Main causes of the problem
The reasons for an unpleasant taste in the mouth can be divided into two groups. The first includes internal ones, associated with various diseases of internal organs, the second - the negative influence of external factors. Why there is an unpleasant taste in the mouth:
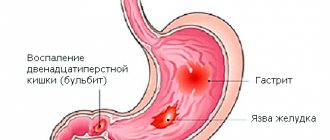
- diseases of the digestive system - gastritis, duodenitis, ulcerative lesions of the duodenum and stomach;
- pathologies of the biliary apparatus - liver, pancreas;
- helminthiasis;
- diseases of the endocrine system - diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism;
- dental diseases - caries, stomatitis, periodontal disease;
- vitamin deficiency;
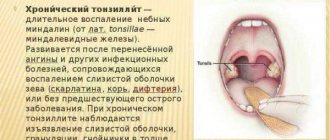
- inflammatory and infectious lesions of the ENT organs - sinusitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis;
- neurological disorders;
- toxicosis during pregnancy.
Among external factors, the main ones are smoking, food or alcohol intoxication, long-term use of antibiotics and other medications that cause disruption of healthy intestinal microflora.
Also, a sharp bitterness in the mouth can occur after eating with the addition of hot spices, hot chili peppers or garlic.
Bitterness in the mouth may be accompanied by additional symptoms - the appearance of a yellow (gastritis) or white coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue, nausea in the morning after sleep (liver pathologies, pancreatic diseases), bad breath (stomatitis), dry mucous membranes and increased sweating (sugar diabetes).
Complications after dental prosthetics
- Sores and chafing after installation of dentures;
- Inflammatory process on the gums under dentures. Stomatitis;
- Diseases of supporting teeth (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.);
- Allergy to materials used to create prostheses;
- Galvanic syndrome;
- Loosening the fixation of removable structures;
- Changing the position of the cheeks and lips.
Let's look at each of the complications in more detail.
Sores and chafing after installation of dentures
A common phenomenon, especially typical for removable structures.
Symptoms
- Unpleasant sensations, pain while eating;
- Feeling of a foreign body in the mouth;
- Profuse salivation.
Treatment
The next day after the installation of a removable structure, there is always a follow-up appointment at the dentist's office. Regardless of the presence or absence of unpleasant sensations, it is necessary to come to the clinic for an examination, otherwise, if this is not done, bedsores will form .
If necessary, the doctor will correct the prosthesis and set a date for the next visit. At least two amendments are required for everyone.
During the first two to three weeks, you get used to the dentures, and discomfort is completely normal. Full adaptation usually occurs by the end of the third week.
Prosthetic stomatitis
Prosthetic stomatitis
One of the most common complications.
Symptoms
- In the first time after installing the prosthesis, in addition to discomfort, excessive pressure on the mucous membrane and pain are felt. Redness of the gums appears, and possibly the formation of pustules on the mucous membrane. Small blood vessels are pinched, and the blood supply to the tissues is disrupted at the site of contact - bedsores form;
- The fixing elements of partial dentures can also irritate the surrounding periodontal tissues and contribute to their inflammation.
Treatment
It is necessary to visit your doctor, who will carry out antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and dentures, prescribe local anti-inflammatory therapy (rinses, mouth baths, ointments, gels), as well as a set of procedures aimed at accelerating tissue regeneration.
Diseases of supporting teeth
In the case of partial dentures, there are teeth in the oral cavity that perform the important function of supporting and securing the denture. Whether the supporting teeth are healthy, covered with crowns or restored with fillings, in any case it is necessary to take care of it and maintain hygiene of the entire oral cavity.
Symptoms
- Visible accumulations of food debris, plaque on teeth, as well as on removable structures;
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth and from the prosthesis;
- Bleeding gums around supporting teeth;
- Painful sensations during meals, from temperature stimuli, night pain.
Treatment and prevention
- Maintain regular and thorough care of dentures and teeth;
- Visit a doctor for professional oral hygiene;
- If pain occurs during chewing, as well as aching, sharp pain, contact your dentist.
Allergy to dentures
Allergy to dentures
An allergic reaction to denture materials can occur when the dentures come into contact with the tissues of the patient's body.
Currently, scientists are trying to minimize the occurrence of such reactions, and today many different materials for the manufacture of removable dentures.
The rate of occurrence of an allergic reaction can vary - from several minutes to several hours, and sometimes days after installation of the prosthesis.
Symptoms
- Rashes on the skin of the face;
- Redness and swelling of the oral mucosa;
- Attacks of bronchial asthma. Suffocation;
- Inflammation of the salivary glands;
- Dry mouth;
- Burning sensation of tongue.
Treatment
- Remove dentures;
- Contact an orthopedic dentist as soon as possible;
- Carry out repeated prosthetics with structures made of a different material.
Galvanic syndrome
This complication after prosthetics is the formation of galvanic current in the oral cavity.
The cause of the occurrence is the presence of dissimilar metals in all structures installed in the oral cavity (for example, used as the base of a prosthesis and as part of crowns) if a particular patient is predisposed to this disease.
In modern dentistry, in the manufacture of dentures, metals and their alloys are used, such as stainless steel, cobalt-chrome, silver-palladium alloys, alloys based on precious metals and others.
It is known that any alloy immersed in an electrolyte solution (in this case, saliva acts as this) acquires a potential unique to it. If metals with different potentials are present in the patient’s oral cavity, then all the conditions necessary for the formation of galvanic current arise.
Symptoms
- Unpleasant sensations while eating;
- Metallic taste in the mouth;
- A bitter and acidic taste in the mouth, especially aggravated when a metal spoon touches the dentures;
- Headache;
- Sleep disorders;
- General malaise;
- Allergic manifestations on the oral mucosa (swelling, erosion);
- Darkening of metal prostheses.
Treatment
- Repeated prosthetics, excluding the presence of dissimilar metals in the oral cavity.
Loosening the fixation of removable structures
Weakening of fixation of removable structures
This complication develops gradually, as the design of lamellar prostheses approaches the end of their service life.
In the case of clasp prosthetics, it is also possible for the plastic parts of the locking prostheses to wear off and the clasps to loosen .
Causes
- Daily use, regular removal from the oral cavity, changes in the anatomical structure of the prosthetic bed (loss of bone tissue with age).
Symptoms
- Sensation of displacement, movement of the prosthesis in the mouth;
- Lack of adherence of the prosthesis to the gums and teeth;
- Loss of structures from the mouth during eating and talking.
Treatment
- Making a new removable denture;
- Using special dental adhesives for fixation.
Correction of fastenings, relining of the prosthesis
Correction of fastenings, relining of the prosthesis
Relining of the prosthesis - correction, restoration of a removable structure in order to obtain a denture base adapted to chewing pressure, clarifying its fit to the prosthetic bed.
Over time, atrophy of the mucous and bone tissue occurs under the base of the removable denture. Atrophy leads to uneven distribution of chewing pressure between the supporting teeth (if any) and the mucous membrane. Failure to reline a removable denture can lead to its breakage and loss of supporting teeth.
Relining can take place either directly in the patient's mouth or in the laboratory.
Method of relining a removable denture in the clinic
- The dentist removes a thin layer of plastic from the surface of the prosthesis adjacent to the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed and applies an even layer of self-hardening plastic to the treated base. After some time, the prosthesis is inserted into the oral cavity, installed and pressed, after which the patient closes his jaws. Excess plastic is removed with a spatula. After this, the prosthesis is removed and placed in a special apparatus, where the final polymerization of the plastic (hardening) takes place;
- Changing the position of the cheeks and lips.
Causes
- Errors at the stages of prosthesis manufacturing: excessive or insufficient thickness of the base in the frontal region, incorrect determination of the height of the lower third of the face and the centric relation of the jaws, inaccurate placement of artificial teeth in the base of the prosthesis.
Symptoms
- “Failed” or, conversely, excessively protruded lips;
- Biting cheeks with removable dentures;
- Deep nasolabial folds;
- Drooping corners of the mouth;
- The ability to close your lips only with force, while in a relaxed state your teeth are visible;
- Feeling of tightness in the cheeks.
A few words about treating bitterness in the mouth
An unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth is a common problem that can affect a person of any age. Its causes can be different - from “errors” in nutrition and long-term use of medications to serious diseases of the liver, gall bladder and gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment for bitterness depends on the cause, age and general health, as well as additional symptoms. Medications are selected only after consultation with a doctor, since incorrectly selected therapy can only aggravate the problem and worsen a person’s well-being.
What does bitterness in the mouth mean?
Sometimes the taste in the mouth becomes bright and unusual, for example, bitter. But if nothing bitter was eaten before, where does the taste come from? Let's look at the possible causes of the phenomenon.
Mechanics of taste
Taste receptors, which are mainly located in the mouth, are responsible for the sensation of taste (don’t be surprised, but these same receptors are also present in other organs, even in the intestines and lungs, but in smaller quantities). The receptors are represented by taste buds located on the tongue, and there is a certain “geography of tastes” on the surface of the tongue: the tip of the tongue recognizes sweet, the side edges at the back - sour, in front - salty, and the root of the tongue - bitter. In order for the papillae to recognize taste, a chemical reaction is necessary - the interaction of the molecule of any substance found in the mouth and the receptor. This information is then transmitted along nerve fibers to the brain.
Bitterly!
Evolutionarily, the bitter taste served as protection for humans from harmful substances, signaling danger - “don’t eat!”
Many animal and plant toxins are perceived as bitter and tasteless. Therefore, the number of receptors that react to bitterness is quite large. The need to recognize poisons has disappeared today, but no one cares about problems with one’s own health. Receptors are still guarding a person’s well-being, but now they tell us about problems “from the inside.”
Gallbladder problems
First place should be given to problems with the gallbladder - cholecystitis, cholelithiasis.
Normally, bile produced in the liver does not stagnate for a long time in the bladder, but enters the intestines. With inflammation or the formation of stones, this process is disrupted, bile is released and supplied unevenly, often in large portions. Stagnation of bile and its inadequate amount in the intestines provoke not only indigestion, but also the reflux of contents into the esophagus. As a result, there is a bitterness in the mouth, as well as pain in the abdomen on the right, especially with errors in nutrition.
Liver diseases
Damage to the liver will also cause a bitter sensation in the mouth. The liver not only participates in the formation and secretion of bile, but also in the neutralization of everything toxic that enters the body. Therefore, here, in addition to the above mechanisms of stagnation and inflammation, internal intoxication is added, which changes the properties of saliva. By the way, hepatitis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease can occur for a long time without significant symptoms, but bitterness in the mouth will appear early.
Gastritis
With this disease, digestion is disrupted, resulting in changes in both the composition of the contents and the speed of its passage. As a result, reflux occurs from the stomach into the esophagus, and then from the intestines, from where bile acids and products released during prolonged stagnation of food come. All this is felt as bitterness, which accompanies typical pain in the pit of the stomach, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, flatulence and a characteristic picture on FGDS.
Reflux disease
Another common cause is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The main manifestation of this disease is the reflux of contents from the stomach into the esophagus. With GERD, the tightness of digestion in the stomach is disrupted due to weakness of the sphincter between the esophagus and the stomach. Throwing is the main manifestation of the disease, which is also characterized by a burning sensation behind the sternum, belching and bitterness in the mouth.
Oral diseases
Diseases such as gingivitis, glossitis and other inflammatory changes in the oral cavity can also cause a bitter taste in the mouth. In this case, harmful bacteria actively multiply, secrete metabolic products and thereby change the internal environment of the oral cavity, which leads to a change not only in taste, but also in smell: along with bitterness, an unpleasant odor from the mouth appears, which is often noticed by others.
Thyroid dysfunction
Thyroid dysfunction may also be accompanied by bitterness in the mouth.
This is largely due to hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. An excess of thyroid hormones leads to dysfunction of other hormonal systems, in particular the sympathoadrenal system. In this case, a spasm of the muscles of the internal organs develops and, as a result, the reflux of bile into the upper parts of the digestive tube. In the same way, a bitter taste is formed during stress. They also cause the activation of adrenaline and prevent the smooth muscles of the internal organs from working harmoniously.
Medicines and nutrition
Some medications do double duty. For example, antibiotics. On the one hand, they are necessary to fight infection, but on the other hand, they contribute to the development of dysbiosis, impaired liver function and can also cause an unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth. This problem usually resolves with stopping the medication and reflects systemic effects. The situation when the bitterness in the mouth becomes constant after the end of the course deserves more attention; this may indicate a more pronounced effect on the liver and intestines.
Not only medications can serve as external causes of bitterness. Dietary habits also contribute. Excessive consumption of legumes can lead to a bitter taste, since these products are difficult to digest and cause tension in all parts of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, the digestion time increases, i.e. the time the food spends in the intestines.
The greater the load on digestion - more digestive juices, more bile, which contributes to the disruption of its outflow. Bitterness appears during eating and increases as you consume your favorite beans or beans. This is not a reason to immediately run to the doctor, but it does mean that you have exceeded the allowable amount of these products.
Bitter is not always bad. A bitter taste is a reason to be more attentive and wary of what we eat and what is happening in our body, so we should not ignore this symptom. It is nonspecific, i.e., it does not relate to any single disease, but it attracts attention and can lead you in the right direction in time.