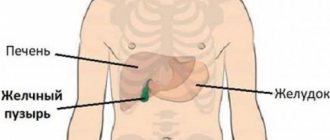
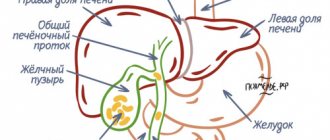
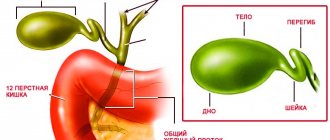
Gallbladder cancer is a rare cancer. Together with malignant tumors of the bile ducts, it is combined under the term “cholangiocellular carcinoma.” In Russia, no more than 4,000 cases of this disease are diagnosed annually. Women get sick more often than men, and the peak incidence occurs in older age groups.
Our expert in this field:
Ryabov Konstantin Yurievich
Chief surgeon, oncologist, endoscopist
Call the doctor
The Medicine 24/7 clinic provides comprehensive treatment for cholangiocellular cancer, radical and palliative interventions of any complexity are performed. Our clinic employs leading hepatologists and surgeons. We accept patients with any stage of malignant tumor.
Causes, risk factors
The most significant risk factor is cholelithiasis. According to statistics, 80% of patients with malignant tumors of the gallbladder have it. Other risk factors:
- Porcelain gallbladder is a condition in which calcification occurs and calcium salts are deposited on the wall of the organ. The cause may be chronic cholecystitis.
- Overweight, obesity.
- Age: The disease is most often diagnosed in people over 65 years of age.
- Female.
- Common bile duct cysts are protrusions in the form of sacs on the wall of the bile duct.
- Polyps in the gallbladder are the most dangerous if they have a diameter of more than 1 cm.
- Anomalies in the development of the bile ducts.
- Chronic infection caused by salmonella.
- Family history: if there are close relatives who have already been diagnosed with cancer in the gallbladder.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis is an inflammation of the bile ducts that leads to the growth of scar tissue.
- There is also some evidence of the influence of risk factors such as smoking and contact with certain harmful substances in workers in various industries.
Types and manifestations of pathologies
There are different forms of RBD depending on where they are located and what they look like:
- Infiltrative cancer is the most common form. It has an irregular shape and also spreads into the wall of the organ.
- Nodular - looks like small round lumps. It often grows through the wall of the organ.
- Papillary - grows into the organ cavity. It looks like a small nipple or cauliflower.
The most common type of gallbladder cancer is adenocarcinoma. It accounts for more than 90% of all cases. There are several subtypes of this tumor, including:
- biliary adenocarcinoma;
- intestinal type adenocarcinoma;
- papillary adenocarcinoma.
Papillary adenocarcinomas spread less frequently than other types of adenocarcinomas, so they tend to have a better prognosis.
Rare types of gastric cancer include squamous cell carcinoma, sarcoma, lymphoma, melanoma, carcinoid, and neuroendocrine cancer.
Symptoms of the disease
The first symptoms of gallbladder cancer are usually: loss of appetite, pain in the liver, nausea, vomiting. These manifestations are nonspecific; most often they indicate cholelithiasis, and this is one of the reasons for late diagnosis.
Late signs of gallbladder cancer:
- Jaundice occurs in 44% of patients.
- Aversion to food.
- Skin itching.
- Enlargement of the abdomen due to enlargement of the liver and gall bladder, ascites - pathological accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- Fever.
If you are bothered by similar symptoms, you need to visit a doctor. At the Medicine 24/7 clinic you will be seen by a highly qualified specialist. With us you can quickly go through all the necessary diagnostic methods, receive an accurate diagnosis and immediately begin treatment.
Our doctors will help you
Leave your phone number
Diagnostic methods
In clinical practice, there are often situations when an intervention is performed for gallstone disease, the gallbladder is removed, and only after that tumor cells are discovered in it.
The simplest, fastest and most accessible diagnostic method for suspected liver and gallbladder tumors is ultrasound. Often they start with it. Then, during the examination, the following procedures may be prescribed:
- Biochemical blood test and liver function tests.
- Computed tomography, MRI.
- Endoscopic ultrasound (endosonography). During this procedure, a fiber endoscope is inserted into the duodenum, at the end of which there is a video camera and an ultrasound sensor. This helps to better visualize the gallbladder area.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The essence of the method is that during endoscopy of the duodenum, the bile ducts are filled with a radiopaque solution using a thin catheter inserted into them. This helps to identify places of tumor stenosis (narrowing) of the bile ducts.
- If ERCP cannot be performed, percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography is performed: contrast is administered using a needle inserted through the skin.
- In some cases, diagnostic laparoscopy is indicated - examination of the gallbladder and neighboring organs using a laparoscope inserted through a puncture in the abdominal wall.
A biopsy for gallbladder cancer is often performed after surgery, after the organ has been removed. Before surgery, it can be performed in different ways: during ERCP, laparoscopy, using a needle inserted through the skin (puncture biopsy).
Treatment
Surgery
Treatment of gallbladder cancer with surgery remains the most effective method. The type of surgery will depend on the size and location of the tumor, as well as its spread.
If the growth is only near the area where it started, it may be possible to remove it completely. If it has spread beyond the bladder, it is removed (cholecystectomy). If there has been spread to other tissues around the organ, the gallbladder and other tissues will be removed.
If the tumor has spread to other parts of the body, it may not be possible to completely remove the pathology.
Surgery may also be done to relieve symptoms of advanced breast cancer, such as a blocked bile duct. This may involve inserting a stent to open a blocked duct or creating a shunt to drain bile blocked by a tumor.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy may be used to relieve symptoms of advanced gastric cancer. Sometimes radiation therapy may be given after surgery (called adjuvant radiation therapy).
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. May be done after surgery (called adjuvant chemotherapy treatment). If surgery cannot be performed or gallbladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, you may be given chemotherapy. Can be used alone or in combination with radiation therapy.
Gallbladder cancer stages
To determine the stage of gallbladder cancer, the international TNM system is used, which takes into account the characteristics of the primary tumor, the presence of foci in regional lymph nodes and distant metastases.
The following stages of the disease are distinguished:
- Stage 0: cancer is “in situ” and has not penetrated beyond the lining of the organ.
- Stage I: The cancer has spread into the lamina propria or muscle layer of the organ wall.
- Stage II: The cancer has spread beyond the muscle layer but has not invaded adjacent organs.
- Stage IIIA: Cancer has spread to the peritoneum, liver, or other nearby organs.
- Stage IIIB: tumor foci in the lymph nodes adjacent to the gallbladder.
- Stage VIA: Cancer has spread to the hepatic artery, portal vein, or two adjacent organs at the same time; there may be lesions in nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IVB: The cancer has spread to the paracaval, para-aortic, superior mesenteric, or celiac lymph nodes, or there are distant metastases.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Treatment of gallbladder cancer at the Medicine 24/7 clinic
Treatment tactics are selected in accordance with the stage of the malignant tumor, the general health of the patient, and concomitant diseases are taken into account. At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, decisions are made at medical councils, which involve clinical oncologists, surgeons, chemotherapists and other specialists.
Surgery
In the early stages, radical surgery is possible: cholecystectomy is performed - removal of the gallbladder. Along with it, nearby lymph nodes, part of the liver, and other neighboring organs can be removed if they are affected by a malignant tumor.
After surgery, adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be prescribed.
If radical surgery is not possible, palliative operations can be performed to restore the flow of bile:
- At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, all types of drainage are performed - diversion of bile through a tube installed in the bile ducts: external, external-internal, nasobiliary.
- Stenting is an endoscopic procedure during which a stent is installed in the bile ducts - a frame in the form of a tube with a mesh metal wall.
- Bypass surgery is a laparoscopic operation during which an artificial connection is created between the gallbladder, bile duct and duodenum.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for gallbladder cancer is used after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to prevent recurrence, as the primary treatment for advanced cancer, and as palliative therapy to control pain and other symptoms. Currently, the possibilities of using more modern antitumor agents—targeted drugs, immunotherapy—in the treatment of cholangiocellular carcinomas are being actively studied.
The Medicine 24/7 clinic uses all types of modern antitumor drugs. When drawing up a treatment regimen, our doctors are guided by the latest versions of international protocols.
Chemotherapy without side effects!
Book your consultation today
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy for gallbladder cancer is used for the same indications as chemotherapy. Modern devices make it possible to generate radiation that exactly matches the outline of a malignant tumor in the gallbladder and causes virtually no harm to surrounding intact tissues.
Oncological center in Moscow
Oncology Center in Moscow ¦ Gall Bladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer is a rather rare disease in which the malignant tumor affects the walls and deeper tissues of the organ. According to statistics, the incidence of gallbladder cancer occurs in 2.8% of cases of the total number of diseases. Among the variety of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract, it ranks sixth. It should be recalled that the gallbladder is a small organ located downstream of the liver and connected to it by the bile ducts. The bladder accumulates bile, necessary for normal digestion, which subsequently enters the small intestine. The gallbladder wall has three layers: mucous, muscular, and serous. The tissues of these layers are connected to each other in the form of connective tissue. Cancer, as a rule, begins to develop in the inner serous layer, growing and affecting further areas.
Doctors note that there is a direct relationship between the development of cholelithiasis and the likelihood of developing gallbladder cancer. This trend is especially noticeable in developed countries. In approximately 80%, or even 100% of cases of detection of a gallbladder tumor, the patient has cholelithiasis. Chronic inflammation and the presence of constant irritants in the gallbladder do not go away without leaving a trace, and in many cases serves as an impetus for the development of cancerous tumors. This disease most often occurs in women, especially after 50 years. They are the risk group that requires regular examinations. Despite the difficulties that arise due to the rather inconvenient location of the organ for examination (it is almost completely covered by the liver), the center’s specialists will be able to carry out an accurate diagnosis and confirm or refute the assumption of cancer.
Who is at risk?
As mentioned above, women are most susceptible to gallbladder cancer. A person’s age, as well as his lifestyle and diet, also make a negative contribution here. The risk of cancer also increases if the patient has chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and the presence of stones. Persons who have previously had cancer of other organs should pay special attention to their health; there is a very high risk of recurrence of the disease. Also, we should not forget about heredity. Often, in families where cancer has previously occurred, a genetic predisposition to cancer develops. All these people need to periodically check their condition.
Symptoms of gallbladder cancer
Most often, gallbladder cancer develops in patients with cholelithiasis, therefore, when visiting a doctor, such patients note that the nature of the pain that bothered them before has changed over time, the breaks between painful sensations gradually disappear, and the drugs prescribed to treat the disease have ceased to do their job. function. Such complaints become a reason for further serious examination. If the patient has not previously suffered from chronic diseases of the liver, gallbladder or ducts, then, against the background of a general disruption of the stomach and small intestine and, as a consequence, loss of appetite, painful sensations develop in the subchondral region on the right. Against the background of these symptoms, the temperature may rise significantly and the so-called “cancer fever” may appear. However, it is not uncommon for the disease to remain asymptomatic for a long time. This, of course, is fraught with great danger, since the course of the disease can go too far. Among other symptoms, one can note an enlargement of the gallbladder itself; sometimes the tumor can even be felt by palpation. Due to increased blood pressure, the liver may also enlarge. As a rule, this does not cause pain. An indirect symptom indicating a malfunction of the gallbladder and the possible development of cancer can be increasing pressure on the veins adjacent to the liver. Prolonged compression of blood vessels can cause swelling of the legs or ascites.
Diagnosis of gallbladder cancer
As already noted, diagnosing gallbladder cancer is not easy, the situation is especially complicated by the fact that the early course of the disease is characterized by virtually no symptoms. And in the presence of cholecystitis or other chronic diseases of the liver or bile ducts, the picture is completely blurred. Only in later stages does cancer manifest itself with common symptoms: weight loss, anemia, loss of appetite and fatigue. In addition, an overgrown tumor can put pressure on the liver, it increases in size, obstructive jaundice and ascites occur.
Among the most accurate diagnostic methods is laparoscopy, during which it is possible to collect biological materials for further histological and cytological examination, as well as determine the size of the tumor, the degree of its growth and the presence of metastases.
In addition, for the primary diagnosis of the disease, the following is carried out:
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder and abdominal organs. This method is widely used when examining patients because it has a number of advantages. This includes the absence of harm to the patient, the absolute painlessness of the procedure, which does not cause any complications, and a fairly high level of information content. In addition, ultrasound allows you to make puncture sampling more accurate.
- CT scan. It allows you to obtain images of both healthy and affected areas of the body, which is especially important in the presence of distant metastases. In addition, when performing a CT scan, a contrast agent is often injected into the patient’s circulatory system, which makes the study even more accurate.
- Blood test to detect carcinoembryonic antigen. In itself, an increase in the level of these antibodies in the blood does not indicate an inevitable oncological disease, but in combination with other symptoms it gives rise to further research.
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography. This method allows you to get a general picture of the condition of the gallbladder and the corresponding ducts. Its essence is to insert a thin needle into the liver and inject a contrast agent. After this, a series of images of the liver, gallbladder and connecting bile ducts are taken. If normal bile circulation is impaired, bile drainage should be performed using a stent before cholangiography. The procedure itself is carried out under ultrasound guidance.
Gallbladder cancer stages
The following stages are distinguished:
- The zero stage, in which cells with an altered structure can become malignant; they are scattered in nature and are located in the inner layer of the gallbladder wall. At this stage, active damage to healthy cells begins.
- First stage. At the first stage, the formation of the tumor itself occurs. This can be roughly divided into 2 stages. In the first stage, tumor cells invade the inner layer and the layer of connective tissue, while the muscle layer is not affected. At the second stage, the tumor grows further, affecting the muscle tissue and the next connective layer.
- Second stage. It is also divided into 2 stages. Initially, the tumor affects the visceral peritoneum, that is, the tissue that covers the gallbladder, and neighboring organs may be affected: liver, small intestine, large intestine, pancreas. The tumor then grows into nearby lymphatic vessels and organs.
- The third stage is characterized by damage to the main blood vessel of the liver, from where infected cells can be spread throughout the body.
- At the fourth stage, distant lymphatic vessels and organs are affected.
Treatment of gallbladder cancer
To prescribe adequate treatment, the tumor is conventionally divided into two forms. The first is characterized by the concentration of cancer cells in the walls of the gallbladder. In this case, surgery is prescribed. If the tumor grows further, it becomes unresectable, and other methods of helping the patient are thought through.
Our cancer center uses three standard treatment methods: tumor resection, radiation and chemotherapy.
The greatest effect in treating gallbladder cancer, of course, comes from surgical removal of the tumor, as well as nearby tissues and lymph vessels. The operation itself is called cholecystectomy and is performed using a laparoscope. During the operation, both the gallbladder itself and the healthy tissue surrounding it are removed; to prevent diseased cells from infecting the areas where the incisions were made, resection of these tissues is also performed. Thanks to the use of advanced technologies in our center, the operation can be performed through minimal incisions, which can significantly reduce blood loss and speed up the patient’s recovery process.
Radiation therapy can be used as an independent type of treatment or in combination with surgery, for example, when it is necessary to significantly reduce the size of the tumor. Thanks to the high-frequency effect on cancer cells, it is possible to stop their reproduction, and therefore the growth of the tumor. There are external and internal radiation therapy. When carrying out external therapy, the tumor is exposed to a device that emits radioactive rays. For internal therapy, radioactive substances are delivered to the gallbladder using a special catheter.
Chemotherapy, courses of which are carried out at the oncology center, is divided into general and local. During general therapy, medications are introduced into the circulatory system of the patient’s body and distributed to all organs and tissues, including those affected by cancer. This allows for a comprehensive effect on both the affected organ and neighboring ones, which helps prevent the development of metastases and tumor growth to other areas. In addition, regional chemotherapy is possible, in which chemicals are delivered precisely to the affected cells. The advantage of this type of procedure is the reduction of the harmful effects of drugs on healthy organs, as a result, maintaining satisfactory well-being of the patient. In addition, in our clinic, radiosensitizers are used to increase the response of malignant cells to the action of drugs.
Survival Projections
It should be remembered that gallbladder cancer is a completely curable disease if the tumor is concentrated in the walls of the organ itself. In this case, timely surgery to remove the gallbladder can save the patient and return him to normal life. In later stages, surgery becomes impossible, however, even here our specialists select suitable palliative treatment that can significantly improve the patient’s standard of living.
(495) 506-61-01 — urgent organization of treatment in the clinic
REQUEST TO THE CLINIC
Survival prognosis
The five-year survival prognosis directly depends on how far the malignant tumor has spread in the body.
If the cancer is located within the gallbladder, the 5-year survival rate is 62%, if neighboring organs or regional lymph nodes are affected - 27%, if there are distant metastases - 2%.
The Medicine 24/7 clinic uses all modern types of cancer treatment at the level of the best foreign clinics. We accept patients with any stages of gallbladder cancer 24/7.
The material was prepared by oncologist, endoscopist, chief surgeon of the Medicine 24/7 clinic, Konstantin Yuryevich Ryabov.