Gastroscopy
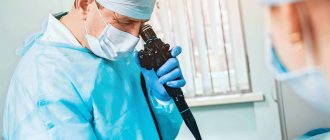
Gastroscopy is an endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach using a video camera attached to a flexible probe.
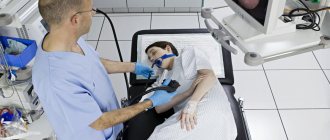
The device is inserted through the patient's mouth. Gastroscopy of the stomach is prescribed as an independent diagnostic procedure or performed during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS) - it depends on the capabilities of the equipment used. The procedure is generally painless, but many patients experience great fear and are unable to swallow the endoscope. In such cases, doctors use sedation. The patient is put into light medicated sleep, which significantly reduces stress levels and allows the doctor to carefully examine all areas of the stomach.
You can have a gastroscopy in Moscow at the Alfa Health Center clinic. We create the most comfortable conditions for each patient, using anesthesia if necessary. We guarantee high accuracy of results and reasonable prices for gastroscopy in a dream. The price list for services is posted on our website.
Fibercolonoscopy (FCS)
This is an endoscopic examination of the colon. The fibercolonoscope tube has a channel for air supply, since the walls of the empty colon collapse, to examine them you need to inflate the colon with air.
Objectives of the study
- Diagnosis of diseases of the colon: ordinary and ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease (chronic nonspecific granulomatous inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract), Hirschsprung's disease (anomaly of the colon), polyps and polyposis, malignant and benign tumors of the colon.
The advantage of the method is that during the study you can take a small piece of tissue for histological examination. Therefore, fibrocolonoscopy is used to diagnose colon cancer. - Removal of benign colon tumors, such as polyps.
How the research works
- Before the study, the intestines must be cleansed using enemas or modern laxatives;
- fibrocolonoscopy is performed without anesthesia, because it is absolutely painless. If fibrocolonoscopy is impossible due to severe pain in the patient, the examination is performed under general anesthesia;
- first, the specialist conducts a digital examination of the rectum;
- then a fiber colonoscope is inserted into the patient through the anus and slowly advanced into the colon;
- air is supplied to the fibercolonoscope;
- after this, the necessary inspection is carried out, and, if necessary, various manipulations are performed.
There may be some discomfort during the examination, but there should be no pain. Pain usually occurs when the patient has inflammation of the rectum, for example, an anal fissure.
Indications for gastroscopy
A referral for examination is issued by a gastroenterologist. A gastroscopy is necessary in the following cases:
- diagnosis of diseases of the esophagus and stomach;
- frequent belching, heartburn, nausea, pain that is difficult to treat;
- the appearance of blood in the stool (melena);
- sudden weight loss for no obvious reason;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- ingestion of a foreign body;
- chemical burn of the digestive system;
- removal of polyps;
- taking a biopsy;
- stopping bleeding caused by damage to varicose veins or ulcers;
- treatment of damaged mucous membranes with drugs;
- monitoring the effectiveness of prescribed treatment, etc.
Based on the results of gastroscopy, gastritis, peptic ulcers, duodenitis, esophageal diverticula, Crohn's disease, benign and malignant tumors and many other pathologies are diagnosed.
Indications for examination under anesthesia
Gastroscopy in a dream is indicated for patients in an anxious state, patients at risk of a hypertensive crisis, a pronounced gag reflex, and various tics. Sedation is used to examine children.
Modern drugs are harmless, fast-acting and have virtually no contraindications, so medicated sleep is used for all patients who want to undergo the procedure without worry and discomfort. Waking up only takes a few minutes. The price of gastroscopy under anesthesia includes the cost of drugs.
Contraindications to the procedure
The study is impossible in case of perforation of the walls of the esophagus and stomach, stroke, acute heart attack, aortic aneurysm, severe shortness of breath. Gastroscopy is contraindicated for patients in shock; the procedure can be performed only after the condition has stabilized.
There are also a number of relative restrictions:
- blood clotting disorder;
- neurological diseases in which the patient is unable to control his movements;
- heart attacks and strokes suffered less than 6 months ago;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- narrowing of the esophagus, for example, as a result of spasm or scarring of the mucous membranes;
- severe curvature of the spine;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- enlarged cervical and retrosternal lymph nodes;
- epilepsy;
- pregnancy;
- allergy to sedatives (if you plan to do gastroscopy in your sleep).
The possibility of examining each individual patient is determined by the doctor. Before the procedure, you must be examined by a specialist and answer his questions. The doctor will also talk about preparation for gastroscopy and the cost of the examination.
Before the procedure, each patient must be examined by a therapist to identify contraindications. For older people and patients at risk, an electrocardiogram is additionally prescribed. Before gastroscopy with anesthesia, the doctor may refer the patient for laboratory tests, fluorography, and consultation with an anesthesiologist to assess possible risks. If you have previously undergone such an examination, take the report with you. This will allow the doctor to assess the dynamics and adjust treatment taking into account changes.
How can I make the procedure easier?
The correct approach to fibrogastroduodenoscopy can significantly improve the patient’s well-being during the procedure. Below are the main recommendations that make FGDS absolutely painless.
Choosing the right doctor
Choosing a qualified doctor with a friendly approach to his patients can significantly reduce anxiety before the procedure, as well as reduce the severity and frequency of side effects.
A good approach from a specialist relieves anxiety and helps the patient relax. This allows the procedure to be carried out without unnecessary trauma (for example, scratching the throat), since the probe advances more easily.
In clinical practice, there are situations when, due to low professionalism, the doctor applies the wrong or insufficient anesthetic . Also, some medical professionals do not explain the essence of the procedure, possible risks, and nuances of patient behavior.
Psychological attitude
Many patients are scared and anxious; they do not know how to withstand a stomach examination. Some people generally cannot tolerate such procedures and do not know what to do or how to pass the FGDS.
It is usually scary to do research due to the lack of reliable information about FGDS, as well as reviews from friends. And if the patient is sure that he will be in pain during the procedure, then the risk of this complaint increases significantly, even if the study went without complications.
It is important to have contact between the doctor and the patient
. This will help make the procedure easier. He must be ready to answer all questions that arise, as well as give truthful and objective information about why FGDS is performed, what its value is and how you can avoid the occurrence of side symptoms.
There is no need to be afraid or ashamed belching, increased salivation or an attack of nausea occurs during the procedure .
These symptoms, to varying degrees of severity, bother most patients, but they are not a sign of the development of complications and quickly disappear after the diagnosis is completed . It is important to remember that medical staff encounter this every day, and therefore, for example, frequent belching does not bother them at all .
Before the procedure begins, the patient is given a small mouthguard that protects the probe from the teeth . In modern clinics, it is selected according to the diameter of the endoscope and the size of the patient’s oral cavity.
The procedure is performed with the patient lying on his side
.
During FGDS, the probe passes through the oral cavity, oropharynx, larynx, esophagus and enters the lumen of the stomach. The doctor examines the condition of the mucous membrane, conducts acidity measurements, as well as a test for Helicobacter pylori infection . If necessary, a biopsy is performed.
Phytotherapy or medications
you tune in correctly to FGDS and eliminate anxiety .
The importance of proper preparation
Proper preparation for FGDS can significantly reduce the severity of side symptoms (especially vomiting) and increase information content. Therefore, on the day of the study, the patient should not eat. The last meal should optimally be no later than 10 hours before the test. For 2 hours, limit the intake of drinks - tea, coffee and even plain water.
To increase information content (especially if a Helicobacter pylori infection is suspected), special medication preparation is required.
It is necessary to discontinue medications that may affect the result - antisecretory agents, antacids, antibiotics, Bismuth preparations and some other medications.
Therefore, when prescribing a study, you should always warn the doctor about the presence of concomitant pathologies and medications taken.
Breathing feature
Before starting the procedure, the doctor must explain to the patient how to breathe correctly during FGDS. Breathing should be through the nose
, deep and smooth.
In this case (despite popular belief) there is no need to swallow
while moving the endoscope through the oropharynx and larynx. When you swallow, your larynx contracts, you touch the endoscope, and the doctor advances it. This leads to microtraumas of the throat and after the procedure you may feel that your throat hurts. Also, during the procedure you will feel that you cannot control the situation and panic.
That’s why it’s so important to relax and trust the doctor , breathe calmly, and burp calmly. This way you will not harm your body and will allow you to complete the procedure faster.
Following these recommendations will help the patient to adjust himself, promote calm and prevent sudden movements, therefore reducing the risk of injury and serious side effects.
How is gastroscopy performed?
The procedure is performed by an endoscopist. At the Alfa Health Center clinic in Moscow, gastroscopy under anesthesia is additionally supervised by an anesthesiologist, who prepares the patient for sedation and helps to safely emerge from drug-induced sleep.
A thin fiber optic tube with a camera and light is inserted into the patient's esophagus. The device is sterilized after each procedure. As it moves through the esophagus and stomach, the camera transmits the image to the monitor. Based on the picture he sees, the doctor can make a diagnosis. Sometimes, to clarify the information, a colonoscopy is prescribed, which is also performed under anesthesia, or fibrogastroscopy (FGS), during which the doctor can take a biopsy or perform other therapeutic and diagnostic procedures.
The examination takes on average 15-20 minutes. Gastroscopy during sleep is performed faster, since the patient is in a relaxed state.
After the examination, discomfort in the throat is possible, which quickly passes. If gastroscopy is performed under anesthesia, doctors recommend refraining from driving for several hours after the examination.
Possible consequences
After completion of the procedure, patients may have the following complaints:
- aching pain in the epigastrium (upper abdomen), neck or behind the breastbone, which may intensify after swallowing;
- weakness, dizziness , headaches, drowsiness (if drug sedation was used);
- cough (entry of stomach contents into the respiratory tract due to improper preparation of the patient);
- allergic reactions (to anesthetic);
- heartburn or burning sensation;
- increased saliva production ;
- loss of appetite ;
- palpitations or increased blood pressure (due to activation of the sympathetic nervous system);
- nausea, which worsens when eating or drinking water.
- Diet . After completing the FGDS, you cannot eat for another 30 minutes (and if a biopsy or sedation was performed, then 2 hours). The first meal should consist of simple foods and dishes: porridge, lean meat or fish, yesterday's bread, dry cookies, hard cheese, honey.
- Peace. Avoid increased physical and emotional stress during the day. Some people feel completely fine after the procedure and are ready to get back to work. But some people feel quite weak, like after a slight poisoning. If you have the opportunity to schedule your sleep after the procedure, take advantage of it.
Non-standard examination methods
In addition to inserting an endoscope through the oral cavity, there are other techniques for performing gastroscopy:
- Transnasal. The endoscope tube is inserted through the nose. The method is rarely used, only in cases of a pronounced gag reflex in the patient. Transnasal gastroscopy is also performed in elderly people with concomitant diseases. One of the advantages of the procedure is the preservation of the ability to speak. Patients tolerate the examination quite well and require sedation less frequently, allowing them to return to daily activities immediately after removal of the endoscope.
- Capsule. The modern method of gastroscopy involves swallowing a special capsule, inside of which an endoscope is placed. The product is small in size and easily passes through the digestive tract. As it moves, the camera takes pictures and videos that are transferred to the computer. The capsule is eliminated from the body naturally a few hours after the procedure. The method does not create discomfort, is painless, but is rarely used, since the doctor does not have the ability to direct the movement of the camera, zoom in on images of areas of interest and carry out the necessary manipulations. Another disadvantage of capsule gastroscopy is its high price.
- Photo
- News
- Reviews
- Vacancies
- Licenses
- Insurance partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- What you need to know about coronavirus infection?
- Rules for patients
- Important! Visiting a clinic during self-isolation.
- Online consultation with a doctor
- to corporative clients
Transnasal gastroscopy is a gastroscopy without swallowing the probe. The gastroscope is inserted through the nose - transnasally. This newest method uses an ultra-thin gastroscope (less than 6 mm in diameter!). Administration through the nose guarantees the absence of a gag reflex and sore throat. In addition, when performing transnasal gastroscopy, there is no need to use sedatives, which allows the patient to drive immediately after the examination and minimizes the risk of any complications.
The study begins with ingesting a tablespoon of medicine to suppress foaming in the stomach, as well as determining which nostril breathes better. Nasal congestion, in most cases, was not an obstacle to transnasal examination. Before the study, I just need to blow my nose and that’s it!
A small amount of a mild anesthetic is injected into the selected nostril (by the way, this procedure can be carried out without any anesthesia at all, but patients often feel more comfortable with pain relief), and a little gel is also injected into the nostril to make the endoscope glide better.
The endoscope is carefully inserted into the nostril, while the process is monitored on the monitor screen. The sensations, of course, are a little strange, but they cannot be called unpleasant.
The examination lasts a few minutes, which is associated with much better examination conditions, because the stomach is calm and there are no gag reflexes. During the study, the mucous membrane is examined, the vessels of the gastric mucosa are examined in a special mode, the acidity in the stomach is analyzed, a Helicobacter test is taken, and, if necessary, a tissue biopsy is performed for further histological examination.
Advantages of the transnasal method:
- The procedure is comfortable. The endoscope does not touch the root of the tongue, and the procedure does not cause a swallowing reflex or vomiting.
- The patient can speak freely with the doctor during the examination, which minimizes discomfort.
- Improved examination conditions, no gag reflexes.
- Reduced examination time due to the absence of strong painkillers or anesthesia.
- Ability to drive a car immediately after the study.
- Increases readiness for repeated research.
According to the results of a patient survey, 94% of respondents would prefer the transnasal method to conventional gastroscopy.
Sign up for an examination by phone
Services and prices
Appointment with a gastroenterologist, therapeutic and diagnostic, primary, outpatient
1,800 rub.
Appointment with a gastroenterologist, candidate of medical sciences, therapeutic and diagnostic, primary, amb.
2,100 rub.
Transnasal video esophagogastroduodenoscopy diagnostic
4,000 rub.
Comprehensive transnasal videoesophagogastroduodenoscopy
5,000 rub.
Biopsy of the digestive tract mucosa during endoscopy (up to 3 fragments)
1,100 rub.
Histology of biopsy material obtained during endoscopic examination. up to 3 teachers.
1,650 rub.
Prilepskaya Svetlana Ivanovna Gastroenterologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 33 years
Kaysina Tatyana Ivanovna Gastroenterologist Work experience: 32 years
Bakhvalova Tatyana Aleksandrovna Gastroenterologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 46 years
Make an appointment
What does gastroscopy show?
Examination of the esophagus and stomach using a video camera provides detailed information about the condition of the mucous membranes, which cannot be achieved using ultrasound, x-rays and other methods. Gastroscopy allows you to accurately determine diseases of the digestive system, determine the extent of the pathology, and conduct differential diagnostics. The procedure helps the doctor predict and prevent complications, for example, assess the risk of penetration of a deep gastric ulcer.
When examining the esophagus, its patency, the presence or absence of food particles in the lumen, and areas with cracks, ulcers, and redness are determined. The doctor examines the blood vessels and cardiac sphincter.
When examining the stomach, attention is paid to the size of its lumen, folds, the presence of bile, mucus, blood, the color of the walls, the condition of the superficial veins, the presence of areas with swelling and redness.
The price of gastroscopy includes a description of the main characteristics of the area being examined:
- severity of relief, shade, degree of shine of the mucous membrane;
- the presence of atrophic changes, inflammatory processes, blood flow disorders;
- location and size of erosion, ulcers, neoplasms, and other pathologies.
A description of gastroscopy is given a few minutes after the examination. If during the procedure the doctor collected material for histological or cytological examination, preparing a report may take several days. The patient will be given the results upon completion of the test.
Differences between gastroscopy and FGS, FGDS, EGDS
The difference between the procedures depends on the equipment used:
- Gastroscopy is performed using a flexible probe equipped with a video camera and lighting. The purpose of the procedure is to examine the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
- EGDS (esophago-gastroduodenoscopy) is a more complex procedure during which the doctor can perform a biopsy, remove a polyp or papilloma, excise adhesions, and remove a foreign body. The procedure is almost always performed under anesthesia.
- FGS (fibrogastroscopy) is performed to examine the stomach cavity. The probe is made using optical fiber. During FGS, it is also possible to perform simple medical procedures.
- FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) is a process of examining the stomach and duodenum, without examining the esophagus. The probe does not involve the use of a microtool.