritious diet as early as possible, taking into account his condition, the state of the gastrointestinal tract and the ability to digest food. Usually on the 12th day the patient is transferred to Diet No. 1 . To reduce the phenomenon of metabolic acidosis, dairy products, boiled vegetables and grated fruits are included in the diet.