Relevance of the problem
Pancreatitis is a very common pathology; over the past 30 years, the incidence rate has doubled. Over the past few years, the disease has become significantly younger: if previously the disorder was found in people aged 50+, now the main pool of patients are patients 35+.
Pancreatitis is increasingly affecting children, due to many factors.
Pancreatitis is a very dangerous disease, which can result in disruption of the entire body. In especially advanced cases, the disease can lead to death.
Pancreatitis - classification of the disease
Now let's talk about what pancreatitis is, symptoms and treatment in adult men and women. But first, let’s figure out why the pancreas is so important for the smooth functioning of the body.
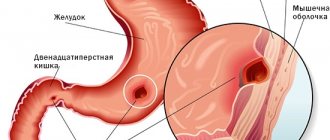
There is an organ in the human body called the pancreas. The pancreas is located at the bottom of the stomach, communicating with the duodenum.
The organ is of great importance for the functioning of the entire human biosystem, as it performs a number of important functions:
- exocrine: synthesis of digestive juice, which contains many enzymes and promotes digestion;
- intrasecretory: synthesis of a number of hormones that affect carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism.
For example, the pancreas produces hormones such as glucagon and insulin, which regulate blood sugar levels. When this system is destabilized, a person may develop diabetes.
You should not use folk remedies to treat pancreatitis.
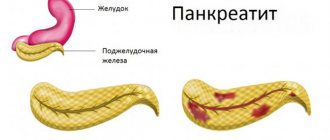
With pancreatitis, inflammation of the pancreas occurs. The activity of the organ is disrupted, which leads to many other disorders. Pancreatitis happens:
- Acute
. Active inflammation, in which a sick man constantly suffers from vivid symptoms of pancreatitis. - Chronic
(most often a consequence of acute pancreatitis). In the chronic form, inflammation “sleeps.” The pancreas works, but with malfunctions. Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by a wave-like course with periods of rest and exacerbation.
Chronic pancreatitis is more dangerous because it is characterized by constant progression of the pathological process. With this form of the disease, irreversible structural and functional damage to the gland occurs, which is why it is gradually destroyed.
Causes of inflammation of the pancreas
Pancreatitis is a multifactorial disease. The main reasons for the development are as follows:
- excessive and frequent consumption of alcohol;
- systematic smoking;
- intoxication;
- abdominal trauma;
- viral, fungal or infectious disease;
- disease caused by parasites;
- obstruction of patency in the pancreatic ducts.
Inflammation of the pancreas often develops as a postoperative complication or complication of cholelithiasis. There is also a hereditary predisposition to pancreatitis.
general information
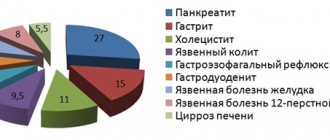
Pancreatitis is one of the most common diseases of the digestive system.
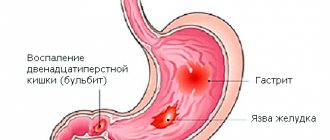
Acute inflammation of the pancreas can lead to destruction of organ tissue and disruption of vital functions. If not treated in a timely manner, the inflammatory process is complicated by a bacterial infection that can spread to other tissues. Usually the first symptom of the pathology is severe pain in the left hypochondrium, however, the chronic form of pancreatitis can have a hidden course. The pancreas is an important organ of the digestive system, necessary for the absorption of nutrients. This organ secretes enzymes that break down proteins, fats and complex carbohydrates in the intestines. Another function of the pancreas is endocrine regulation, which is necessary for the storage and use of glucose in the body. During acute inflammation, digestive enzymes are retained in the organ and begin to destroy tissue.
Clinical picture of pancreatitis
The clinical picture directly depends on the form of the disease. The main symptom of acute and chronic forms is pain, which is girdling or diffuse in nature.
In acute pancreatitis and exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis, the symptoms are the same.
In acute pancreatitis, the pain is very persistent, localized in the upper abdomen (epigastric region) and radiates to the back. The symptom worries constantly and does not stop even at rest. This form is also characterized by the following phenomena:
- vomiting mixed with bile (a bitter taste appears in the mouth), after which the patient does not feel better;
- hyperthermia;
- the skin becomes pale and cold.
Characteristic symptoms of chronic pancreatitis are frequent nausea, increased salivation, belching, problems with stool, bloating and flatulence. Due to an imbalance of enzymes and inhibition of the functioning of many biosystems, the patient may begin to lose weight.
Some patients develop obstructive jaundice against the background of pancreatitis, which is manifested by yellowing of the skin, lightening of the stool and darkening of the urine.
Also, with acute pancreatitis, the patient may develop pinpoint angiomas on the skin (purple droplets), pain on palpation of the pancreas, and hypotrophic changes in the skin over the organ.
Causes
Acute pancreatitis is recorded in adults 30-40 years old. The male population is more at risk than the female population. The incidence of the form is higher in people who abuse alcoholic beverages and suffer from pathologies of the biliary tract, such as:
- dyskinesia of the bile duct of the hypertensive type;
- cholecystitis in chronic or acute form;
- cholelithiasis.
Other causes of pancreatitis:
- hypertriglyceridemia;
- disruptions in the circulatory system of glandular tissue;
- cystic fibrosis;
- hemolytic-uremic syndrome;
- hyperparathyroidism;
- abdominal injuries;
- heredity;
- autoimmune diseases;
- blockage of the pancreatic or common ducts;
- damage to the canals and gland during surgery;
- uncontrolled use of drugs;
- consequences of severe acute respiratory viral infections, mumps, mycoplasmosis, pneumonia, hepatitis;
- various gastrointestinal diseases.
Acute pancreatitis can occur in two forms:
- mild – organs and systems are slightly affected. The disease responds well to treatment, recovery occurs quickly;
- severe - pronounced disorders are observed in tissues and organs, tissue necrosis, abscesses and cysts cannot be excluded.
The clinical picture of this disease in severe form may also be accompanied by:
- there is an accumulation of fluid inside the gland;
- tissue infection and necrosis;
- false cyst;
- pus accumulates in the gland or on tissues adjacent to it.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
If you experience symptoms that are remotely similar to manifestations of pancreatitis, do not delay and immediately consult a doctor. In the absence of proper therapy, the disease can become chronic.
First of all, you should contact a therapist. The doctor will collect anamnesis, conduct an initial examination and examine the patient’s condition in detail. If he suspects pancreatitis, he will redirect the patient to a highly specialized doctor - a gastroenterologist. A doctor of this specialization specializes in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterologists diagnose the disease in several stages:
- Inspection
. Particular attention is paid to the symptoms of acute and chronic pancreatitis. - Lab tests
. General and biochemical analysis of blood and urine, sometimes analysis of stool. When examined, biological fluids reveal an increased amount of enzymes (not always in the acute form) and inflammatory factors. When analyzing blood, special attention is paid to amylase, and urine - to diastase. A stool test is done to evaluate the function of the gland. With pancreatic insufficiency, the level of digestive enzymes and fats changes in patients. - Imaging examinations
. This may be X-ray, ultrasound, CT or MRI, ERCP, endoscopic ultrasonography. These tests can determine whether there are structural changes in the pancreas or related organs, whether there are blockages or other abnormalities.
After diagnosing and determining the type of pancreatitis, the gastroenterologist prescribes treatment. The treatment technique for acute and chronic forms is different.
Prevention
Prevention of exacerbation of pancreatitis includes several important points. Firstly, following a diet will ensure restoration of the digestive system and long-term remission. Secondly, taking prescribed medications will improve the functional state of the pancreas. Thirdly, eliminating factors related to the causes of exacerbation of pathology will reduce the risk of recurrent attacks to the maximum extent.
Other preventive measures:
- regular intake of vitamin complexes;
- rejection of bad habits;
- elimination of excessive emotional and physical stress;
- compliance with the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
Video on the topic: Effective treatment of the pancreas without drugs or with drugs.
Treatment tactics for pancreatitis
As already mentioned, the treatment tactics for acute and chronic pancreatitis are different. If the inflammation is very active, the patient may be admitted to the hospital.
In the acute form, the main goal of therapy is to relieve symptoms and create complete functional rest of the pancreas. To combat the symptoms of the disorder, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- proton pump inhibitors, which block the synthesis of hydrochloric acid (it stimulates the pancreas to produce digestive enzymes);
- digestive enzymes, which will additionally relieve the gland;
- antispasmodics that relax the pancreatic duct sphincter.
If the patient has metabolic disorders, he is prescribed vitamins. In case of electrolyte imbalance, appropriate medications are prescribed.
If cysts, stones and other formations are detected in the patient, endoscopy/stenting is performed to remove them.
In acute pancreatitis, nutrition is completely limited. Therapeutic fasting is introduced for several days so that the pancreas can “rest” and not take an active part in the synthesis of digestive enzymes. To avoid negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract, the patient is prescribed parenteral nutrition (intravenous administration of nutrients). On average, it takes three to five days to stabilize a patient with acute pancreatitis.
After treatment of acute pancreatitis, the patient can be prescribed a therapeutic diet Pevzner No. 5P.
It exists in two variations, the type is selected depending on the patient’s condition. For therapeutic purposes, medicinal mineral waters are prescribed (Narzan, Essentuki No. 7 and 14).
Results
- exacerbation of pancreatitis can develop in a latent form or in the form of a sudden attack;
- in case of exacerbation of the pathology, the patient must be provided with qualified medical care;
- during an attack, food consumption is excluded (therapeutic fasting for two or three days);
- in the presence of complications, pain may persist for two weeks;
- After the attack has stopped, nutrition is resumed gradually;
- The basis for creating a menu is the principles of the 5p Diet.
Features of the treatment of chronic pancreatitis
Therapy for chronic pancreatitis is more global. The specifics of treatment depend on the type of disease (pancreatitis can be hypersecretory or hypoenzymatic).
Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is treated in the same way as acute pancreatitis.
Treatment of the disease consists of two parts. The first is pain control and slowing the progression of pancreatitis. For this, the patient may be prescribed:
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors;
- gabapentin;
- pregabalin;
- tricyclic antidepressants.
In especially severe cases, the doctor may prescribe opioid painkillers. But this is rarely done, since there is a high risk of developing dependence. Patients with chronic pancreatitis are also prescribed drugs with digestive enzymes. They reduce the synthesis of these substances in the organ itself, thereby unloading it and reducing pain.
In people with chronic pancreatitis, the risk of developing diabetes mellitus increases significantly, since due to structural changes in the pancreas, the number of islets of Langerhans (responsible for the balance of insulin and some other hormones) decreases.
Diet for pancreatitis
Nutrition is the most fundamental part of pancreatitis therapy. Almost everything depends on it: the patient’s condition, the rate of progression of the disease, the number of exacerbations, etc. List of foods that should be completely avoided for this disease:
- barley and corn porridge;
- legumes;
- fat milk, kefir and other dairy products;
- soups fried in strong broth;
- fatty meat and fish (pork, lamb, mackerel, etc.);
- all semi-finished products, canned food (meat, fish, fruit and vegetables), pickles;
- sauces, especially store-bought ones;
- some vegetables: eggplant, onion, bell pepper, cabbage, radish;
- sweets;
- mushrooms;
- Rye bread;
- soda, strong tea and coffee, juices.
The daily caloric intake for a patient with chronic pancreatitis is approximately 2500 kcal. You need to eat in small portions. Dishes cannot be prepared by frying; it is allowed to steam or boil food. It is recommended to limit the consumption of salt and fat.
With chronic pancreatitis, the patient will have to almost completely change his lifestyle. You need to completely give up such bad habits as drinking alcohol and smoking.
It is necessary to minimize the amount of stress and intense physical activity. You should exercise and control your body weight. Only with an integrated approach can you keep the gland healthy (as far as possible with chronic pancreatitis) and minimize the number of exacerbations.
Example of a weekly menu
Many patients believe that nutrition for pancreatitis and the menu for every day, taking into account all the contraindications and nuances, turns out to be very boring and not varied, but this is not so. People with damaged pancreas can also eat tasty food. Here is a sample menu for a week for a patient with chronic pancreatitis:
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
| Breakfast: oatmeal with water + low-fat cottage cheese + weak tea. Snack: yogurt. Lunch: light soup with vegetable broth. Snack: oven-baked pear. Dinner: boiled meat or fish with steamed vegetables. | Breakfast: buckwheat on water + steamed beef. Snack: banana. Lunch: vegetable puree + steam cutlet. Snack: kefir. Dinner: vegetable salad + boiled egg. | Breakfast: two-egg omelette + chamomile tea. Snack: some cottage cheese. Lunch: broccoli soup + a piece of bread or crispbread. Snack: vegetable slices of cucumber and tomato. Dinner: baked chicken meatballs + grated beet with carrots. | Breakfast: rice porridge + chicken/turkey meatball. Snack: berry jelly (can be made from strawberries). Lunch: vegetable stew + a couple of pieces of cheese. Snack: two low-fat cheesecakes with grated berries. Dinner: vegetable salad with turkey meatballs. | Breakfast: mashed potatoes + steamed fish. Snack: kefir. Lunch: light chicken broth with noodles. Snack: vegetable slices. Dinner: cottage cheese casserole. | Breakfast: curd pudding + drink to taste. Snack: fruit salad. Lunch: vegetable puree + fish or meat patty. Snack: cottage cheese. Dinner: baked fish + light salad. | Breakfast: oatmeal with water + protein omelet. Snack: oven-baked fruit (apples or pears). Lunch: milk soup + apple or banana. Snack: a glass of jelly. Dinner: a couple of sandwiches with cheese + tea. |
It is important that the food is not very structured. To further reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract, you can crush it in a blender.
Fruits, vegetables, lean meat (beef, chicken, rabbit), vegetables and fruits, some cereals, herbs, seeds (flax and others) - all this can be eaten with pancreatitis of the pancreas. You can create the menu yourself, taking into account these recommendations.
Surgery
Often, with chronic pancreatitis, patients develop stones that block the channels and ducts of the pancreas. They can worsen the condition of the organ or become a source of pain, so they are removed surgically.
When dilatation of the pancreatic duct is present, a bypass is performed from the organ to the small intestine. When there are structural changes in the gland or a large amount of inflamed mass, partial excision of the organ is performed.
How long does it last
The pancreas is not able to quickly recover during the inflammatory process. This nuance explains the long period of exacerbation of pancreatitis. Intense pain symptoms can last up to two weeks (the average is from five to seven days). The situation can be aggravated by the lack of adequate therapy and poor diet. Restoration of the functional state of the digestive organs in this case will be slow or completely absent (progression of complications). The sooner treatment begins for exacerbation of pancreatitis, the shorter the duration of the attack.
First aid
If pancreatitis worsens, the patient must call an ambulance. Before the brigade arrives, a number of actions should be taken to alleviate his condition. It is important to provide three factors - cold, hunger and peace. The patient should be in a horizontal position. You can apply a cold compress to the source of pain (left hypochondrium). Eating any type of food is strictly prohibited.
Following these recommendations will help reduce the intensity of pain and slow down the progression of the inflammatory process.
In case of pancreatic necrosis, the patient needs urgent surgery.
How to relieve an aggravation
Patients diagnosed with chronic pancreatitis, in most cases, can independently determine the onset of exacerbation of the pathology. If alarming symptoms occur, you should begin to relieve them as soon as possible. First of all, the diet is adjusted. If the attack is intense, then the body is provided with fasting for a maximum of two days. If the exacerbation is mild, the menu is adjusted taking into account dietary rules (excluding all harmful foods).
A strong pancreas is the key to a healthy body
The pancreas affects a person’s well-being, his weight and even his psycho-emotional state, so you need to carefully monitor its health. To ensure that the organ performs its function correctly and does not suffer from pancreatitis, adhere to the following rules of prevention:
- give up or reduce to a minimum alcohol consumption and smoking;
- stop eating soda, processed foods, fast food and other food garbage;
- reduce too spicy and fatty foods in your diet;
- in your diet, give preference to lean meats, vegetables, herbs and other healthy foods.
If you experience pain or other unpleasant symptoms, contact your doctor and do not wait for them to go away on their own. Remember, timely identification of the problem is the key to its successful treatment.