Giardiasis is an infectious disease that affects entire organized groups of children who bring the disease to their family - mom and dad. Adults get sick four times less often than children, because their teams are not so united, and adults wash their hands more often and better. It is not known exactly how many people have giardiasis, but between 2% and 10% of adults are thought to be infected.
Our expert in this field:
Nagibina Margarita Vasilievna
Infectious disease doctor, MD
Call the doctor
From a third to a quarter of Giardia carriers are unaware of their infection, because the symptoms of the disease are not pronounced, the rest may suffer from chronic enteritis or cholecystitis, perennial allergic dermatitis and simply weakness with headaches and irritability, completely unaware of the cause that caused persistent health problems . And the cause of that suffering is microscopic lamblia.
What kind of parasite is this
The first Giardia was seen 335 years ago by the famous inventor of the microscope, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, he saw it in the feces of a person suffering from diarrhea and that’s it, he didn’t get acquainted further, he didn’t set out to trace the life path of the parasite, and Giardia was not yet considered a parasite, and the name is glib flagella did not have either.
170 years later, Giardia was seen and studied by the Czech doctor Vilem Dusan Lambl, who devoted part of his life to Russian medicine. Professor Dushan Fedorovich Lambl, as an unambitious person, named the flagellated creature Cercomonas intestinalis, without intending to give it his own name. Dr. Lambl was the first to recognize in Giardia not only the simplest flagellated creature, but also a parasite living in the human intestine. These parasites inhabited the feces of those suffering from diarrhea in abundance.
A quarter of a century later, Germona was renamed Giardia - giardia. An attempt to officially name the protozoan in honor of its discoverer, Dr. Lamblia, was not successful; nomenclature rules did not allow it, however, Russian experts always called it only that - Lamblia intestinalis, and in foreign literature it is only Guardia intestinalis or Guardia duodenalis and even a compromise Guardia lamblia.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
How does lamblia live?
The simplest, because the structure of a cell, in fact, is very simple, capable of movement and life exclusively at someone else’s expense, because such a “lightweight” structure of a single-celled organism does not allow for any other way of life. A quirk of nature that cannot live without a host, without a host it freezes - it is preserved for weeks, turning into a cyst. Cysts lie in the ground, on dirty vegetables, in warm water. When the cyst is lucky enough to get inside a person, the “tin can” in the gastric juice - the shell of the cyst dissolves, the flagella unwind and Giardia is ready to move on.
Giardia has surprisingly adapted to live in the small intestine and, possibly, in the gallbladder, although no one has ever found them there, but symptoms of gallbladder damage in patients are not at all uncommon. On the abdomen of the active form of Giardia, which bears the dissonant name of trophozoite, there is a special suction cup that helps it stay on the villi of the small intestinal mucosa. It receives everything Giardia needs for life from the cell to which it is attached, and after eating, it divides among its own kind; it takes no more than a quarter of an hour for the entire reproduction process.
If it wants, the trophozoite will detach itself from the villus and swim to another, fortunately nature has given four flagella. It can turn into a cyst and come out along with the feces, this is how millions of cysts leave the intestines to get into another host, where it all starts again. The cysts are “picked up” by pets and caught on flies’ legs. Cysts are able to withstand freezing, but for a very short time, so they are not present in frozen vegetables, just as they are not present in vegetables treated with boiling water; cysts do not tolerate hot water at all.
Treatment of giardiasis
The ultimate goal of treatment is to eliminate Giardia from the intestines. The treatment uses various components of nutritional and drug treatment, which are aimed at various parts of the parasitic effect on the human body and contribute to its recovery.
Diet therapy
The dietary regimen is followed throughout the treatment. Nutrition is aimed at creating conditions that worsen the reproduction of Giardia, and the introduction of products that are food sorbents. Restriction of carbohydrates is required, especially sugar, cookies, white bread, pasta.
Introducing increased amounts of protein :
- dairy products,
- fish,
- bird,
- meat
and dietary fiber :
- porridge,
- wheat bran or grain bread,
- dried fruits,
- baked apples, pears, berries (lingonberries, cranberries),
vegetable oil.
An increased water regime (up to 1-1.5 liters per day). Fasting during giardiasis is contraindicated.
Drug therapy
Choleretic agents:
- Allohol 2 tablets 3 times after meals for 20 days,
- Hofitol 1 dr. 3 times 20 days 20 minutes before meals,
- Hepatofalk 1 caps. 2 times 20 minutes before meals for 20 days,
- Cholenzym 1 dr. 3 times after meals, etc.
Drugs that reduce body intoxication and enhance the detoxification function of the liver:
- Heptral 400 mg intravenously in 200 ml of saline solution No. 10 once a day in the morning or
- Gepatosan 1 capsule 2 times a day before meals for 10 days.
Choleretic drugs are prescribed to reduce intoxication of the body. They normalize bile secretion and intestinal function and have a detrimental effect on Giardia and many protozoa.
It is effective to cleanse the biliary system of the body before using antiparasitic drugs : 1 tablespoon of sorbitol is diluted in 300 ml of boiled water and drunk within 2 hours in the morning on an empty stomach in sips. Then, during the day, a fasting diet is followed: boiled rice, baked fruits (apples and pears) and vegetables (any), high-liquid regime up to 1.5-2 liters. Duration 1 day.
Enterosorbents
More often prescribed to those patients who have allergic manifestations. The drug that has proven itself to be the best is Smecta (Smectin), 1 packet at night. Smecta has an effect on the cells of the small intestine where Giardia lives. It is possible to take Allochol simultaneously, 2 tablets 3 times a day.
Enzyme preparations
Wobenzym has proven itself well , especially during the period of taking antiparasitic drugs. Take 2-3 tablets 3 times a day for 14 days. 40 minutes before meals.
Antihistamines
They are used for antiparasitic treatment or for manifestations of allergic diseases, for example. Suprastin 1 tablet. since morning.
Antiparasitics
You can choose a one-day or multi-day course of treatment, but the latter gives a better effect and fewer adverse reactions. There are quite a lot of drugs and they are used more often than others: Metronidazole, Furazolidone, Nifuratel, Albendazole, Ornidazole, Tiberal, Tinidazole, Vermox, Decaris.
The choice of drug remains with the doctor.
In recent years, there has been a revision of priorities in the use of antiparasitic drugs, based on the observed possible recurrences of the disease after treatment and side effects of the drugs. In both pediatric and adult practice, the most preferred drug is currently Nifuratel , whose trade name is Macmiror .
If a parasitic infection is detected, it is necessary to consult an infectious disease specialist or gastroenterologist, carry out treatment and be sure to monitor it; if cysts are detected in other family members, the whole family should be treated.
What is giardiasis like?
They say about giardiasis that no two identical clinical cases exist, however, among the incredible variety of symptoms, it was possible to form a classification of the disease.
First of all, Giardia can manifest itself with quite clear symptoms of the disease - this is clinically pronounced giardiasis. You may not have symptoms, but have giardia - this is giardia carriers or asymptomatic giardiasis, in a quarter to a third of all cases. There is also an intermediate form with unexpressed manifestations - subclinical giardiasis, it is observed in half of those infected. In this case, the patient does not seem to have any symptoms, but examination may reveal some functional disorders, for example, not entirely correct absorption of substances in the small intestine.
Based on the prevalence of clinical manifestations, there are possible variants of the course of giardiasis: intestinal and hepatobiliary. There are also clinical syndromes: allergic, astheno-neurotic, pain and dyspeptic. The last two account for the absolute majority, but each patient can have all four syndromes, just one is maximally manifested, and the rest are, as it were, “in the shadows.”
2. Reasons
Giardia enters the external environment with feces, and it is the degree of fecal contamination that largely determines the epidemiological situation regarding giardiasis. However, other routes of infection are also possible - primarily through unboiled water, as well as through food, through touching household items, etc. Giardia cysts are found on flies and domestic cockroaches. The likelihood of infection from infected animals has not been proven. The direct and most significant risk factor is non-compliance with culinary and personal hygiene standards.
In general, giardiasis can be classified as a so-called “diseases of unwashed hands”, and it is no coincidence that among newly ill people there is a significant (up to 70%) predominance of children and young adolescents - at least, this is the situation in the Russian Federation.
Once in the small intestine, lamblia damage its surface mechanically (up to a million trophozoids can parasitize on one square centimeter), causing specific irritation and inflammation, as well as intoxication of the body with metabolic products and cellular decay.
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Allergy to parasite
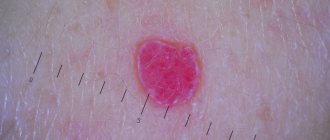
Allergic syndrome in every sixth patient is manifested by dermatitis, often atopic, which was previously called neurodermatitis. Severely itchy rashes of various shapes appear symmetrically on the skin; patients associate the cause of their appearance with nervous life, as if provoked by chronic stress. Only in winter, against the background of this constant stress, skin manifestations worsen, and in summer they decrease, although they should not react to the weather. A blood test shows evidence of an allergy—an increased level of eosinophils.
Not only the skin is affected, but also the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose, and as with any allergy, sooner or later, the bronchial tree is involved - asthmatic bronchitis develops. Only, unlike “normal” allergies, this condition with nasal congestion, regular lacrimation, itchy skin and even pain in large joints exists constantly, somewhat decreasing in the warm season, but not going away completely, and without any connection with external allergens . In general, this is an allergy, but to an intestinal parasite. And even after successful treatment of giardiasis, allergic manifestations may go away immediately, or even after a few months.
Treatment
Against the background of the therapy - anthelmintic drugs, intestinal antiseptics, enzyme preparations, probiotics, choleretic drugs - improvement was noted: regression of skin itching and skin rashes, relief of pain, reduction of bitterness in the mouth and bloating, normalization of stool, cleansing of the tongue.
The patient is recommended to follow a diet 4-5 times a day with a limit on fatty, fried foods and flour products.
Continue therapy with choleretic drugs followed by ultrasound monitoring of the abdominal organs after 3 months.
How Giardia spoils the nerves
Apparently, this microscopic creature secretes some kind of toxins that irritate the nerve endings. Whether this is due to the special toxicity of the Giardia population that has settled in humans or to a large number of parasites, or perhaps to the characteristics of the nervous system of the host itself, is not clear, but a “nervous reaction” of varying degrees of severity to the presence of Giardia is observed in more than half of the patients.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome is manifested by constant weakness, rapid fatigue with little physical activity, sleep disturbance, headaches, and inadequate irritability. Not all symptoms may be present at once; any set is possible. But what’s interesting is that in the initial absence of headaches, sleep disturbance will certainly cause them, and vice versa. Fatigue will eventually affect your sleep patterns, and vice versa. One symptom attracts others, so that over time it is no longer possible to discern what was a symptom of giardiasis and what was a complication of this primary symptom. This variant of the course of giardiasis is not at all uncommon.
Typical manifestations of giardiasis
This happens most often, which is justified by pathogenesis - the affinity of the parasite with the small intestine and the duodenum passing into it. Giardia, when existing in the intestine for a long time, gradually moves from the upper sections to the middle and lower sections, but does not go away at all. Serious disputes arise over the possibility of their living in the gall bladder, maybe they don’t live there, but it’s not for nothing that the gastrointestinal tract is called a tube, in the tube everything flows from one thing to another and everything is interconnected. A disease in one department will inevitably affect all the others, even without organic damage, but it will definitely disrupt the functions.
Intestinal syndrome with giardiasis manifests itself in the form of functional disorders of the duodenum: nausea and pain in the stomach, loss of appetite can be almost constant, and attacks are possible against the background of complete health. Damage to the mucous membrane of the small intestine - enteritis manifests itself as pain in the peri-umbilical region, not associated with food, constant flatulence, frequent loose stools, which alternate with constipation, stool becomes as if fatty - steatorrhea.
Hepatobiliary syndrome is similar to banal cholecystitis: pain in the right hypochondrium, as a reaction to spicy and fatty foods, nausea and vomiting of “bile”, bitter belching, the same steatorrhea, flatulence. An ultrasound examination reveals changes in the tone of the sphincter and the gallbladder itself, and stagnation of bile is noted.
In general, the clinical manifestations of giardiasis are completely non-specific and for a long time the infection can exist under the guise of allergies, neurosis, duodenitis, enteritis, cholecystitis. These “diseases” can be present in a person individually or all together, and their standard treatment may be completely unresponsive until either the main enemy, Giardia, is discovered, or for some other reason the person takes Trichopolum (metronidazole), which is fatal for Giardia.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Which doctor treats giardiasis in adults. Diagnosis of the disease
Often, with a chronic form of giardiasis, patients visit a doctor, primarily an allergist or dermatologist.
Indications for diagnostics to exclude giardiasis are:
- diarrhea,
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- dermatitis,
- hives,
- autonomic disorders,
- dyspeptic complaints (nausea, feeling of fullness in the epigastric region, loss of appetite, body weight),
- intestinal discomfort (bloating, rumbling).
Without laboratory diagnostics, it is impossible to say that a person has giardiasis, but it is possible to suspect this infection and be sure to conduct special studies:
- clinical blood test, which is characterized by constant but moderate eosinophilia! (increased blood eosinophils),
- A non-invasive diagnostic method is stool microscopy, always three times with an interval of 7-8 days. It is believed that the release of Giardia cysts occurs after 8-14 days and this interval must be used to detect Giardia in the feces and conduct an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the presence of Giardia antigen in the feces.
Attention! It should be borne in mind that vegetative forms of Giardia are found in warm duodenal contents or liquid feces; this form is most often diagnosed in infectious diseases hospitals.
In the chronic course of giardiasis, detection of cysts will help make a diagnosis, which is the basis for anti-giardiasis therapy.
A study of evening stool cannot be ruled out; this test is highly informative. The diagnostic value of such a test is high, because with its help it is possible to examine children and adults for giardiasis with the phenomenon of cystic discharge (Kornienko E. A. 2009). The use of choleretic drugs increases the likelihood of detecting Giardia.
Within 70 days after the start of therapy, stool is specifically examined for Giardia every 8-14 days. According to E. A. Kornienko, the most informative diagnostic method is stool examination (coproscopy), which gives an answer in 96% of cases. Also applicable
- immunoenzyme and immunochromatographic test systems that detect specific antibodies in the blood, determination of total immunoglobulins (IgG, A, M) and specific immunoglobulins of class M in blood serum and antibodies in feces. The sensitivity of these tests is 70% and specificity is 92%.
- endoscopic research methods - gastroduodenoscopy, which reveals hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue (bulges) on the surface of the duodenal bulb and lymphangiectasia at the level of the Vater papilla.