General description of the disease
Intestinal prolapse can be congenital or acquired. In a normal state, all organs of the abdominal cavity are protected from displacement with the help of the muscular and ligamentous apparatus; the intestinal section is supported by the mesenteries. As soon as the slightest weakening of muscle and ligament tone is observed, intestinal displacement begins. Muscles can weaken due to poor nutrition, gastrointestinal diseases, increased body weight and other reasons.
A change in the position of the intestines immediately provokes a displacement of the stomach, after which changes begin in all internal organs. The disease can develop rapidly or over several years. It is impossible to predict the rate of complications of bowel prolapse.
Causes of colonoptosis
Most experts believe that the problem of intestinal prolapse is congenital. The pathology can be acquired during life due to improper build, when the patient has a small chest, excessive thinness and small shoulders.
In other cases, the following factors may contribute to the development of the disease:
- multiple births and multiple pregnancies, which negatively affect the muscular system and gastrointestinal tract;
- difficult childbirth and complications after it, usually with the need for prolonged straining;
- surgical interventions of the cavity type on the gastrointestinal tract;
- rapid loss of body weight, including due to poor nutrition;
- eating large amounts of fatty and fried foods;
- increased body weight and obesity;
- mechanical damage to the abdominal organs and gastrointestinal tract.
Attention! In exceptional cases, the disorder may be caused by pulmonary dysfunction. Usually the triggering factors are pleurisy and eczema of this system.
Signs of prolapse
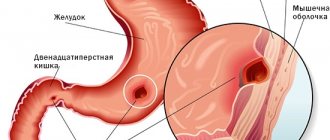
When problems arise with the functioning of the intestine and its displacement, most often failures are detected in the large intestine; the colon often suffers.
Most often, the disease manifests itself with the symptoms described below:
- severe problems in gastrointestinal motility, which manifests itself as constipation and bloating;
- the patient has heaviness in the abdominal cavity and unstable appetite;
- due to the displacement of the stomach and intestines, rapid saturation is noted, as the lumen in the organs becomes minimal;
- a painful syndrome, which at the initial stage of the pathology has an intermittent aching character, taking into account complications, the pain becomes more intense and constant;
- attacks of nausea often occur, followed by vomiting;
- due to insufficient saturation and disturbances in the breakdown of food due to displacement of the gastrointestinal tract, discomfort in the head and dizziness are noted;
- Due to constipation, abnormal pressure on the organs of the urinary system increases, which can lead to an inflammatory process in them.
If timely treatment is not started, the symptoms of the pathology begin to increase, worsening the patient’s condition several times. Due to pain in the peritoneal area and painful defecation, the patient may experience hemorrhoids, anal fissures and bleeding from this area. The pain may increase due to the slightest movement.
This is interesting: Worms in adults. Symptoms, causes of infection, course of the disease, complications
Causes
The causes of rectocele are the same as for other forms of prolapse: childbirth and pregnancy, heavy physical activity, chronic constipation and, of course, a hereditary factor. Despite this, it is with this type of vaginal prolapse that labor and constipation play a special role.
The first factor is especially important in the case of episiotomy (perineal incision during childbirth) and perineal ruptures (large fetus, rapid (very fast) labor, incorrect obstetric care).
At this moment, the main “defender” of the posterior wall of the vagina, the perineum and pelvic floor muscles, suffers; without them, the entire load falls on the thin fascia separating the vagina and rectum. That is why any surgical treatment always includes reconstruction of the perineum. The second most important factor is chronic constipation.
In the presence of this pathology, the supporting structures of the posterior wall experience constant high loads, as a result of which a rupture of the fascia occurs, through which part of the rectum emerges.
| Most patients receive care for free (without hidden additional payments for “network”, etc.) as part of compulsory health insurance ( under the compulsory medical insurance policy ). | Application for treatment under compulsory medical insurance |
Features of the disease
The human abdominal cavity is characterized by a large number and variety of anatomical and physiological anomalies. Intestinal prolapse is a fairly common and dangerous disease. If this concerns the thick part of it, then this disease is called “coloptosis” or “colonoptosis”. The length of the suction organ reaches less than four meters. Its loops tend to gradually fall below the place where they need to be. This phenomenon can initiate displacement of internal organs and significantly affect human health. In medicine, this disorder is called ptosis. This pathology causes disturbances in blood circulation, spasms of muscle fibers and the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Treatment of the disease should be carried out only by a special doctor. After all, the symptoms of pathology can be hidden and mislead not only the patient. And classic coloptosis can cause a whole host of serious troubles for a person. For example, prolapse of the intestines into the pelvis can cause hemorrhoids.
Treatment course in the fight against pathology
Intestinal coloptosis: symptoms and treatment is a relevant topic for many, since most often the disease affects the large intestine. However, regardless of where exactly the violation occurred, the treatment complex has an identical focus and principles.
Treatment of the disease involves the use of surgery only when conservative therapy does not bring the desired result. Surgery may be prescribed if there is a disruption in blood flow and intestinal obstruction develops.
In most cases, treatment involves a combination of several mandatory areas: special gymnastics, normalization of the diet, taking medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and the use of a bandage.
Physical therapy for colonoptosis
The main reason for organ prolapse is the patient's lack of mobility. The abdominal muscles and ligaments in the abdominal cavity begin to weaken, which leads to disorders. It is important to begin treatment immediately, which also includes physical therapy.
Exercises for prolapse:
- The patient is placed on a hard surface, and a 30 cm high cushion is placed under his back. It takes 5 minutes to remain in this position to return the intestines to the desired state.
- Useful exercises for this pathology include straight leg raises, a bicycle, bending the legs while tensing the abs, and pulling the lower extremities toward the abdomen.
- You should also do some stretching exercises. When the stomach prolapses, the best option is an exercise in which the patient sits on the floor, brings his straight legs together and tries to reach his fingertips, bending his back. 3-5 such stretches are performed.
- To train the ligaments and strengthen the abdominal muscles, you need to perform leg turns while lying on your back. The legs rise at a right angle and rotate together 10 times in one direction and the other.
- You should move on to lifting your torso to strengthen your abs only after 5-6 weeks of regular exercise.
- At first, charging should take no more than 10 minutes. Every day its duration can be increased by one minute until its duration reaches 20 minutes.
- For 12 weeks, the patient should not do more than 1-2 sets of exercises. You can move on to three approaches only after three months.
- After completing therapeutic exercises, you need to rest for at least 30 minutes, ideally lie down on a horizontal surface, completely relaxing your arms and legs.
Attention! After starting therapy, any physical exercise for the first 5-7 days is performed in a horizontal position. Then you can do vertical exercise.
Symptoms
Manifestations of colonoptosis can be very roughly divided into local and general.
Local signs
These are all the symptoms associated with a violation of the movement of the food bolus:
- bloating caused by interruption of food passage;
- flatulence or excessive gas production;
- constipation that cannot be treated with conventional remedies;
- abdominal pain, somewhat relieved in a horizontal position;
- urinary disorders and even inflammation of the urinary organs due to compression.
Be sure to read: Typhlitis (inflammation of the cecum): symptoms and treatment methods
Bloating and constipation impair the digestion of food, patients may lose weight due to refusal to eat. Concomitant inflammation of the digestive canal is common.
General signs
These are signs of fecal intoxication due to untimely removal of decay products, as well as disturbances in other organs:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- headache;
- weakness;
- decreased appetite and mood;
- phlebeurysm;
- haemorrhoids;
- menstrual irregularities in women and prostatitis in men.
Treatment
Treatment of colonoptosis is aimed at strengthening the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the intestine and eliminating unpleasant symptoms. Treatment of the disease involves adjusting the diet and lifestyle, doing physical therapy, taking medications and performing surgery.
Non-drug
Non-drug therapy for colonoptosis is the basis of its treatment. It includes the following methods:
- lifestyle changes;
- specialized diet;
- gymnastics classes;
- wearing a bandage;
- use of folk remedies.
Correction of nutrition and lifestyle
In order to activate intestinal motility and strengthen the ligaments that support it, it is necessary to lead an active lifestyle. It involves daily walks in the fresh air and adequate physical activity. Such measures prevent constipation and improve the general condition of the patient.
The diet for colonoptosis is aimed at preventing constipation and flatulence, as well as accelerating intestinal motility.
The diet includes the following nutritional recommendations:
- inclusion in the diet of products containing coarse plant fibers - bran, unground cereals, raw fruits and vegetables;
- drinking enough water – up to two liters per day;
- limiting foods that provoke flatulence - baked goods, legumes, fresh cabbage, grapes;
- restriction in the diet of foods that slow down intestinal motility - mucous soups and cereals, crushed food;
- The consumption of fatty, spicy foods, marinades, smoked meats, and spices is excluded.
To determine the most suitable diet, it is recommended to seek the help of a doctor. He will create a diet taking into account the course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body.
Gymnastics and wearing a bandage
Prolapse of the colon can also be treated with the help of physical therapy. Exercise therapy classes are aimed at strengthening the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, which helps to gradually lift the intestines. A few of the most effective exercises:
- Starting position – lying on your back, cushion under the lumbar region. Next, you need to lift your legs alternately without bending them at the knee joints. You need to do the exercise 5-6 times.
- Exercise “bicycle” (performed in a horizontal position).
- Get into a knee-elbow position, lower your stomach and raise your hips. Stand in this position for 2-3 minutes.
All exercises are performed in a horizontal position, at a calm and measured pace. Sudden movements and turns are unacceptable.
A bandage for intestinal prolapse is used to correct its position and prevent further prolapse. This device is an elastic belt that is worn on the abdominal wall. Its use greatly facilitates the patient’s condition and life and helps to gradually raise the transverse colon. It is recommended to wear the bandage all day, putting it on in the morning and taking it off in the evening. The manipulation is carried out in a lying position.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies helps the patient cope with constipation and flatulence, and also stimulates intestinal function.
The most common recipes are:
- A decoction of medicinal herbs. Ingredients: wormwood and yarrow leaves. Preparation: chop and mix the plants in equal proportions. Then pour 30 g of the mixture into 250-300 ml of boiling water and keep in a water bath for several minutes. Application: strain, dilute with a glass of water and drink 15 ml 3 times a day before eating.
- Infusion of medicinal herbs. Ingredients: dill, fennel, cumin. Preparation: mix the plants in equal quantities, pour 50 g of the mixture with a liter of hot water and leave for several hours. Application: consume 15 ml, drinking 1 glass of infusion during the day.
- Buckthorn decoction. Ingredients: buckthorn bark Preparation: chop the bark, add 15 g to 200 ml of boiled water and put on low heat. Wait until half of the broth has evaporated. Application: dilute the decoction with water in a 1:1 ratio, drink 100 ml 2 times a day.
Medication
At this stage, therapy for colonoptosis involves taking medications. If all of the above methods are ineffective or complications occur, surgery is prescribed.
Conservative
Symptoms and treatment of the disease with medications are closely related. Medicines prescribed for colonoptosis are aimed at eliminating its unpleasant manifestations.
Symptomatic treatment is carried out using the following medications:
- Antispasmodic drugs - aimed at relaxing long-term contracted muscle fibers of the organ: Droteverine, No-shpa, Platyfillin, Papaverine.
- Analgesics – eliminate severe pain: “Ketorol”, “Analgin”, “Ketorolac”, “Ibuklin”.
- Sorbents and carminative medications – reduce the phenomenon of flatulence: “Sab Simplex”, “Espumizan”, “Enterosgel”, “Smecta”.
- NSAIDs - prescribed when inflammatory processes occur: Nurofen, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Meloxicam.
Taking laxatives for colon prolapse is not recommended. These drugs have a tendency to become addictive, which can further worsen the movement of feces through the intestines. Usually, a properly selected diet helps eliminate constipation.
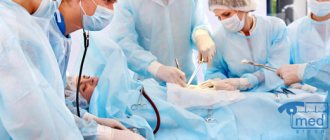
Surgical
Surgical treatment of colonoptosis is prescribed only in extreme cases. Indications for surgical intervention are the following situations:
- ineffectiveness of other treatment methods;
- rapid progression of the disease;
- prolapse of the intestine into the pelvis;
- intestinal bleeding;
- intestinal obstruction;
- rectal prolapse;
- circulatory disorders of the digestive organs.
The operation consists of creating several additional loops of ligature threads, with the help of which the specialist fixes the intestines to the strongest places in the abdominal cavity. But surgical intervention is dangerous due to the development of a complication such as adhesive disease - this condition can aggravate the course of the disease. Therefore, surgery for colonoptosis is used only if all other methods of therapy are ineffective.
This is interesting: Diseases of the anus: signs, diagnosis and treatment of pathologies
How is an MRI of the intestine done?
Before the procedure, the patient must warn the specialist about existing contraindications and concomitant diseases. The scan is carried out in a lying position, the session lasts from 15 to 45 minutes. Hydro-MRI begins with the introduction of a contrast agent into the intestinal lumen, for which the patient is asked to drink a special solution half an hour before the scan.
Intravenous injection is carried out using a catheter and an automatic device that ensures a constant rate of injection of the “coloring” substance.
The patient is positioned face up on the tomograph table, his body is fixed with bolsters and holding devices. Remaining still is necessary to obtain clear images of the scanned area. To protect against the noise of a working device, use headphones.
Medical personnel are located behind a partition; communication with the patient is carried out through a microphone. This measure prevents the interaction of external electromagnetic pulses with the force field generated by the tomograph.
The table with the patient is rolled into a wide tunnel. Scanning is carried out in transverse, direct and lateral projections.
The clinic staff will tell you how to do an MRI of the intestines before the procedure.
After a series of native images, a gadolinium solution is injected through a previously installed catheter. The procedure is continued after the drug fills the vascular bed in the area of interest (after 10-15 minutes).
MRI of the intestine is performed both on open tomographs and on closed-loop devices; the image quality in the second case is much higher than in the first. Good resolution of layer-by-layer photos is possible with a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla. Closed-type devices have the required power.
Diagnostic measures
It is difficult to identify the disease based on clinical manifestations alone. To make a diagnosis with high accuracy, you should consult a doctor. Diagnosis begins with the patient’s complaints, recognizing the symptomatic picture and taking an anamnesis. After this, the doctor needs to conduct a thorough physical examination and palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity.
Informative research methods are:
Laboratory research methods allow for correct differential diagnosis. Therefore, patients may be prescribed:
After this, the doctor differentiates the disease from other diseases with a similar clinical picture in the form of:
In some cases, consultation with a pediatrician, therapist, parasitologist or gastroenterologist is required.
Will an MRI show colon cancer?
Malignant neoplasms of the digestive system occur equally often in men and women. An asymptomatic course in the initial stages makes timely diagnosis difficult, so suspicion of the development of oncology is one of the main indications for intestinal MRI.
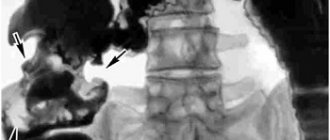
Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to study the pathologically changed area in detail. If a tumor is present, the doctor evaluates the size, localization of the lesion, and the interaction of the tumor with surrounding structures. The malignant process is characterized by the absence of a clear contour; atypical cells “grow” into healthy tissues.
A cancerous tumor accumulates gadolinium chelates more slowly on contrast-enhanced MRI of the intestine. This occurs due to the pathological tortuosity of its own blood vessels. Magnetic resonance scanning shows formations with a diameter of 3 mm, suggesting the nature of the process. The final diagnosis is made based on the results of laboratory tests.
Diagnosis of the disease in patients
The patient may suspect organ prolapse based on the presence of the symptoms described above. But only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis after collecting all complaints and prescribing laboratory procedures. When visiting a therapist or gastroenterologist, a preliminary diagnosis will be made after an in-person examination.
Such control is as follows:
- the patient is diagnosed with a saggy belly even if he has normal weight;
- having placed the patient on the couch, the doctor notices clear beats in his abdominal aorta, which indicates retraction of the intestine in the upper part of its base;
- if the doctor slightly pulls the abdominal cavity upward, the pain in the digestive tract completely disappears or weakens;
- the patient is accompanied by prolonged pain, which may intensify after physical activity and after eating food;
- when palpating the peritoneal area, the doctor determines a clear displacement of the gastric pylorus and feels a bulge in this area.
After an in-person examination, the manipulations described in the table are prescribed.
Table 1. Diagnostic methods
| Diagnostics | Its essence | How do they do it? |
| Gastric juice analysis | Determines the amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. When problems arise, reduced acidity is observed. | On an empty stomach, using a soft pipe of 4-5 mm. It is left for 1-2 hours directly in the stomach and taken every 15-20 minutes. The probe can be inserted through the mouth or nose if the gag reflex is severe. |
| Irrigoscopy | This is done to determine the degree of intestinal displacement and to identify any violations that have occurred due to this. | The patient is injected with contrast through the rectum and a photo is taken in a position on his side, lying on his stomach. At the end, a double contrast is made using the previously introduced substance and air to identify ulcers and neoplasms. |
| Colonoscopy | It is used to assess possible disorders and the current state of the mucosa, to determine the intestinal lumen and to collect material for biopsy. | The patient lies on his left side with his legs crossed. The doctor lubricates the patient's anal area and inserts an endoscope, slowly moving it along the intestines to assess his condition. |
Attention! If a patient has contraindications to colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy is used to assess bowel function.
Operation
Of course, they will not replace damaged ligaments and fascia. Surgical treatment for severe forms of prolapse is the only effective treatment method. The most popular, studied and natural operations are those performed through the vagina. In this case, it is possible to restore all parts of the pelvic floor and achieve excellent cosmetic results with minimal risks for the patient.
hybrid techniques have become widespread.
, which allow you to restore the natural anatomy of the pelvic floor through a combination of organ-preserving techniques, maximum use of the patient’s own tissues and targeted/targeted use of synthetic materials in the busiest areas.
Symptoms
The first sign of pathology is excessive gas formation. Very often, people simply ignore this external manifestation, attributing it to other disorders.
Ceco-transversoptosis has the following symptoms:
- disruption of the bowel movement process, which most often results in constipation;
- the occurrence of a pain syndrome localized at the bottom or in the middle of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, the pain is constant, pressing and aching in nature;
- a sharp increase in the intensity of pain during straining, which occurs during the act of defecation - often increased pain is observed after eating food or against the background of excessive physical activity, but the pain decreases in a horizontal position of the body;
- periodic occurrence of nausea, which only occasionally leads to vomiting, which does not bring relief;
- severe headaches;
- increased irritability;
- insomnia;
- emotional instability;
- increased heart rate;
- increase in blood tone;
- the appearance of signs characteristic of coronary heart disease;
- rapid fatigue and decreased ability to work;
- general malaise and weakness;
- discomfort when emptying the bladder in men;
- painful course of critical days among female representatives;
- formation of hemorrhoids.
It is advisable to relate all clinical manifestations to patients of any age category.
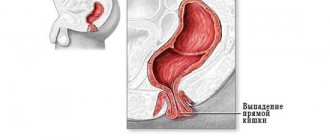
Classification of types and degrees of rectal prolapse
Like most pathologies known to medicine, rectal prolapse does not have a single classification, but there is still a classification that doctors most often use in their practice. This classification was developed based on the quantitative ratio of the prolapsed section of the rectum, as well as the degree of inclusion in the process of the nearest parts of the colon or only the anus. This classification implies that each of the forms of rectal prolapse is a certain degree of a single pathological process. To date, there are four degrees of rectal prolapse:
- partial prolapse of the rectum (mainly its mucous membrane);
- complete prolapse of the colon with eversion of the dentate line (mucocutaneous border) of the anal canal;
- prolapse of the rectum, as well as intussusception of the higher located parts of the large intestine.
As for the typology of rectal prolapse, it is presented in two options:
- the hernial type of rectal prolapse is caused by the displacement of the anterior wall of the rectum downward and its exit through the anus;
- The intussusception type is characterized by indentation of the sigmoid or rectum between the walls of the anus.
What diagnostic methods are used?
One of the important stages in making a diagnosis is conducting diagnostic studies.
At the first appointment, the doctor collects anamnesis and clarifies the identified symptoms. Based on the data obtained, he prescribes subsequent diagnostic procedures.
When detecting bowel prolapse, the following is used:
- A general and biochemical blood test, which allows you to determine the content of necessary elements, confirm or exclude the development of the inflammatory process.
- X-ray examination. In this case, the pelvis is examined. Diagnostics allows you to determine the department of the violation and obtain basic data on changes in position.
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs. A pelvic examination allows you to more accurately visualize the condition of the intestines and nearby organs.
It is important to note that making such a diagnosis on your own is impossible. The therapeutic prognosis depends on the timeliness of seeking help.
Traditional methods of treatment
Home treatment is not aimed at raising the intestines to the correct position, but at eliminating the unpleasant symptoms that such a condition provokes. Traditional recipes help in the fight against constipation, bloating and flatulence.
Joster grass
For treatment, you need to take 5-10 g of medicinal herb and pour 250 ml of boiling water over it. The mixture is brought to a boil and boiled for five minutes. After cooking, the roast is kept in a thermos or under a lid for another two hours. After the allotted time, the thicket is removed and the zoster is taken daily before going to bed. The dosage is 100 ml of the finished solution. Treatment is continued for 2 weeks.
Senna officinalis
Has a mild laxative and calming effect on the gastrointestinal tract. A tablespoon of herb needs to be poured into 250 ml of boiling water and kept covered for two hours. After filtering, the solution is taken in small sips 1-2 hours before bedtime. You can take the medicine for up to two weeks.
Buckthorn
For treatment, you need to finely chop the bark and pour 250 ml of water into it. The mixture is placed on low heat to evaporate half the solution. As soon as the medicine has cooled, you need to add enough boiled water to the container to make 200 ml. Treatment is carried out for 1-2 weeks, taking 100 ml of the drug before breakfast and after dinner.
Cumin seeds
Treatment involves using 5 g of cumin per 250 ml of boiling water. The seeds are steamed for at least two hours, after which the infusion is carefully filtered. It takes 2-3 days to drink this amount of water, taking small sips of the infusion every day every 2-4 hours. It is better to take cumin seeds between meals.
Health-improving physical exercises
Strengthening the abdominal muscles is a reliable way to treat the disease. Physical exercises are designed to increase muscle tone and significantly strengthen the diaphragm. Thus, the general condition of the stomach can be normalized. The load is carried out in a supine position. The legs should be slightly raised to form an inclined plane. The gymnastics methodology is as follows:
- The man lies down on his back. A book should be placed between the ribs and the umbilical area. The arms are located along the body. Legs are straight. Next, you should breathe evenly. The diaphragm will gradually rise and fall. Exhale slowly, stretching the abdomen.
- The person lies on his back and completely relaxes. Arms and legs are straightened. In the exercise, you should alternately raise/lower your arms and legs. In this case, you should hold the limbs for 5 seconds. For variety, you can add a special leg movement - “scissors”. These exercises help restore gastric motility.
- The man lies down on his back. The pelvis should be raised through the formation of support on the feet, elbows and back of the head. The movement should be done slowly and persistently until slight fatigue. This is the only way the treatment will give a successful result. Symptoms of the disease will gradually disappear.
- The man lies down on his back. His task will be to bend two legs at the knees and press them to the stomach. To reduce the load, it is recommended to use hands that will press the limbs. Use at least 2 sets of 10-20 times.
- A person lies on his back and imitates riding a bicycle. If your general condition does not allow it, then you can skip the exercise.
Vertical body position:
- Walking while raising your hips to a high level (1 minute).
- Legs are brought together. Hands are in a lower position. When inhaling, the arms are raised with parallel movement of the legs back (alternating left and right). The toe of the foot should touch the surface of the floor. You can take the starting position while exhaling.
- The person stands with his back to the wall (distance from the surface is 35 cm). The legs are placed shoulder width apart. The arms are in a bent position. The patient turns the body and touches the wall itself with his palms. The contact delay should be 10 seconds. An alternative would be to turn in the opposite direction. Then back to the original place.
Gymnastics should be done daily. Treatment is based on the principles of moderate and gradual loads. Exercises should be performed after meals (2-3 hours) with a duration of 15 minutes. Also, folk remedies can significantly help the patient in treating constipation, flatulence and optimizing stomach function. For this, infusions and special decoctions are used.
Herbal medicine is designed to normalize metabolism in the body, create favorable microflora in the intestines, painlessly remove waste from the body and eliminate malignant symptoms.
What medicinal plants should be used?
- The fruits of laxative joster and hay leaves (cassia angustifolia) are often used in infusion of decoction. 1 tablespoon of fruit is poured into a glass of water. The mixture is brought to a boil and stirred for about 5 minutes. The container is hermetically sealed and left for several hours. The decoction should be carefully strained and taken 100 ml before bedtime. Cassia angustifolia will be needed to create an aqueous infusion (1 tablespoon of the plant + a glass of boiling water), which the patient drinks after infusion and straining, if the patient’s condition requires it. Relaxation in the human body occurs on the third day. This treatment is contraindicated in pregnant women and nursing mothers who are experiencing symptoms of the disease.
- Buckthorn bark (brittle or alder bark) is a high-quality remedy to combat constipation. The cooking recipe is quite practical. 1 spoon of crushed bark needs to be poured into 250 ml of boiling water. The process of boiling the mixture continues until 50% of the liquid has evaporated. Take half a glass in the morning and evening.
- Cumin seeds are great for chronic flatulence. The spicy-tasty plant is brewed with boiling water and infused for about 5 hours. Drinking the decoction occurs in doses throughout the day.
- A special place is occupied by brewing dill and fennel seeds. This recipe is also useful for stomach problems.
What should a person do to avoid developing pathology (including colonoptosis)?
- Proper and high-quality nutrition;
- Rational and gradual physical activity of a person. Refusal to lift heavy weights;
- Regular cycling + long distance walking + swimming;
- Gymnastic exercises to maintain active tone;
- Timely treatment of other ailments. Negative symptoms must be neutralized in a timely manner.
Follow simple rules and stay healthy. As W. Shakespeare wrote: “Health is more valuable than gold.”
Preventive methods
If the problem of intestinal prolapse is associated with congenital anomalies, preventive measures are no longer useless and can only be used as a means to prevent complications and even greater prolapse of organs.
The development of acquired colonoptosis can be prevented by following the following recommendations:
- It is important to maintain good tone of the abdominal muscles, which support the intestines and other internal abdominal organs.
- Do not lift heavy objects. If such actions are necessary, you should follow safety precautions and lift weights without putting a strong load on the abdominal area.
- Prevent the development of diseases of the digestive tract. When diagnosed, undergo treatment courses in a timely manner and avoid severe attacks of exacerbation.
- It is necessary to establish a healthy diet that will not cause attacks of heartburn, vomiting, nausea, or heaviness in the abdomen. A proper diet will also help prevent gastrointestinal diseases, which can become an indirect cause of intestinal prolapse.
Attention! During pregnancy, a woman needs to wear a special support bandage that will protect her from colonoptosis. To avoid the development of pathology after childbirth, it is recommended to wear support corsets for 2-8 weeks until the uterus returns to its previous state.
With congenital pathologies, it is quite difficult to do anything to prevent complications. The patient is forced to resort to physical activity all the time; in case of severe pathologies, surgical intervention is performed. In other cases, it is enough for the patient to lead a healthy lifestyle, maintain good physical shape and periodically visit a doctor for early diagnosis of the disease. What to take after antibiotics you will find the answer in the link.
Is it possible to do an MRI of the intestine?
Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed:
- In case of insufficient information content of other types of hardware diagnostics.
- If there are contraindications to alternative methods of examining the digestive system.
The doctor may recommend a scan at the patient's initial visit. The gastroenterologist conducts an examination, listens to complaints, studies the results of previous examinations and decides whether there is a need to prescribe an MRI of the intestines.
The method is one of the safest types of radiation diagnostics. Existing limitations are associated with the effect of a magnetic field on some metals. MRI is not prescribed if patients have:
- pacemakers, insulin pumps and other electronic devices;
- non-removable metal medical structures in the scanning area;
- breast implants (for women) with magnetic guides;
- tattoos made with metal-containing inks.
Tomography is contraindicated for women in the first trimester of pregnancy; starting from the 13th week, native scanning can be done. Children over 5 years of age are examined in the presence of their parents. Whether it is possible to do an MRI of the intestine for a younger child is decided by the attending physician.
Contrast enhancement is not prescribed to pregnant women; lactation is not a contraindication to the use of gadolinium solution. For children under 12 years of age, intravenous injections are given in a hospital setting.
Colon tumor (indicated by arrow) on magnetic resonance imaging images
End-stage liver and kidney diseases are considered a limitation for enhanced MRI. The drug is eliminated with the participation of the filtration organs and can cause decompensation of existing pathologies.
Relative contraindications to MRI diagnosis of intestinal diseases in men and women are:
- claustrophobia;
- overweight (body weight more than 150 kg, chest and abdominal circumference more than 120 cm);
- unstable psycho-emotional background;
- severe pain syndrome.
In the presence of these factors, MRI of the intestine requires additional preparation. In some cases, the procedure is carried out with certain restrictions.