What is hiccups and where does it come from?
Hiccups occur when the diaphragm reacts to certain factors by contracting. Medicine suggests that hiccups are necessary for the fetus in the womb to ensure the movement of amniotic fluid through the respiratory system. Often, a pregnant woman can feel the rhythmic tremors of the unborn baby, which are hiccups.
Medicine knows several cases of prolonged hiccups, the duration of which was more than two decades. Separate studies have identified settlements in which hiccups appear more often than in the rest of the country. The curiosity of scientists forced them to pay special attention to a number of factors that provoke hiccups, which prevail in each specific region.
The diaphragm is a flat, broad muscle that separates the chest from the abdominal cavity. When it contracts sharply, a spasm of the lungs occurs, which does not go unnoticed by the entire respiratory system. Air passing past the vocal cords may be accompanied by sound.
What happens to a woman during pregnancy?
24.07.2020
The polite one suddenly becomes aggressive, the calm and reasonable one becomes nervous and whiny.
Being and Consciousness
Metamorphoses are not accidental. The body of pregnant women undergoes complex hormonal changes. The level of progesterone increases: this hormone not only relaxes the uterus , preventing it from contracting excessively, but also affects the emotional background. The woman becomes a little inhibited and more sensitive.
Little things that were not touched at all before are painfully touched; as soon as there are tears.
An increase in estrogen levels awakens hitherto dormant instincts, such as the protection of offspring. The baby has not yet been born, but his mother is already protecting him. Often pregnant women are aggressive, preventing a possible threat from others, experience irritation when touched by strangers, and feel anxiety in the crowd.
The body also produces a new hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin. It changes the psyche in accordance with the upcoming event, making you either fly with happiness or indulge in despondency.
Emotions monthly
The first trimester of pregnancy is the most stressful. Joy and euphoria are interspersed with excitement and even fear. Increased irritability and excitability are observed, emotions become more superficial, laughter or tears are possible for no reason.
In the second trimester, anxiety decreases and a positive mood prevails. The hormonal background, changes in which caused problems in the first months, stabilizes, emotions stop overflowing. Nausea disappear , ailments become less acute. The expectant mother begins to feel her pregnancy more realistically; she feels the first movements and tremors of the baby, during an ultrasound examination she sees his arms, legs, head, and hears his heart beating.
But in the third trimester, anxiety appears again, which is now associated with the upcoming birth . It's not just the fear of pain. A woman is afraid of the changes that will happen in her life after the child is born: a new regime, responsibilities, responsibility for the baby. Questions torment me: What will I do with it? Can I handle it? What if I can’t become a good mother to him?
Baby sensations
Scientists say that a mother's emotions significantly influence the condition of the unborn baby. Observations made during an ultrasound examination show that the baby behaves differently depending on the woman's mood. When she is nervous, he becomes restless and sometimes has hiccups. When the mother is in a good mood, the baby is peaceful, and on a 3D ultrasound you can see his smile.
If we explain the relationship between mother and baby from the point of view of biochemistry, then at the moment of manifestation of strong negative emotions, the level of adrenaline in the blood . vessels narrow , fetoplacental (uterine) blood circulation worsens. The baby in the womb does not have enough oxygen, it becomes cramped and uncomfortable. The mother’s positive emotions, on the contrary, give the baby endorphins, hormones of joy. And even in the perinatal period, the child develops what psychologists call basic trust in the world.
The relationship also occurs at the cellular level: different emotional states correspond to a certain structure of intracellular components. Changes in it are perceived by the child either negatively - as anxiety, threat, lack of resources, or positively - as pleasure, joy, a sense of security.
Published in Pregnancy, pregnancy management Premium Clinic
Causes of hiccups
Hiccups can occur for several reasons:
- with hypothermia;
- due to stress;
- when overeating or consuming food quickly;
- due to dry food.
There are also neurological disorders that provoke reflex contraction of the diaphragm. For example, if the vagus nerve, which transmits a signal from the lungs to the brain that a breathing movement needs to be made to inhale or inhale, begins to send false commands to contract the diaphragm.
A nerve irritated by external factors sends false impulses not only to the brain, but also to the spinal cord. As a result, the central nervous system causes the muscles of the respiratory system to contract. These movements can be compared to convulsions. The respiratory center of the brain loses its ability to control the process. The epiglottis occupies a position in the trachea that is characteristic of the swallowing reflex. The vocal cords close together.
This contraction of the respiratory system can occur both during inhalation and exhalation. It is impossible to stop the process with one effort of will. Rare episodes of hiccups do not pose any health hazard. However, regularly occurring spasms should be a reason to seek help from a specialist.
Why do fetuses have hiccups?
Every expectant mother should clearly understand that both periodic manifestations of hiccups in a child and their complete absence are not a reason to worry about the development of the fetus. Hiccups in a baby during intrauterine development can occur due to internal and external causes. External causes include, for example, periodic ingestion of amniotic fluid in large quantities. This can happen when the baby is actively thumb sucking in the womb. As a result, active contractions of the diaphragm appear. Internal causes are manifestations hypoxia or individual symptoms of this phenomenon. Due to hypoxia, the child’s nerve center in the brain, which is responsible for the motor function of the diaphragm, is irritated. As a result, rhythmic contractions of the diaphragm occur.
If the causes of fetal hiccups during pregnancy are external, then the woman should not worry. Hiccups in this case indicate only the normal functioning and activity of the fetus. But if hiccups are a consequence of irritation of the motor nerve center of the diaphragm, then it is necessary to constantly monitor the development of the fetus. Hiccups caused by a lack of oxygen (hypoxia) are usually accompanied by some severe symptoms. The child in the womb behaves very actively, he has a decreased heartbeat, hiccups appear very often and do not go away for a long period of time. All these signs should be a reason to visit a doctor. Sometimes additional examinations and close monitoring may be required.
Complications that hiccups can lead to
There is an opinion that a person can die from prolonged hiccups. However, this is a myth. Death from hiccups has never been recorded. But the cause of hiccups can be deadly.
For example, if hiccups are caused by cancer or problems with the cardiovascular system, the patient risks losing his life, but the hiccups are not to blame.
Frequently occurring intense attacks can lead to insufficient oxygen saturation of the blood, and at the same time to its oversaturation with carbon dioxide. This is a direct path to hypoxia of brain tissue. Therefore, if you suffer from hiccups often, you need to talk about it first with a therapist. After collecting anamnesis, he will refer you to a specialist. This serious condition is extremely rare, but it does happen.
Severe hiccups can also cause side pain, which is often experienced by beginner athletes while running. This is due to the constant shocks of the diaphragm, which, with its contractions, also affects the abdominal organs.
If hiccups are painful day after day, it interferes with sleep, which is why a person does not get enough sleep, feels exhausted and is constantly tired. In this case, hiccups provoke depressive disorders.
During business negotiations, a cat puts a person in an awkward position. In this state, not everyone will dare to approach a manager or partner to resolve serious issues.
How to get rid of hiccups
The most effective method of stopping hiccups is called breathing into a bag. This is explained by the fact that by saturating the blood with carbon dioxide, we concentrate the vagus nerve on the fact that the body needs a full breath. And this allows you to stop the random sending of signals to the brain, causing the diaphragm to contract in spasms.
The second effective way to get rid of accidentally attacked hiccups is to drink water, standing in a bird pose: fix your arms along your body, like folded wings, and tilt your body forward to reach a glass of water. This requires outside help, because someone has to hold the glass. You need to drink in small sips, stretching your neck.
The third, and most famous method is to take more air into your lungs and hold your breath for as long as possible. In this way, it will be possible to push through the diaphragm with your lungs and keep it in a calm position.
Hiccups in pregnant women
Hiccups during pregnancy are normal and do not require medical intervention. It occurs especially often in the later stages, when the uterus occupies most of the abdominal cavity, constricting all other organs. And the fetus, with its periodic physical activity, adds inconvenience not only to the bladder and intestines, but also to the diaphragm and lungs.
Along with obvious physiological changes associated with the location of internal organs, hormonal changes can also cause hiccups. Toxicosis is another phenomenon that causes hiccups in the early stages. If each morning begins with nausea and vomiting, this may affect the spasms of the diaphragm, causing hiccups.
It's worth discussing frequent hiccups with your obstetrician if they cause pain or other problems. If hiccups come from time to time and go away on their own without causing obvious discomfort, it does not require treatment, because it is not dangerous for the expectant mother.
Hiccups
Herpes
Encephalitis
25861 03 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. According to the International Classification of Diseases, hiccups are considered under the section “Abnormal breathing”. The mechanism of this involuntary physiological reaction involves the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, which, convulsively contracting, initiate a short inhalation, and the sudden closure of the airways by the epiglottis is accompanied by a characteristic sound.
Varieties
If the duration of hiccups does not exceed 10-15 minutes, it is called short-term, or episodic. Sometimes hiccups last longer - up to two days, and then they are called persistent. Finally, intractable, i.e., unresolved persistent hiccups are possible, which last for two or more months. Only persistent or intractable hiccups warrant a visit to the doctor, as they may be a symptom of diseases or injuries that cause convulsive contractions of the diaphragm. The function of the diaphragm is subordinate to the work of the nervous structures of the brain located in the medulla oblongata and hypothalamus. The diaphragm is innervated by two (right and left) phrenic nerves, which originate in the neck (segments CIII - CIV). The cause of persistent and intractable hiccups are pathologies leading to damage to the structures of the reflex arc. Depending on the level of damage, central and peripheral hiccups are distinguished. Hiccups of central origin occur with damage to the brain and/or spinal cord, peripheral - with damage to the phrenic nerve, which can occur as a result of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system. There is another type of damage - toxic, which is caused by the effects of alcohol, nicotine, toxic metabolic products and drugs on nerve endings.
Possible causes of hiccups
In adults, short hiccups serve as an evolutionary mechanism aimed at displacing air from the stomach. The entry of excess air into the stomach can be caused by improper and rapid eating, laughter, during which a series of sharp breaths occur. In addition, irritation of the vagus nerve, leading to hiccups, can be provoked by an overfilled stomach, hasty dry food, or hypothermia. In young children, hiccups often occur as a result of air entering the stomach during feeding, as well as stretching of the stomach due to overfeeding. If the hiccups stop after a few minutes, they do not require special attention. However, if hiccups persist, you should consult a doctor.
Prolonged, intractable hiccups of central origin can occur with a stroke
brain in older people or in patients with vascular diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus.
In addition, prolonged hiccups can be a symptom of a tumor of the brain
and its stem.
Cerebellar artery aneurysm
can also lead to hiccups.
Hiccups may indicate brain injury
, accompanied by the formation of a hematoma.
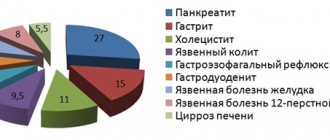
Hiccups, caused by peripheral nerve irritation, are a symptom of conditions such as hiatal hernia.
large sizes (>3 cm),
neoplasms of the esophagus, pancreas and stomach
.
Persistent hiccups can be observed in pathologies of the cardiovascular system: myocardial infarction
, heart rhythm disturbances, since they increase the excitability of the endings of the vagus nerve.
Respiratory diseases, in particular laryngitis, bronchitis and pneumonia
, as well as
mediastinal tumors
can cause hiccups due to irritation of the phrenic nerve.
There is evidence of persistent hiccups in patients with herpes
.
In these cases, the pathological process is triggered by the herpes virus, which multiplies in the nerve ganglia. The cause of hiccups can also be compression of the spinal root of the fourth cervical vertebra by a hernia, as well as neck tumors. Other factors that cause long-term hiccups include autoimmune diseases
(neuromyelitis optica, multiple sclerosis),
epilepsy, encephalitis, meningitis, Parkinson's disease
.
Toxic hiccups occur when metabolic disorders occur due to damage to the nerves by toxins accumulating in the blood. Such hiccups can occur with diabetic neuropathy in diabetes mellitus, intoxication with uremia (the last stage of kidney disease
), electrolyte imbalance due to hypocalcemia (
diseases of the parathyroid and thyroid glands
) and hypokalemia
(Cushing's syndrome, vomiting, diarrhea, etc.
).
Toxic hiccups can develop when taking medications:
antiparkinsonian drugs, drugs used in psychiatry, azithromycin (an antibiotic), morphine.
Chemotherapy drugs
used in the treatment of cancer patients, as well as
drugs administered during anesthesia
and epidural anesthesia, can also cause prolonged hiccups.
Diagnostics and examinations
The diagnostic algorithm for prolonged hiccups sometimes involves a complete examination of the patient to identify the cause of this pathological condition. The doctor conducts a thorough interview of the patient, clarifies the names of medications taken by the patient, and assesses the neurological status.
First of all, it is necessary to exclude cerebral stroke and myocardial infarction. To do this, a consultation with a neurologist and a cardiologist is prescribed, as well as an MRI of the brain, an electrocardiogram, and clinical and biochemical blood tests.