“Space diet” by Sergei Sivokho: without denying himself anything, the comedian lost 42 kg in 3 months
Gastric and duodenal ulcers are a serious disease that requires treatment to avoid exacerbations. In addition to the doctor’s medication recommendations, adherence to a therapeutic diet aimed at sparing the stomach is indicated. Proper nutrition will help relieve pain during exacerbation and promote effective treatment and recovery.
Basic nutrition rules
The diet for duodenal ulcers has its own distinctive features. Not only the range of products is important, but also the method of preparing them, the time of consumption, and the size of the portions. Therapeutic nutrition involves split meals. Some rules must be followed exactly as prescribed. Only by taking into account all the nuances will the process of healing the disease be accelerated, and you will feel significant relief from your condition.
The main principles of diet, as well as selection of foods for duodenal ulcers:
- meals should be frequent - approximately every 3 hours;
- food should not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum;
- the diet should have increased nutritional value and include a sufficient amount of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, mineral salts and vitamins (necessarily A, C and B vitamins);
- products included in the diet should not have a strong juice-containing effect;
- Eating very hot or cold food is prohibited; it should be at room temperature;
- it is necessary to reduce the daily consumption of table salt to 10-12 g;
- food should not mechanically irritate the gastric mucosa; try to eat all food in pureed form;
- One meal should not contain a large amount of food.
The main task in the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers is to restore the functioning of all processes occurring in the body. Ordinary milk copes well with this task, being one of the most useful food products for people with peptic ulcers. Milk contains a large number of substances necessary for the body.
General rules
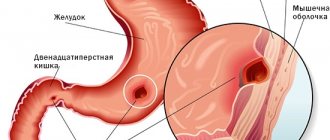
Peptic ulcer disease is a chronic disease, the manifestation of which is a recurrent ulcer. Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum occurs against the background of an imbalance between aggressive factors, which are Helicobacter pylori and the acid-peptic state, and protective factors - the mucus of the duodenum and stomach and the ability of the mucous membrane to repair. Today we will touch on duodenal ulcer and nutritional characteristics during different periods of the disease.
In the typical version, the ulcer is localized on the posterior or anterior wall of the duodenum and more often in the bulb (this is the part of the duodenum closest to the stomach). Functionally, this part is associated with the intake of acidic gastric contents, which here acquire an alkaline reaction. The duodenal glands produce an alkalizing secretion, and normally stomach acid is neutralized. The alkalization process is also affected by bile and pancreatic juice (the bile duct and pancreatic juice open into the bulb).
The causes of duodenal ulcer are:
- infectious pathogen Helicobacter pylori, which is detected in 70-80% of patients;
- eating disorders (consumption of fried and fatty foods, fast food, starvation diets, consumption of alcohol and excessively spicy foods);
- long-term stressful situations, which in the case of an ulcer of the bulb cause disruption of the nervous regulation of its function (the secretion of protective mucus is disrupted).
For these reasons, the secretory function of the duodenum is disrupted and its protective barrier is reduced, constant irritation of the mucous membrane is maintained, ultimately leading to an ulcerative defect.
The main complaint with this disease is pain. Its intensity depends on the state of the nervous system, age and individual sensitivity of the patient to pain. The pain takes on a nocturnal and “hungry” character and is significantly reduced when eating. A characteristic rhythm of pain is noted: hunger-pain-eating-pain-free interval-hunger-pain again.
Dyspeptic disorders are also typical - heartburn , vomiting, nausea and belching. As the duration of the disease increases, the number of these symptoms increases. Some patients may have a decreased appetite and often experience a tendency to constipation or diarrhea .
Treatment is aimed at eliminating aggression factors and includes:
- suppression of gastric secretion;
- anti-Helicobacter therapy;
- correction of the patient’s psychoneurological status;
- stimulation of reparative processes in the mucosa.
In order to suppress secretion, H2 blockers ( cimetidine , ranitidine , famotidine ), which have recently been used less and less because they do not completely block acid synthesis. They were replaced by proton pump blockers, which are 3-10 times H2 blockers The era of PPIs began with Omeprazole , later this group was replenished with Lanzoprazole , Pantoprazole , Pariet ( rabeprazole ) and Esomeprazole .
Effective regimens have been developed for anti-Helicobacter therapy - 3-component and 4-component, prescribed for 7 days. Due to the risk of developing dysbiotic changes in the intestines, probiotics ( Bifiform , Linex ) are included in parallel.
Normalization of autonomic tone is achieved by taking Atarax , Adaptol or Grandaxin . As a result, autonomic reactivity is restored, which ensures an adequate response of the body to external stimuli. Due to the restoration of psycho-vegetative balance, an acceleration of scarring of ulcers is noted.
Among the agents that enhance reparative processes, one can name Gastritol , which includes plant components that promote the rapid restoration of damage to the mucous membrane. Next, the issue of maintenance therapy is resolved. For multiple ulcers, continue taking De-nol and PPIs for up to three weeks. With concomitant gastroesophageal reflux disease, the duration of taking antisecretory drugs is increased to 6-8 weeks.
Violation of the diet and consumption of food that irritates the mucous membrane is one of the causes of peptic ulcer disease, therefore therapeutic nutrition is an important component of treatment. The diet for duodenal ulcers is aimed at eliminating pain and dyspeptic symptoms. Therapeutic nutrition for peptic ulcers should help reduce the acid factor, the activity of which is most often increased, and stimulate ulcer healing.
At any stage of the disease, secretion stimulants and mucosal irritants are excluded (to one degree or another). Eating small portions of food is gentle on the mucous membrane and reduces inflammation of the duodenum. Regular and small meals greatly facilitate the digestion and absorption of foods.
During different periods of the disease (exacerbation, unstable remission, stable remission), the diet is different and the following tables can be prescribed sequentially:
- No. 1A with maximum limitation of all types of effects on the mucous membrane;
- No. 1B with a mild limitation of all types of aggression on the stomach, the average treatment time is up to two weeks;
- №1 with moderate sparing of the stomach.
The timing of these diets depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of pain and dyspeptic syndrome. The sequential assignment of tables with a gradual expansion of products and different methods of preparing them prepares the gastrointestinal tract for the transition to a common table.
What diet is used during exacerbation of the disease? It depends on the severity of the exacerbation. For severe pain, Diet 1A , which maximally limits all factors of influence (mechanical, chemical and thermal). The diet includes warm, pureed dishes, the consistency of which is liquid, but as the process subsides, it becomes mushy. Products that have a weak juice effect are consumed (milk, eggs, pureed cereals with milk, boiled fish and meat in various forms of preparation). This dietary food is prescribed for the period of severe exacerbation - 7-10 days.
- It is recommended to eat six meals a day with limited portion sizes.
- Food is prepared in liquid or jelly form, which spares the mucous membrane as much as possible and promotes ulcer repair.
- Only slimy soups (with water or milk), prepared from oatmeal, semolina or rice. Mucus soups are decoctions obtained by cooking cereals, which are filtered and the cereals are removed. You can add a little salt to the finished soup and add butter to it. This type of soup can be prepared from ground cereal flour.
- Meat, chicken and fish dishes in the form of puree or steam soufflé. For cooking, choose lean varieties of meat and fish, peeled from skin and tendons and passed through a meat grinder several times.
- Porridge made from buckwheat, rice and oatmeal. They are well boiled, rubbed and diluted to a liquid state with water (milk). A small amount of butter is added to the finished porridge.
- Milk, calcined cottage cheese, milk jelly and cream (in soups). Whole milk - 4 glasses per day.
- Soft-boiled eggs or steam omelet. The patient can eat 2 eggs daily.
- Kissels and jellies from sweet berries, berry and fruit juices, diluted with boiled water with the addition of sugar or honey. You can drink weak tea (with milk, cream), rosehip infusions and a decoction of wheat bran.
Table No. 1A provides for the exclusion of secretion agents and mucosal irritants from the diet: any broths, sour drinks and juices, fermented milk drinks, any vegetables, coarse cereals and bread.
Food should be light and easily digestible, so mushrooms, tough meat with tendons, poultry and fish skin are not allowed. Eating excessively cold and hot foods is not allowed. Because sharp food temperatures have an adverse effect on the mucous membrane and slow down the regeneration processes of the mucous membrane.
After a week, as the condition improves, the patient can be transferred to Table No. 1B . This table is less restrictive and gradually increases the content of nutrients and calories. The cooking methods and the main list of products remain the same, but dried wheat bread, vegetable and fruit purees are added (can be used for baby food). Instead of slimy soups, pureed soups are used, and meat and fish can be used to make quenelles, purees and cutlets.
During the recovery period after an exacerbation, as well as during mild exacerbation, patients are prescribed moderately gentle and physiologically nutritious nutrition - Table No. 1 . Previously, there were recommendations for a patient to remain on this therapeutic diet for a long time (up to six months). However, if you feel well, the time spent on Diet No. 1 is reduced to 2-3 months.
The absence of strong irritants in food (meat, mushroom broth, fish soup, strong tea, fried foods, coffee, carbonated drinks, marinades, mustard, alcohol) creates conditions for successful treatment and a long relapse-free period.
The diet is expanded by not pureed food and raw vegetables and fruits are added (sweet plums, apples, apricots, peaches, nectarines, and tomatoes). When carrying out anti-relapse treatment in the autumn-spring periods, you should again switch to gentle nutrition for 2-4 weeks (first Table No. 1B , and then No. 1 ).
A perforated ulcer (the formation of a through defect in the wall of the duodenum) is one of the most dangerous complications, since the contents of the intestine enter the abdominal cavity and cause peritonitis . This condition is considered urgent and surgical intervention is indicated. In most cases, the perforated ulcer is sutured.
After surgery for a perforated ulcer, the diet is very gentle; dishes are steamed without oil or salt. Dishes high in carbohydrates are kept to a minimum, liquid intake and portion sizes are limited.
- the first two or three days - hunger;
- from the fourth day, rosehip decoction, weak tea, fruit jelly with a small amount of sugar are allowed;
- from the fifth day, pureed liquid rice or oatmeal, pureed vegetable soup, soft-boiled eggs are introduced;
- from the seventh day - vegetable puree, soufflé and chicken cutlets and boiled chopped fish.
Actually, this is the diet of Tables No. 1A and No. 1B , the timing of which is strictly individual and depends on the condition of the postoperative patient. After 10-14 days, the patient is transferred to dietary Table No. 1 , which will be discussed below. Food should only be consumed warm, as cold foods take a long time to digest, and hot foods irritate the mucous membranes. The amount of food consumed decreases. Frequent meals up to 5-6 times a day are recommended. Basic cooking techniques - boiling, stewing.
Since stomach and duodenal ulcers tend to worsen seasonally, special attention should be paid to nutrition in the spring and autumn. During this period, it is better to abandon foods that provoke exacerbation (spicy, smoked, deep-fried) and switch to light foods that do not irritate the mucous membranes. It is important to follow a diet and avoid long breaks between meals.
The diet for stomach and duodenal ulcers is based on the same principles. The most suitable diets in the autumn-spring periods, depending on the severity of the exacerbation, are No. 1B or No. 1 . Perhaps during this period the doctor will prescribe you to take medications, although preventive anti-relapse treatment is now being abandoned. It is better for patients to keep an observation diary and note the factors that provoke exacerbations (stress at work, exams, dietary errors, etc.).
Diet No. 1
Follow table 1. Diet No. 1 is the recommended standard for patients with peptic ulcer disease. During the period of exacerbation, for ten to fifteen days, adhere to “table 1a”, which involves eating foods in liquid or jelly form.
In the future, it is recommended to switch to “table 1b”, which corresponds to pureed and mushy food. During the period of stable remission, one should be guided by the rules of the standard “diet 1”, which provides for the loose consistency of products, their consumption in grated or well-chopped form.
What can you eat?
Your diet should consist of foods that allow the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid in smaller doses.
Allowed foods for stomach ulcers:
- Bread: 1st and 2nd grade wheat, stale, crackers, dry biscuits.
- Dairy products: milk, cream, non-sour kefir, yogurt, non-sour cottage cheese and dishes made from it (cheesecakes, dumplings, casserole, pudding), non-sour sour cream.
- Meat: chicken, turkey, beef, veal. Chopped meat is better - cutlets, meatballs, boiled or baked meatballs. You can eat it as a whole piece, but boiled.
- Soups: vegetable, pureed, in a slimy broth with the addition of boiled vegetables; milk soups; soups with the addition of pureed meat, oatmeal soup, rice soup, with pureed cereals.
- Vegetables: zucchini, pumpkin, beets, carrots, cauliflower, potatoes. Better boiled or stewed.
- Fish: low-fat varieties - pike perch, perch, pike, cod, hake, navaga, etc. boiled, baked, in whole pieces or in the form of cutlets, in jellied fish.
- Eggs: up to 2 times a day, soft-boiled, in the form of a steam omelet or eggs in dishes.
- Mild cheese, grated.
- Greens: parsley, dill, etc.
- Porridge: semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat, rice, ground cereal.
- Pasta, vermicelli, boiled in water or milk.
- Ripe fruits and non-acidic berries: strawberries, raspberries, wild strawberries, baked apples or in the form of puree, jelly, compotes.
- “Doctorskaya” sausage, milk sausages.
- Unsalted butter with sandwiches or in dishes, vegetable oil - without frying.
- Sweet dishes: jelly, honey, jam, preserves, marshmallows, marshmallows.
- Warm mineral waters (all hydrocarbonate) are recommended, 50-100 ml 1.5 hours before meals.
- Drinks: weak tea with milk, vegetable juices (carrot, apple-carrot), juices from sweet fruits and berries 1:1 with water, rose hip decoction.
Is it possible for a peptic ulcer...
Drink soda?
Many patients take soda to relieve heartburn and discomfort. Soda can neutralize the effect of hydrochloric acid, which is produced in large quantities during peptic ulcers. But a vicious circle arises: as soon as the soda leaves the stomach and goes into the duodenum, the body produces a new portion of acid in even larger quantities. In addition, when soda and hydrochloric acid interact, carbon dioxide is produced, which swells the walls of the stomach, and this is a danger of perforation. Therefore, soda is prohibited.
Smoking?
Smoking is prohibited if you have an ulcer, since tobacco smoke has an irritating effect on the gastrointestinal tract and provokes an increase in the symptoms of the disease - pain, belching, heartburn. Nicotine enters the stomach and with saliva, slows down the scarring of the ulcer, inhibits regeneration, and also irritates the mucous membrane and intestines in the same way as food, i.e. activates the production of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. If the stomach is empty, the mucous membrane will suffer from the aggressive action of gastric juice. If you smoke on a full stomach, the activity of the digestive glands and motor function will also increase, which leads to the release of gastric contents into the esophagus, especially in people with cardia deficiency. A sad statistical fact is that smokers suffer from this disease 5 times more often than non-smokers.
Smoking an electronic cigarette?
The E-cigarette, which is positioned as safe, is also prohibited. Patients who do not adhere to this advice will agree that “safe smoking” results in heartburn, belching, dryness and a sour taste in the mouth. The vapor that occurs when smoking is by no means so safe and contains many harmful substances (and, according to studies by Japanese and American scientists, carcinogens). Harmful chemicals settle in saliva and enter the stomach when swallowed.
Drink alcohol?
Some people claim that vodka, cognac and other strong drinks speed up the healing of stomach ulcers and reduce pain. However, doctors are categorical on this issue - alcohol is prohibited. Any alcohol, be it 20-year-old whiskey or cheap brandy, increases inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, increases the acidity of gastric juice, and slows down motor function. Alcohol often causes exacerbation of the disease and provokes gastric bleeding.
Cheese
A healthy dairy product with a lot of protein and calcium can be introduced into the diet during the remission stage. Unleavened cheeses with a fat content of about 15% are allowed: ricotta, feta, Arla Oltermani, Viola Polar. But fatty varieties of cheese are prohibited.
Kefir
The fermented milk product is rich in amino acids, vitamins (water- and fat-soluble), enzymes, macroelements and minerals, therefore it has high value for the body and is quickly absorbed by the digestive system (3 times faster than milk). In the stage of stable remission, you can drink kefir: fresh, not sour (for example, for children), slightly warmed, no more than 1 glass per day. In the acute period, kefir is prohibited.
Milk
Without exaggeration, milk can be called the number one product for peptic ulcers. Milk coats the gastric mucosa, relieves pain and discomfort, and also eliminates heartburn. Pasteurized low-fat cow's milk is allowed. Nutritionists also advise patients to drink goat’s milk without heat treatment, but first dilute it by half with boiled water.
Butter
You can add oil to dishes, the main requirement is natural and fresh. With butter, the recommendation about low-fat dairy products is not relevant: you just need to buy high-quality butter with high fat content (82.5%), but use it as an additive to porridge in limited quantities. But inexpensive, low-fat oils most often contain a milk fat substitute.
Sea buckthorn oil
This useful product can be purchased at the pharmacy. Sea buckthorn has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect, accelerates the healing of ulcerative defects and gently envelops the mucous membrane. You can take 1-2 tbsp. sea buckthorn oil per day, before meals.
Eggs
Chicken eggs are included in the list of foods that you can eat: the protein is rich in low-calorie fats, proteins, amino acids and is quickly absorbed by the body. The yolk is rich in vitamins (D, E, A, B) and minerals and emulsifying fats. During the period of remission, you can use 2 pcs. eggs a day (D-0) soft-boiled or as a steam omelet. Raw eggs on an empty stomach are also useful - they create a protective film on the gastric mucosa, but doctors do not recommend this option of consumption, since the risk of salmonellosis infection is high. No less useful are quail eggs, which suppress pain, relieve inflammation, are completely absorbed by the body, and have an antibacterial effect. Recommendations for consumption are the same, 4-5 quail eggs per day.
Tea
During the period of remission, you can drink weak black, green tea with milk, herbal tea (if there is no allergy), you can use herbal teas from the pharmacy, which are called stomach teas. Strong black tea is rich in theophylline, which activates the production of hydrochloric acid, i.e. increases acidity and you can’t drink it when it’s strongly brewed.
Coffee
People who cannot imagine their life without an invigorating aromatic cup will have to give up coffee (natural and instant) if they are diagnosed with a stomach ulcer. A hot drink irritates the gastric mucosa and increases existing inflammation. Coffee is saturated with chemicals that cause an increase in hydrochloric acid levels. Immediately after drinking coffee, heartburn occurs, a nagging pain in the stomach. In the stage of stable remission, when the ulcer has already healed, you can drink natural coffee with milk once every 7-14 days, but not on an empty stomach. An alternative option is chicory, but, again, only with the permission of a gastroenterologist.
Nuts and seeds
Rich in vitamins, minerals, unsaturated fatty acids, seeds and nuts are prohibited at any time during the course of the disease: they irritate the stomach wall, cause heartburn and take a long time to digest. In addition, hard pieces injure the mucous membrane.
Bananas
The fruit is included in the list of permitted and even recommended products. Banana pulp envelops the gastric mucosa, improves digestion, reduces acidity, and has high nutritional value. Some researchers claim that bananas contain a substance that has a detrimental effect on Helicobacter pylori. Bananas must be ripe, preferably chopped.
Cabbage
White cabbage, including early cabbage, is contraindicated because it contains indigestible fiber, increases gas formation, irritates the mucous membrane, and slows down healing. But cabbage juice during remission is possible and even necessary!
Beetroot
The vegetable is rich in hard-to-digest fiber and contains a number of natural acids that increase the pH of gastric juice. You can’t eat beets during the acute period, but during the period of remission you can, not a lot. There is evidence of the benefits of beetroot juice, which can be carefully included in the diet, diluted with water 1:1 and in a small amount, after letting it sit for 3 hours.
Pepper
Both hot and bell peppers are prohibited. Everything is clear about hot peppers, but sweet peppers contain a substance with an irritating effect - the alkaloid capsiacin. Pepper also provokes the production of hydrochloric acid.
cucumbers
Most experts unanimously prohibit cucumbers in any form both during the period of exacerbation and during the period of remission, since they increase acidity. But in the absence of increased acidity during the period of remission, you can eat young fresh cucumbers without skin in crushed form, for example, grated on a coarse grater, no more than 200 g. per day.
What can't you eat?
We exclude products that especially increase the release of hydrochloric acid. Prohibited foods for ulcers:
- Fresh rye and white bread, puff pastry and pastry products; it is better to eat dried bread.
- Fatty, stringy meats (pork, duck and goose).
- Strong meat, fish broths, mushroom and strong vegetable broths.
- Vegetables: white cabbage, onions, cucumbers, rutabaga, turnips, sorrel, radish, spinach, pickled and pickled vegetables.
- Smoked and fried foods, fried fatty, salted fish, canned food.
- Sour, unripe berries; sour dairy products.
- Ice cream, chocolate.
- Cereals: millet, corn, pearl barley.
- Fried and hard-boiled eggs.
- Spicy, salty snacks, smoked meats, canned food.
- Fat: lamb, beef, pork.
- Fried foods.
- Carbonated drinks, kvass, strong tea, black coffee.
- Spicy meat, mushroom, tomato sauces, spicy cheese, pepper, vinegar, garlic, mustard, horseradish.
Diet after surgery
The standard recommendation is to fast for up to two days for the initial healing of the sutures. In the future, the following requirements are adhered to.
- On day 3. The patient can eat in accordance with the 0a diet, provided that he does not have bloating. Meals are split, up to seven times a day. The consistency of the dishes is exclusively liquid or in the form of jelly. The first meal should be the smallest, in the amount of one teaspoon. In this quantity, the patient is offered hourly juices diluted with water, fruit jelly, and weak meat broth. Over the course of two days, the volume of a single serving is increased and the patient is transferred to six to seven meals a day.
- On day 6. Gradual expansion of the diet and bringing it to the standard diet of table No. 1 by introducing pureed porridges, slimy soups, soft-boiled eggs or in the form of a steam omelet.
The diet should contain the maximum amount of protein components and vitamins, while carbohydrates, especially simple ones, should be kept to a minimum. This will allow you to saturate the diet with the spectrum of nutrients necessary for the patient in a small portion size.
Products that have a healing effect
There are three products available that have a healing effect.
- Fresh potato juice. A simple superfood that can be used for healing. It has regenerating, wound-healing, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Potato juice also destroys pathogenic flora that is present in the stomach. Prepare juice from fresh, high-quality potatoes and drink immediately. Take outside the period of exacerbation, half an hour before meals, for 3 weeks in a row. Volume: start with a few spoons, increase to 150 ml per day. It is better to take it diluted with water, 1:1.
- Low fat milk. Envelops the walls of the stomach, protects the organ from the aggressive effects of foods and gastric juice, accelerates the regeneration process, dulls or even relieves pain.
- Honey. You can eat honey in small quantities every day: the product is rich in microelements, vitamins, and has a beneficial effect on the entire gastrointestinal tract. As for the ulcerative process, honey helps relieve inflammation, reduces secretion, neutralizes the effect of hydrochloric acid, and relieves pain. Honey reduces nausea and heartburn inherent in the disease, and increases the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Fresh cabbage juice. Contains a stable form of ascorbic acid and anti-ulcer vitamin U. The juice has been proven to be effective in accelerating wound scarring and against Helicobacter pylory.
They can be included in the list of dishes, the only caveat is about cabbage juice: you can drink it freshly prepared, diluted with water (1:1), no more than 100 ml at a time, 2-3 times a day. The most important thing is only during the period of remission!
Menu during an exacerbation period
During the acute period of the disease, you must carefully monitor your diet. Steam or boil food; sometimes you are allowed to bake food. Use a slow cooker - you can use it to make many tasty and healthy dishes that do not contradict the principles of therapeutic nutrition.
- First breakfast. A few soft-boiled eggs, wash down with a glass of milk. Instead of milk, you can drink herbal tea.
- Lunch. Weak herbal tea, fruit juice or milk, fruit for a snack - a baked apple, banana or peach.
- Dinner. Oatmeal soup or oatmeal. As an option, you can use steamed chicken soufflé, as well as fruit or berry jelly.
- Afternoon snack. Creamy curd dessert, vitamin infusion with rose hips. If you want something sweet, you can eat low-fat yogurt.
- Dinner. Milk porridge with rice (pre-mashed), one glass of milk. Another option is vegetable puree or boiled chicken breast.
- After dinner. Before going to bed, it is recommended to drink a glass of milk again, do not eat anything else, so as not to burden the stomach.
Sample menu
Diet for 2 days, designed for 1 person. Portion sizes are approximate. You can reduce or increase them, depending on how you feel.
- Breakfast: sandwich (white wheat bread with butter) - 1 piece; yogurt - 100 g; mineral water without gas - 200 ml.
- Second breakfast: soft-boiled eggs - 2 pcs.; rice porridge - 150 g; fruit puree - 100 g; milk - 200 ml.
- Lunch: chicken soup - 250 ml; cutlet; boiled pasta - 100 g; white bread - 1 slice; fruit soufflé - 100 g; applesauce - 100 g; dried apricots (soaked in water) - 3 pcs., milk - 200 ml.
- Afternoon snack: steam cutlet - 150 g; mashed potatoes - 150 g; white wheat bread - 1 slice; raisins (soaked in water) - 40 g; rosehip decoction - 200 ml.
- Dinner: boiled beef - 150 g; soft-boiled eggs - 2 pcs.; vegetable salad - 150 g; white wheat bread - 1 slice; fruit jelly - 100 g; milk - 200 ml.
Second day:
- Breakfast: sandwich – 1 pc. mineral water without gas – 200 ml.
- Second breakfast: steam omelette of 2 eggs; semolina porridge – 150 g; tea with sugar – 200 ml.
- Lunch: vegetable soup - 300 ml; beef meatballs - 1 50 g; green peas - 100 g; jacket potatoes - 100 g; white wheat bread - 1 slice; fruit jelly - 100 g; tea without sugar - 200 ml.
- Afternoon snack: oatmeal porridge - 200 g; white wheat bread - 1 slice; milk - 200 ml.
- Dinner: boiled fish - 150 g; vegetable puree - 100 g; soft-boiled egg - 1 pc.; white wheat bread - 1 slice; milk - 200 ml.
If the peptic ulcer is quite severe and you are experiencing severe pain, it is best to stick to the above menu.
Nutrition during recovery
The principle of any therapeutic diet for peptic ulcers is as follows: the menu should include food that does not affect the walls of the affected internal organs either chemically, thermally, or mechanically. If you feel pain after eating any food, remove it from your diet.
- First breakfast. Omelet or steamed eggs prepared using two eggs or semolina with milk. Wash it down with a glass of milk.
- Lunch. Weak tea, milk or warm creamy cocoa. You can snack on fruit: banana or peach.
- Dinner. Milk soup with crushed rice, a piece of steamed meat, a small portion of mashed potatoes. For dessert - fruit jelly.
- Afternoon snack. A glass of rosehip infusion, a few crackers. Also eat jelly or cheesecake if you want something sweet.
- Dinner. Steamed curd soufflé, fruit jelly or fruit drink. Another option: rice patties with chopped lean beef or stewed zucchini.
- After dinner. Milk, a light salad of prunes and boiled mashed beets.
A properly chosen diet restores gastric secretion, relieves inflammation and irritation of the mucous membrane of damaged internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract, and also promotes rapid and painless healing of peptic ulcers. Use the tips described above and you will be able to help your body fight the disease and avoid possible negative consequences.
What are the beneficial qualities of nuts for ulcers?
Various nut fruits consist mainly of oils that regulate tissue metabolism. Strengthening metabolic processes helps to quickly restore damaged cells, including those damaged due to the formation of ulcers.
A diet for stomach damage involves light meals containing plenty of fluid. Many people do not get enough of this food and remain hungry, which negatively affects their well-being. In this case, crushed nuts for ulcers are an ideal food component, since they are quite filling and nutritious, and most importantly, healthy.
The vitamin and mineral composition contained in the fruits enriches the body and heals it, which is necessary for a person to live a normal and fulfilling life.
Nuts are rich in their composition, which is necessary to restore normal blood flow. In case of illness, blood flow helps to carry oxygen to damaged tissues for their rapid recovery.
Cooking recipes
The range of permitted and prohibited foods for duodenal ulcers is only at first glance frightening with a large number of changes in the usual diet. Dietary food is a special section of cooking. From a simple set of products it is easy to prepare many tasty and healthy dishes. The main thing in this case is to adhere to the rules for processing and consuming individual ingredients. Here are some delicious and easy recipes:
- Diet pumpkin pudding. To prepare the dish you will need: 150 g pumpkin pulp, 10 g semolina, 10 g honey, 20 g low-fat milk, 140 g apples, 2 eggs. Grind the apples and pumpkin in a blender. Add semolina and milk, bring the mixture to a boil. Add honey and beaten eggs to the prepared mixture. The pudding should be prepared by steaming or in a slow cooker.
- Oatmeal with pumpkin. For 1 cup of rolled oats, prepare 2 cups of skim milk, 1 cup of finely grated pumpkin pulp, butter, two tablespoons of honey. Boil oatmeal with milk until tender. Mix the porridge with pumpkin and leave the mixture for 10-15 minutes, covering the pan with a lid. Add a small amount of butter and also honey.
- Vegetable cream soup. To prepare this dish, prepare the following ingredients: potatoes, carrots, turnips, skim milk, butter. Select the quantity of ingredients at your discretion. Boil all vegetables and chop in a blender. To dilute the mixture to a puree consistency, use vegetable broth and milk. Before eating the soup, place a small piece of butter in the plate.
The duration of a gentle diet depends on the general well-being of the patient. If therapy proceeds without complications, there is a tendency towards recovery, and you can adjust your diet after three to four months. The standard duration of diet therapy is six months.
Pros and cons of diet No. 1
From a medical point of view, the diet has no disadvantages. Gastroenterologists recommend it for various gastrointestinal diseases - as practice shows, such a diet reduces the load on the digestive system, speeds up recovery and improves well-being. The correct diet allows you to take control of the disease, i.e. live fully with a chronic disease and minimize drug therapy.
A very conditional disadvantage is the fact that certain foods and drinks must be abandoned, but patients who have at least once experienced an exacerbation of an ulcer due to a diet failure and have known all the “delights” of this condition can easily make the right choice. Of course, you will have to cook for yourself separately from the whole family, think through the menu and diet, but this is also a gainful endeavor: 2-3 weeks, and such nutrition will become the norm of life!
Author:
Sabuk Tatyana Leonidovna hygienist, epidemiologist