January 29, 2021
The idea that nutrition is important becomes even more important when it comes to treating patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. The patient’s diet must be complete and balanced so that the body has the ability to independently resist the disease and adequately respond to the drug therapy.
Food is fuel for our body.
The digestive system converts this fuel. Patients with Crohn's disease and UC begin to eat less food due to the pain syndrome that develops after eating it. The situation is aggravated during an exacerbation of the disease when the digestive process is disrupted, as a result of which nutrients are poorly absorbed (malabsorption), which leads to the development of malnutrition syndrome (malnutrition).
Malnutrition syndrome can develop in patients with nonspecific inflammatory bowel diseases: due to loss of nutrients due to bleeding and diarrhea; taking medications taken by patients with enteritis and colitis; due to surgical removal of part of the intestine due to a decrease in the absorption surface of the intestinal mucosa). Patients with nonspecific inflammatory bowel diseases should be highly alert for malnutrition syndrome, which develops very quickly. With the development of malnutrition syndrome in Crohn's disease and UC, patients quickly lose weight, there is a deficiency of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, essential vitamins and minerals, which creates favorable conditions for the development of complications and the occurrence of other diseases.
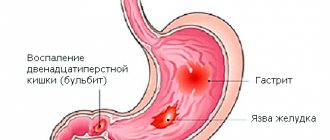
Symptoms and signs of Crohn's disease
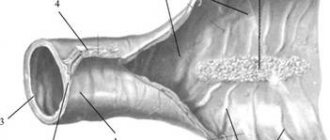
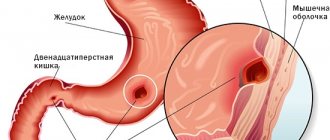
The disease can affect the mucous membranes of the entire digestive system. Inflammation occurs purely locally. Areas of the intestine affected by Crohn's disease alternate with areas of the mucous membrane where there are no pathological changes.
The small intestine is most often affected. Also, Crohn's disease has symptoms similar to those of ulcerative colitis. Typical manifestations of the disease:
- pain in the gastrointestinal tract;
- diarrhea - all the time or at night;
- bloating;
- traces of blood and mucus in the stool;
- false urge to have a bowel movement;
- thirst;
- vomit.
During exacerbation of Crohn's disease, increased body temperature is observed. The patient loses weight, has no appetite, has signs of anemia, and feels weak and chronically tired. In addition, Crohn's disease in adults is characterized by general systemic pathologies of the functioning of the body: the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth become inflamed, inflammation occurs in the anal area, pain is felt in the joints (arthralgia), and the lymph nodes also suffer. Inflammation can also occur in acute form. But that doesn't happen often.
Are you experiencing symptoms of Crohn's disease?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Is there a special diet for patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis?
There is no universal nutrition system (in the usual sense) for patients. An individual nutrition program should be developed for each patient, taking into account the severity of the disease and the level of damage to the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, the course of the disease changes over time, so it is necessary to adjust the diet. Since healthy eating habits, which include a rational and balanced diet, have a pronounced positive effect in healthy people, in patients with inflammation of the intestinal mucosa are of paramount importance, taking this fact into account, the Nestle® Research Center developed the Modulen® IBD medicinal mixture in 1996 .
Causes of Crohn's disease
What exactly causes Crohn's disease is unknown. It is believed that the pathology can be provoked by infectious and viral pathogens. There is also a version that the cause is a deviation from the norm in the natural balance of the gastrointestinal microflora. The influence of immunological factors is also considered important. The immune system reacts abnormally to the body's own tissues, or perhaps there is a specific food antigen, a non-disease-causing microbial agent. It can provoke an abnormal immune response.
Other factors:
- a person is genetically predisposed to the disease;
- leading a not very healthy lifestyle, for example, smoking, frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages, medications;
- negative environmental situation;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- sometimes there is a relationship with the use of oral contraceptives;
- unbalanced diet (if the food contains little or no fiber).
Does proper nutrition matter for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC)?
Undoubtedly. Particularly patients with small intestinal damage are at risk of malnutrition for a number of reasons: Loss of appetite—as a result of severe nausea, abdominal pain, or taste disturbance—reduces food intake. The chronic course of the disease increases the body's need for energy and calories. This is especially true during periods of exacerbation. Inflammatory bowel disease, especially Crohn's disease, is usually associated with problems with the digestion and absorption of all nutrients and fluids. This condition is called intestinal malabsorption syndrome (malabsorption) and leads to the fact that most of the food consumed passes through the intestines, and the body does not receive the plastic material it needs. A balanced diet is the basis for the health of the whole body. In patients, decay processes predominate over tissue building processes, immunity decreases, i.e. the body is in a weakened state. Restoring and maintaining normal nutritional status is a leading component of treatment for several reasons: The effectiveness of drug therapy for Crohn's disease and UC increases, drugs are better absorbed, and the number of side effects is significantly reduced.
Since nutrients are poorly absorbed, there is a need to take larger amounts of food, and this is often very difficult against the background of severe clinical symptoms (nausea, lack of appetite). Impaired digestion and absorption of protein and other nutrients, lack of energy leads to retardation in the growth and development of children and adolescents. Weight loss due to intoxication in girls and women leads to pronounced hormonal changes.
How does nutrition affect growth in patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis?
Young people who become ill before puberty experience delays in growth and development. Poor nutrition against the background of the disease aggravates the situation. Thus, healthy eating habits and caloric intake are very important. As mentioned above, the effectiveness of drug therapy increases, and in the case of surgical intervention, wound healing time is reduced and overall well-being improves.
How to reduce pain after eating in Crohn's disease and UC?
During periods of exacerbation of the disease, eating may be accompanied by colic and severe pain. You can reduce discomfort in the following way: eat food often, in small portions (five meals a day every three to four hours, not three meals a day with several changes of dishes). Reduce your consumption of fatty and fried foods. Butter, margarine, sauces and pork can cause diarrhea and flatulence due to incomplete absorption of fats. Limit your intake of milk and dairy products if you do not tolerate milk sugar (lactose). Many healthy people cannot digest milk sugar because they lack the enzyme that breaks it down (lactose).
Lactose intolerance is accompanied by intestinal colic, severe abdominal pain, flatulence, diarrhea, and belching. Reduce your intake of fiber-rich foods such as nuts, seeds, corn, raw vegetables and fruits. Consumption of these products can cause colic and diarrhea. Therefore, a low-fiber, waste-free diet is recommended. However, even following all the recommendations, many patients experience digestive discomfort. In this case, it is necessary to resort to the help of medications recommended by the doctor.
What is a low fiber diet that is recommended for patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis?
In 2/3 of patients with small intestinal Crohn's disease, narrowing of parts of the intestinal tube (stricture) develops. For such patients, a low-fiber diet or a special liquid diet is advisable to reduce pain and other symptoms. The recommended diet reduces the intake of foods that are difficult to digest (raw fruits, vegetables, seeds, nuts and corn) and increases the content of indigestible particles in the stool. Typically, such dietary recommendations are temporary and are applied at the time of exacerbation.
Is food digested or not in patients with nonspecific inflammatory bowel diseases - Crohn's disease and UC?
In most cases, yes. Patients whose inflammatory process affects only the large intestine digest food normally. Patients with Crohn's disease may have problems with digestion if the small intestine is also involved. They may eat enough food, but will not be able to digest and absorb it adequately. About 40 patients with Crohn's disease primarily do not metabolize carbohydrates. In such a situation, flatulence, increased gas formation, and diarrhea may occur, against the background of which there will be a loss of essential nutrients. Insufficient fat absorption is another problem that accompanies Crohn's disease, observed in approximately 1/3 of all patients. The risk is increased in patients with terminal ileal resection. The degree of malabsorption depends on what level of the small intestine is affected in Crohn's disease or what area was surgically removed. If in a patient with Crohn's disease only the last 30-60 cm of the ileum are involved in the inflammatory process, the absorption of all nutrients, especially vitamin B12, will be normal; if more than 60 cm, impaired fat absorption may be observed. If the upper parts of the small intestine are involved in the inflammatory process, then the situation becomes significantly more complicated, since impaired absorption of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals and many vitamins is observed. Some medications, especially 5-ASA, interfere with the absorption of folate, an essential nutrient that helps prevent cancer and birth defects, so this needs to be taken into account when planning your diet.
What is nutritional support for nonspecific inflammatory bowel diseases?
In case of NIBD, especially in Crohn's disease, additional nutritional support of the patient is required with special liquid nutrition, ready for consumption and absorption in the small intestine - enteral nutrition (Modulen® IBD).
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) involves inserting a catheter into a large venous vessel, usually the subclavian vein. With this type of diet, nutrients bypass the intestines and allow the intestines to rest. Total parenteral nutrition can cause a large number of complications, unlike enteral nutrition; it is expensive and requires specialized training.
What is nutritional therapy?
The main goal of therapeutic nutrition for nonspecific inflammatory bowel diseases is to eat mechanically, chemically and thermally gentle food.
During the period of exacerbation of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, split meals are prescribed 5-6 times a day. For persistent diarrhea, it is recommended to increase the protein content in food to 1.3-2 g kg per day. Milk is excluded if it is intolerant and the amount of coarse plant fiber is limited, especially with intestinal strictures. These conditions correspond to diet 4, then 4b.
In case of extensive damage to the small intestine with the development of malabsorption syndrome and short bowel syndrome, a multi-element, balanced, lactose-free mixture made from whey protein split into oligopeptides and containing medium-chain triglycerides, Peptamen®, produced by Nestle®, is recommended. Due to the fact that the severity of inflammatory bowel diseases, the duration of periods of exacerbation and the effectiveness of treatment are directly related to adequate nutrition, there is a need to find optimal nutrition that can take into account the entire range of nutritional needs of patients and has a therapeutic effect on the patient’s body, reducing the severity of inflammatory process and improving digestion. Classical dietetics recommends the following types of diets for Crohn's disease and UC: Diet 4, diet 4b, diet 4c.
Indications for prescribing diet 4A: acute and chronic intestinal diseases during the period of profuse diarrhea and pronounced dyspeptic symptoms. Diet 4 can be prescribed after 1-2 “fasting” days or immediately during an exacerbation of Crohn’s disease and UC.
After 4-5 days, the patient is prescribed diet No. 4b.
Diet No. 4b is prescribed for 4-6 weeks until stool is completely normalized and exacerbation of inflammatory phenomena in the intestines is eliminated. Then the patient is recommended diet No. 4c.
What's new in dietary therapy for patients with Crohn's disease and UC?
The main concept in the treatment of nonspecific inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease and UC) is that nutrition should help the intestines heal itself, and a huge number of experimental studies prove this. The use of fish oil and flaxseed oil in the diet or as an additional component of nutrition prevents inflammation in the intestinal wall in NIBD. Dietary fiber complexes activate bacteria in the large intestine, after which they begin to produce short-chain fatty acids. These fatty acids promote repair (healing) of the colon mucosa. Another tactic of using probiotics, which is only now gaining evidence, is also a means of helping with nonspecific colitis and enteritis. Probiotics are “good” bacteria that restore the balance of the intestinal microflora living in the intestines of every person. Lactobacillus preparations and yoghurts with live cultures are very beneficial. Quite a lot of work has been done on the use of diets and supplements, and quite a lot more should be studied.
Complications
Many patients with Crohn's disease with complications of the disease experience the following phenomena:
- weight loss to the point of extreme exhaustion;
- problems with metabolism in the body due to poor absorption of nutrients;
- ulceration of the mucous membranes, perforation of the intestinal wall, bleeding, release of feces into the abdominal cavity;
- fissure of the anus (anus);
- spread of fistulas to nearby organs, the abdominal cavity, and the surface of the skin. Spread of abscesses in the intestinal wall, lumens of fistulas;
- dysbacteriosis and hypovitaminosis.
Crohn's bowel disease can also develop into colon cancer if left untreated.
When to see a doctor
The symptoms of Crohn's ulcer disease are similar to many other pathologies. To diagnose it, you need a comprehensive, comprehensive examination. The disease is most often diagnosed by a specialist such as a gastroenterologist.
You should consult a doctor if the following phenomena occur:
- frequent diarrhea that does not go away;
- incessant pain in the gastrointestinal tract;
- rapid weight loss without objective reasons;
- traces of blood in the stool.
In all these cases, you must make an appointment with a gastroenterologist. A gastroenterologist will conduct an in-depth diagnosis of the disease, prescribe treatment, and, if necessary, give a referral for consultation to other specialists.
A general examination will also be carried out, laboratory and instrumental tests will be prescribed. In difficult cases, doctors of other specializations may be involved. For example, you may need to consult an infectious disease specialist, surgeon or coloproctologist. All these and many other specialists work at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitberg).
Preparing for a visit and a doctor's visit
A gastroenterologist diagnoses and treats gastrointestinal diseases. Before visiting a specialist, prepare for the fact that you may be asked the following questions:
- the onset of symptoms when ailments manifest themselves for the first time;
- symptoms are present all the time or unpleasant phenomena occur periodically;
- Do the symptoms intensify due to some events, provoking factors (after stressful situations, taking certain medications, certain foods, etc.);
- your general condition - how uncomfortable the manifestations of the disease are, how much your well-being has worsened and how this is manifested, whether your quality of life has decreased, whether there are any restrictions on any type of activity or taking certain foods;
- whether you took medications after the first signs of the disease appeared and whether you are currently taking certain medications (list).
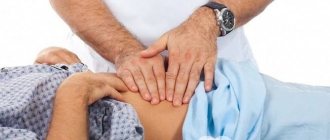
Based on the information received and a comprehensive clinical examination (palpation of the abdomen, examination of the oral cavity), the specialist draws up a subsequent examination regimen.
Does the amount of fluid consumed matter in Crohn's disease and UC?
Yes. Chronic diarrhea is always accompanied by dehydration. If fluid intake is less than fluid loss, kidney function is impaired and the risk of stone formation increases. In addition, dehydration and loss of salts from the body cause a feeling of constant weakness. In this regard, sufficient fluid intake is recommended, especially in hot weather, when the loss of fluid and salts is maximum. On average, fluid consumption per day is 30-40 ml per 1 kg of body weight. You need to drink liquid in small sips to avoid swallowing air, which can cause digestive discomfort in the form of belching.
Diagnosis of Crohn's disease
A general examination most often includes:
- blood test - to detect anemia and the hidden presence of infection;
- general stool analysis - determines how food is digested, whether there are obvious or hidden traces of blood, whether there are inflammatory cells;
- colonoscopy to examine the inside of the intestine, using a flexible tube with a video camera. In addition to the camera, these devices have tools for performing biopsies, removing foreign bodies, cauterizing blood vessels;
- Capsule endoscopy is a type of endoscopy;
- double balloon enteroscopy;
- visual diagnostics (X-ray, MRI, CT, including using a contrast agent).
High-quality comprehensive diagnostics are offered by Meditsina JSC (academician Roitberg’s clinic). The above-listed modern methods for diagnosing Crohn's disease are used here. The clinic is located in the central district of the capital, near the Belorusskaya, Chekhovskaya, Tverskaya metro stations.
Treatment
This disease is very dangerous and, unfortunately, cannot be completely cured. However, it is possible to achieve a transfer of the active phase into stable remission. If the disease is advanced, complications begin, or the case is severe, then surgical intervention is prescribed. In all other cases, treatment occurs with the help of medications:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- immunosuppressants;
- antibacterial agents (in case of infectious infection).
Antidiarrheal or painkillers, etc. may also be additionally prescribed. In cases where the prescribed medications and diet for Crohn's disease do not produce results, surgical intervention is prescribed.
New Year's diet for people with gastrointestinal diseases
New Year is a delicate matter... Especially when such a colorful, joyful holiday is anticipated by a gastroenterology patient! There are many questions:
“What can you eat?”
“What can’t you eat?”
"What can you drink?"
“What can’t you drink?” or “Not a bit!”
What should be on the holiday table during a period of exacerbation?
Here I would like to clarify right away. Almost every disease of the gastrointestinal tract has periods of exacerbation and remission (subsidence).
If on the eve of the New Year and Christmas you are in a period of exacerbation of the disease, then you should treat yourself and your body with all the attention! We must understand that the stomach, intestines, pancreas or bile ducts need to be “calmed”. To this end, the diet should be limited both in terms of preparation method and in terms of quality composition and serving size. We steam, boil, sauté in water or poach. We do not add hot spices! We use dill, bay leaf for aroma, turmeric for color. We leave smoked meats, pickles, marinades for the guests! We also move soda and alcohol to the guest side of the table.
When sitting down at the table, we look at a medium-sized plate, visually dividing it into quarters. We fill up to 3/4 with a side dish in the form of thermally processed vegetables or cereals, give ¼ to fish, poultry or lean, lean meat. We make meatballs, hedgehogs, and steamed cutlets from meat. If you want to add onions, first sauté them in some water and only then add the grounds to the meat. For our beloved self, we prepare a compote of non-acidic berries and fruits, or better yet, jelly! For breakfast we prepare a variety of cereals, omelettes (steamed or covered) as a snack with toasted white bread. Let the tea be weak, the coffee weak even after meals! We use low- or lactose-free milk. Mineral water - without gas!
Believe me, efforts and hardships will be rewarded with good health during the New Year and Christmas holidays!
How to expand your diet during remission?
If the attending physician noted an improvement and said the magic phrase: “The diet can be expanded!”, this does not mean that the diet can suddenly be returned to the primary version.
The diet needs to be expanded gradually, one day we add something more filling, the next we evaluate our well-being. If everything is great, we continue to introduce new products. Also with vegetables and fruits: add soft vegetables (salad, herbs) or sour fruits to the main meal, observe.
You need to approach the New Year with the understanding that a balanced diet with some restrictions on the fat content of dishes and serving size is suitable for you. Visually divide the plate into ½ for vegetables and two ¼ for poultry, fish or meat and long-awaited salads, respectively.
Meat and side dish can be baked in the oven, in foil or covered.
If you have already felt like a completely healthy person, remember the great phrase: “Everything is poison, everything is medicine. Both are determined by the dose.” The sound is ambiguous, but it suits us! 
With such preparation for New Year's Eve, the holiday is simply bound to be carefree!
Tips for people with food intolerances
Patients with food intolerances deserve special attention! “Olivier!”, “Herring under a fur coat,” “Napoleon”... How to survive the holidays without a chicken egg, wheat flour, cow's milk or cream?!
There is a solution! It takes time and some equipment. We make mayonnaise from quail eggs, replace sausage with your favorite type of meat or poultry, make vegetable salads in vegetable oil, prepare boiled pork for sandwiches, canapés, make desserts with milk substitutes (coconut, soy, nuts, etc.), cookies and pastries ( pies, muffins, charlotte, etc.) are made with the addition of coconut oil and allowed gluten-free flour (rice, corn, flaxseed, etc.), pancakes can be made with juice. You can even have jellied meat!
The main thing is not to be discouraged, but look around and there will be many options, because the main recipe for a memorable holiday is a good mood!
Drinks deserve special attention in the article!
Among non-alcoholic drinks, you should give preference to non-acidic compotes and jelly (especially during an exacerbation). It is better to limit carbonated sweet drinks; even mineral water is better to use non-carbonated water. Consume juices after the main meal, and dilute freshly squeezed juices and smoothies with water 1:1.
If you have a gastroenterological disease and your attending physician has strictly prohibited any alcoholic beverages , then alas (as sad as it is) there are serious reasons for this. Violating the recommendations can ruin the entire New Year holidays! If you have not clarified this information with your doctor and are not in a period of exacerbation of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (no pain, bowel problems, heartburn, bloating, etc.) and you really want to celebrate the New Year with alcohol, then the snack should be strictly dietary!
And if you plan to break your diet and allow yourself products that are not recommended, you will have to do without alcohol. Because alcohol + fatty, heavy foods = a powerful blow to the pancreas.
In addition, do not forget about the rule of “bad taste”: we do not mix alcoholic drinks from different raw materials (grape - brandy, cognac; grain - vodka, whiskey). Don’t forget that carbonated alcoholic drinks (champagne, cider, beer) should also be consumed with caution; it is better to let them “fizzle out” and continue the holiday.
Alcoholic drinks for people with food intolerances
People with true food intolerance to gluten (gluten) without exacerbation of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract need to exclude grain drinks - beer, beer drinks, whiskey, vodka. Among low-alcohol drinks, give preference to cider and wine; among strong drinks, give preference to cognac, tequila, and rum. Gin is a controversial product; often the label does not clearly indicate the composition of the raw materials.
You say: “I only drink light cocktails.” Cocktail is different from cocktail! Danger lurks everywhere: soda, sour citrus fruits, syrups with chemical dyes. For patients with lactase deficiency or food intolerance to cow's milk, cream or animal milk in their favorite drink (Bailey's, White Russian, Irish Coffee, etc.) may be an unpleasant surprise. It’s one thing if you make a cocktail yourself: you’ve chosen the permitted products and observed all the proportions. And a completely different matter is a cocktail called “In a Public Place.”
Beverage temperature
Temperature also makes a difference. If for a healthy person a combination of hot food and an ice-cold drink is the norm, then if digestion is unstable, the temperature contrast can change your plans for the evening radically. Use our tips so that the holidays go according to plan, without disappointment.
Be healthy and happy in the New Year!
Gastroenterologist-nutritionist of the Expert Center, Svetlana Igorevna Kovaleva.
We offer dietary recipes for the New Year's table
Beetroot salad with cheese and prunes (Gluten, egg and lactose free)
Ingredients:
- 3-4 medium beets;
- 6-7 pcs. prunes;
- 50 - 100 g hard cheese;
- 1-2 tbsp. l. olive oil.
Cooking method:
- First, bake the beets in the oven in foil or steam them and cool.
- Grate beets and cheese.
- Wash the prunes, dry and chop and add to the grated beets, add cheese.
- Drizzle with olive oil and stir.
Salad with mozzarella and caprese tomatoes (Gluten and egg free)
Ingredients:
- 2 fresh medium tomatoes
- 200 g brine mozzarella
- 2-3 tbsp. l. olive oil
- spices
- 10 basil leaves or arugula sprigs.
Preparation:
- Pour boiling water over the tomatoes and remove the skins.
- Cut mozzarella and tomatoes into slices.
- Place on a plate alternating mozzarella and tomatoes, drizzle with olive oil and sprinkle with spices and basil or arugula leaves.
Ready!
Baked turkey or chicken fillet with vegetables (Gluten, egg and lactose free)
Ingredients:
- 700 g turkey or chicken breast fillet
- vegetable supplement (you can use various vegetables):
- 1-2 carrots;
- 200-300 g cauliflower or broccoli or kohlrabi;
- 100 g celery or 1 pc. leek;
- 200 g pumpkin;
- 1 PC. purple onions;
- 1 PC. tomato or apple optional;
- salt and spices or fresh herbs (it’s time for sprigs of parsley or rosemary);
The composition of the vegetable supplement can be varied. For example, remove the celery and add bell peppers, replace the pumpkin with zucchini, eggplant or sweet potatoes, add kale, frozen green peas or beans, etc.
Preparation:
- Cut the poultry meat and vegetables into approximately equal parts and mix, adding salt and spices or herbs. If desired, you can add olive oil to the mixture.
- Mix the whole mixture well to distribute the seasonings and salt evenly throughout the entire volume and leave for 30 minutes.
- After infusion, place the mixture of poultry and vegetables in a baking sleeve and bake for 45 minutes in a hot oven.
- 5 minutes before the end of the baking process, cut the sleeve and finish baking the dish uncovered to remove excess moisture. Sprinkle with herbs if desired.
Ready!
Whole Oven Baked Trout (Gluten, Egg and Lactose Free)
Ingredients:
- 1 PC. medium-sized fresh trout;
- salt and spices;
- garnish of your choice.
Preparation.
- Wash gutted but unpeeled medium-sized trout, rub with salt, lemon juice and spices and leave for 2 hours in the refrigerator in film or a saucepan.
- Place on a baking sheet and bake in the oven for approximately 30 minutes.
- Serve with a side dish of your choice (fresh vegetable salad, rice, mashed potatoes, baked vegetables).
Ready!
Rice charlotte (Gluten and lactose free)
Ingredients:
- 150-200g (1 cup) rice flour;
- 4 pcs chicken or 16-20 pcs. quail eggs;
- 180-200g. (1 cup) + 2-3 tbsp. Sahara;
- 500g apples or 300g. – purified;
- 1 tsp slaked soda.
Cooking method:
- Mix sugar with eggs.
- Add flour, mix.
- Add soda slaked with vinegar and cinnamon.
- Add apples, mix with a spoon.
- Place in the oven, bake at 180 degrees for 35-40 minutes.
- From 2-3 tbsp. Make powder with sugar in a coffee grinder, sprinkle on the charlotte before serving.
Ready!
Orange Jelly (Gluten, Egg and Lactose Free)
Ingredients:
- 3 ripe sweet oranges;
- 200 g sugar;
- 20 g gelatin;
- cinnamon to taste.
Cooking method:
- Pour gelatin into 200 ml of cold boiled water. Leave for the time indicated on the package.
- Squeeze juice from oranges. Coarsely chop the peels.
- Pour 1 liter of water over the crusts. Boil. Boil for 10 minutes.
Strain. Cool to 40–50 degrees.
- Add sugar and swollen gelatin. Bring to a boil, but do not boil. Add squeezed juice.
- Remove from heat. Pour into molds (or bowls). Place in the refrigerator for 5–6 hours.
Ready!
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of Crohn's disease
Among the main myths it is worth voicing the following:
- the disease can be treated at home or can be cured by a healer, energy biotherapist, etc.;
- If you follow a diet, then treatment is not necessary.
Diet cannot cure this disease, but it can normalize the patient’s well-being. You should seek help only from qualified specialists who work in a trusted clinic. Only they will be able to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment. If the disease is left to chance, it can turn into cancer. Therefore, treatment exclusively with alternative means of medicine or turning to psychics or healers will only complicate the picture of the disease and lead to complications, after which, at best, only surgery can save a person.