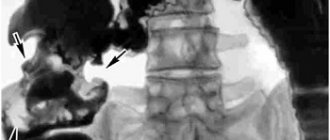
The invention relates to medicine and can be used for direct passage of an endoscope through the Bauhinian valve during colonoscopy. The endoscope is inserted into the dome of the cecum, removed from the lumen of the cecum, and advanced into the small intestine. When the bauhinium valve is in the upper and lower fields of vision, the device is carried out in a translational motion, turning it counterclockwise and positioning the patient on the left side. When the shutter is in the left corner of the field of view, the device is carried out by turning it counterclockwise and positioning the patient on his back. When the shutter is in the right corner of the field of view, the device is carried out without turning and positioning the patient on the right side. The method allows to reduce the period of endoscopic examination.
Insufficiency of the Bauginian valve
articles:
The Bauhinian valve (valva ileocecalis) is a pylorus: it opens and closes, allowing intestinal contents to pass in only one direction. The barrier begins its active functioning when the child reaches the age of 3 years.
The anatomical structure keeps the intestinal contamination in the volume necessary for the full functioning of the body. Insufficiency of the bauginian valve (ileocecal valve) causes bauginitis (actually, its inflammation) or other factors.
To accurately determine the cause, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
Why is pathology dangerous?
The failure of the pylorus causes the reflux of more than a billion microbes from the large intestine into the small intestine. The phenomenon is extremely unfavorable for the condition of the body. There is a dense placement of foreign microflora on the walls of the small intestine. This creates convenient conditions for the progression of the process of rotting and fermentation inside it.
The waste products of pathogens have a detrimental effect on the mucous membrane of the small intestine. These substances include phenol, cresol, carbolic acid, hydrogen sulfide, ethane. Immediately after absorption into the blood, the products provoke the phenomenon of autointoxication.
It is quite difficult for the body to remove them completely; the detoxification process becomes more complicated if a person has liver pathologies. As a result, the intestinal wall undergoes toxic, invasive, destructive changes. But most of all, microbes are predisposed to tissue death.
In the absence of diagnosis and adequate treatment for a long time, the likelihood of degenerative and even necrotic processes within the mucous membrane is high. The intestinal wall loses its barrier function. The body becomes defenseless against microbial aggression.
Causes of development of insufficiency of the bauhinium valve
There are several factors that negatively affect the state and function of the physiological shutter: • Abrupt refusal of a certain type of product. • Severe inflammatory processes of the digestive organs.
• Presence of pathologies of neurological origin. • Congenital malformations of the digestive tract. • Previous surgical interventions or trauma to the abdominal cavity. The exact causes of the disease cannot always be determined.
In this case, the pathology is classified as idiopathic.
Symptoms of insufficiency of the bauhinium valve
With dysfunction of the ileocecal valve, doctors are approached with a variety of complaints. Symptoms are characteristic of 95% of diseases of the digestive system: • Pain syndrome - unpleasant sensations are localized in different parts of the abdominal cavity. • Dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting). • Absence of bowel movements for 3 days (in 25% of patients).
• Loud intestinal motility, ending with the urge to defecate. • Flatulence, tension in the anterior abdominal wall. • Problems with defecation – 75% of patients with this pathology experience diarrhea. • Bitter taste in the mouth, heartburn, gray or white coating on the tongue.
Additionally, patients are concerned about increased fatigue, weight loss while maintaining the same appetite, and insomnia.
Diagnostics
Laboratory tests reveal the presence of dysbacteriosis, as well as nonspecific bacteremia. Taken together, the phenomena indicate that the intestine has become the entry point for infection. Due to the transition of the pathology to a chronic form, lymphoid tissue throughout the gastrointestinal tract is also subject to negative effects. A blood test can detect deficiency of immunoglobulins A and M.
Of the instrumental diagnostic methods, irrigoscopy and manometry
. Normally, the pressure inside the colon is no higher than 10-20 mmHg. Art., during defecation it rises to 200 mm Hg. Art.
In gastroenterology, they focus on the classification of ileocecal valve dysfunction. The system is designed taking into account the results of irrigoscopy: • 1st degree - the reflux of the contrast suspension is visualized only into the terminal loop of the ileum. The stage is characterized by valve enlargement and pain on palpation. Emptying the colon from the contrast mass does not increase retrograde reflux. • 2nd degree - the reflux of the contrast mixture into the ileum occurs simultaneously with the contrasting of 2-3 loops. There is a painful reaction to palpation. Increased pressure inside the lumen does not cause an increase in reflux. • 3rd degree - the reflux of a large volume of contrast suspension into the ileum is visualized. It fills several loops at once and is combined with an enlargement of the lips of the ileocecal valve and deformation of both frenulums. The disadvantages of irrigoscopy are significant radiation exposure to the patient, the lack of clear evaluation criteria and objective indicators of the disorder in question. Cases of false positive results are common. This diagnostic outcome is caused by the peculiarities of the procedure. The dome of the cecum is densely filled with a contrast mixture. As a result, there is a natural opening of the natural shutter. Excessive distension of the cecum is the result of deep palpation, massage and contraction during defecation. There is an assumption that dysfunction of the natural shutter is associated with connective tissue dysplasia. Therefore, we cannot exclude the possibility of developing oncology with insufficiency of the bauhinium valve.
Treatment
Therapy begins with nutritional correction - giving up fried, hard-to-digest foods, sour, spicy, smoked foods. Coffee, alcohol, carbonated drinks are contraindicated. Follow the regime - eat at the same time, at least 4 times a day, in portions of up to 400 g (depending on the type of food).
Limit exposure to stress factors, eliminate neurological disorders if present. Drug treatment is aimed at eliminating primary valve dysfunction.
1. Magnesium orotate
– a drug that is a combination of magnesium and the non-steroidal anabolic orotic acid.
The effect of the medicine is aimed at normalizing the absorption of this microelement by tissues. Magnesium orotate is prescribed orally: dosage – 1.0 g three times a day for 3 months. Then the prescription is adjusted - take 0.5 g 3 times a day for the next 3 months.
Contraindications to the use of the drug are the presence of renal failure in the patient.
2. Drug therapy involves the administration
of Proserin, Coordinax
- to stimulate motor skills by improving the tone of the digestive organs.
3. To relieve nausea (and, accordingly, the urge to vomit), intramuscular administration of Cerucal
.
4. Normalization of intestinal microflora occurs through the use of probiotics
.
5. Vitamins (C, B6, B2)
more often prescribed parenterally (the injection route allows for faster relief of hypovitaminosis).
Absolute insufficiency of the bauhinium valve is an indication for a surgical approach. Operations to normalize the condition of the ileocecal valve in case of its dysfunction are technically simple and safe. Modern surgeons perform them without opening the lumen of the digestive tract, thereby reducing the risk of postoperative complications. A common technique for normalizing the diameter of the ileocecal valve is the application of staples to the lips of the valve during colonoscopy. In 99% of cases, complete clinical recovery occurs. The advantages of this method are that there is no need for heavy anesthesia, and there are no postoperative scars. Frequent anesthesia for the patient is not required (after traditional operations, an analgesic is administered at least once every 2 hours).
Conclusion
Insufficiency of the Bauginian valve is a condition that is difficult to identify without the use of diagnostic methods. It is at a doctor’s appointment, during an examination, that the presence of a disorder is confirmed.
Signs of the disease resemble the manifestations of many other pathologies. The specialist conducts differential diagnostics, prescribes treatment, and gives recommendations regarding nutrition.
The success of therapy largely depends on the professionalism of the gastroenterologist, but the timeliness of seeking medical help plays an important role.
Post-radiation enteritis and proctitis
Radiation therapy is the mainstay in the treatment of both primary and recurrent gastrointestinal and pelvic malignancies. Combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation
In detail Types of colostomy bags and their use
The number of patients requiring artificial fecal diversion is continuously growing. Adequate rehabilitation is vital for these patients, and various
In detail What does NOT help with constipation
Constipation (or constipation) is the stagnation of digested (or partially broken down) food masses in the intestines. The reason is the inability to defecate, which predisposes
In detail Constipation: myths and facts
Constipation is a condition that almost every person has experienced. For some, the problem resolves easily, but for others, especially older patients, the lack of bowel movements is chronic.
Details
Directory
Clinics and doctors
- Clinics in your city
- Doctors in your city
Insufficiency of the Bauginian valve: symptoms and treatment
Bauginian valve insufficiency is a condition that is characterized by impaired functional activity of the ileocecal valve, which separates the cavities of the small and small intestines.
The valve is a muscle formation that closes the intestinal lumen at rest and opens only during the digestion process.
When it is insufficient, muscle tone decreases, as a result of which the passage of the contents of the digestive system is disrupted.
Causes of the disease
The Bauhinian valve, the shape of the opening of which can be open round, closed-lip-shaped, semi-open-slit-shaped, may stop performing its natural functions for the following reasons:
- congenital anatomical anomalies and defects;
- consequences of surgery;
- inflammatory processes in nearby organs, for example the ovaries;
- the presence in the body of pathogenic microbes that enter with food;
- neurological diseases.
Insufficiency due to psychosomatics
Separately, I would like to highlight the causes of a psychosomatic nature, which are the provocateurs of almost half of all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Psyche and somatics (soul and body) are an integral, unified system with a strong interconnection of components.
Any deep emotional experience affects a person’s physical health, and, conversely, poor health directly affects thoughts, mood, and behavior.
The Bauginian valve, the treatment of pathologies of which is successful in most cases, is also no exception and can become inflamed for psychosomatic reasons.
Prevention
Many gastrointestinal diseases arise from failure to comply with basic sanitary standards when preparing food. In order to prevent pathogenic microbes from entering the body and causing the development of bauginitis, only fresh products should be used for preparing dishes. This is especially important when purchasing meat, fish, and dairy products.
Be sure to adequately cook foods. If these are vegetables and fruits, or herbs intended to be used raw, wash them thoroughly. It doesn’t hurt to pour boiling water over such products.
There should be separate cutting boards for each product. And not only for vegetables and meat, but also for fish. After use, they are thoroughly washed, as are all kitchen utensils in which dishes are prepared and served.
It will also not be amiss to observe personal hygiene: mandatory hand washing, especially before eating, regular wet cleaning of the house, treating the bathroom and toilet with disinfectants.
Diet also plays an important role in the prevention of bauginitis. Food with a sufficient content of vitamins, as well as micro and macroelements, is one of the factors contributing to normal intestinal function. The diet must contain products of protein origin.
If the disease does occur, then a therapeutic diet plays an important role in this regard. If the colon is inflamed, you should eat more often, but not overeat. Food should be gentle, and during an exacerbation, eating certain foods, for example, raw fruits and vegetables, needs to be limited.
It is not recommended to consume foods that have a laxative effect, as well as those that cause fermentation. Grapes, plums, prunes, as well as cabbage and beets are excluded from the diet. Kvass and fermented milk products are not allowed. It is worth excluding hot seasonings from your menu and limiting your salt intake.
Another most effective means of prevention is, of course, regular visits to the family doctor, and in the case of chronic inflammatory processes in the area of the bauginian valve, a gastroenterologist. Increases the chance of recovery and sanatorium-resort treatment in gastrointestinal institutions.
Specific methods of prevention have not been developed. It is necessary to seek medical help in a timely manner in order to identify and treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the early stages. It is recommended to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and eat foods high in fiber every day.
The outcome depends on the degree of organic defect of the bauhinium valve and the timeliness of detection of the pathology.
The prognosis is relatively favorable for patients who underwent early surgical treatment of ileocecal valve insufficiency (the effectiveness of the operation reaches 87%).
To prevent the disease, early diagnosis and adequate treatment of inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract are necessary. Patients are advised to monitor their diet and include foods rich in plant fiber in their diet.
Acute bauginitis in most cases ends with complete recovery. In the chronic version of the disease, the prognosis is less favorable; there is a risk of relapse after treatment.
To prevent bauginitis, it is necessary to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment of any pathologies of the digestive tract, thoroughly clean and heat treat food products, balance the diet, and use immunostimulants if there are signs of immunosuppression.
Symptoms of the disease
Insufficiency of the Bauginian valve is a little-studied disease, as it is characterized by rather nonspecific symptoms:
- flatulence (excessive accumulation of gases),
- bowel dysfunction: diarrhea and constipation;
- seething in the abdomen, which is especially well heard when pressing on the abdomen, namely in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- bad breath, presence of bitterness in the mouth;
- heartburn, nausea, belching;
- pain in the right side. The pain is mild, intermittent, and often occurs some time after eating;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased fatigue;
- weight loss.
In most cases, insufficiency of the bauhinium valve is detected completely by accident (during an examination of the body or during screening) and can be mistaken for another disease.
What is a bauhinium valve and what are its functions?
For a simple person not associated with professional medicine, the phrase “bauhinium valve” evokes a certain association - this is some kind of partition. Indeed, this organ in its structure is a special, dense fold that connects two sections of the intestine - thin and thick. Another name for the organ is the ileocecal valve.
This valve has the main purpose - it tightly covers the final section of the small intestine (ileum or ileum) and the beginning of its thick section (cecum or caecum), does not allow mixing of the microflora of these sections, and the reverse “reflux” of intestinal contents. If such a phenomenon does occur and is repeated regularly due to dysfunction of the bauhinium valve, a focus of inflammation may develop in a person’s intestines. A dangerous process can affect not only the intestines, but also spread to other organs involved in digestion - the stomach and pancreas, liver, gall bladder. Inflammation is accompanied by intoxication of the body, causing allergic reactions, diseases of the respiratory system, heart, blood vessels, and metabolic disorders.
Read: what symptoms indicate intestinal megacolon.
We recommend that you learn what a gluten-free diet is.
Why does ileocecal valve insufficiency occur?
The Bauhinium damper may not cope with its functions for a number of reasons. The main one is the anatomy of the organ. The ileocecal valve can be endowed with congenital anomalies and defects. The septum is capable of acquiring changes during development, growth of the human body and in adulthood. Insufficiency of the bauhinium valve may be associated with:
- with surgical operations performed in the abdominal cavity, especially in the presence of complications;
- with inflammatory processes developing in the stomach, liver, kidneys, ovaries, and other parts of the intestines;
- with pathogenic microorganisms entering the digestive system;
- with diseases of a neurological nature.
What symptoms are used to determine pathology?
Some symptoms help to suspect insufficiency of the bauhinium valve. They are not specific to the pathological process in question, but often indicate a general “disorder of digestion and intestinal function.” The patient may note several manifestations:
- tendency to increased formation of gases that remain in the intestines for a long time, causing a feeling of seething in it;
- stool disturbances are possible, both diarrhea and constipation occur;
- the presence of heartburn, which may be accompanied by belching and even vomiting;
- there is a bitter taste in the mouth, an unpleasant odor is possible;
- periodically (usually after eating) mild pain is observed in the right side;
- deterioration in general well-being, frequent feelings of weakness and extreme fatigue;
- the appearance of dizziness, disruption of the rhythmic functioning of the heart (increased rhythm);
- decreased appetite and body weight.
Insufficiency of the Bauhinium valve: symptoms, causes and treatment methods
Bauginian valve insufficiency is a condition that is characterized by impaired functional activity of the ileocecal valve, which separates the cavities of the small and small intestines.
The valve is a muscle formation that closes the intestinal lumen at rest and opens only during the digestion process.
When it is insufficient, muscle tone decreases, as a result of which the passage of the contents of the digestive system is disrupted.
Symptoms
- bowel dysfunction (constipation or diarrhea);
- periodic nagging pain in the lower right side of the abdomen (in the right iliac region);
- increased discomfort approximately 30 minutes after eating;
- nausea;
- bad breath;
- flatulence, bloating;
- belching, heartburn;
- constant rumbling in the stomach.
Causes and risk factors
- congenital developmental disorders;
- autoimmune processes, collagenosis;
- neurological pathologies (psychosomatic influence of the nervous system on the intestines);
- surgical interventions on the intestines;
- enteritis and enterocolitis;
- specific inflammatory processes (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis);
- inflammation in neighboring organs (for example, in the ovaries);
- poor nutrition.
General recommendations
- maintain a sleep schedule, get up and go to bed at the same time every day;
- eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions;
- maintain a water regime, drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water daily;
- give up bad habits - drinking alcohol, smoking;
- reduce your stress level and, if necessary, consult a psychotherapist.
| Recommended Products | Not Recommended Products |
|
|
Medical treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the severity of the symptoms of the disease and the presence of backflow of intestinal contents into the overlying sections - reflux. The decision on the need for one or another therapy is made individually by the patient’s attending physician.
Treatment of the cause of its occurrence is of great importance in the fight against the disease.
Inflammatory processes in the intestines are controlled by antibacterial therapy, autoimmune processes by the administration of glucocorticosteroids, in the presence of psychosomatic disorders, neurotropic drugs are used and rational psychotherapy is carried out.
In some cases, the condition resolves after eliminating the etiological factor. Thus, with a mild course of the disease, valve insufficiency can be eliminated through lifestyle correction and appropriate etiotropic treatment.
In case of severe disorders, drug therapy with magnesium orotate is prescribed.
This drug is especially effective in cases where the insufficiency of the ileocecal valve is of primary origin, that is, it does not depend on other intestinal pathologies.
Magnesium orotate adversely affects normal microflora, therefore, after its course, probiotics or prebiotics are prescribed to restore balance in the bacterial system.
If medications are ineffective and the patient develops active reflux, then surgery is required. The procedure is minimally invasive and can be done during endoscopy or using laparoscopic instrumentation. During the operation, the bauhinium valve narrows, thereby eliminating the return passage of chyme into the small intestine.
Diagnostics
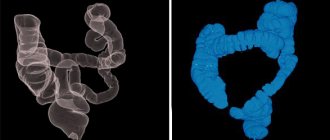
- Irrigoscopy. The study is a method of contrast radiological diagnostics. During irrigoscopy, a contrast agent (barium suspension) is injected into the patient's intestines through the anus. After the organ cavity is completely filled, a series of x-rays are taken, on which the condition of the ileocecal valve can be assessed and a violation of the passage of contrast through the intestines can be detected.
- X-ray with oral contrast. In some cases, contrast contrast with the introduction of barium suspension through the mouth may be used. The technique allows you to evaluate the distribution of contrast under physiological conditions - when moving from the small intestine to the large intestine. Despite good visualization of the valve, both radiological techniques cannot unambiguously confirm the diagnosis of valve insufficiency. This is due to the fact that it is a functional disorder, and x-rays can only statically evaluate the organs; they do not provide data on valve movements.
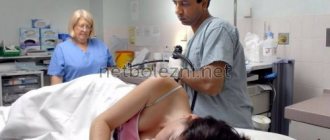
- Colonoscopy. The technique is a mandatory component of diagnosing valve insufficiency. During a colonoscopy, the doctor examines the intestinal cavity in real time using a special device - a colonoscope. The image is displayed on the screen in high resolution. If the valve is functioning normally, it will contract and relax rhythmically, releasing small portions of chyme. The damper will close tightly, without any clearance. The presence of even a small gap during the rest period indicates valve insufficiency.
- Capsule endoscopy. The patient must swallow a disposable mini-camera that passes through the entire digestive system and records data on the condition of the organs. The recording is examined and transcribed by doctors who note ileocecal valve insufficiency. The technique is highly informative; among endoscopic methods, it is the only one that allows you to examine the entire length of the small intestine. However, capsule endoscopy has a number of disadvantages. The obvious disadvantage of the technique is its price - at the moment, not every patient is able to pay for the study. In addition, the procedure cannot take a biopsy, which can be taken during a colonoscopy.
Insufficiency of the Bauhinium valve: what is it, symptoms and treatment
The intestinal valve is a tightly closed fold of natural origin formed at the junction of the small and large intestines. Its functional purpose is to ensure the movement of intestinal contents in the direction from the ileum to the cecum.
Insufficiency of the ileocecal valve (another name for this organ) causes the reflux of food masses in the opposite direction. The Bauginian valve, when its functionality is impaired, leads to congestion of the small intestine with the microflora of the large intestine and, as a consequence, its inflammation. Regular manifestation of this pathology causes a disease called chronic enteritis.
Bauhin's valve: description, causes, symptoms, forms and treatment features
The intestinal valve is a tightly closed fold of natural origin formed at the junction of the small and large intestines. Its functional purpose is to ensure the movement of intestinal contents in the direction from the ileum to the cecum.
Insufficiency of the ileocecal valve (another name for this organ) causes the reflux of food masses in the opposite direction. The Bauginian valve, when its functionality is impaired, leads to congestion of the small intestine with the microflora of the large intestine and, as a consequence, its inflammation. Regular manifestation of this pathology causes a disease called chronic enteritis.
Causes of development and risk factors
- foodborne illness, which develops when bacteria enter the intestines along with food;
- enteritis or colitis (secondary spread of inflammation to the bauginian valve);
- an allergic reaction to eating foods to which the patient is hypersensitive;
- helminthic infestations;
- nervous disorders, constant psycho-emotional stress;
- endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis);
- nutritional errors - unbalanced diet, insufficient intake of protein in the body (for example, against the background of a vegetarian diet);
- obesity and other metabolic disorders;
- low physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- disturbances in peristalsis, frequent constipation or diarrhea.
general information
As a rule, the disease is observed with enteritis and colitis. The cause is pathogenic microorganisms that enter the body along with food and poor, low-quality products.
Due to the influence of unfavorable factors, the regeneration of the intestinal mucosa is disrupted, then inflammation and swelling develop.
In the development of bauginitis, impaired intestinal motility and the neuroendocrine factor play an important role.
Bauginitis can be suspected based on the main symptoms - cramping pain in the right iliac region, rumbling in the abdomen, flatulence, nausea, belching, and bowel movements.
Using laboratory tests, disorders of the bacterial flora and digestive function of the intestine are detected. X-rays can detect signs of enteritis or colitis.
Endoscopically, swelling, areas of redness and atrophic changes in the mucous membrane are observed.
Bauhin's valve: diagnostic methods
You can see the Bauhinian valve and accurately determine its functionality by performing a colonoscopy, which allows you to examine in detail the ileum, the mucous membrane of the small intestine, and also identify inflammatory processes present in the body.
The pathology of the ileocecal valve can be diagnosed using several methods, one of which is irrigoscopy, which involves injecting a barium-containing contrast agent into the rectum and then taking x-rays. The manipulations performed allow us to see the distribution of the contrast agent and make a presumptive diagnosis based on what we see, which can be confirmed by endoscopic examination.
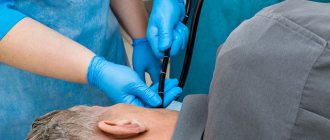
A fairly effective and expensive diagnostic method is capsule endoscopy, during which the patient is required to swallow a miniature video camera equipped with a power source. To date, this method is the most reliable and the only one that allows you to completely examine the inside of the small intestine.
4Careful diagnostics
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. Today, there is a sufficient amount of modern equipment and methods that ultimately help to arrive at a competent diagnosis.
Irrigoscopy - this modern method of diagnosing diseases involves the introduction of a special contrast agent into the patient’s rectum and subsequent radiography. This research method provides effective assistance in visualizing the condition of the large intestine, how it functions correctly, and whether there are significant violations of its boundaries.
With proper colonoscopy, you can very clearly see the entire Bauhinian valve. Colonoscopy allows specialists to observe first-hand the condition and functioning of the organ.
In addition, the tip of a colonoscope is inserted into the patient’s small intestine, which makes it possible to examine the condition of the ileum, the mucous membrane of the small intestine, and also identify foci of the inflammatory process.
If the bauhinium valve is insufficient, its sponges do not close completely, which results in the ejection of the contents of the cecum into the ileum, thereby causing an inflammatory process.
Capsule endoscopy almost always guarantees an accurate result in diagnosing a patient, but this method is not cheap. It is based on the fact that the patient must swallow a miniature video camera. To date, this method is the most reliable.
A study is carried out using the X-ray method and barium. On the eve of the study, the patient must drink a certain amount of a substance with a high barium content.
After this, he is sent for an x-ray, where photographs of the abdominal cavity are taken to monitor the distribution of the substance drunk. However, it is worth considering that the research method used does not allow making an accurate diagnosis.
To confirm the disease, the patient additionally undergoes an endoscopic examination.
Insufficiency of the Bauhinium valve: treatment
Identified pathology of the ileocecal valve is treated exclusively in a hospital setting and only using an integrated approach. If the development of inflammation occurs due to the presence of an infection in the body, doctors prescribe antiviral drugs and antibacterial agents.
If the disease is anatomical, treatment is carried out not only with medications (containing magnesium), but also with surgical intervention, which consists in narrowing the bauhinium valve. Such manipulations can reduce the volume of contents returning back to the small intestine.
A method for directly passing an endoscope through the Bauhinian valve during colonoscopy
Bacterial flora, as well as digestive dysfunction, are determined through fairly serious laboratory tests, microscopic and bacteriological.
To restore the health of patients diagnosed with “bauhinium valve insufficiency,” treatment with folk remedies is possible. The use of any of them is permitted only after consultation with a doctor.
For diarrhea, the cause of which is secretory insufficiency of the stomach, drugs of the so-called digestive enzymes - festal, pancreatin - are indicated.
If the disease does occur, then a therapeutic diet plays an important role in this regard. If the colon is inflamed, you should eat more often, but not overeat. Food should be gentle, and during an exacerbation, eating certain foods, for example, raw fruits and vegetables, needs to be limited.
The key to health is the correct daily routine
Therapy is aimed both at eliminating symptoms and at relieving inflammation and swelling. The problem of the pathological condition of the ileocecal valve is almost always solved by normalizing lifestyle, provided that the causes of the disease are due to functional reasons.
Therefore, first of all, you need to establish a daily routine and normalize your own diet. You need to eat in small portions, about 6-7 times a day. This will normalize the functioning of the valve system of the gastrointestinal tract and regulate the mechanism of unilateral movement of food masses.
The menu should be diversified with mechanically gentle food: slimy soups, steamed fish and meat cutlets, meatballs. It is recommended to consume fruits in the form of purees, juices, and compotes. Baked apples are very useful.
It is important to give up fried and spicy foods, black bread, beets, cabbage, limit coffee consumption, and also give up bad habits: alcohol and smoking. Patients are under medical supervision for six months.
Since the Bauhinian valve can often become inflamed due to psychosomatic disturbances, it is necessary to prevent stress factors from entering your life. For help in this matter, you can contact a psychologist or psychotherapist.
Its pathology in each specific case requires an individual therapeutic approach, which is determined only by the attending physician, taking into account the diagnosis and assessment of risk factors.
The Bauhinian valve (valva ileocecalis) is a pylorus: it opens and closes, allowing intestinal contents to pass in only one direction. The barrier begins its active functioning when the child reaches the age of 3 years.
The anatomical structure keeps the intestinal contamination in the volume necessary for the full functioning of the body. Insufficiency of the bauginian valve (ileocecal valve) causes bauginitis (actually, its inflammation) or other factors.
To accurately determine the cause, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
Bauhin's valve: description, causes, symptoms, forms and treatment features
The intestinal valve is a tightly closed fold of natural origin formed at the junction of the small and large intestines. Its functional purpose is to ensure the movement of intestinal contents in the direction from the ileum to the cecum.
Insufficiency of the ileocecal valve (another name for this organ) causes the reflux of food masses in the opposite direction. The Bauginian valve, when its functionality is impaired, leads to congestion of the small intestine with the microflora of the large intestine and, as a consequence, its inflammation. Regular manifestation of this pathology causes a disease called chronic enteritis.
What diagnostic methods are needed to confirm the disease?
If there is a suspicion of dysfunction of the ileocecal valve, the patient may receive a referral for instrumental diagnostics. He is invited to undergo tests (their choice is determined by the availability of certain equipment in the medical institution, as well as the patient’s ability to carry out diagnostics for a fee):
- colonoscopy (total);
- endoscopic examination (capsule);
- irrigoscopy (involves administering contrast through the rectum, then using a radiograph).