Table of contents
- Why does a person have an appendix?
- Remove appendix to…prevent appendicitis
- What now?
- The appendix is an important organ of the immune system
- The appendix is a repository of beneficial bacteria
- Conclusion
Why does the body need a small appendage in the intestine, which scientists once recognized as useless? Why store something that is so easy to become inflamed and bring a person to the operating room? Maybe it's easier to remove the appendix right away? For clarification, we turned to therapist Alexandra Viktorovna Kosova, who prepared this article for the ABC of Health.
Causes and factors provoking appendicitis
Appendicitis does not select people; everyone is susceptible to it, regardless of gender and age . The exact reasons for its appearance have not yet been established - they are individual for each person, and it is impossible to single out a single cause for all patients. The main factors that can provoke this disease are:
- blockage of the appendix at the entrance to the rectum, which leads to inflammation of the walls of the appendix. It can be caused by various foreign bodies, poorly digested food, fossilized feces and the presence of adhesions;
- the presence of pathogenic bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci and E. coli), which, when the immunity of the appendix deteriorates, successfully penetrates the mucous membrane of the organ;
- the presence of fusobacteria in the appendix, which can lead to serious purulent-inflammatory processes in a very short time;
- intestinal diseases caused by infections and parasites (tuberculosis, typhoid fever).
- the body’s predisposition to frequent constipation (a polluted intestine is the best place to activate bacteria);
- unhealthy diet high in proteins and deficiencies in plant foods, overeating;
- abdominal trauma, heredity.
The appendix is an important organ of the immune system
A more detailed study of the appendix revealed an abundance of lymphoid tissue in its wall - tissue that provides the protective capabilities of the immune system. Lymphoid tissue makes up 1% of a person's body weight. Lymphocytes and plasma cells are formed in the lymphoid tissue - the main cells that protect the human body from infection and fight it if it does penetrate inside. Lymphoid tissue is distributed in the body in the form of lymphoid organs: lymph nodes, spleen, thymus gland (thymus), tonsils, Peyer's patches in the digestive tract. A particularly large number of Peyer's patches are found in the appendix. It is not for nothing that the appendix is called the “intestinal tonsil” (tonsils, like the appendix, are rich in lymphoid tissue - see figure).
Fig.4. Lymphoid tissue in the digestive tract:
1 – serous membrane (covers the intestine from the outside);
2 – muscular layer (middle layer of the intestine);
3 – mucous membrane (inner layer of the intestine);
4 – mesentery of the small intestine (anatomical structure in which vessels and nerves approach the intestine);
5 – single lymphoid nodules;
6 – group lymphoid nodule (Peyer’s patch),
7 – circular folds of the mucous membrane.
Rice. 5. Cross section of the appendix (histological specimen). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
1 – numerous depressions (crypts) in the mucous membrane of the appendix;
2 – lymphatic follicles (Peyer’s patches);
3 – interfollicular lymphoid tissue.
Rice. 6. Microscopic structure of the palatine tonsil:
1 – tonsil crypts;
2 – integumentary epithelium;
3 – lymphoid nodules of the tonsil.
In other words, the appendix has a very powerful lymphatic system. Cells produced by the lymphoid tissue of the appendix are involved in protective reactions against genetically foreign substances, which is especially important considering that the digestive tract is a channel through which foreign substances constantly enter. Peyer's patches (a collection of lymphoid tissue) in the intestines and, in particular, in the appendix “stand” like guards at the border.
So, it has been absolutely proven that the appendix is a very important organ of the immune system.
Symptoms of appendicitis
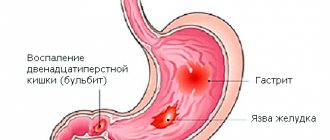
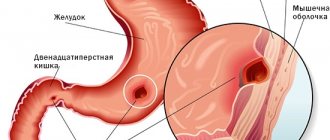
The localization of severe pain during acute inflammation of the appendix will depend on where the appendicitis is located in a person.
Almost every person knows which side the appendix is on: in most patients it is located on the right side, between the navel and the ilium . There is an infrequent localization of the appendix in the lower pelvis or right hypochondrium . Well, very rare cases - the left-sided location of the organ in “mirror people” .
The attack begins with a dull pain (the main symptom) in the navel area, with frequent difficulty in determining its location. The wandering acute pain lasts up to 10-12 hours, and then the pain syndrome moves directly to the location of the appendix. Pain can also radiate to the hypochondrium, lower back, groin area and leg
The appendix is a repository of beneficial bacteria
In 2007, Duke University Medical Center (Durham, North Carolina, USA) published an article stating that the appendix is a repository of good bacteria (“Appendix isn’t useless at all: it’s a safe house for good bacteria”). .
Microorganisms involved in digestion live in the human intestine. Most of them are beneficial (Escherichia coli, bifidobacteria, lactobacilli), and some are conditionally pathogenic, which cause diseases only with reduced immunity (nervous stress, physical overload, alcohol intake, etc.). Normally, a balance is maintained between opportunistic and beneficial microorganisms.
With intestinal diseases (for example, dysentery, salmonellosis and many others), accompanied by diarrhea (loose stools), as well as with the activation of conditionally pathogenic microflora, the number of “useful” microorganisms sharply decreases. But in the appendix, as a repository of “useful” bacteria, they remain and contribute to the new colonization of the intestines after recovery and cessation of diarrhea. People without an appendix are more likely to develop dysbiosis after an intestinal infection (compared to people who have a preserved appendix). However, this does not mean that such people are doomed. Currently, there is a group of prebiotics and probiotics that help a person restore normal intestinal microflora.
The entrance to the appendix, as mentioned above, is only 1–2 mm in diameter, which protects the appendix from the penetration of intestinal contents, allowing the appendix to remain a so-called “incubator”, a “farm” where beneficial microorganisms multiply. That is, the normal microflora of the large intestine is stored in the appendix.
Clinical stages of appendicitis
Due to the individual anatomical features of the location of the appendix, there are several clinical forms of this inflammation:
- Acute appendicitis: catarrhal (damage to the mucous layer of the appendix)
- phlegmonous (damage to the submucosal layer, accumulation of pus)
- gangrenous (necrosis of the walls of the appendix)
- perforative (destruction of the walls of the appendix, leakage of pus into the abdominal cavity)
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis);
Diagnostics
When diagnosing inflammation of the appendix, palpation and visual inspection are used. In this case, painful sensations appear when pressing the lower abdomen on the right, the abdomen becomes tense, an increase in right-sided pain and when the patient turns over on the left side. But this does not always make it possible to accurately diagnose the disease.
Additionally, the patient is sent for a detailed blood and urine test (detection of elevated levels of leukocytes and ESR). If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, ultrasound, computed tomography and MRI methods are used. Diagnostic laparoscopy may also be performed - examination through an opening in the abdominal wall of the abdomen using a probe equipped with a camera.
There are additional studies that help carry out correct diagnosis in women:
- examination of the vagina with retention of the cervix (the diagnosis of appendicitis is confirmed if there is no increase in pain);
- pressing on the area below the navel while lying down (if the appendix is inflamed, the pain increases when standing up).
Signs of appendicitis in men can be diagnosed by spontaneous pulling up of the right testicle (Larocque's symptom) and detection of severe discomfort in this area when the scrotum is pulled back (Horne's symptom).
Difficulties in identifying appendicitis in children under five years of age are due to the fact that the symptoms of this disease in them are not as pronounced as in adults. Often, inflammation of the appendix can masquerade as an upset stomach. The child often cannot explain exactly where and how his stomach hurts. The main guidelines for determining the disease in this case should be diarrhea, high fever and coated tongue.
A characteristic feature of appendicitis in older people is the absence of pain, which is the reason for inaction on the part of patients and their late seeking medical help. Therefore, in this group of patients all kinds of complications of this pathology are very common.
Remove appendix to…prevent appendicitis
Although the small appendix in humans is part of the gastrointestinal tract, it does not take part in the digestion process. But the risk of developing appendicitis remains. Acute appendicitis has always been and remains one of the most common surgical diseases of the abdominal cavity. That is why scientists of the last century came to the conclusion: it is necessary to remove the appendix for preventive purposes.
In general, the conclusions of scientists of the 19th and 20th centuries were so quick and, so to speak, superficial that those organs for which they did not find use in the human body were declared rudimentary and subject to removal. “Rudimentum” from Latin means an underdeveloped, residual organ, which in the process of evolution has lost its original function, but in its infancy is passed on from ancestors to descendants. This direction of scientific thought was largely promoted by the evolutionary theory of Charles Darwin (1809 - 1882), according to which variability, as the cause of differences between ancestors and descendants, is due to the influence of the external environment and the characteristics of the organisms themselves. In other words, the vermiform appendix no longer performs its digestive function, because on the ladder of evolution man has risen one step higher than his animal predecessors (according to Charles Darwin’s theory, man descended from animals), and the human digestive system has become different from that of animals. Therefore, the appendix began to be considered a dangerous vestige, capable of causing a terrible disease - appendicitis.
Many countries have begun to introduce various methods of preventing appendicitis. For example, in Germany in the 30s of the last century, it was decided to remove the appendixes of infants for preventive purposes. But this was soon abandoned, because it was noticed that these children’s immunity decreased, the number of diseases increased and, as a result, mortality increased.
There was a similar sad experience in the USA. Americans began removing appendixes from babies. After the operation, such children were unable to digest mother's milk and were retarded in mental and physical development. It was concluded that such disorders are associated with impaired digestion - a determining factor in normal growth and development. Therefore, the Americans abandoned this method of preventing appendicitis.
Scientists of the 19th-20th centuries classified many organs as rudiments, the functions of which they could not determine: tonsils (tonsils - a misnomer from a medical point of view), thymus (thymus gland), spleen, etc. At the beginning of the 20th century, scientists counted about 180 rudimentary “useless” organs and anatomical structures in the human body. Nobel Prize winner Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov (1845 – 1916) believed that the human digestive system is poorly adapted to the modern diet. He expressed this idea at the beginning of the 20th century, when the idea of poisoning the body with waste products of putrefactive bacteria living in the large intestine was widespread. That is why it is not surprising that in “Studies about Nature” I.I. Mechnikov wrote: “Now there is nothing daring in the assertion that not only the cecum with its appendage, but even all human colons are superfluous in our body and that their removal would lead to very desirable results.”
The British surgeon-surgeon of the early 20th century, Baronet Sir William Arbuthnot Lane, in contrast to I.I. Mechnikov did not limit himself only to discussions about the negative role of the large intestine in the human body. He removed the entire colon (and with it the putrefactive bacteria). The surgeon performed nearly 1,000 such operations, “leaving countless victims,” the researchers wrote. And only in the 30s. In the 20th century, W. Lane’s activities began to be criticized.
Treatment of appendicitis
Due to the high likelihood of complications, treatment (removal) of appendicitis is performed exclusively surgically .
It is carried out immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, using incisions (laparotomy) or punctures (using endoscopic instruments).
Prevention
There are many simple and accessible methods to prevent appendicitis. Since appendicitis is a component of the digestive system, the main prevention of this disease is the establishment of a proper diet.
must be present in every person’s diet .
Thanks to its fibers, it serves as a cleanser for the intestinal walls, and therefore ensures that the appendix remains uncontaminated.
Your food should contain all kinds of fruits and fresh vegetables, mushrooms, legumes and greens. Also, do not neglect fermented milk products, which, thanks to their beneficial bacteria, will quickly help strengthen the immune system. But seeds and berries with seeds are undesirable components of your diet.
In addition, it is necessary to minimize the presence of constipation - one of the main causes of intoxication in the body. To do this, twenty minutes before eating, you should drink a glass of warm water. To this you need to add an active lifestyle, which will contribute to the proper functioning of internal organs.
To prevent appendicitis, it would not be amiss to change your drinking regime. It is worth drinking more pure water, herbal decoctions and infusions. Water perfectly rejuvenates the body and is an excellent way to cleanse the intestines.
Forecast
In general, the prognosis for the treatment of appendicitis is favorable. If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner, complications after surgery are unlikely.
When treating the pathology at a later stage, inflammation of the appendix can spread to other internal organs or cause peritonitis. In this case, the body is exposed to mortal danger, and the nature of the prognosis depends on the condition of the body and the skills of the surgeons. Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo a timely examination and receive qualified medical care.
What now?
Currently, scientists believe that it is time to abolish the list of “useless” organs, because Years of research show that previously called vestigial organs perform an important function, and sometimes more than one. According to biologists, the appendix has been preserved and evolved for at least 80 million years. Nature would not leave an unnecessary organ. Perhaps it is worth replacing the list of “unnecessary” organs with a list of organs whose functions are not yet known to us?