A gastroenterologist is a doctor who deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and timely prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach, various parts of the intestines, esophagus).
The doctor also treats diseases of the liver, pancreas, and gall bladder. Typically, with abdominal pain and digestive disorders, older people go to a therapist, and children are referred to a pediatrician. After a standard examination, if indicated, the general practitioner will refer you to a pediatric/adult gastroenterologist.
Such a specialist works in clinics, hospitals, scientific and practical medical centers.
Who exactly is a gastroenterologist?
The content of the article
Many of us, when thinking about the digestive system and human gastroenterology, limit ourselves to the stomach and intestines. However, the specialization of a gastroenterologist includes the diagnosis and treatment of the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, pancreas, gallbladder, bile ducts, liver dysfunctions and diseases.
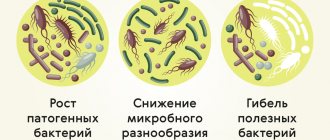
As more and more research establishes a definite connection between human health and changes in intestinal microflora, microbial imbalance is also becoming one of the areas of focus for gastroenterologists.
Is there a gastroenterologist at the clinic?
Each city clinic is required to have such a set of specialists as prescribed by the Ministry of Health in its order. A gastroenterologist is not a mandatory physician for medical institutions providing outpatient care to fewer than 50 thousand people. If a city clinic serves an area whose population does not exceed 49 thousand people, it is not required to employ a gastroenterologist.
However, for medical institutions in larger areas, this specialist becomes mandatory, as do a number of other doctors of narrow specialties. In addition, such clinics must be equipped with everything necessary for organizing rehabilitation rooms, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography machines.
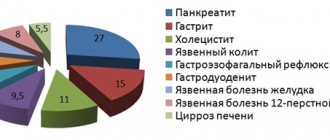
Diseases treated by a gastroenterologist
The most common diseases and disorders that are diagnosed and treated by gastroenterologists are:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS);
- Celiac disease (gluten intolerance);
- Inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease);
- Gallbladder diseases (stone disease, polyps, dyskinesia);
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- Hemorrhoids, anal rupture;
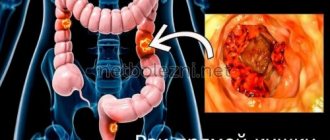
- Gastrointestinal polyps;
- Ulcer (ulcers of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum);
- Acute and chronic inflammation of the pancreas.
Haemorrhoids
Gastrointestinal polyps
We can identify six situations in which you should consider consulting a gastroenterologist:
Where does a pediatric gastroenterologist see?
You can make an appointment with a pediatric gastroenterologist at both a municipal and private medical center.
Many parents prefer the services of private doctors, as this provides a number of advantages:
- It’s easy to get an appointment – electronic registration is valid, there are no queues;
- the ability to choose a convenient time for consultation - you won’t have to miss work, or your child will miss kindergarten or school;
- use of modern diagnostic techniques - usually private medical centers have advanced equipment that allows you to quickly and accurately determine the condition of the gastrointestinal tract without pain for a young patient.
Private medical centers employ highly specialized doctors, so if you need to consult another specialist (for example, a pediatric endocrinologist or urologist), you do not have to go to another institution. Another advantage is the presence of our own laboratory, which significantly speeds up the processing of analyzes and the preparation of research results.
If you want to make an appointment for your child with a pediatric gastroenterologist, you can contact the medical office.
3
4
8
Article rating:
5 out of 5 based on 1 rating
Author: [anchor href=»onclinic.ua/doctors/omelchenko-elena-vladimirovna»]Omelchenko Elena Vladimirovna
Pediatric gastroenterologist. Highest qualification category. Work experience 29 years.
Defecation disorder
- Constipation
. If you defecate less than three times a week, this may be a manifestation of not only pathologies of the intestine itself, but also problems with neurological, endocrine or microbial imbalance. Constipation can also be caused by poor diet and low fiber and water intake. A gastroenterologist will determine what is causing your constipation. - Diarrhea (diarrhea)
. This is frequent bowel movements with watery, loose stools three or more times a day. Many people experience this disorder several times a year or more. Diarrhea can be acute or chronic. Acute diarrhea often lasts one or two days, while chronic diarrhea can last several months.
Appointment with a gastroenterologist
What does a gastroenterologist do? To establish the nature and cause of the pathology that worries the patient, the gastroenterologist prescribes a comprehensive examination. To differentiate diseases, a number of measures are used:
- listening and analyzing patient complaints. Information helps determine the localization of the destructive process and suggest possible organ dysfunctions
- palpation examination gives the doctor the opportunity to assess the size of internal organs and confirm some assumptions
- blood test (detailed, biochemical, with phosphatase, amylase) allows to identify disorders of internal organs
- urine test (general, sugar). The study reveals problems with the pancreas and liver
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs
- fibrogastroduadenoscopy (FGDS)
- X-ray of the stomach, esophagus, duodenum is prescribed when it is not possible to perform an FGDS (high gag reflex)
- CT scan can detect or exclude the presence of a tumor
- endoscopy. It is carried out if an ulcer or tumor is suspected.
Frequent heartburn
Many people know what heartburn is. It is important to understand that occasional heartburn should not be a cause for concern. However, if you feel heartburn constantly and there is a frequent need to take antacids, you should not think that this is the norm.
Frequent heartburn
Frequent heartburn can be a sign of gastritis, ulcers, dysbiosis, candidiasis, or gastric hernia. If your heartburn is accompanied by any of the symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, food getting stuck, or painful swallowing, you should see a gastroenterologist immediately as this could be a sign of cancer.
When reflux is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed, and in rare cases, even surgical treatment may be recommended for a gastric hernia.
When to contact
When digestive problems occur, the processes of breakdown and absorption of nutrients are disrupted. Some of them, turning into toxins, accumulate in the body and poison it. As a result, health deteriorates, immunity decreases, and performance decreases.
That is why, if a number of signs are detected, you should immediately go to an appointment with a gastroenterologist. These include:
- abdominal pain of varying localization, nature and intensity;
- heartburn after eating;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- poor appetite or lack thereof;
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing);
- belching after eating;
- bad breath;
- bloating and rumbling in the stomach;
- problems with stool (diarrhea, constipation);
- blood in stool;
- heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium;
- feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- change in color and consistency of stool;
- peeling and rashes on the skin in the absence of infectious diseases;
- causeless deterioration of the condition of the skin, hair and nails.
It would be a good idea to visit a doctor for people who have undergone chemotherapy, radiation, or have been taking antibacterial drugs for a long time. Almost always they suffer from a violation of the microflora in the intestines.
Painful swallowing (odynophagia) or food getting stuck (dysphagia)
Certain digestive disorders can cause difficulty swallowing or an inability to swallow food or even liquids. If you experience frequent esophageal pain and difficulty swallowing, or if swallowing becomes difficult over time, see a gastroenterologist.
In such cases, endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach (gastroscopy) is necessary to determine the cause of the complaints.
If you're considering choosing a specialist, remember that gastroenterologists are specially trained to treat complex digestive system conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, ulcers, or SIBO, and are always available to help you.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
How does a gastroenterologist work?
Regardless of whether the specialist is conducting the consultation: paid or free, the algorithm of his actions should remain identical. The initial examination involves palpation and measurements of common indicators such as pulse and blood pressure to create an overall clinical picture.
The doctor will also review the medical history, if any, and listen to all the patient’s accumulated complaints. Based on the information received, the patient is prescribed a number of referrals for tests. And after their results are received and the need for additional diagnostics arises, the patient may be sent for instrumental studies.
If it is necessary to use auxiliary diagnostic techniques, many patients have to undergo examination on a commercial basis. But in this case, you should not spare money, because there is a high probability that outdated methods of detecting the source of inflammation will simply fail.
The following modern methods are used as assistants to establish the truth:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- fibrocolonoscopy;
- EGDS;
- MRI of the abdominal organs with and without contrast;
- liver fibroscanning;
- virtual colonoscopy;
- retrograde cholangiography.
Sometimes the hospital insists on additional DNA testing. These new generation tests are necessary when genetic disorders or rare diseases are suspected.
Treatment will be prescribed strictly based on the data obtained, so it often does not coincide even in those patients who have been given identical diagnoses, but their overall health status differs. The following areas can be taken as the basis for therapy, both together and separately:
- use of pharmaceuticals;
- herbal medicine or similar options for help from a naturotherapist;
- dietetics and scheduling of rational nutrition and lifestyle;
- non-drug treatment methods, such as physiotherapy, acupuncture, laser therapy, pressure chamber, physical therapy.
Sometimes surgery is necessary. This means that the patient will need to consult a surgeon.
When to go to a gastroenterologist?!
— Elena Evgenievna, what complaints do patients most often come with?
— The most common: abdominal pain and heartburn. There are many causes of abdominal pain: from functional disorders due to stress to serious illnesses.
Often there is pain in the right hypochondrium due to dysfunction of the biliary tract, and a feeling of discomfort in the epigastric region due to gastritis. In spring and autumn, peptic ulcer disease often worsens. The situation may worsen due to stress and dietary errors. Moreover, as a rule, these two factors are interrelated: a stressful state for many is a trigger for eating disorders: someone’s appetite increases or, conversely, disappears, and the person eats irregularly or overeats, reduces control over the quality of food, etc. All this inevitably leads to problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Heartburn is not a separate disease, but a symptom: a burning sensation behind the sternum. In fact, this is a chemical burn from the acidic contents of the stomach when it is thrown into the esophagus, where the environment is often alkaline. This leads to damage to the esophageal mucosa by hydrochloric acid and the protein-breaking enzyme pepsin. Sometimes with reflux disease there is no heartburn, but there is a feeling of a lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing, pain in the chest, which is confused with angina. All this significantly reduces the patient’s quality of life. This disease can and should be treated. Frequent reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus, especially with an admixture of bile from the duodenum, can even lead to cancer of the esophagus. Treatment is usually long-term, since the situation has developed over the years, and it cannot be changed instantly. In addition to medication, changes in lifestyle and eating habits are required. With the help of medications, we can reduce the amount of acid produced, which will lead to less of it being thrown into the esophagus, and accordingly, heartburn will appear less. There are also a number of drugs that absorb acid and remove it. These are quick-acting remedies. They help get rid of heartburn for 30–40 minutes. Typically, these are the drugs that are actively promoted in advertising and will be offered by the pharmacist at the pharmacy. The patient must, of course, follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Meals during reflux disease should be in small portions so that the volume of food eaten does not exceed the volume of the stomach, and for better control of appetite, frequent portions: 4-5 times a day. Food must be chewed thoroughly to break it down as much as possible and release more saliva, which, having an alkaline reaction, neutralizes the acid.
For reflux disease, boiled, baked, stewed vegetables, liquid porridges, pasta, lean meats, poultry, seafood, eggs, cottage cheese, stale bread and crackers, jellies, mousses, jelly, puree soups, and dairy products are recommended. They increase acid formation in the stomach and therefore are not recommended: smoked foods, fatty, spicy, salty foods, mushrooms, raw vegetables, sour fruits and juices, carbonated drinks, brown bread, baked goods, fast food, strong tea and coffee
— Does heartburn result from poor nutrition or is its occurrence genetically determined?
- Both. The peculiarity of the sphincters between the esophagus and stomach is genetically determined. A fairly common problem is connective tissue dysplasia, that is, its increased elasticity, which results in flat feet, varicose veins, “unstable vertebrae,” and weakness of many sphincters, including the esophagogastric and esophageal opening of the diaphragm. That is, they do not close tightly enough, and food easily passes from the esophagus into the stomach.
The number of parietal cells in the stomach is also genetically determined, which determines the quantity and quality of hydrochloric acid they produce. Heartburn in pregnant women
Pregnant women often complain of heartburn. This is due to two main points. Firstly, as the baby grows and the uterus enlarges, intra-abdominal pressure increases, the load on the stomach and intestines increases, which can provoke the reflux of acid and bile into the esophagus. By the way, this often leads to constipation in pregnant women. Secondly, pregnant women have a special hormonal background aimed at reducing the tone of the uterus and, at the same time, the sphincters of the esophagus relax, which can result in acid reflux. If you have similar problems, you don’t have to endure and wait that “it will go away on its own after childbirth”... Contact a gastroenterologist right away. The doctor will select treatment: there are drugs approved for use during pregnancy. Also, together with a gastroenterologist, you will discuss how to change your diet and lifestyle in order to get rid of this problem. Ideally, contact a gastroenterologist at the stage of pregnancy planning - this way you can avoid many problems with the gastrointestinal tract that arise during this period in a woman’s life.
— One of the very common diagnoses is gastritis. What is the reason for this and how is it treated?
— Gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa. This diagnosis is, indeed, very often made, and often without proper grounds. This diagnosis is made morphologically, that is, after a morphologist describes the existing inflammatory changes as a result of a biopsy of the gastric mucosa. Then it’s gastritis. Only on the basis of complaints, a competent doctor can write only “functional dyspepsia syndrome” in the diagnosis. Complaints with gastritis are quite varied: it can be pain, a feeling of a full stomach even with a small amount eaten, belching, vomiting, etc. This depends on the characteristics of the production of gastric juice, on the vegetative status of the patient, on the characteristics of his lifestyle, eating pattern - everything is very individually.
Myth
Probably everyone has heard the opinion: “if you eat dry food, you will get gastritis.” In fact, this is not true! Food should be without additional liquid; it should not be washed down with water, tea, coffee, etc. Liquid dilutes the acidic contents in the stomach and impairs the quality of food digestion. But eating “on the run” is really not worth it - the most important thing for a good digestion process is chewing food thoroughly! A large amount of saliva released during chewing is necessary for the absorption of food. What causes gastritis? Stress, systematic violation of the diet, violation of the frequency of meals, abuse of semi-finished products, concentrates, spices, sour, hot, peppery, salty, smoked, fried, too hot, too cold or otherwise thermally, chemically or mechanically irritating foods, carbonated drinks, coffee , alcohol, smoking; lack of thorough chewing of food.
In addition, gastritis is often caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. This bacterium needs acid-free conditions to exist; for this, it “envelops” itself in a cloud of urease, an enzyme that creates an alkaline environment. All this damages the mucous membrane to the point of its atrophy, and can also lead to the development of stomach and duodenal ulcers, significantly increasing the risk of developing stomach cancer. 95% of gastric ulcers and 85% of duodenal ulcers worldwide are associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Other causes of damage to the gastric and duodenal mucosa are frequent use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In the treatment of gastritis and peptic ulcers, drugs are used that reduce the acid production of the gastric mucosa and improve its healing, and if Helicobacter pylori is detected, a course of antibacterial therapy is used. The patient must be prescribed a gentle diet. All these measures are prescribed only by a doctor. Self-medication can be not only ineffective, but also harmful to the patient.
— Is stress also one of the reasons for the development of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)?
— Yes, the classic triad for making this diagnosis: stress, pain, bowel dysfunction (diarrhea, constipation or their alternation). The very name of the disease contains its essence: the intestine is irritated, sensitivity is increased.
The unusual thing about this disease is that the patient has no visible damage to the intestinal mucosa. No examination can establish what is actually happening to the human body, but the disease clearly manifests itself. The mechanism of symptoms is related to the characteristics of the intestines. The intestine has its own nervous system, which is part of the autonomic nervous system. In stressful situations, the entire nervous system of the body begins to malfunction; the brain gives incorrect signals to the intestines, which incorrectly inform the brain about the processes occurring in it. As a result, intestinal motility is disrupted, the pain sensitivity threshold is reduced, and even minor discomfort causes severe attacks of pain.
In addition to stress and a low pain threshold, the risk of developing IBS is increased by poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, hormonal imbalances (for example, in pregnant women), and genetic predisposition. IBS can also develop after certain infectious bowel diseases. The main difficulty in IBS is that the symptoms are very unpleasant, and correction must be carried out, first of all, on the psycho-emotional state, which is quite difficult without the help of a competent psychologist. At the same time, there is still a problem that often patients do not even admit to themselves that they need psychological help. When making this diagnosis, it is very important to be oncologically alert. However, in our time this is always important, even in young patients, but especially in older people. IBS appears more often in young people, so if similar symptoms are observed in mature patients, the doctor must first rule out cancer.
— During antibiotic therapy, doctors often advise taking probiotics or prebiotics. Is this really necessary?
— Antibiotics affect the intestinal flora, this is indisputable. Often, against the background of antibacterial therapy, a patient develops dysbiosis (“dysbacteriosis”), that is, a qualitative and/or quantitative change in the ratio of microorganisms that live in the intestines. Dysbiosis is manifested by stool disturbances, flatulence (excessive gas formation), and the presence of inflammation on the mucous membrane. To prevent the development of this unpleasant condition, it is recommended to take pro- and prebiotics. Probiotics are medications or biologically active food additives that contain live microorganisms that are representatives of the normal human microflora. They are designed to restore the disturbed balance of microorganisms inhabiting various human mucous membranes, and therefore are used for the treatment and prevention of immunodeficiency, dysbiosis and related diseases. Probiotics stimulate the immune system at all levels, which has been proven in numerous clinical studies.
Prebiotics
- These are food ingredients that are not digested by human enzymes and are not absorbed in the upper sections of the gastrointestinal tract. They stimulate the growth and vital activity of beneficial microflora: breaking down into fatty acids, they increase acidity in the colon, inhibiting the growth of opportunistic microflora, which also creates favorable conditions for the development of normal microflora. Prebiotics are found in dairy products, corn flakes, cereals, bread, onions, chicory, garlic, beans, peas, artichokes, asparagus, bananas and many other foods. They also exist in the form of dietary supplements.
There is an opinion that probiotics in tablet and liquid forms are less effective, since they cannot always pass through the highly acidic environment of the stomach, where bile is aggressive to bacteria. And only capsules are designed to dissolve in the colon - where bacteria should live. Not so long ago, symbiotics appeared on the market - combination drugs that combine pre- and probiotics. Today they are considered to have the most advanced mechanism of action. I recommend choosing drugs that normalize the microflora together with your doctor - because it is quite difficult for a non-specialist to understand all the variety of existing drugs, and it is unlikely that you will be able to understand what is suitable in each specific case on your own.
— Why are constipation dangerous?
— Constipation is a condition characterized not only by a decrease in the frequency of bowel movements: less than 3 times a week, but also by the appearance of dense, dry stool or the absence of a feeling of complete bowel movement or bowel movement with straining or the use of additional techniques by patients to empty the bowel. Long-term constipation causes: chronic intoxication (poisoning), which leads to sleep disturbances, unmotivated fatigue, increased fatigue and, finally, to depression, deterioration of the skin and hair; the formation of intestinal diverticula (protrusions of the wall), which can cause abdominal pain, and if an infection occurs, inflammation of the intestinal mucosa (diverticulitis) and the need for intensive antibacterial therapy or surgical treatment if intestinal obstruction occurs; varicose hemorrhoidal veins, chronic anal fissures; colon cancer. You need to start solving the problem of constipation not with self-medication, but with a visit to a gastroenterologist. There are many reasons for constipation. These can be very serious diseases. Only a competent specialist can understand this. By solving the problem of constipation on your own, you can significantly worsen your condition.
— Is such a delicate problem as flatulence treated?
— Flatulence (increased gas formation) is associated with fermentation. There can be many reasons: insufficient bile secretion, insufficiently concentrated bile, disturbances in the secretion of pancreatic juice - usually problems with the sphincter of Oddi. All this leads to changes in the bacterial flora of the intestines. As a result, flatulence develops. This is a common problem, but it can be solved. Although I won’t say that it’s always simple and fast. The main thing is to find the root cause, since flatulence can be a symptom of various diseases.
— Sometimes a person suffers from bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Is this a symptom of some disease?
- Halitosis - bad breath - can occur for various reasons. First of all, I would recommend visiting a dentist and checking the condition of your teeth and oral cavity. In second place are ENT diseases. If everything is in order in these areas, then, indeed, halitosis may be a consequence of digestive problems. As for the taste in the mouth, this can be a symptom of certain diseases. But here everything is very individual: the taste can be sweet, bitter, sour, metallic, etc. It can be constant or appear only after eating or, conversely, on an empty stomach, etc. Therefore, you need to look and look for the reason.
— Often, patients who have undergone an ultrasound of the abdominal organs find out that they have a kink in the gallbladder - how serious is this?
— Deformations of the gallbladder - kinks, membranes, etc. increase the risk of bile stagnation. The gallbladder should normally empty almost completely after each meal. Because the gallbladder has to work harder to contract, some patients may experience pain. After its reduction, part of the bile may remain behind the bend and “stagnate,” which can lead to the formation of stones. I recommend that patients with gallbladder deformation monitor their condition: see a doctor, do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs once a year to see the condition of the bile and gallbladder. If an ultrasound diagnostic doctor notes that the bile is “viscous,” “heterogeneous,” “inhomogeneous,” etc., it is important to immediately contact a gastroenterologist and undergo a course of therapy to prevent the formation of stones. It is especially important to take gallstone prevention seriously if anyone in your close family has these problems.
— What methods can be used to prevent gastrointestinal diseases? Maybe I need to take medications or have tubing done?
— You should not use any preventive medications without a doctor’s prescription. All medications have side effects and are not recommended to be taken unless indicated. To carry out tubage (a procedure that involves taking choleretic drugs to simultaneously empty the gallbladder), certain indications and contraindications are also required. More often, the doctor prescribes this procedure in combination with other therapeutic measures, selects medications, etc.
The best prevention of gastrointestinal diseases is proper nutrition: small portions, thoroughly chewing food to a pulp. You need to eat at least 4-5 times a day, be sure to have breakfast within an hour after a night's sleep. The volume of water drunk per day should be at least 1.5 liters.
Try to minimize the amount of food that provokes the development of diseases. We have already listed them above: fast food, pickles, smoked foods, fried, spicy, etc. Add physical activity: it has been proven that a sedentary lifestyle contributes to gastrointestinal problems, while abdominal exercises, brisk walking, and yoga have a beneficial effect on intestinal function. Organize your lifestyle in such a way as to maintain health for a long time - and you will protect your body from many unpleasant problems.
What happens if you delay your trip to the gastroenterologist?
If the digestive tract does not function as it should in any part of it, then incomplete absorption of food is not the worst problem that arises for this reason. It is much worse when improperly or incompletely broken down nutrients turn into organic toxins over time. Thus, the body poisons itself for a long time, which leads to various somatic disorders, deterioration of health and appearance, decreased ability to work, and a weakening of the general level of immunity. And if this happens from an early age, dysfunction of the digestive system will negatively affect the growth and development of the child.
You should not too often attribute discomfort in the digestive tract to the fact that the food turned out to be inappropriate. Even if the cause of poor health really lies in food, you need to find out from a gastroenterologist how and what to eat in order to avoid problems in the future.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Gastrointestinal diseases in older children:
Unfortunately, experts note a significant “rejuvenation” of other gastrointestinal problems in children - the following diseases are increasingly being identified in preschool and school age:
- gastroduodenitis
- gastritis
- pancreatitis
- colitis
- chronic constipation
- loss of appetite
The ABIA clinic has a special approach to the treatment of children's diseases - an individual treatment program is developed for each small patient, including diet selection, medication and physiotherapeutic treatment.