What is constipation?
Constipation or constipation is a defecation disorder that includes a complex of symptoms: difficult and/or infrequent bowel movements, a feeling of incomplete bowel movement and excessive hardness of stool.
In this case, defecation occurs less than 3 times a week. Constipation is a very common problem among the population. According to statistics, it affects 30 to 50% of adults and 5 to 20% of children [1]. In old age, this disorder is observed approximately 5 times more often [2].
Causes of long-term constipation
The main causes of long-term constipation are commonplace:
- improper diet;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- insufficient water intake;
- intestinal dysbiosis:
- disruption of the functioning of other organs of the digestive system;
- endocrine diseases;
- pregnancy in women;
- diseases accompanied by high fever and increased fluid loss;
- diseases of the nervous system that contribute to the absence or decrease of peristalsis;
- impaired blood supply to the intestine, which leads to failure of the muscular layer of the intestine and sphincters;
- pathology of the anatomical structure of the intestine and much more.
If there are pathologies of other organs, it is necessary to first direct efforts to treat them and only then treat the constipation itself.
Main causes of constipation
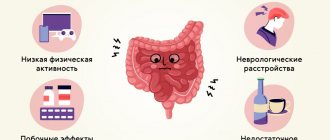
Constipation can be caused by a large number of factors - from functional disorders to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other body systems. Most often, this violation has the following causes (Fig. 1) [3]:
- Lack of physical activity, sedentary lifestyle.
- Chronic stress.
- Insufficient amount of water consumed and foods rich in dietary fiber (fiber).
- Side effects of medications: strong painkillers, antihypertensives, antidepressants, iron supplements and antacids, chemotherapy drugs.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Neurological pathologies: Parkinson's disease, multiple (multiple) sclerosis, spinal cord injuries.
- Pregnancy.
- Tumors of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diseases of the thyroid and parathyroid glands: hypothyroidism, hyperparathyroidism.
Figure 1. Main causes of constipation. Source: MedPortal
Constipation in young children
The gastrointestinal tract of newborns and infants functions with certain characteristics. For example, the absence of bowel movements for 7 days in a breastfed child is normal.
However, constipation also occurs in young children. The most common reasons are [4]:
- Introduction of new mixtures into the baby's diet.
- Food allergy to complementary foods.
- Psychological discomfort and stress, especially during potty training.
- Hirschsprung's disease.
- Congenital anomalies of the intestines and anal sphincter.
Constipation often becomes a problem when a child goes to kindergarten; this type of constipation is called “September constipation.” The reasons for its appearance are simple. In kindergarten, it is inconvenient for a child to poop; there he is fed unusual food; in kindergarten, children experience more stress and drink less fluid.
In childhood, constipation may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Tension and bloating.
- General lethargy, low mobility.
- Restless sleep, difficulty falling asleep.
- Decreased appetite.
- Excessive irritability.
Reason 2. Taking certain medications
If your doctor has prescribed you any medication, be sure to read the instructions for use, which always indicate possible side effects. One of them may be constipation. The following groups of drugs can have this effect: antispasmodics and analgesics, antidepressants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, antiulcers, antiepileptics and antituberculosis, systemic antifungals and other drugs.
Find out from our video what to do for “medicinal constipation”
Up to contents
What problems can constipation cause?
Despite significant discomfort, isolated episodes of defecation disorders are not dangerous. However, chronic constipation can be a provoking factor for a number of diseases and disorders, including:
- Fecal impaction is the accumulation of dry stool in the final intestine that cannot be passed without additional intervention.
- Rectal bleeding and anal fissures associated with rupture of the soft tissues of the rectum and anal sphincter.
- Proctosigmoiditis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
- General decrease in quality of life and depression [5].
- Damage to the blood vessels of the rectum.
Constipation can act as one of the primary symptoms of more dangerous intestinal diseases, for example, colorectal cancer.
“Colon cancer has gotten younger. In St. Petersburg, colorectal cancer is the leader among cancer diseases: in 2010, 2,700 new cases were identified, in 2015, 3,654 cases were identified. The most important organ for eliminating toxic and carcinogenic substances suffers because attention is not paid to functional constipation. Indoles, phenols, skatole, cadaverine (cadaverine) should be released every day. In addition, constipation increases the risk of inflammatory diseases, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, diverticulosis, and hemorrhoids.” Konstantin Aleksandrovich Shemerovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of the Department of Physiology of Visceral Systems named after. K.M. Bykov Institute of Experimental Medicine (St. Petersburg)
Risks of vascular damage due to constipation
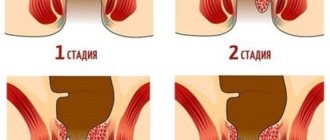
One of the most common complications of prolonged constipation is hemorrhoids. It represents inflammation, thrombosis and excessive dilation of the venous vessels located in the rectal area. It manifests itself as pain in the anus, bleeding and prolapse of hemorrhoids (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Stages of development of hemorrhoids. Source: CC0 Public Domain
The basis for the development of hemorrhoids during constipation is direct damage to the blood vessels by dry feces and excessive straining necessary for defecation in this disorder. Also, these two disorders have common provoking factors, which increases the risk of injury to local veins.
Tactics for dealing with long-term constipation
If constipation lasts 3-7 days or more, accompanied by severe pain, you must visit a doctor to rule out intestinal obstruction or other serious pathologies.
If you don’t have the opportunity to go to see a doctor, and you believe that constipation is not a consequence of serious illnesses, but the result of some temporary factors, you can try to help the body yourself.
Of course, if your constipation lasts only two or three days, you can try to use milder methods of combating it - eating foods that weaken you, folk remedies. But if an adult has constipation for 5 days, what should you do? Definitely, take more drastic measures - laxatives. And if this problem has been haunting you for a week, then you cannot do without an enema, since waiting for other remedies to work means subjecting your body to a serious test of intoxication.
Constipation as a symptom of cancer
Malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract develop for a long time without obvious symptoms. Constipation is often one of the early manifestations of cancer.
This symptom is caused by mechanical blocking of the intestinal lumen by the tumor, which complicates the passage of feces through the intestinal sections. It can also be a side effect of ongoing chemotherapy.
Other possible clinical signs of gastrointestinal cancer include:
- Loss of body weight without changes in diet.
- The appearance of blood impurities in the stool.
- Chronic weakness and malaise, headaches.
It is also believed that constipation caused by other reasons may increase the risk of developing malignant tumors due to the content of carcinogens in the feces.
Constipation in colon cancer
The most common symptom of a malignant tumor of the colon is a violation of bowel movements. In this case, both an intensification of an existing disorder and alternating attacks of constipation and diarrhea can be observed. Patients also experience pain in the area of the tumor, and there may be fresh, unchanged blood or mucus in the stool [6].
Constipation in colorectal cancer
When the tumor is localized in the rectal area, possible symptoms, in addition to constipation and other signs of colon cancer, are the sensation of an empty bowel. Because of this, the patient experiences severe discomfort and a constant urge to defecate [6].
Constipation in stomach cancer
In case of malignant tumors of the stomach, constipation most often occurs as a consequence of impaired intestinal motility (paresis) as a result of chemotherapy.
Clinical manifestations of stomach cancer are similar to those of colorectal cancer: pain in the abdomen, alternating constipation with diarrhea, weight loss, general weakness. In this case, feces most often acquire a dark brown or black color due to the reaction of the blood with hydrochloric acid.
In advanced stages of cancer, the tumor may block the lumen of the outlet connecting the stomach and duodenum. As a result, food stops getting into the intestines, which causes stool retention. Clinically, this is manifested by vomiting of partially digested food a short period of time after eating.
Vomiting after eating, along with constipation, may be evidence of stomach cancer. Photo: jcomp - ru.freepik.com
Prevention and treatment of constipation
The main goal of treating constipation is to prevent the disorder from becoming chronic and the formation of associated complications. It is based on simple approaches and advice aimed at changing diet and lifestyle [7]:
- Drink 1.5-2 liters of unsweetened, caffeine-free liquids daily.
- Limit your intake of alcohol and caffeinated drinks.
- Add fiber-rich foods to your diet, such as raw fruits and vegetables, whole grains, beans, prunes, or bran cereal (Figure 3).
- Aim for about 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Best options: swimming, cycling, walking.
- Add yoghurts and kefir with live active probiotic cultures to your diet. There are studies proving their effectiveness for chronic constipation [8].
Figure 3. Foods that help relieve constipation.
Source: MedPortal Drug treatment of constipation should be carried out with extreme caution. Laxatives are initially very effective in helping to combat defecation disorders, but with prolonged use, a person may lose the ability to defecate independently.
Treatment of constipation in children
Due to the fact that with constipation, a child experiences pain while going to the toilet, he may begin to be afraid of pooping, will begin to retain feces in himself, and this will worsen the situation. After all, the longer the fecal bolus is in the intestines, the more pain it will come out with.
At the first sign of constipation in a child, you should consult a doctor. Pediatricians advise using an enema as an urgent measure (before a course of laxatives, if there is no bowel movement for more than 3 days, if bowel movements cause pain or bleeding), while the main treatment consists of selecting laxatives. In this case, the dosage of drugs should be selected by a specialist.
“What will help in the long run? Only laxatives. Such a child needs a long (2-4 months) course of laxatives, the goal of which is to make the stool soft for the entire duration of treatment. How to give laxatives? If only it were possible to clearly calculate the effective dose in advance and tell it to parents... But each child has his own dose, so laxatives are administered in 4 phases.*
*In the first phase, the child is given an increasing dose of the drug in order to reach a dose at which mild diarrhea will be observed. This dose is then maintained for several months, after which the drug is gradually discontinued. -Ed.
When used correctly, the effectiveness and safety of osmotic laxatives are very high. Of course, in addition to laxatives, you should try to correct stools with diet: give the child more water (a liter per day or more). Introduce more vegetable fiber (salads, vegetable stews), juices (plums, prunes), fermented milk products (yogurt), laxative foods (beets, pickles), etc. But all this is easier said than done: as a rule, children with constipation are small-fed and picky, sit on pasta with sausages, carry sweets and turn their nose up at everything else.”
An excerpt from the book by pediatrician Sergei Butria “Child's Health. How to learn to cope with illness and your own panic.”
How to give a cleansing enema to a child?
For an enema, you should use a syringe with a volume of 300–400 ml. It can be filled with saline solution (0.9% sodium chloride solution) or hypertonic solution (2–5% sodium chloride) at room temperature. After this, the tip of the syringe and the child’s anus are lubricated with a rich cream, the child is placed on his left side, the legs are brought to the stomach and the tip is carefully immersed 4-5 cm into the anus. When the enema is inserted, the child’s buttocks are squeezed and the solution is slowly introduced into the rectum. After the enema is given, the buttocks should be kept closed for at least 2 minutes before placing the child on the potty.
Correction of the diet menu
To understand how to avoid constipation while dieting, it is important to review the composition of your diet. Without the use of fermented milk products, dishes rich in dietary fiber, and vegetable oils, this is unlikely to be possible. In addition, it is worth considering that a diet that strictly excludes these foods can hardly be considered effective.
So-called mono-diets have proven harm to the body. It is better to consult a nutritionist to develop a suitable menu. Thus, it is strictly not recommended to give up vegetable oils. Oils are a source of beneficial substances and, when consumed in moderation, do not affect the volume of the figure.
Fermented milk products can be consumed if there are no health restrictions (for example, lactase deficiency), and to achieve the desired effect of the diet, you can choose low-fat products. You can add bran in small quantities to fermented milk drinks - this will help you get your daily intake of dietary fiber.
There are several rules for a healthy diet that will help maintain normal bowel function.
- Try not to skip breakfast: firstly, it will recharge your energy. Secondly, a hearty morning meal stimulates the necessary reflex. For breakfast, you can choose steamed omelets, porridge (except rice) with the addition of dried apricots, prunes, honey or berries, bread with avocado and/or low-fat cottage cheese, etc.
- It is important to drink enough water during the day: you won’t be able to get the required 1.5-2 liters of water in the evening; you need to drink it in the morning and afternoon hours.
Remember that your diet should include fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, and berries. If the diet is aimed at weight loss, try to choose low-calorie fruits and berries - oranges, strawberries, peaches, avocados, grapefruits, lemons, etc. Among vegetables, it is better to give preference to those that do not cause increased gas formation and have some laxative effect - beets, carrots, celery, etc.
Sources
- Parfenov A.I. “Constipation: from symptom to disease” Consilium Medicum. Volume 05, No. 12, 2003
- Privorotsky V. F., Luppova N. E. Modern approaches to the treatment of functional constipation in children. RZHGGK. - 2009. - T.19. - No. 1. - P.59-65.
- What is Constipation? WebMD, 2019
- Adam Felman “What to know about constipation.” MedicalNewsToday, 2021.
- Iovino P., Chiarioni G., Bilancio G., Cirillo M., Mekjavic IB, et al. (2013) New Onset of Constipation during Long-Term Physical Inactivity: A Proof-of-Concept Study on the Immobility-Induced Bowel Changes. PLOS ONE 8(8)
- Colorectal cancer. The Royal Marsden
- Danielle Moores "What You Should Know About Constipation." Healthline. 2019
- Magro DO, de Oliveira LM, Bernasconi I, Ruela Mde S, Credidio L, Barcelos IK, Leal RF, Ayrizono Mde L., Fagundes JJ, Teixeira L. de B., Ouwehand AC, Coy CS Effect of yogurt containing polydextrose, Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactis HN019: a randomized, double-blind, controlled study in chronic constipation. Nutr. J. 2014 Jul 24;13:75.