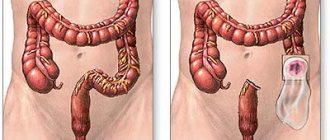
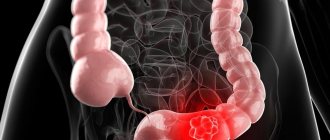
The fourth stage of intestinal cancer is a very advanced, last stage of oncology. The malignant process with such an anomaly spreads to the entire intestine, actively metastasizes, and affects the lymphatic system and nearby organs. The fourth stage of the disease does not respond to traditional methods of treatment, therefore a palliative method is used. But, because by this time the metastases have already penetrated all organs, mainly the liver, patients die suddenly.
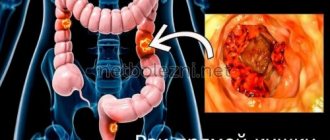
Growing aggressively, affecting neighboring organs, stage 4 intestinal cancer is located in any part of the large intestine: rectum, cecum, sigmoid colon, sometimes in the area of the transition of the sigmoid to the rectum.
Tumors of the intestinal tract of grade 1-2 can be treated quite successfully, and a favorable prognosis is possible. As soon as alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. At stage 4, the disease is incurable, the patient is prescribed palliative therapy, a strong pain reliever. Surgical intervention will not win, but will only alleviate the suffering of the unfortunate person. It is impossible to predict how long they live at this stage; the period depends on the age, immunity of the patient, and the adequacy of treatment.
Reviews from our patients
- Review of the treatment of obstructive jaundice
Review of the treatment of obstructive jaundice April 9, 2021The patient was admitted with severe signs of jaundice. During hospitalization, his condition stabilized. For this purpose, drainage of the bile ducts was carried out, as well as exposure to medications. After receiving the results of the histochemical study, further treatment tactics will be determined.
read more
- “They have golden hands”...
“They have golden hands”... April 7, 2021
Patients are being treated at the Medicine 24/7 clinic. During the treatment, they managed to become friends and this time decided to record a joint review. They thank all the clinic staff for the high organization of all processes and the effectiveness of the procedures.
read more
- Chemotherapy - review by Olga Stepanovna
Chemotherapy - review by Olga Stepanovna April 6, 2021
The patient is hospitalized for the third time. During a comprehensive examination, a puncture of the tumor was performed. Histological analysis made it possible to verify the diagnosis and determine treatment tactics. At the first stage of treatment, surgery was performed. The tumor was radically removed. Drug treatment is now being carried out to prevent the possibility of relapses. To date, the first course of chemotherapy has been completed. The patient was discharged home in satisfactory condition.
read more
- “You are the only clinical organization that brings benefits to people”...
“You are the only clinical organization that brings value to people”... April 6, 2021
The patient was admitted for treatment of cancer. The hospitalization lasted a week. The patient notes that they immediately responded to all his problems and provided assistance in a timely manner. He compares the Medicine 24/7 clinic with other medical institutions. Patient o...
read more
- Review of the attending physician M.Kh. Mustafaeva
Review of the attending physician M.Kh. Mustafaeva April 2, 2021
The patient was hospitalized in serious condition. Complex treatment was carried out. A positive effect has been achieved. The patient’s wife thanks her husband’s attending physician Milana Khanlarovna Mustafaeva. She says: “From the first day, from the first minute, as soon as we came to you, we immediately felt and understood each other. You understood the patient, you understood me. You have defined to the depth of the volume that we need. Although I couldn't explain how...
read more
- Feedback on the treatment of breast disease
Feedback on the treatment of breast disease April 1, 2021
The patient was hospitalized with breast disease. By decision of the council, surgery was performed at the first stage of treatment. It was successful. On the third day the patient was discharged home. After histological examination, further treatment tactics will be determined.
read more
- Feedback on the treatment of ascites
Review of the treatment of ascites March 30, 2021
The patient contacted the Medicine 24/7 clinic for treatment of ascites and pleurisy. These conditions are characterized by abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdominal and pleural cavities, respectively. This happens with cancer. A laparocentesis procedure was performed, during which the fluid was evacuated. The patient's condition improved markedly.
read more
Possible therapy for late stage colon cancer
The fight against an advanced cancer process will take a lot of time and effort, and is done in several approaches. A full course of therapy does not guarantee healing; the prognosis is disappointing: during treatment, toxins enter the liver through the bloodstream, causing complications.
Traditional treatment methods include:
- Surgical resolution is complete resection of the tumor along with removal of metastases. In some cases, the tumor grows so large that the doctor is forced to remove most of the intestine, making it impossible to stitch it together. As a result, the surgeon forms a colostomy - he brings the intestine to the wall of the peritoneum with the attachment of a colostomy bag to empty the intestines. Sometimes the same method is used for inoperable tumors to eliminate obstruction and alleviate the patient’s suffering.
- Radiation therapy is used to prepare for surgery, slowing down the spread of cancer cells. This method is based on radioactive rays.
- Chemotherapy - along with radiation treatment, is used to reduce the size of the tumor, slows down the oncological process, without prolonging the patient’s life, but facilitating resection.
- Traditional methods - despite the skepticism, such remedies have an effective positive effect on the patient’s condition, but only in conjunction with professional treatment.
Traditional medicine is in demand, despite the development of traditional medicine. In a complex of measures in the fight against metastases, decoctions and tinctures of herbs are used, sometimes containing poisons in small dosages.
Treatment of a malignant process in the intestine at stage 4 is directly dependent on the capabilities of the human body, on the type of tumor that has penetrated the organs.
When a diagnosis of stage 4 intestinal cancer is made, the prognosis for healing is disappointing, because by this point metastases have affected almost all organs, the person is rotting from the inside, doctors are unable to help, they can only alleviate the agony.
What will you have to fight with?
Oncological foci at the terminal stages are characterized by the following processes:
• infiltrative growth; • deep penetration into nearby tissue structures (this provokes their destruction); • metastasis; • mutational cellular changes, and mutated cells easily reach distant (from the primary tumor focus) organic systems; • pain of high intensity.
Often, the progression of a cancer lesion is accompanied by a sharp and systematic pain syndrome present in the area of its localization. As a rule, such pain remains even after taking painkillers. For this reason, morphine-based drugs are the only salvation. Further in the article we will talk about what kind of help can be provided for stage 4 cancer with metastases and how long they live when using the methods described below.
Types of cancer
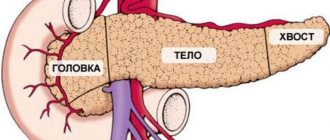
To determine the degree of malignancy and prognosis of the disease, the histological classification of tumors of the sigmoid colon is important. In total, there are 4 types of malignant neoplasms:
- Adenocarcinoma . The most common type of tumor process, which is diagnosed in 75-80% of cases. The tumor develops from glandular epithelial cells located in the intestinal mucosa.
- Mucous adenocarcinoma . A type of adenocarcinoma in which more than 50% of the tumor volume is occupied by extracellular mucus. Always has a low degree of cell differentiation and a high level of aggressiveness.
- Signet ring cell carcinoma . Another variant of a poorly differentiated tumor with a poor prognosis. Histological examination reveals that more than 50% of the space inside the cells is filled with mucus.
- Undifferentiated tumor . The most dangerous type of neoplasm, which progresses rapidly. The atypia of carcinoma cells is so pronounced that it is not possible for a histologist to determine their origin. Glandular structures make up no more than 5% of the biopsy sample examined.
In practical oncology, classification according to the degree of tissue differentiation is important, on which the prognosis for the patient and the risks of metastasis depend. There are 3 types of cancer:
- highly differentiated (more than 95% of cells have a glandular apparatus);
- moderately differentiated (glandular structures account for up to 50-95% of the volume of the formation);
- poorly differentiated (glands are found in 5-50% of tumor cells).
Symptoms
Manifestations of stage IV colon cancer depend on the location of the tumor and metastases. Typically, patients experience:
- severe constipation - up to the development of intestinal obstruction;
- the appearance of blood, mucus and pus in the stool ;
- severe abdominal pain;
- jaundice (with metastases in the liver);
- weakness , sudden loss of body weight and other manifestations of cancer intoxication.
Treatment
Although patients with this stage of the disease are considered to have few treatment options, stage IV cancer can be cured completely in some cases. When this is not possible, proper treatment can prolong patient survival and improve their quality of life.
Patients with stage IV colon cancer can be divided into 2 groups:
- inoperable patients with numerous metastases;
- patients with metastases in one organ.
If the metastasis affects a single organ (for example, the liver), the patient may benefit from treatment aimed at destroying the metastasis.
Modern treatment methods - new combinations of chemotherapy drugs, complemented by targeted therapy - significantly increase patient survival. Such treatment methods are also used at the Ikhilov Cancer Center.
Chemotherapy
For more than 30 years, the standard treatment option for metastatic colon cancer has been the chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil. This drug is usually combined with leucovorin, a substance that is similar in structure and function to the essential vitamin folic acid. Leucovorin enhances the antitumor properties of 5-fluorourocil.
The choice between modes will vary in each situation. The most appropriate option will depend on what types of treatment a person has had before, their overall health, and their response to treatment.
Recently, it has been discovered that adding targeted drugs to this regimen increases its effectiveness.
Most people with stage 4 colon cancer will receive chemotherapy or special targeted treatments to help control the cancer's progression or symptoms.
Get cancer treatment in Israel
Targeted therapy
In the Ikhilov Oncology Center, targeted therapy is widely used for stage IV colon cancer. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, this type of treatment targets only cancer cells, rather than all of the body's rapidly dividing cells. Recently, targeted drugs have revolutionized the treatment of end-stage colon cancer.
In Israel, targeted drugs are used to treat metastatic colon cancer:
- bevacizumab (Avastin);
- cetuximab (Erbitux);
- panitumumab (Vectibix).
To accurately select a targeted drug, a special analysis is performed to detect the presence of certain genetic mutations in the tumor.
Removal of tumor metastases
Most often, colon cancer metastasizes to the liver or lungs. In this case, if possible, surgery is performed to remove the metastases. If liver metastases cannot be removed with conventional surgery, the following procedures may be performed:
- radiofrequency ablation – destruction of the tumor focus using high temperatures;
- cryoablation – freezing of tumor tissues;
- chemoembolization - blocking the vessels supplying blood to the tumor using tiny particles - microspheres with a chemotherapy drug.
Doctors may also need to perform additional surgery if the cancer is likely to block the colon or is already blocking it. In some cases, minimally invasive surgery, such as placing a stent, is possible. Surgeons may place a stent, which is a hollow tube that is usually made of metal mesh or plastic, into the colon during a colonoscopy. If successful, the stent could help keep the colon open and make more invasive surgery unnecessary.
Doctors may also recommend a diverting colostomy, which essentially cuts the colon above the cancerous tissue and drains waste from the body through a small hole in the skin.
Radiation therapy
Doctors may also recommend radiation therapy for advanced colon cancer to help reduce symptoms such as pain and discomfort. This treatment may even shrink the tumor for a while, but it does not usually cure the cancer.
Hepatic artery infusion
Hepatic artery infusion may be a treatment option for people with colon cancer that has spread to the liver. Hepatic artery infusion is a type of regional chemotherapy that involves delivering a chemotherapy drug directly to the hepatic artery in the liver. This treatment can help destroy cancer cells without harming healthy liver cells.
Ablation or embolization
Ablation or embolization may be appropriate for people who have metastatic or recurrent colorectal cancer that causes multiple tumors in the lungs or liver that are smaller than 4 centimeters across.
Ablation uses radio frequencies, microwaves, or alcohol (which people also call percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI)) to target and kill cancer cells while leaving surrounding tissue relatively unharmed.
During embolization, the doctor injects substances into the blood vessels to try to block or reduce blood flow to cancer cells in the liver.
Stages
When assessing the extent and severity of the disease, oncologists take into account 3 parameters:
- primary tumor size (T);
- the presence or absence of atypical cells in regional lymph nodes (N);
- presence/absence of distant metastases (M).
In total, there are 5 stages of cancer pathology. At stage zero, carcinoma in situ is diagnosed, which does not grow beyond the basal lamina of the epithelium. This is the most favorable option, which can be successfully cured surgically and has an almost 100% survival rate.
If the problem is not diagnosed at the in situ stage, the tumor progresses:
The first stage is characterized by the spread of atypical cells into the submucosal or muscular layer of the intestinal wall, but the outer parts of the wall remain intact. There are no regional or distant metastases.
The second stage is diagnosed when a malignant neoplasm completely grows into the wall of the sigmoid colon and spreads to the fatty tissue and surrounding organs. There is no metastasis at this stage.
The third stage is assigned to any size of the primary tumor focus. Its distinctive feature is the presence of secondary foci in regional lymph nodes (with damage from 1 to 6 lymph nodes).
The fourth stage of cancer is characterized by distant metastasis to the internal organs and peritoneum. In this case, the size of the primary tumor and the presence of regional foci can be any.
Diagnostic methods
The patient's examination begins with a standard physical examination, palpation of the abdomen, and assessment of nutritional status. One of the main diagnostic studies is colonoscopy with collection of material for histological examination. The endoscopic method makes it possible to visualize tumor and inflammatory processes, assess the exophytic growth of a neoplasm, and identify threatening complications (decay, bleeding, perforation). To increase sensitivity and specificity, modern imaging techniques are used: magnifying endoscopy, narrow-spectrum endoscopy.
The instrumental diagnostic plan is drawn up individually and may include:
- irrigoscopy with double contrast if colonoscopy is not possible;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- CT ABP with intravenous contrast;
- MRI of the abdominal organs to clarify CT results and a detailed assessment of the condition of the liver;
- PET-CT for more accurate detection of metastases;
- diagnostic laparoscopy if the doctor suspects active spread of tumor foci throughout the peritoneum;
- X-ray or CT scan of the chest;
- bone scintigraphy to exclude metastatic formations in the bones.
Laboratory methods include clinical blood and urine tests, an extended biochemical blood test, and a coagulogram. A standard coprogram and stool test for occult blood are performed. The level of tumor markers CEA, CA 19-9 is assessed in the blood.
A histological examination of tumor biopsies is required to determine the degree of differentiation and type of sigmoid colon cancer. If distant metastases of adenocarcinoma are suspected, atypical cells should be analyzed for RAS gene mutation - this helps in prescribing targeted therapy in the later stages of cancer pathology.
Given the association of colorectal cancer with hereditary factors, genetic testing is recommended for patients. To exclude Lynch syndrome, mutations in the MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 genes are examined, and if familial adenomatosis is suspected, testing for the APC and MYH mutation is performed. If the test results are negative, a consultation with a geneticist is indicated to identify more rare genetic syndromes: Li-Fraumeni, Peutz-Jeghers, Bloom, Cowden.
Causes of cancer
Heredity plays a significant role in the formation of malignant tumors. The most dangerous mutation of the APC gene, which causes familial adenomatous polyposis. The disease is asymptomatic in most cases, but has an almost 100% chance of developing cancer in patients over 40 years of age. The second typical precancerous pathology is Lynch syndrome or hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal carcinoma (HNPCC). In 40% of patients with this syndrome, malignancy occurs during their lifetime, and in general, NNPCC causes up to 6% of all cases of colorectal neoplasms.
Epidemiological studies prove the connection between the increased risk of cancer and dietary features - the predominance of red meat and animal fats in the diet, lack of fiber from fresh vegetables and fruits. Such nutrition leads to a slowdown in intestinal peristalsis, regular constipation with the accumulation of feces in the sigmoid colon and its microtraumatization.
The likelihood of developing the disease increases in patients with a family history (even in the absence of genetic mutations) if they suffer from bad habits - a long history of smoking, alcohol abuse. Important predisposing factors of oncopathology are inflammatory bowel diseases - Crohn's disease, nonspecific ulcerative colitis (UC). At the same time, there is a linear relationship between the length of the disease and the risk of developing cancer.
In the UK, a study was conducted over 23 years on the effect of antibiotics on the likelihood of colorectal cancer. As a result, it was found that the most negative effects have drugs that destroy anaerobic bacteria. It is assumed that medications disrupt the normal intestinal microflora and promote the proliferation of carcinogenic microbiota.