Today, there are several methods to identify Helicobacter pylori: analysis for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori, stool analysis by PCR, urease breath test, biopsy, cytology. The most effective are IFA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) for Helicobacter and stool analysis (PCR).
Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori is carried out using two methods:
- invasive (endoscopy with biopsy)
- non-invasive (laboratory methods).
A reliable method for determining Helicobacter is invasive. A test for the bacterium is carried out for everyone who complains of pain and discomfort in the stomach.
Detection of pylori igg antibodies is routine in studies of the epidemiology of infection.
Breath test - definition and its types
A breath test to detect Helicobacter pylori is a diagnosis of infection that allows you to identify the activity of Helicobacter pylori and assess the level of infection. Gastroenterologists, therapists, and pediatricians often use it in their practice. The Helicobacter pylori breath test is used for the initial diagnosis of the bacterium. They are also used to monitor the treatment process of the disease and check the effectiveness of therapeutic treatment.
The method is absolutely safe, the most effective and in demand in medicine today. The analysis shows the waste products of bacteria in the air that the patient inhales.
There are two main types of method. They differ in the reacting component:
- carbon
- ammonium
Carbon breath analysis provides a more accurate result.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
This respiratory method has its advantages:
- The result is ready in a short period of time (20-25 minutes).
- Reliability of the result is 90-95%.
- The test does not harm the human body.
Since the method has only advantages, it has no contraindications. But the result will be accurate only if you prepare for the test correctly.
Preparing for a breath test
In order for the test to give the most accurate results, special preparation for the breath test is recommended:
- one month before the test, you should not take antibiotics;
- three days before the examination, do not drink legumes and alcoholic beverages;
- 6 hours before the test, do not eat anything;
- 14 days before the examination, avoid taking drugs that suppress the course; physiological and enzymatic processes in the body;
- You can’t chew gum or smoke for a few hours;
- the last meal no later than 22 hours, it should be a light dinner;
- one hour before the examination you can drink no more than 10 ml of water;
- for the analysis result to be accurate, the patient should not move;
- Before the examination, thoroughly clean your teeth and mouth.
It is very important to prepare for the test correctly, otherwise you will not get an accurate result. If the patient was unable to comply with all the rules, he must inform the doctor about this and another time will be assigned to him.
How the test is carried out
The procedure is carried out in a hospital setting under the supervision of a specialist. If the examination is carried out using a tube, the manipulation lasts no more than 15 minutes. If an electronic device is used, the procedure time is 10 minutes.
The procedure is simple:
- the patient takes a comfortable position
- a plastic tube is placed in the mouth, and breathing should be normal
- it is advisable not to touch the tube with your tongue and palate so that saliva does not get there
- if saliva accumulates, you can spit it out or swallow it, pull out the tube and take an air sample
- the first stage of manipulation lasts 6 minutes
- the patient is given a carbamide solution to drink
- the tube is placed back in the mouth
- the second stage also lasts 6 minutes, air testing is carried out
- after this the result is displayed.
Interpretation of analysis results and normal indicators
The norm is when the difference between the indicators of the first and second stages of the survey is zero. If there is Helicobacter in the body, the indicator will be above zero.
With the indicator:
- trace value is 1.5 -3.5, the microorganism is in an inactive phase and can be quickly gotten rid of;
- 3.5 - 5.5 – low level;
- small - up to 7 ppm;
- from 7 to 15, the bacteria is in the active phase, multiplying, the treatment process becomes difficult;
- above 15 – high level of contamination.
With any positive result, therapy should be started immediately, this will avoid complications and pain. But the Helicobacter treatment regimen must be drawn up by a doctor.
Contraindications for carrying out
The method has no contraindications, as it does not include any interventions or stress. It can be used for everyone, without restrictions.
Treatment of helicobacteriosis
Before starting therapy, an assessment is made of the degree of damage to the stomach and the contamination of its walls. The fact is that in some people Helicobacter pylori gradually becomes one of the types of opportunistic microorganisms. Therefore, the bacteria may not manifest itself in any way.
The destruction of bacteria is carried out using antibiotics. If a pathogenic microorganism is diagnosed not only in a patient with helicobacteriosis, but also in his relatives, then therapy can be carried out for the whole family to prevent re-infection. Nowadays, most doctors most often agree that Helicobacter does not need to be treated if a person does not have any symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases.
If the microorganism does not harm the health of the carrier in any way, then therapy is usually not carried out. But when treating an infection, it is necessary to use powerful antibacterial drugs, which weaken the immune system and can cause intestinal dysbiosis.
Most often, the patient is prescribed 2 drugs, which are selected individually, so the treatment regimen requires an integrated medical approach. It is also necessary to prescribe a drug from the group of proton pump inhibitors.
The duration of treatment is determined by the gastroenterologist after assessing the severity of the patient and a comprehensive examination. The course duration is usually 2-3 weeks. After this, repeated laboratory tests are carried out.
You cannot use folk remedies in the treatment of helicobacteriosis. They can only temporarily remove symptoms, causing the patient to postpone his trip to the doctor. But the disease will only progress during this time. The use of folk remedies can lead to serious complications.
Blood tests
If the patient complains of pain in the stomach, any discomfort, with functional digestive disorders, with gastritis and peptic ulcers, a blood test is taken for Helicobacter pylori. Antibodies to helicobacter pylori in the blood are an indicator of human infection with the bacterium helicobacteriosis.
It is recommended to donate blood for Helicobacter bacteria if:
- weak immunity
- hereditary predisposition to stomach cancer
- as a preventive diagnosis
- to evaluate the treatment received for the infection.
How to prepare for the analysis?
Before the analysis, you must not eat food, coffee, tea, alcoholic drinks, or smoke 8 hours before the test. This test for Helicobacter pylori determines the amount of immunoglobulins. When a certain toxin enters the human body, a virus, microbe, immunoglobulins interact with them and neutralize these harmful substances. The analysis shows the interaction of the pathogen and immunoglobulins, which makes it possible to determine whether Helicobacter pylori is in the stomach or duodenum.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of this test:
- the diagnostic procedure is not expensive;
- high accuracy of the result;
- analysis is available to everyone.
The test for Helicobacter pylori has its drawbacks:
- there are factors that influence the result of the analysis;
- some patients experience fear when taking blood;
- thorough results are obtained in 4-6 days.
Analysis transcript
Deciphering the result of a blood test for Helicobacter pylori can be done without medical skills. Antibodies are divided into categories A, G, M. Opposite each category there is a result on the form. If all blood test parameters for Helicobacter pylori do not exceed the norm, then there is no bacteria in the body:
- immunoglabulin LgG is absent or significantly lower than normal: bacteria are absent in the body;
- LgG detected: helicobacteriasis is present or has been previously experienced;
- immunoglabulin LgM was not detected or below the norm: conditional norm for Helicobacter pylori;
- LgM class detected: initial stage of the disease;
- immunoglabulin LgA is not detected in the blood: this may indicate an early stage of the disease, recent antibiotic therapy, or the patient is in the recovery stage.
Contraindications
A blood test for Helicobacter is not performed:
- for convulsions
- with increased excitability of the patient
- if there is skin damage at the injection site.
A blood test for antibodies is also not prescribed for venous phlebitis.
Helicobacteriosis (Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter pylori infection, Helicobacter pylori, H. pylori)
Gastritis
Ulcer
Iron deficiency
Vomit
Diarrhea
28198 January 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Helicobacteriosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
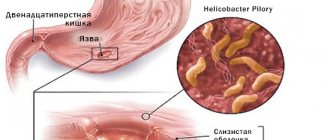
Helicobacteriosis is an infectious disease that affects the pylorus of the stomach, or pylorus, and duodenum. Its causative agent is a unique pathogenic microaerophilic gram-negative bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). The bacterium got its name from the section of the stomach in which it lives - the pyloric.
As a result of its vital activity, H. pylori forms a “cloud” of alkaline environment around itself, which allows this bacterium to survive in the aggressive acidic environment of the stomach, causing accelerated secretion of hydrochloric acid, as well as a decrease in alkali secretion in the duodenum.
As a result, the microorganism further colonizes the mucous membrane, forms its increased susceptibility to hydrochloric acid and provokes inflammation, leading to the development of ulcerative defects.
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium 3.5 microns long and 0.5 microns wide. It has flagella, with the help of which it moves freely along the wall of the stomach or is securely attached to it. The bacterium H. pylori is very variable; its strains (varieties) differ from each other in their ability to attach to the gastric mucosa, cause an inflammatory process, and have varying degrees of pathogenicity.
Helicobacter pylori, which colonizes the gastric mucosa, is a common cause of its inflammatory changes; it is recognized as the etiological factor of gastritis, and gastritis itself is an infectious disease. Depending on the state of the protective factors of the stomach, the resulting infectious process can occur latently or with severe clinical symptoms of inflammation. According to modern concepts, H. pylori causes chronic gastritis in all infected individuals. This can lead to peptic ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis, gastric adenocarcinoma or low-grade gastric lymphoma. H. pylori is a first-order carcinogen.
The results of numerous studies suggest a possible pathogenetic or indirect role of H. pylori infection in the development and/or course of diseases not related to digestion: cardio-, cerebrovascular, autoimmune diseases, diseases of the blood, skin, nervous system and many others.
The pathogen is relatively resistant to the environment: when boiled, Helicobacter bacteria die almost instantly, and when treated with disinfectant compounds, they die within a few minutes.
Causes of helicobacteriosis
You can become infected with the bacteria through contact with contaminated water or food. Infection is possible during endoscopy and when using other poorly sterilized medical instruments that have had direct contact with the patient’s gastric mucosa.
Household transmission (for example, through kisses, personal belongings, etc.) is also possible, as evidenced by the release of bacteria from saliva and dental plaque.
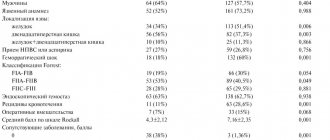
The prevalence of infection varies depending on the geographic region, patient age, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. According to the Moscow Department of Health (2019), the prevalence of this infection in Moscow is 60.7–88%, in St. Petersburg - 63.6%, in Eastern Siberia reaches 90%.
Classification of diseases
Diseases associated with H. pylori:
- gastritis,
- duodenitis,
- gastroduodenitis,
- esophagitis,
- stomach ulcer,
- duodenal ulcer,
- iron deficiency anemia of unknown origin,
- stomach cancer,
- duodenal cancer.
Symptoms of Helicobacteriosis
The main manifestation of Helicobacter pylori is chronic inflammation of the stomach. In the case of rapid primary manifestation of the pathogen, the acute period of helicobacteriosis lasts about 10 days. The general condition of patients usually remains satisfactory, sometimes there is a short-term low-grade fever and decreased performance.
The main complaint with which patients with signs of Helicobacter infection consult a doctor is stomach pain. The localization of the symptom may change and move to the area of the duodenum.
The pain can be sharp, aching, dull, and occurs in the upper abdomen on the left and in the center in the umbilical region. Discomfort can occur during prolonged fasting, on an empty stomach, or after a certain time after eating.
Symptoms of helicobacteriosis depend on the clinical form of the disease and may include:
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- loss of appetite associated with sudden attacks of nausea (if the gastric mucosa is severely injured);
- causeless vomiting against the background of normal body temperature;
- heartburn (burning sensations in the esophagus and even larynx) and belching with an unpleasant sour or bitter taste;
- chronic constipation (lack of bowel movements for three days or more);
- liquefaction of stool, the appearance of a foamy or watery consistency;
- intestinal cramps and bloating.
If there is a strong contamination with Helicobacter, a number of atypical symptoms may occur, which indicate significant infection and progression of the disease:
- loss of appetite to its complete absence;
- nausea may be replaced by vomiting with blood clots;
- a sharp decrease in body weight that is not normal;
- dry mouth and metallic taste;
- the appearance of a white coating on the tongue;
- bad breath in the absence of caries;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- bleeding gums.
In the chronic course of the disease and atrophic damage to the gastric mucosa, signs of iron deficiency anemia appear - frequent headaches and dizziness, pallor of the skin, decreased blood pressure and tachycardia.
Diagnosis of helicobacteriosis
For a long time, helicobacteriosis may not manifest itself in any way, while provoking the development of ulcers, adenocarcinoma or gastric maltoma. People whose relatives have a history of these diseases are at particular risk.
Diagnosis can be invasive (endoscopy followed by biopsy of gastric tissue) and non-invasive (laboratory tests).
According to international recommendations, the methods of choice for diagnosing the bacterium and assessing the effectiveness of treatment for H. pylori are a breath test with 13C-labeled urea and determination of specific H. pylori antigens in stool using an immunochromatographic method.
Stool analysis
PCR – what is it? This is a sensitive way to detect infection. It recognizes the DNA or RNA of the pathogen. For PCR, the material for research is feces.
A stool test for Helicobacter antigen is the most convenient test for the elderly, children and seriously ill patients. In this case, the presence of the patient in the laboratory is not required and the procedure is not associated with injury to the body. By the way, we will talk about Helicobacter pylori in children separately.
But detecting bacteria in stool is not easy. In the intestine, the microorganism is exposed to unfavorable conditions for it (bile acids, lack of oxygen). Therefore, active organisms adapt to new conditions, change their shape and their number sharply decreases.
A special method of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used, which allows you to determine the DNA fragment of a microorganism. The accuracy of the result is 95-96%.
What not to do before donating stool
It is important to know how to get tested for Helicobacter. Before donating stool, it is not recommended to take a lot of dietary fiber, coloring foods, inorganic salts, or medications that increase intestinal motility for 3-4 days.
Stool after an enema or laxative is not suitable for testing for Helicobacter.
A stool test for Helicobacter pylori is carried out before starting treatment. If the patient has previously taken antibiotic therapy for the treatment of any disease, it is better to prescribe a different method of examination.
Analysis transcript
The test result for helicobacter pylori can be positive or negative. A positive result indicates the presence or past infection. Negative data - about the absence of disease or incorrect conduct of the study.
Cytological analysis
Cytology is one of the most accurate methods for detecting Helicobacter pylori in the gastric mucosa. With this method, testing for Helicobacter pylori practically does not give false positive results.
For research, a biopsy material is taken during fibrogastroduadenoscopy (fgds), a smear is an imprint of the mucous membrane. The result can be positive or negative. According to the degree of contamination:
- weak - with a magnification of 360 times, up to 20 bacteria are detected in the field of view;
- moderate – 20-40;
- high – more than 40 bacteria.