Increased salivation should alert a woman and force her to understand the causes of such a disorder. Saliva production is an important mechanism by which the oral mucosa remains moist and maintains healthy microflora. Few people know that digestion begins in the mouth, under the influence of salivary enzymes. Hypersalivation can become a real problem, which reduces the quality of life and causes a lot of inconvenience to a woman.
Causes of hypersalivation
Hyperfunction of the salivary glands is the main cause of excessive salivation in women.
But there are others that are also quite common:
- Taking certain medications, which requires dosage adjustment or discontinuation of the medication;
- Exacerbation of diseases of the stomach and intestines: often the cause of increased salivation in women lies in ordinary gastritis, which is accompanied by nausea, pain, heartburn;
- Worm infestations can increase the amount of saliva, while the woman feels overwhelmed, tired, suffers from drowsiness and may lose weight;
- Exacerbation of infectious diseases affecting mainly the ENT organs;
- The development of stomatitis, which not only increases the activity of the salivary glands, but is also accompanied by soreness of the mucous membrane, the formation of ulcers, and the appearance of a characteristic plaque.
Sometimes salivation is not a pathological manifestation, but only indicates that it is time to have a snack. Temporary hypersalivation appears in almost all people who are hungry.
One of the causes of hypersalivation is dental procedures.
accompanied by damage to the mucous membrane. In this case, there is a short-term increase in saliva production. Gum injuries can occur not only during dental treatment, but also when using dentures. During the period of adaptation to dentures, there is a lot of saliva in the mouth, but this will go away over time. Avoid damaging the mucous membrane, use special gels with regenerating and anti-inflammatory effects.
Symptoms of nausea
The main symptom is a feeling of heaviness and pain in the stomach, accompanied by copious saliva in the mouth and possible vomiting. Vomiting alleviates the condition and removes undigested food and toxins from the body. After it, your health improves, your stomach is freed.
- Deterioration in health;
- Severe dizziness;
- Increased salivation (hypersalivation);
- Paleness of the skin;
- Poor appetite;
- Cramps in the abdominal area;
- The mouth is abundantly filled with thick saliva;
- Sweating increases;
- Apathy, want to sleep;
- Decrease or increase in pressure;
- Chills, increased body temperature;
- Diarrhea;
- Vomiting;
- Weight loss;
- Breathing becomes difficult, shortness of breath appears;
- Heart rate increases.
Short-term nausea is not dangerous to humans, but can serve as an alarming symptom of other diseases.
Hypersalivation during pregnancy
During pregnancy, some complain of hypersalivation, which occurs mainly at night or in the morning. Increased salivation is one of the signs of toxicosis
, which is combined with nausea, vomiting and malaise. Hypersalivation occurs for a few minutes, usually before an attack of vomiting. Sometimes salivation continues throughout the day, accompanying the first months of pregnancy.
The reason for this disorder is hormonal changes in the body.
. To get rid of salivation, you need to suppress nausea.
In the first months, the body adapts to new conditions, and usually after the first trimester, drooling stops.
Women are not recommended to take diuretics to combat hypersalivation and nausea. It is better to use traditional methods, for example, use citrus peels: they must be chewed in the morning when the pregnant woman feels unwell, as well as during the day if an attack of nausea is approaching. Nausea is one of the common accompanying symptoms of hypersalivation. Hypersalivation is often accompanied by additional symptoms:
- feeling of nausea;
- heartburn, belching;
- difficulty and pain when swallowing food; temperature increase;
- general physical weakness;
- signs of intoxication;
- changes in the functioning of taste buds.
There is also a decrease in human activity, a deterioration in the psycho-emotional background due to discomfort associated with intense saliva production. With excessive salivation and sore throat, redness is visible, which indicates the development of an inflammatory process. Hypersalivation is manifested in particular by drool appearing in the corners of the mouth. At night, salivary fluid leaks onto the pillow.
Increased salivation and thirst can be symptoms of diabetes.
Diagnosis is carried out taking into account associated factors, which, in combination with hypersalivation, indicate a specific problem. Excessive production of salivary fluid with constant nausea indicates problems in the digestive system or pregnancy. When the cause is eliminated, the functionality of the glands is quickly restored.
In combination with thirst, increased salivation indicates the likelihood of developing diabetes. Problems in the larynx (severe tonsillitis, sore throat) are also possible. The feeling of a lump in the throat with intense saliva production signals inflammation occurring in the larynx. Sometimes a lump in the throat prevents you from swallowing liquid, causing pain.
Informpedia
Any single symptom can be a sign of one to several dozen diseases. To make an accurate diagnosis, they should be considered together. This article mentions three symptoms that occur in a huge number of people. These are salivation, belching and nausea. These symptoms accompany diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. There are several such diseases. We'll look at them in order of greatest likelihood.
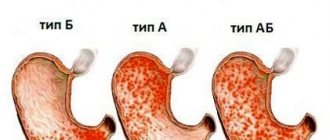
Gastritis of the stomach
Most often, based on the combination of the above symptoms, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, that is, gastritis, is diagnosed. Additional symptoms:
- Cutting pain in the upper abdomen.
- Hyperthermia
- Feeling of fullness in the stomach.
- Vomiting and dizziness.
- Bloating, loose stools, or constipation.
- Weakness, lack of appetite.
- The belching is sour or bitter, the breath is unpleasant.
Chronic gastritis is caused by Helicobacter pylori or untreated acute gastritis. The symptoms are the same, but acute manifestations alternate with remission.
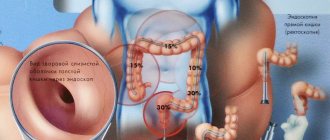
Reflux esophagitis or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
GERD is a disease caused by dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter. This leads to stomach acid entering the esophagus and reacting there with the alkaline environment, creating favorable conditions for the development of inflammation.
Reflux esophagitis, in addition to the triad of symptoms mentioned above, is accompanied by heartburn after eating, pain in the chest (usually on the left), a feeling of heaviness or fullness, and impaired passage of food through the esophagus (dysphagia).
People at risk for this disease include obese people, pregnant women, and patients with hiatal hernia. Frequent vomiting or the use of a nasogastric tube can trigger GERD.
Chronic pancreatitis
Acute and chronic form of inflammation of the pancreas. Salivation, belching and nausea accompany it very often. Symptoms such as aversion to food or, conversely, severe hunger and thirst, pancreatic diarrhea, rumbling in the stomach and bloating are also observed.
The cause of chronic pancreatitis is irregular and unhealthy diet, alcoholism, infectious diseases, helminthiasis, and heavy metal poisoning. Pancreatitis threatens the development of diabetes mellitus.
Achalasia cardia
This is another disease of the esophagus, a neuromuscular disorder that occurs due to the fact that when swallowing there is no reflex opening of the cardia (the opening between the stomach and the esophagus). As a result, the patency of the esophagus is disrupted, causing difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), vomiting and pain in the retrosternal region. Accompanied by attacks of irresistible nausea, belching and drooling. The reasons for the development of achalasia have not yet been found.
All these diseases are connected in one way or another, one can transform into another. If left untreated, they increase the likelihood of developing esophageal or stomach cancer. You cannot ignore these three seemingly harmless symptoms; you need to go to the hospital for a thorough examination. Be healthy!
Hypersalivation as a sign of another disease
Hypersalivation often develops secondary, against the background of another disease. If a woman feels pain in the throat, it is necessary to examine it for signs of tonsillitis
.
During the first day of the disease, the temperature may not rise, but dry mucous membranes appear, weakness and slight swelling of the tissues occur. On days 2-3, the throat turns red, and drooling may persist throughout the course of the pathology.
With disorders of the thyroid gland and some neurological pathologies, saliva flows from the mouth during a conversation. When the underlying disease is corrected, this symptom usually disappears. Digestive disorders almost always occur with moderate or increased hypersalivation
. Additional signs include heartburn, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite.
Infectious processes in the oral cavity can increase drooling
. In this case, hyperthermia is often observed, as well as signs of intoxication, which indicate the active reproduction of pathogens and the release of toxins.
If salivation is increased, you need to look for the causes of the disorder. This is the only way to solve this problem and avoid relapses.
Preventive measures
Prevention first of all consists in determining the cause that causes the unpleasant condition. Also, to prevent the problem from occurring you need to:
- Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth on time and always.
- Be examined by a dentist at least 2 times a year.
- Adjust your diet and eat a healthy, balanced diet.
- Lead a healthy and active lifestyle.
- It is always necessary to promptly and completely treat infectious, viral and other infections of the body, and diseases of the oral cavity.
- From time to time it is recommended to take anti-worm tablets.
If increased salivation appears at night during sleep, and there are no diseases, then the following means can be used for prevention:
- Salty and pickled dishes, bitter foods and other foods that irritate the mucous membranes are completely excluded from the menu.
- It is necessary to quit smoking, consume alcohol and stop using chewing gum; if you chew chewing gum, you need to chew it for up to 5 minutes. It is better to stop eating seeds.
- When using medications, you need to know all the side effects.
- For prevention, you can make a mouthwash from sage, chamomile or oak bark. These substances can reduce saliva production; it is enough to rinse your mouth before going to bed.
Excessive salivation is not normal and this symptom should not be ignored. This is often a sign of various diseases or failures of internal organs.
How to get rid of excess saliva?
Increased salivation and the discomfort it causes cause people a strong desire to get rid of this problem as quickly as possible. Treatment, in turn, directly depends on the causes of its occurrence. The process of diagnosing a disease plays no less a role than the treatment itself. First of all, you need to contact a doctor: this could be a dentist or therapist. If the problem of hypersalivation is beyond their competence, they can redirect the patient to an ENT specialist or dentist.
If excessive saliva production needs to be stopped, doctors may prescribe medications to suppress overactive salivary glands (such as Ribal). But if the cause is not specifically in them, but in diseases of other organs or systems, then this will not be the treatment of the disease, but the suppression of its symptoms.
You can completely get rid of this problem only after completely eliminating its source.
If the source of the disease is the salivary glands themselves, doctors can remove them, but this only happens as a last resort. Most often, a course of treatment is prescribed, for example, cryotherapy, which stimulates the swallowing reflex. Some medications may be injected into the salivary glands to slow down the secretion.
First aid for nausea
Painful sensations in the stomach disrupt the usual rhythm of life, you want to be free from discomfort. To help yourself deal with this, try these tips:
- Take a horizontal position - lying down, a person feels better, especially important for dizziness;
- Wash with cool water;
- It is worth limiting physical activity, it is advisable to maintain complete rest;
- Ventilate the room, fresh air will help improve your well-being;
- Rinse your mouth after vomiting;
- Eat healthy foods (fruits, vegetables, dietary meat);
- Eat often, in small portions, plenty of fluid intake is important (salty, spicy, iron-containing foods are not allowed);
- Drink a glass of water with lemon;
- Try to restore your breathing and relax;
- Turn on calm music, your favorite movie. It is important to calm the nervous system;
- Take antiemetics at night;
- If you have problems with stool, take prebiotics.
Read also: Dry mouth
As soon as the nausea subsides, consult a doctor to determine the cause. Pay close attention to changes in how you feel.
Causes of excessive salivation in men
The causes of this disease can be very different, but the result is always the same - severe discomfort. The fact is that men and women in the modern world are forced to communicate a lot with other people. Normal communication is impossible if you do not make a pleasant impression on the interlocutor.
Increased salivation does not allow you to look good. A sick person is forced to avoid communication with other people. A psychological complex develops when the patient thinks that everyone around is paying attention to his problem. This is followed by a decrease in self-esteem, and depression sets in.
Increased salivation in medical practice is called hypersalivation.
Increased salivation is explained by increased work of the salivary glands. There are 3 pairs of them in the human oral cavity. The main task of these glands is to secrete saliva in the required volumes. However, if their function is impaired, saliva is produced in excess. It literally floods the oral cavity, which is why the patient is forced to constantly spit it out or swallow it. At the same time, it looks completely unattractive. In addition, the person cannot eat normally: problems with swallowing arise.
This problem in adults is caused by various pathological changes in the body. Increased salivation is often caused by various diseases of the digestive system. Also, drooling may begin to flow profusely after taking certain medications. The cause of hypersalivation can be excessively hot or spicy food, etc. In any case, the problem cannot be dealt with unless the source of the disease is accurately determined.
Problem in children
In small infants, increased salivation is considered normal. At this age, children drool due to reflexes, so parents do not need to worry and carry out treatment.
Also, in children under one year old, when teeth appear, there may also be a strong secretion of saliva; this should not alarm relatives, since the process is normal, natural.
When teeth are cut, regardless of age, the glands begin to work more actively, and a lot of fluid appears in the oral cavity.
In the case of salivation for other reasons, this refers to the pathological condition of the child. The cause may be various types of head injuries or concussions.
In some cases, an infant may have a problem with gastrointestinal diseases, as well as viral infection of the body.
In some cases, the reasons may be hidden in psychological factors if the child often experiences stress, fear and anxiety.
The last reason for excessive salivation is infection of the body with worms, which appear quite often in children.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at combating the underlying disease. The specialist must identify the reasons
and select effective therapy based on the information received. In some cases, the patient needs consultation from other specialized specialists.
To suppress the increased activity of the glands, special drugs are prescribed that reduce salivation. It must be remembered that such medications have one unpleasant side effect in the form of dry mucous membranes.
, against the background of which other diseases may develop and infection may occur. Saliva also performs protective functions, so it is necessary to take the remedy for increased salivation carefully, preferably in short courses.
In advanced cases, surgical removal of the salivary glands is performed.
. The operation is considered complex and is accompanied by the risk of damage to nerve endings and future problems such as facial asymmetry.
The treatment regimen for hypersalivation may include physical therapy, massage sessions, and folk remedies: rinsing the mouth with tinctures prepared from shepherd’s purse or viburnum berries. Sometimes the problem occurs due to the habit of rarely swallowing saliva. In this case, it is necessary to resolve the issue with the help of self-discipline.
Try to treat your teeth and gums on time
, as well as the digestive organs, the dysfunction of which often results in an excess of saliva. Hypersalivation is possible with an incorrect diet, which contains a lot of hot and sour foods, seasonings and spices. Review your eating habits if they are leading to this problem.
What medications will help?
Saliva production is a natural process controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Its violations are evidence of either general health problems or pathologies of individual organs and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Let's take a closer look at the causes and treatment of excessive salivation in adults. If excess fluid in the oral cavity reduces the quality of life, in addition to general therapy, the doctor prescribes symptomatic treatment - anticholinergics:
- scopolamine;
- riabal;
- platiphylline.
Scopolamine has fewer contraindications - only glaucoma. Platiphylline has glaucoma, organic kidney and liver diseases. Riabal is taken during pregnancy, but it is contraindicated for problems with the prostate, gall bladder and kidneys, intestines, cardiovascular system and many other diseases. Platyphylline has the least side effects - dry mouth, blurred vision, difficulty urinating and rapid heartbeat.
A quick but temporary effect is achieved by intramuscular injections of Botox into the area of the salivary glands - in the cheeks and cheekbones. Botox blocks the nerve signals that the salivary glands transmit to the brain, and due to this, a strong response to irritation of the glands does not occur and saliva is not released in large quantities. Facial massage is useful for hypersalivation of a neurological nature.
Nausea and increased salivation
Everyone has a feeling of nausea, regardless of age - both adults and children. This is an unpleasant sensation that causes discomfort in the stomach, dizziness, increased salivation, poor health, and pale skin.
Nausea before vomiting can occur even in a healthy person. This is usually associated with disruption of processes in the digestive tract, cardiovascular or central nervous system. If you feel sick for a long time, periodically, this can be a symptom of a number of diseases (cholecystitis, gastritis, meningitis), which occurs during toxicosis during pregnancy.