Dirty hands, unwashed food, unboiled water - all these are ways of contracting rotavirus infection in adults and children. Every person has encountered unpleasant symptoms of an intestinal disorder, but let's figure it out a little.
What is rotavirus and is it really all around us? Rotavirus infection is shed from the intestines of an infected person in the feces. How is the pathogen transmitted? After visiting the toilet, viral particles often remain on the hands and are transferred to objects touched by an infected person.
Handrails on the bus, door handles in public places, and money that is touched by the hands of a large number of people are dangerous. Then, through unwashed hands, the pathogen enters the gastrointestinal tract of a healthy person and causes rotavirus disease with symptoms of vomiting and diarrhea.
Other names for rotavirus infection are intestinal flu, rotavirus gastroenteritis. From the moment rotavirus enters the body, the incubation period ranges from several hours to 5 days. On average - 16 hours.
The source of the disease is an infected or sick person. There are cases of asymptomatic disease. An example is medical workers who regularly encounter the pathogen and have developed some immunity to it, but nevertheless the virus is localized in their intestines and is excreted in their feces into the external environment.
What is rotavirus
Rotaviruses are established mainly in the intestine - they infect the villi of the small intestine, which leads to structural and functional changes in the epithelium.
The triple protein shell makes them resistant to the acidic environment of the stomach and digestive enzymes in the intestines.
Enteroviruses of another species that also cause intestinal infections, noroviruses, act in much the same way.
The disease has a cyclical development: the incubation period lasts from one to ten days, the acute period lasts seven days, recovery occurs after another three days.
Children. Virus.
CC0.
Rotavirus is often called intestinal flu. In fact, it has nothing to do with the influenza virus.
Fact
According to WHO, every year, noroviruses cause 64 thousand episodes of diarrhea requiring hospitalization, 900 thousand visits to clinics with children in developed countries, and up to 200 thousand deaths in children under 5 years of age.
Is it possible to become infected with rotavirus again?
Doctors are often asked the question: is it possible to become infected with rotavirus again after being ill, and how long can you rest assured that infection will not happen?
Unfortunately, immunity to rotavirus infection is not stable and lifelong, so re-infection is quite possible. Of course, the body of a person who has been ill produces antibodies that remain in the blood for some time, preventing him from getting sick with intestinal flu again. The duration of the antibodies varies.
When a person’s immune system is in good working order, protection lasts for a year or a year and a half. If the general immunity is weakened, then the specific immunity will not be so long and intense; a person can get rotavirus infection quite often. However, repeated illness is still easier to tolerate.
There is an observation that even the incubation period of the disease depends not on the infectiousness of the pathogen, but on the degree of intensity of the immune system. The stronger the immune system, the later the disease will manifest.
Thus, a clinically healthy young person, in whose body an infection is already developing, can infect a child or an old person, without being clearly sick himself. In this case, in a child or an elderly person, symptoms can begin within a few hours, and in the person who infected them, much later, within several days.
A good way to protect against rotavirus is through mother's breast milk. It is known that it is rich in immunoglobulins, which help prevent infection without putting a strain on the child’s own immunity.
How can you get infected?
Main routes of transmission:
- food - eating unwashed vegetables or fruits;
- aqueous - drinking liquids contaminated with a virus;
- contact-household - use of contaminated dishes and household items; unwashed hands.
Airborne transmission is not typical for intestinal infections.
Pandemic. Virus
unsplash.com
A person infected with the virus is contagious during the acute phase of the disease and for the next 48 hours. That is, although he feels completely healthy, he remains dangerous to others.
Komarovsky about rotavirus
Dr. Komarovsky notes: with watery diarrhea, it is necessary to replenish lost fluid. Dehydration is considered a dangerous consequence. With diarrhea, the body loses copious amounts of water. Urine production decreases, blood pressure drops, convulsions occur, and damage to the nervous system occurs.
E. coli causes pneumonia regardless of where the child gets sick - at home or at school. The main causative agent of pneumonia is a lack of fluid in the body. Due to deficiency, the lungs become infected.
Antibiotics do not need to be prescribed to a sick child - they will not destroy the bacteria that caused the infection. Capable of suppressing the growth of protozoa. An antibiotic is prescribed if blood appears in the stool, during cholera, giardiasis.
What are the symptoms of rotavirus
A child who catches rotavirus in kindergarten or school can easily and quickly put the whole family out of work.
Symptoms of infection can easily be confused with food poisoning:
- profuse vomiting and nausea that disappear within 24 hours from the onset of the disease;
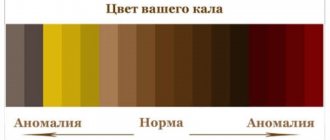
- diarrhea with pain in the middle and upper abdomen, with the release of watery and foamy masses of a yellow-green hue;
- rumbling and transfusion in the abdomen;
- signs of general intoxication - headache, fever, feeling of weakness;
- characteristic respiratory symptoms - runny nose, fever, swelling and redness of the throat;
- signs of dehydration caused by diarrhea and excessive vomiting.
Rotavirus is more likely to cause diarrhea than norovirus.
Disease, ARVI.
CC0
In most cases, the disease is relatively mild, and the patient is given a favorable prognosis. Less commonly, severe vomiting and diarrhea cause dehydration. If the immune system is weakened, secondary infection is possible.
Sometimes it seems that the disease is quite mild - for example, diarrhea three or four times a day and vomiting the same number of times a day at a temperature of 37.2, but already on the third day, disturbances in water-electrolyte metabolism will be noticeable in the body. They are accompanied by convulsions and loss of consciousness.
Signs of illness
The first sign of the disease is usually a sharp increase in body temperature, chills, and flu-like aches. Then spasmodic pain in the abdomen appears, severe flatulence, accompanied by loose stools and nausea. At the same time, gurgling in the intestines is pronounced.
The development of symptoms occurs very quickly. The general condition of the patient is lethargic, activity and performance are reduced, and there is no appetite. Vomiting and diarrhea lead to dehydration, the skin becomes pale, the mucous membranes are not sufficiently moisturized, lips are cracked, and the tongue is coated with a white coating. But not all cases exhibit such obvious classic symptoms.
Sore throats are sometimes observed, especially in children, which is why intestinal flu is often confused with sore throat. In these cases, the patient is bothered by a mild dry cough, rhinitis with swelling of the nasal mucosa, the tonsils and lymph nodes become inflamed and increase in size, inflammation of the conjunctiva leads to redness of the eyes and lacrimation.
It is also possible for the disease to be asymptomatic. In this case, the person does not have any clinical signs of the disease, but carries the pathogen and excretes it with feces into the external environment.
Who gets sick and when?
Viral intestinal infections are seasonal. There are more of them against the backdrop of an increase in the incidence of ARVI. There are always more children among the sick - 94% of all those infected.
The risk group for rotavirus also includes patients with disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, when it is suppressed; with chronic intestinal diseases; with violations in the diet, as well as when changing baby food; not observing the rules of personal hygiene.
Cold. Runny nose.
CC0
Symptoms
There are incubation periods of infection (up to 5 days), acute (3-7 days) and recovery (after illness, up to 5 days). Rotavirus infection begins abruptly - the child’s temperature rises, diarrhea and vomiting appear. On the first day of infection, the diarrhea is yellow, on the second day it is gray-yellow, clay-like.
The febrile state lasts up to 3 days, the temperature does not rise above 38-39C. The child feels weak, lethargic, and has a decreased appetite. With rotarvirus infection, diarrhea lasts up to 1 week. In the first days of infection, acute abdominal pain appears.
Children complain of pain in the larynx when swallowing. A runny nose and cough appear. Manifestation of rotavirus infection: the child wakes up in a lethargic state and is capricious. He feels nauseous and may vomit with mucus. The appetite decreases, the baby vomits what he has eaten. During the day the temperature rises. The stomach growls, the child cries, constantly wants to sleep.
An adult cannot avoid the disease. Most people mistake the symptoms of the disease for a gastrointestinal disorder. Nausea and vomiting may not appear, weakness is noted, appetite decreases, and body temperature rises. The period is characterized by diarrhea and does not last long.
The disease is easier: adults have a stable immune system than infants and children. If there is an infected person in the family, upon contact with the patient, rotavirus manifests itself within 3-5 days.
Why the number of rotavirus infections is decreasing
Of all the reported cases, only 888 are rotaviruses and noroviruses. Back in 2021, this figure was twice as high.
According to Olga Egorova, last year was “quite exotic” due to the emergence of a new coronavirus infection that can suppress other viruses. As long as the coronavirus continues to circulate, there will be fewer other infections.
“The decrease also happened because we all finally learned to wash our hands,” says Galina Filippova, the chief specialist of the Altai Territory on infectious diseases in children.
Prevention of infection
To avoid getting sick, wash your hands more often - before eating, after going to the toilet, or walking outside. Wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly, make sure that the products are not expired. Rotavirus is easily transmitted from household items; a small dose of viral bacteria is sufficient to cause infection.
Tap water is a cause of contamination. The main task is to provide the population with drinking water and carry out sanitary and hygienic measures.
Considering the contagiousness of intestinal flu in winter, take prevention seriously in families with children. Boil water for drinking and washing dishes. It is better to bathe your baby in boiled water.
You can get intestinal flu from a sick person. The patient is isolated for 10-15 days; in case of mild forms, they are left at home under the supervision of a family doctor. If the infected person remains at home, it is advisable to isolate him from others: allocate a separate room, dishes, things.
It is prohibited to walk on the street, in crowded places. If you cannot avoid walking, choose uncrowded places. This will prevent an epidemic at work and in educational institutions (kindergartens).
The correct action if a colleague develops diarrhea at work: immediately take sick leave, knowing the danger to others.
Wrong actions: the mother took the sick child to kindergarten, causing the epidemic to grow in the group.
Laboratory studies have confirmed that the virus is found on toys, household items, and surfaces. Disinfection of rooms and furniture is mandatory.
Duration of the anti-epidemic regime
The illness period lasts two weeks. Follow preventive measures for at least another week.
A rotavirus vaccination will come in handy. Contains live viruses that cause disease. After administration, immunity is formed in the body, which lasts up to several years.
What to do if you get sick
Contact a doctor immediately, especially if your child is sick. In severe forms of infection, the patient requires hospitalization, in mild cases - outpatient home treatment.
Be sure to wash your hands.
Pixabay.com
Only a doctor can distinguish a viral intestinal infection from any surgical pathology, for example, from signs of appendicitis. It is best to call a doctor on the first day, as soon as symptoms are noticed, and not prolong the illness.
Galina Filippova warns parents against giving their children painkillers for rotavirus. This can blur the clinical picture, and it will be difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis. Also, you should not drink a lot, it provokes vomiting, and then hospitalization is inevitable.
You need to drink little by little, at certain intervals and in small sips.
Water.
CC0
How to bring down the temperature
If the temperature is below 38 degrees, there is no need to bring it down provided the patient is feeling normal. To reduce fever, use Tsefekon suppositories (suitable for children up to one year old).
Older children are given Paracetamol. If it doesn't help, give Paracetamol in combination with a quarter of Analgin. Keep a break between tablets. At least 2 hours.
Rubbing with a weak solution of vodka helps. Follow the rule - wipe your body, do not allow temperature changes. Rubbing begins if more than 30 minutes have passed after taking the pill and no relief has occurred.
In order not to become infected with rotavirus, communication with the patient is limited - the transmission mechanism is fecal-oral: through hands, things, surfaces. If treated correctly, the virus goes away quickly and no complications arise. Contact with children is prohibited to avoid infecting them.
The virus that provokes the onset of the disease dies at 38 degrees. Medications that reduce fever are used. A vodka solution will help - rub the body with the product.
How is rotavirus treated?
There is no specific treatment regimen for rotavirus infection. As with all viral diseases, antibiotics will not help. For treatment, antiviral drugs and antipyretics are used, depending on the condition.
With a mild course of the disease, the symptoms go away on their own. Patients are prescribed a diet, it is necessary to exclude alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, rough foods that irritate the stomach and intestines.
The American Association of Pediatrics does not recommend giving children boiled milk, salty broth or soup, and does not advise trying to make a formula to replenish lost minerals yourself.
Enterosorbents that mitigate the symptoms of diarrhea and vomiting can help cope with the symptoms of a viral infection. Patients are also prescribed drugs to restore fermentation in the digestive system.
Glass of water
CC0
The main danger of rotavirus is dehydration. Its pronounced symptoms are dizziness, headache, fatigue, dry mouth, dry lips and eyes, and rare urination (less than three to four times a day).
If you don't replace lost fluids, dehydration will worsen and complications such as low blood pressure and kidney failure may occur. This can be fatal.
Characteristics of the pathogen
The name of the pathogen comes from the Latin word “rota”, which means “wheel”. When viewed through an electron microscope, rotaviruses have the appearance of a wheel, hence the name.
The resistance of the infection in the external environment is very high. The virus retains its viability and pathogenic properties both in hot and dry weather and in severe frost conditions. When it gets into products, it finds a favorable environment there and persists for up to 30 days, and in reservoirs even longer - up to several months.
Related article: What can adults and children eat if they have rotavirus infection?
In rooms where they are regularly cleaned and even disinfected, the virus can nevertheless exist for quite a long time. To cope with it, you need to know at what temperature the infectious agent dies. Unfortunately, only boiling can be guaranteed to kill it.
Are there vaccinations against rotavirus?
Fatal outcomes from intestinal infections, according to Elena Filippova, most often occur in children in the first or second year of life. The disease at this age is characterized by prolonged diarrhea and dehydration.
There is a vaccine that can protect a child from severe forms of rotavirus; it is given starting from two months of age. The complex consists of drops in the mouth and includes three doses. Vaccination must be completed strictly before eight months.
Syringe. Graft.
CC0
The deputy chief physician of Barnaul children's clinic No. 3 says that more often parents vaccinate their second or subsequent children because they suffered with the first. True, vaccination is not included in the national calendar, so it can only be done for a fee.
There is no vaccine against intestinal infections for adults.
Rotavirus in children
In children, the disease has its own specifics. In young patients, as in adults, all intestinal symptoms can be expressed, but often they are accompanied by damage to the ENT organs. Sore throat is a common symptom accompanying rotavirus infection in children. A runny nose also appears, and cases of otitis media are not uncommon.
The disease poses a particular danger to infants. Rapid dehydration leads to metabolic disorders, and inaction in this case can be fatal. Therefore, when refusing breastfeeding, it is necessary to give the child something to drink; in severe cases, the doctor prescribes intravenous infusions of solutions that restore fluid exchange in the baby’s body.
Children often become infected with rotavirus infection because they still have little control over themselves, put dirty hands in their mouths, and examine unfamiliar objects. Children are inquisitive, spontaneous and not fully accustomed to hygiene, so their contact with infection is more likely. In addition, the immune system of children is not formed, so a child is more likely to become infected with rotavirus than an adult.