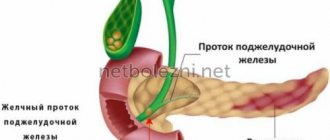
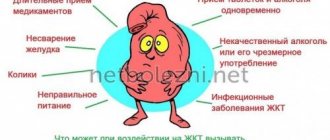
We are used to thinking that the main digestion occurs in the stomach. Actually this is not true. The stomach carries out mechanical processing of food: it grinds it, “disinfects” it with hydrochloric acid to kill as many pathogenic bacteria as possible, and sends it to the intestines. This is where the main stage of digestion occurs. And it is impossible without the enzymes produced by the pancreas. If a person has few enzymes, this inevitably affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the entire body.
Inflammation of the pancreas
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas and can be acute or chronic. Causes – poor diet, stones in the bile ducts, poisoning, smoking, chronic alcoholism, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach, duodenum), viral diseases, infections, etc. Symptoms of acute pancreatitis – nausea, vomiting, heartburn, aching, monotonous pain in abdomen, in the left hypochondrium, persisting for several days. As well as spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen, flatulence, abnormal bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation), chills or excessive sweating, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, and changes in skin color.
Symptoms
Often, clinical manifestations alone may indicate a completely different disease. And the person is in no hurry to see a doctor, but in the meantime the disease progresses, and the person learns about a completely different pathology while already in a hospital bed. If a person complains of pancreatic spasm, the symptoms in this case are:
- cramping pain in the upper part of the stomach;
- nausea and vomiting;
- violation of stool, calla stool acquires a liquid structure;
- diarrhea;
- a sharp increase in body temperature.
Vomiting usually worsens as pain increases. The higher they are, the more often vomiting occurs. Symptoms worsen with any human movement and subside slightly when the person is immobilized.
Treatment of pancreatic inflammation
Treatment of acute pancreatitis should take place in a hospital.
First aid - you need to apply an ice bag to the left hypochondrium, avoid eating any food. Drug treatment includes taking antispasmodics, painkillers (opioid analgesics), and antiemetics. In the acute phase, infusion drugs are administered intravenously. For complications, antibiotics may be prescribed. Fasting is observed for three to five days or parenteral nutrition is used.
Therapy for the chronic form of the disease is based on quitting smoking, drinking alcohol, diet therapy with a small amount of fat in the diet, using painkillers, taking enzyme preparations; antidepressants (pregabalin, gabapentin) can be prescribed to relieve pain, as well as treatment of complications.
If there are stones in the gland ducts, then it is rational to perform lithotripsy and endoscopic therapy.
Surgical treatment is performed when drug therapy is impossible or the body is tolerant to their action.
The duration of treatment depends on the form and complications of the disease, and on the body’s susceptibility to therapy.
Pancreatic tumors
A pancreatic tumor can be of two types – cancer and a hormonally active tumor.
Men are more often affected; the average age is 55 years. Most often the tumor is localized in the head of the gland. Factors that provoke the development of pancreatic cancer include smoking, chronic pancreatitis, high body mass index, and male gender.
Symptoms of cancer depend on the part of the gland that is affected. If the head of the gland is affected, jaundice may develop, because compression of the bile duct occurs. Skin itching appears. When the body and tail are affected, diabetes mellitus, varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach, and the risk of bleeding develop.
Treatment is surgical or chemotherapy.
Consequences of gland dysfunction
Dysfunction of the pancreas, whether it concerns external secretion or the production of hormones, leads to disturbances not only in the activity, but also in the structure of the organ, if measures to normalize it are not taken in a timely manner. Dangerous diseases include pancreatitis and diabetes. Their diagnosis and treatment in the early stages helps to avoid severe complications in the form of pancreatic necrosis, damage to the kidneys, fundus vessels, legs and, in parallel, pathology of other organs. The prognosis for these complications is in many cases unfavorable. Therefore, it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it.
Bibliography
- Ivashkin V.T. Horizons of clinical gastroenterology. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Coloproctology. 1993 No. 1 pp. 6–12.
- Kalinin A.V. Disorders of cavity digestion and its drug correction. Clinical perspectives of gastroenterology, hepatology. 2001 No. 3, pp. 21–25.
- Korotko G.F. Pancreatic secretion. M.: "TriadaX" 2002, p. 223.
- Maev I.V., Kazyulin A.N., Dicheva D.T., Kucheryavyi Yu.A. and others. Chronic pancreatitis Textbook. 2003 M.: VUNMC Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. Page 80.
- L.N. Valenkevich, O.I. Yakhontova. Diseases of the digestive system: a guide to gastroenterology for doctors. St. Petersburg Publishing house DEAN, 2006
Pancreatic stones
Pancreolithiasis is the formation of stones in the pancreatic ducts.
Often stones form if there is a cyst or tumor; this is one of the complications of chronic pancreatitis. Stagnant processes occur in the organ, the secretion of the pancreas thickens, and the protein precipitates. The ducts dilate, the pressure in them increases, and symptoms of pancreatitis appear. Symptoms of pancreolithiasis:
- burning pain in the abdomen radiating to the back and shoulder blade;
- nausea, vomiting with bile;
- steatorrhea – “fatty” stool;
- diabetes;
- increased salivation;
- obstructive jaundice.
How can you notice pancreatic dysfunction?
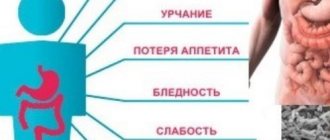
If you pay close attention to your body, you can pay attention to changes in the functioning of the pancreas at the very beginning of their manifestation. If exocrine function is impaired, a person gradually loses appetite and becomes excessively tired even in the absence of heavy loads. And he also develops unmotivated weakness, growing lethargy, apathy, nausea, sometimes unstable stools (mushy or constipated), and bloating. The general condition worsens, there is constant discomfort from the digestive organs. Over time, the symptoms worsen, causing constant pancreatic diarrhea (liquid feces with a greasy sheen and a foul odor, mixed with undigested food residues - steatorrhea), rumbling in the stomach, nausea. In severe cases, with a sharp decrease in functions, vomiting occurs, which does not bring relief. These are symptoms of pancreatitis - a disease that requires treatment from the moment the first symptoms appear. According to statistics, men who abuse alcohol are more likely to get sick. Overweight women who do not limit themselves in diet and lead a sedentary lifestyle are also susceptible.
When a disturbance in the intrasecretory activity of the pancreas occurs, the first signs of its dysfunction can be noticed in both an adult and a child: a person begins to drink more water, he is bothered by dry mouth, constant thirst, frequent urination - polyuria (large amounts of urine) occurs. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, without delaying the process, disorders are easily determined by several tests: elevated blood sugar is detected, and in severe advanced cases, glucosuria (sugar in the urine) is detected.
Diagnosis of pancreatic diseases
To diagnose diseases of the pancreas, the doctor examines and palpates the abdomen and prescribes laboratory and instrumental methods.
A biochemical blood test examines the level of pancreatic enzymes (amylase, lipase), blood glucose, and liver function tests.
A stool analysis is carried out to assess the deficiency of enzyme production, the presence of undigested food, fat, and certain enzymes (pancreatic elastase) is examined.
Visual instrumental examinations are carried out using transabdominal ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity), CT, radiography, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
Diet for diseases of the pancreas
The diet should include soft, well-chopped food.
Steam, bake, boil, stew foods. Include puree soups and cream soup in your diet. Bread can be consumed dried, yesterday's bread made from first and second grade flour. Meat - chicken, turkey, lean parts of beef, low-fat fish is allowed. Eggs should be in the form of omelettes, steamed in the oven. You can eat non-acidic types of fruits, baked fruits. You can drink rosehip decoction, sugar-free compote, herbal teas, water. Of the fats in the diet, butter with 82.5% fat content and sunflower oil should be present, but limited. Food should be taken warm. It is necessary to exclude sausages, smoked meats, fatty, fried, canned and pickled foods.
Forbidden:
- alcohol;
- spicy food;
- coffee;
- energy, carbonated sweet drinks;
- chocolate;
- ice cream;
- duck, goose meat, pork, lard, bacon;
- legume products;
- garlic, cabbage;
- grapes, bananas.
The severity of the diet depends on the disease of the pancreas. In the acute period, fasting is prescribed for three to five days; in case of exhaustion, parenteral and special enteral nutrition is used.
How to stimulate the organ?
The doctor will explain in detail how to properly stimulate the functioning of the pancreas in case of impaired functions. The pancreas is such a delicate and sensitive organ that any external or internal negative influences lead to massive death of its cells. Areas of the pancreas that die are not restored: they are replaced by connective (scar) or fatty tissue, which are not able to perform the normal functions of digestion and hormone production. With each subsequent pathological process in the gland, the amount of normally functioning parenchyma of the organ decreases, and the patient’s condition progressively worsens.
When you consult a doctor with the first signs of poor health, it is still possible to restore the partially changed activity of the pancreas. To do this you need:
- follow the diet prescribed by a specialist,
- change lifestyle,
- regularly engage in physical therapy,
- take drug therapy.
Together, this will improve the functions of the pancreas and the condition of the body as a whole.
Normalization of functioning
To restore normal functioning of the gland, it is recommended to completely change your lifestyle. First of all, this applies to alcohol consumption. It is one of the main factors leading to disruption of the organ. It is a toxin that causes damage to the blood vessels that supply nutrients to the pancreas. Lack of normal blood supply leads to the death of pancreatic cells. Alcohol also has a direct damaging effect on the cells of any organ, including the pancreas. For some people, drinking a small amount of alcohol-containing drinks is enough for acute pancreatitis to develop in a catastrophically quick time. The use of alcohol is especially dangerous for a patient with existing pancreatitis. In such cases, you need to give up even low-alcohol drinks.
It is recommended to drink enough non-carbonated alkaline mineral water. In the absence of contraindications, the doctor may prescribe 2-3 liters of water per day. This indirectly stimulates the functioning of the pancreas and helps the production of pancreatic juice. The amount and duration of mineral water intake is regulated by the doctor.
The patient should include regular moderate physical activity and therapeutic exercises in his routine. During exacerbations, intense physical labor is contraindicated.
Methods for stimulating the pancreas
If the disease is not advanced, treatment can be done without taking medications. The doctor will prescribe a specific diet, which should be strictly followed to prevent the development of the disease.
In cases with a verified diagnosis, medications are prescribed to stimulate the pancreas, which, depending on the impaired function, can make the organ’s activity normal. This is one of the effective methods if you strictly follow the recommendations.
If pancreatitis is detected, the patient should take enzyme replacement therapy. It is prescribed by a doctor: the selected drug is strictly dosed, since with high doses of external enzymes in tablet form, iron may stop producing them on its own. Taking a small dose of enzymes is needed to stimulate the body's production of its own enzymes.
For diabetes mellitus, glucose-lowering therapy is prescribed. If there is significant damage to pancreatic tissue, when insulin production has stopped, insulin replacement therapy is also prescribed. Without taking insulin, severe complications of progressive diabetes mellitus will quickly occur. Large doses are not prescribed so as not to disrupt the synthesis of your own hormone by the remaining intact cells.
In addition to basic replacement therapy, a number of drugs are prescribed that help reduce inflammation in tissues, reduce swelling during exacerbation, relieve pain and dyspeptic symptoms accompanying exacerbation. A significant improvement in the general condition due to the stimulation of organ activity, which leads to the normalization of all functions, explains why it is necessary to take the prescribed complex treatment.
Diet to improve organ function
To normalize the functioning of the organ, diet plays a paramount role. It is special nutrition within the framework of treatment table No. 5 according to Pevzner for pancreatitis (there are several options, taking into account the condition of the organ) and various formations in the gland, and table No. 9 for diabetes mellitus that can reduce pain and discomfort caused by disorders in the organ. This is explained by a decrease in the functional load on the damaged organ. Moreover, not only the quality of certain products plays a role, but the frequency and quantity of food eaten at one time. You need to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions at fixed times, with equal time intervals.
Fatty, spicy, fried and smoked foods are strictly excluded. When consuming this food, the gland requires a large amount of pancreatic juice with a high content of enzymes, as well as a long time to process harmful products.
If a dish is eaten in large pieces, chewing poorly, the load on the organ similarly increases: in order to digest a large piece, the secretion of the gland must also be increased. At the same time, a large amount of produced pancreatic secretion due to the inflammatory process can be retained in the ducts, not having time to quickly exit into the lumen of the small intestine. This is dangerous because enzymes enter the pancreas parenchyma and trigger the process of autolysis—self-digestion of the gland. The pathology worsens, the disease worsens, and the gland further reduces its functions.
The basis of nutrition for impaired pancreas function is porridge cooked in water, vegetable soups, for which you can use non-rich broths, mild low-fat cheeses, poultry, rabbit, beef, veal, and weakly brewed tea. The method of preparing dishes is important: the food is boiled, steamed, stewed, but not fried. Butter is limited; vegetable oil can also be consumed in limited quantities.
The same measures will help stop destructive processes at the onset of the disease. Since pancreatic pathology is often accompanied by dysfunction or diseases of the gallbladder, general recommendations must be followed to exclude the development of gallstone disease.
Carbohydrate intake in diabetes mellitus is sharply limited, sometimes completely eliminated for a while. This allows you to reduce the functional load on the organ and reduce the dose of glucose-lowering drugs (insulin).
For any pathology of the pancreas, fast food, dishes with large amounts of salt, sugar, juice seasonings, preservatives and other harmful additives are strictly prohibited.