Several diagnostic methods are used to identify intestinal diseases. Laboratory methods and computed tomography are considered the most complex. Endoscopic diagnostic methods are simpler and more accessible; they require much less time. These methods of examining the intestines are very similar to each other, but still have some differences.
Which method is better: ultrasound of the intestine or colonoscopy
The most important advantage of intestinal ultrasound is that it has virtually no contraindications to the study due to its complete harmlessness to the patient’s body. In addition, during the examination, the patient does not experience any unpleasant or painful sensations. It is for these reasons that ultrasound can be performed an unlimited number of times, including for pregnant women, children, and seriously ill patients.
Also, one should not lose sight of the fact that the patient’s sensations during ultrasound and colonoscopy are very different. Thus, endorectal ultrasound scanning brings significantly less discomfort than using a probe during endoscopy. It is for these reasons that diagnosis is not carried out for the elderly and children.
Both ultrasound and colonoscopy provide the opportunity to determine the existing pathological process in the gastrointestinal tract. At the same time, the most informative method is still a colonoscopy, since it allows you to identify diseases at the initial stage of their occurrence, which allows you to begin timely therapy.
Comparison of two types of diagnostics
Depending on the presence of specific symptoms, after the initial examination, the doctor decides what diagnostics the patient will need to undergo: intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy.
In addition, a proctologist or gastroenterologist can decide which diagnostic method will be more accurate in a particular situation and will cause minimal discomfort to the patient. Therefore, there can be no talk of any self-appointment. Only a specialist can give an adequate assessment of the patient’s condition and prescribe an ultrasound of the intestine or colonoscopy based on the medical history.
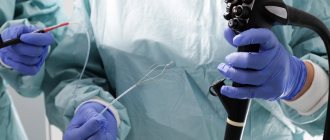
To perform a colonoscopy, special video equipment is used, which is fixed on an elastic probe. The probe is inserted into the patient's intestines. In order to ensure good visibility, a certain volume of air is pumped into the gastrointestinal tract. During the examination, the doctor assesses the condition of the intestines using images that appear on the computer screen. A specialist can notice the changes that have appeared from the inside, which makes it possible to give a real assessment of the structure of the organ’s tissues.
Intestinal ultrasound provides the opportunity to visualize inflammatory processes and neoplasms, the boundaries of the pathological process, and also identify the stage of the disease.
Many patients wonder whether an ultrasound doctor will be able to diagnose intestinal cancer during an examination. The latest generation of ultrasound machines provide this opportunity. After all, the examination is carried out using a special technique. Thanks to the use of an ultrasensitive sensor, it is possible not only to examine the tumor in detail, but also to identify its features.
Both colonoscopy and ultrasound diagnostics provide the opportunity to take high-quality images, which will be used in the future for a more detailed analysis of the pathological process, as well as to assess the dynamics of the treatment.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
Preparation for a colonoscopy is based on four components:
- Testing and functional diagnostics.
- Following a slag-free diet.
- Purgation.
- Correction of medications.
Testing and functional diagnostics
Colonoscopy is preceded by the following diagnostic measures:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Hemostasiogram.
- ECG.
- Isoserological study (group and Rh factor) and biochemical blood tests (according to indications).
- X-ray of the chest organs.
It is important to obtain advice from a therapist, endoscopist, as well as an anesthesiologist (if the procedure will be performed under anesthesia).
Slag-free diet
3 days before rectosigmocolonoscopy, it is important to exclude any foods that can cause fermentation or gas formation. Especially undesirable foods include legumes, lettuce, fatty meat, milk, brown bread, any fresh fruit, and chocolate.
Moreover, rolled oats, millet and pearl barley should be excluded from the diet for several days. Instead, vegetable broths, boiled chicken, lean fish, white bread (preferably yeast-free), cottage cheese, and kefir are welcome in the diet.
Purgation
Colon cleansing can be done through an enema or using special medications.
You can qualitatively cleanse the intestines with an enema if you have a volumetric enema (not a syringe, but an Esmarch mug) and an assistant (the best option is a medical worker). Giving an enema yourself is problematic. Someone must fix the clamp, directly install the enema, and remove air from it. The procedure is done on the left side with the right leg tucked towards the stomach.
The tip of the Esmarch mug is inserted into the anus to a depth of at least 7 cm. About 1.5 liters at room temperature are poured into the intestines. To ensure proper results, it is recommended to perform enemas two evenings in a row before the procedure. An alternative to enema is cleansing the intestines with the help of special medications that contain the ethylene macrogol. Fortrans is best known. But this is only one of the possible names of drugs that contain macrogol. The drugs are presented in the form of powders, from which solutions must be prepared.
Depending on how much weight a person has and whether he or she has a tendency to constipation, preparing the solution may require from 2 to 4 liters of water. The intestinal cleansing solution is drunk on the eve of the procedure in portions over an hour and a half. If for some reason a person cannot drink such a volume of liquid in 1.5 hours, the doctor may recommend a two-step cleansing scheme. In this case, for example, 3 liters of solution should be drunk in the evening, and 1 in the morning. In this case, at least 3 hours should pass between the last dose of macrogol and the colonoscopy procedure itself.
To make the cleansing process as effective as possible, it is recommended to perform active movements while taking solutions containing macrogol. This can be bending, exercises with a hoop, squats. Which cleansing option is preferable - with the help of an enema or medications - is decided by the doctor, taking into account each specific situation. Medications with macrologue cleanse the intestines most efficiently, but nevertheless, these drugs are contraindicated in cases of severe dehydration (dehydration), intestinal obstruction and an increased amount of magnesium in the blood.
Correction of medications
- If the patient has chronic diseases: for example, endocrine heart disease, he constantly takes other medications, then on the day of the colonoscopy it is important to remember: it is important to stop taking the medications at least 2 hours before the rectosigmocolonoscopy.
- When taking Coumadin or other anticoagulant drugs that prevent blood clotting, it is advisable to stop them a week before the procedure. This is due to the fact that if a colonoscopy is performed with a biopsy to microscopically examine a small piece of tissue, bleeding may occur when taking such drugs.
- Three days before the colonoscopy, you should refrain from taking iron supplements (mainly most medications for anemia).
How to properly prepare for research
Before performing an ultrasound of the intestines or before a colonoscopy, patients will have to follow certain recommendations of a similar nature:
- a few days before the study, patients need to exclude from their diet any foods that cause increased gas formation;
- approximately 24 hours before the examination, food intake should be minimized and dinner should be replaced with a light snack;
- in the evening or early in the morning you need to empty the intestines of feces. If this cannot be done naturally, then you should definitely resort to a cleansing enema.
- In order to fully cleanse the intestines, absorbent drugs can be very effective, such as:
- "Enterosgel";
- "Smecta";
- "Polysorb".
Before the study, experts also advise taking medications to reduce gas formation. Compliance with all preparatory measures will guarantee a highly informative survey.
How is ultrasound diagnostics and colonoscopy performed?
Many patients believe that undergoing an ultrasound of the intestine is a study during which a specialist will perform exclusively external manipulations, as is done when examining many organs. An intestinal ultrasound is performed a little differently.
First of all, a special catheter is inserted into the patient through the rectum to a depth of 5 cm. Its diameter is very small and does not exceed 8 mm. With its help, a special liquid is introduced into the intestine - a contrast agent, the purpose of which is to better visualize the walls of the organ.
During the examination, the patient does not experience pain. This diagnostic procedure is not very different from other types of ultrasound examinations.
As for colonoscopy, this is a much more unpleasant and sometimes even quite painful procedure. During the examination, a special device is inserted into the patient's intestines through the anus - an endoscope, which is a flexible tourniquet with a camera at the end.
For a complete examination of the intestines, the specialist will need to insert the endoscope deep enough, which causes pain to the patient. Another significant disadvantage of endoscopy is that it takes much longer to perform than ultrasound diagnostics.
The essence of sigmoidoscopy, its advantages and disadvantages
The technique is based on a visual assessment of the rectal lumen, examination of the mucous membrane for the presence of areas of ulceration, polypoid growths, space-occupying formations, tissue damage leading to bleeding.
The study is carried out using a sigmoidoscope, which is a tube equipped with an eyepiece and an air supply system.
The disadvantages of the technique are:
- limiting visualization only to the rectum and the initial parts of the sigmoid;
- the likelihood of damage to the wall during aggressive conduction;
- subjective discomfort of a psychological nature.
Has a number of significant advantages:
- causes less inconvenience to the patient, therefore it is often performed without anesthesia in an outpatient setting;
- no need to stay in the hospital after the procedure;
- minimal number of contraindications (except for massive bleeding, pronounced narrowing of the lumen);
- The duration of the manipulation is no more than 7 minutes.
Is it permissible to perform an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity after a colonoscopy?
It is not advisable to perform an ultrasound examination after a colonoscopy. In exceptional cases, specialists can still resort to ultrasound examination, for example, if there is a question about performing a biopsy, removing polyps, or stopping intestinal bleeding. In such cases, ultrasound will help monitor the dynamics of the treatment. In all of the above cases, ultrasound diagnostics are carried out exclusively through the peritoneal cavity.
As a rule, the patient is initially prescribed an ultrasound examination, and only then a colonoscopy. The choice of a specific method depends on the medical history, the patient’s condition and existing complaints.
Features of video colonoscopy
Video colonoscopy is no different from regular colonoscopy, except for the name. It allows you to display a multiply enlarged image transmitted by the colonoscope on the monitor screen. During the procedure, a colonoscope with a camera at the end is used, which displays an HD+ quality image on the monitor.
The device package includes:
- Probe;
- Backlight;
- Eyepiece for video transmission;
- Forceps for biopsy and removal of growths;
- Loops for removing polyps.
During the video colonoscopy procedure, the patient feels minimal discomfort due to the flexibility of the colonoscope. And the i-scan function allows you to detect colon cancer at a very early stage.
Indications, contraindications and stages of preparation for video colonoscopy are the same as for colonoscopy.
Which type of diagnosis is better?
It is impossible to unequivocally answer the question of which type of diagnosis is better: intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy, for the simple reason that these two examination methods simply cannot be compared in terms of effectiveness and significance. They have completely different purposes. Each of the methods can be used only if there are certain indications, and the final decision on prescribing one or another diagnostic method can only be made by a doctor.
However, most often, patients are initially prescribed ultrasound diagnostics, and if it turns out to be uninformative, then after this the patient is sent for a colonoscopy.
What to expect from intestinal endoscopy?
The subjects are most concerned about thinking about upcoming pain. Proper preparation for the study - a slag-free diet, preliminary cleansing of the intestines with enemas or mild laxatives - allows you to avoid a painful reaction during manipulation. The difference between sigmoidoscopy is that the manipulation is performed without anesthesia, since the procedure takes a limited amount of time and the rectoscope is inserted to a shallow depth. The inlet of the anus and intestine is first expanded with the inserted anoscope.
It is believed that examination of the intestines during colonoscopy is more painful than during sigmoidoscopy. This is not entirely true. Colonoscopy can be performed under local anesthesia of the rectal sphincter (if indicated) and under general anesthesia or under medicated sleep (in the case of an individual increased pain threshold). There is no pain during the manipulation, since the endoscope tube has a soft, flexible base.
In some cases, the colonoscopy procedure may be performed under general anesthesia.
Discomfort is caused by inflating the intestinal wall to improve visualization. Pain can occur as a result of an acute inflammatory process, which is why performing manipulation in such conditions carries the risk of perforation or bleeding. Such risks are excluded by preliminary examinations (radiographic examination) and careful collection of anamnesis.