Causes of the disease and symptoms of papillomas
A virus is responsible for the formation of formations in the perianal area, which can be caught during sexual intercourse with an infected partner. Modern methods of contraception do not provide complete protection; in addition, the insidious virus can be transmitted through mucous membranes and skin.
Symptoms of papillomas in the anus are listed below:
- Excess moisture in the anal area.
- Burning, itching.
- Pain during bowel movements, sometimes accompanied by blood.
It is important to understand that many proctological problems have similar symptoms, and in order to understand what kind of disease you have been exposed to, you need to see a doctor. And the sooner, the more accurate the diagnosis will be made, and the easier it will be to go through the treatment phase.
Rectal tumors
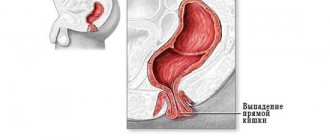
Benign tumors of the rectum are often asymptomatic, especially when they are small. If the neoplasm is large, it manifests as intestinal obstruction and slight bleeding from the anus. Benign neoplasms usually do not disturb the general condition of the patient and are not accompanied by copious discharge from the rectum, although the development of the inflammatory process against the background of multiple polyposis can lead to chronic bleeding, diarrhea with the release of large amounts of blood-stained mucus, anemia of the patient, an increase in general weakness and exhaustion. Polyps located in the anal sphincter area can fall out and become pinched.
Malignant tumors of the rectum in the early stages of development may not manifest themselves in any way. The situation is further complicated by the fact that many patients often do not pay due attention to the symptoms. Most patients diagnosed with rectal cancer have chronic proctological pathology, for example, hemorrhoids, anal fissure, rectal fistula or paraproctitis. These diseases have clinical symptoms similar to tumors. Therefore, patients may perceive colorectal cancer clinics as just another manifestation of their chronic disease. In general, people go to the hospital only if they have severe symptoms.
Tumors of the rectum are manifested by discharge from the anus, symptoms of intestinal irritation, impaired stool patency and signs of deterioration in general condition. The discharge may be mucous or bloody. When the tumor is low localized, the discharge looks like scarlet blood. If the neoplasm is located in the ampullary, middle and upper segment of the rectum or in the rectosigma, then mucous-bloody discharge during defecation is characteristic. A symptom of rectal irritation is paroxysmal pain. Patients may also experience discomfort in the lower abdomen and a feeling of squeezing of the intestines. Patients note the appearance of a false urge to defecate.
Initially, the disease may manifest itself as stool disorder, followed by intestinal obstruction. Large rectal tumors, on the contrary, manifest themselves predominantly as constipation. The disease is often accompanied by symptoms such as bloating and painful rumbling. If a patient has developed a violation of intestinal patency, he is worried about retention of stool and the passage of gases, intense pain along the intestines, vomiting, etc. As rectal cancer progresses, it manifests itself with general symptoms, such as unmotivated general weakness, pallor of the skin, decreased performance, decreased weight body up to cachexia, loss of appetite. Also, with this disease, long-term persistent low-grade fever is often observed.
For early detection of rectal cancer, it is very important to know all possible clinical manifestations of the disease. Early signs of malignant tumors of the rectum are mostly nonspecific. They can be observed in many other diseases. However, prolonged persistence of symptoms such as general weakness, low-grade fever, constipation and discomfort in the rectum should alert the patient and the doctor. Blood discharge during bowel movements and signs of intestinal obstruction indicate late stages of the disease.
Diagnosis and choice of treatment method for papillomas
In addition to the obligatory visit to the proctologist, for the final confirmation of the diagnosis it is necessary to take control blood and urine tests, consult with related specialists and undergo a sigmoidoscopy procedure. This study allows you to carefully examine the rectal mucosa, obtain reliable information about the condition of the intestines, and, accordingly, prescribe appropriate treatment.
No method of combating papillomas provides an absolute guarantee of complete recovery. Such viral diseases are dangerous due to their relapses; in addition, growths can develop into malignant formations. Therefore, it is most often suggested to remove them.
Excision of papillomas can be done in several ways:
- Laser.
- A surgical scalpel.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Electric shock.
To achieve the best result, it is necessary to cut out all formations present on the patient’s body. The method of excision should be agreed upon with the attending physician after all tests have been completed.
Characteristics of benign and malignant tumors
There are clear criteria:
- Delineation of the tumor from adjacent tissues.
- Growth rate.
- Ability to metastasize.
- Histological portrait of cells.
- Patient survival.
Benign tumors are clearly demarcated from healthy tissue and often have a capsule. Cancer grows into surrounding tissues, penetrates into blood vessels, and its contours are more amorphous.
Most benign tumors can grow for years without showing symptoms. Carcinomas grow quickly, disrupting organ functions and poisoning the body. Growth is accompanied by fatigue, weakness, weight loss, and pain.
Benign formations “sit” in one place, gradually grow and push apart healthy tissues, and are mobile when palpated. Cancer cells are loosely attached to each other, are easily separated and spread by lymph and blood throughout the body. They settle in the lymph nodes, bones, and internal organs, forming new tumor foci - metastases. On palpation, the node is fused to the tissues and does not move.
A biopsy provides a lot of information. The study shows that benign cells are similar to healthy ones, their structure is clearer. The structure of malignant cells is greatly altered due to pronounced mutations. The less the cells resemble the tissue from which they grew, the worse the prognosis for treatment and life.
A benign tumor, such as prostate adenoma, can be removed and a complete cure can be achieved. If a relapse occurs, it will be in the same place where the primary lesion was found. Malignant tumors are difficult to remove completely. Even one remaining cell will give rise to a new tumor either in the old place or where it got through the vessels. The survival rate of patients is significantly lower.
Difference between condylomas and papillomas
Condylomas and papillomas that occur on the human body have a common nature - a viral type pathogen. In addition, the signs of the presence of these pathologies in the rectum are also similar. But there are also differences between them:
| Appearance | Infection method | Treatment | |
| Condylomas | “hang”, protrude forward, are formations of the papillary type. | appear as a result of sexual contact with an infected partner. | must be excised. |
| Papillomas | similar to warts - pathologies that have grown into the mucous membrane or skin. | may occur even after contact with the patient’s personal belongings. | sometimes it is not necessary to remove them, since they do not always cause pain, discomfort and are not so dangerous. |
Benign tumors of the small intestine
During an objective examination of patients, in some cases it is possible to palpate the tumor through the anterior abdominal wall: neoplasms of the jejunum are determined in the navel or to the left of it, neoplasia of the ileum - in the right iliac region. Benign tumors of the distal small intestine are recognized during a rectal or bimanual gynecological examination. On palpation, the tumor is felt as a smooth, mobile formation in the abdominal cavity. When the intestinal lumen is stenotic, a splashing sound may be heard and visible peristaltic movements of the intestine may occur.
Anemia and positive stool occult blood test results are detected only in tumors complicated by hidden or overt bleeding. A more accurate diagnosis is based on a comprehensive X-ray, ultrasound, and endoscopic examination. Radiocontrast studies include radiography of barium passage through the small intestine, probe enterography, and irrigoscopy. The X-ray picture is characterized by the presence of round or oval filling defects with clear, even contours, narrowing of the intestinal lumen, deformation of the mucosal relief, suprastenotic expansion of the intestinal lumen with the presence of fluid and air.
Enteroscopy - endoscopic examination of the upper parts of the small intestine (jeunoscopy) is performed using a modified fibrogastroduodenoscope; The terminal parts of the small intestine (ileoscopy) are examined through a fibrocolonoscope. If tumors are localized in these areas, an endoscopic biopsy can be performed and morphological verification of the tumor can be carried out. Modern methods of endoscopic diagnosis include capsule endoscopy. The method consists of a visual examination of the small intestine using a miniature capsule swallowed by the patient, containing a video camera and transmitter.
In addition to radiography and endoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, CT, scintigraphy, laparoscopy are used, especially when it is necessary to differentiate tumors of the small intestine from tumors of the colon, uterus or ovaries; specific - tuberculosis and syphilis and nonspecific processes - appendicitis, Crohn's disease, foreign bodies, kidney dystopia, pancreatic cyst.
Prevention of papillomas
It is not easy to get rid of a virus that causes formations on the human body. But there is a small set of measures to help protect yourself from infection or eliminate the possibility of relapse:
- Work to improve your immunity: sports, hardening, good sleep, healthy eating, giving up bad habits.
- The use of immunostimulating drugs is allowed, as agreed with the attending physician.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene.
- Vaccination against several strains of the virus is possible. However, in our country this vaccination has not yet been fully studied, and therefore it is not included in the preventive vaccination calendar. You can do it either under the direction of a specialist, or at your own request.
- Be attentive to your sexual partners, and also, if possible, avoid being in large crowds of people in saunas, baths, swimming pools - in places with a warm and humid environment that is favorable for the spread of the virus. You also need to be careful with other people's personal hygiene products.
- Regularly see a proctologist to monitor the condition of the rectum.
Types of tumors
Benign:
- cysts;
- nevi or moles;
- nodules whose name has the oma suffix: fibroma, myoma, adenoma, papilloma - depending on the specific tissue.
Malignant:
- formations whose name is appended with the word carcinoma, sarcoma, blastoma, blastosis (fibroblastoma, myosarcoma, adenocarcinoma);
- oncological diseases of the blood - lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia and others;
- skin cancer - melanoma, basal cell carcinoma.
The differences are not always obvious. A thorough diagnosis is needed to look for atypical cells.
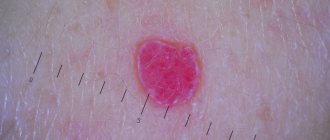
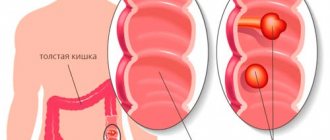
Rectal papillomas are formed on the mucous membrane of the rectum and anus as a result of infection with the human papillomavirus. The incubation period varies and can last up to six months. As a rule, papillomas in the rectum form against the background of weakened immunity. Papillomas bring many problems to the patient, ranging from unpleasant sensations to the possibility of papillomas transforming into cancer.
Rectal papillomas are usually divided into three categories:
- Single, small size.
- Single, large.
- Multiple, forming united areas.
Visually, they look like a wart with a mottled surface on a thin stalk, but sometimes their size exceeds 2 cm in diameter. The color of papillomas can be different: light or dark.
Causes of the disease and symptoms of papillomas.
You can become infected with rectal papilloma during sexual intercourse with an infected partner. Modern methods of contraception do not provide complete protection; in addition, the insidious virus can be transmitted through mucous membranes and skin.
Symptoms of papillomas in the rectum:
- Sensation of moisture in the anal area.
- Burning, itching in the anus.
- Pain during defecation, blood in stool.
Almost all proctological diseases, such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, papillomas, cancer, have similar symptoms, so in no case should you self-medicate if you experience discomfort in the anus.
You need to contact a professional doctor - proctologist at the Only Clinic, undergo a proctological examination for an accurate diagnosis and strictly follow the treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment of rectal papillomas.
At an appointment with a proctologist at the Only Clinic, to finalize the diagnosis, you will be prescribed blood and urine tests, as well as anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy procedures. These proctological examinations allow a thorough examination of the rectal mucosa, so that reliable information about the condition of the intestine can be obtained, and, accordingly, appropriate treatment can be prescribed.
It is impossible to cure papillomas forever. The virus is dangerous because of its relapses, and papillomas can develop into cancer. Therefore, most often, proctologists offer patients removal of papillomas.
Treatment, that is, removal of papillomas, can be carried out in several ways:
- Laser.
- A surgical scalpel.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Electric shock.
Difference between condylomas and papillomas.
Condylomas and papillomas have different forms, but the nature of their origin is the same: the cause of their appearance on the human body is the HPV virus.
In addition, the symptoms of papillomas and condylomas are also similar.
The differences between these diseases are as follows:
Condylomas have a hanging appearance, protrude forward, have the shape of papillae, and the method of infection is through sexual contact. Condylomas must be removed.
Papillomas are similar in appearance to warts and can be transmitted through household contact. If they do not cause pain, papillomas do not need to be removed.
Prevention of papillomas.
It is very difficult to get rid of a virus that causes formation in the rectum. It is easier and simpler to take precautions to avoid becoming infected with this virus:
- You need to lead a healthy lifestyle and constantly improve your immunity, then go in for sports, exercise, moderately combine work and rest, get enough sleep, eat right, and give up bad habits.
- You can take immunostimulating drugs after coordinating the use of medications with your doctor.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- You can get vaccinated against strains of the virus. You can do it either under the direction of a specialist, or at your own request.
- Avoid casual sex
- Do not use other people's personal hygiene products
- Be careful in crowded places: swimming pools, baths, saunas, gyms.
- Regularly, at least once a year, undergo examination by a proctologist at the Only Clinic.
Watch your health! Don't start the disease!
If you suspect the appearance of anal diseases, consult a doctor - proctologist!
Self-medication of proctological diseases is not only ineffective, but also dangerous!
Call us, we will help!